您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
上一篇文章寫了vue和typescript的整合,發現很多小伙伴對vue-cli構建出來的項目很感興趣,所以今天打算寫寫怎么在vue-cli3.0的架子上,在進一步完善,整合出具備基礎功能的前端架子,主要包括以下幾個功能點:
webpack 打包擴展
vue-cli3 最大的特點就是 零配置 ,腳手架把webpack相關的配置都隱藏在@vue\preload-webpack-plugin中,默認的配置可以滿足大部分應用場景,優點是我們可以節省很多折騰配置的時間,webpack對于新手來說,還是有點門檻的,這樣一來,新人上手可以更關注于vue的編碼上。缺點也很明顯,對于想自己進行自定義配置的時候,就會稍微麻煩些。
查看當前webpack的詳細配置
使用 vue inspect 可以查看到詳細的配置列表
擴展webpack配置
當我們想要修改或者擴展webpack配置項時,可以在根目錄下新增 vue.config.js 文件,列舉個我自己寫的簡單小栗子
// webpack 擴展
module.exports = {
baseUrl: 'production' === process.env.NODE_ENV ?
'/production-sub-path/' :
'/',
chainWebpack: config => {
config.module
.rule('images')
.use('url-loader')
.tap(options => Object.assign(options, { limit: 500 }));
},
devServer: {
open: 'darwin' === process.platform,
// host: '0.0.0.0',
port: 8088,
https: false,
hotOnly: false,
// proxy: 'https://api.douban.com' // string | Object
proxy: 'http://localhost:3000' // string | Object
},
lintOnSave: false
};
官網Vue.js 開發的標準工具 的介紹非常詳細,而且還有中文版,非常易懂,
sass支持
<style lang="scss"></style>
<style lang="scss"> @import "./assets/style/app"; </style>
在組件中使用自定義的 functions 和 mixin,我暫時沒找到全局引用的辦法,只能在需要使用的組件文件中手動引用,如下
<style lang="scss">
@import "../assets/style/functions";
@import "../assets/style/mixin";
.rem {
height: px2rem(187.5px); //自定義的函數
}
.mimi {
@include clearfix(); //自定義的mixin
}
</style>
為了抹平各個瀏覽器間的差異,我們需要引入 normalize.css
// app.scss @import "./node_modules/normalize.css/normalize"; //引用第三方normalize @import "custom_normalize"; // 自定義的normalize
rem布局
在移動端下使用rem布局是個不錯的選擇,既然我們使用里的scss,那么可以使用函數來簡化我們的重復計算的工作。設計給到的通常是2倍圖,寬為750px,那么我們可以將基準設為 document.getElementsByTagName('html')[0].style.fontSize = window.innerWidth / 10 + 'px'; 然后寫個轉換函數,如下:
// _functions.scss
@function px2rem($px) {
$rem: 75px;
@return ($px/$rem) + rem;
}
我們在使用的時候,就可以這么寫
.rem {
height: px2rem(300px); // 2倍圖下的寬是300px,
}
轉換成css就是
.rem {
height: 4rem;
}
路由設計
主要包括路由懶加載、路由前置檢查、合法性校驗邏輯,以下是我寫的一個簡單路由
import Vue from 'vue';
import Router from 'vue-router';
// 路由懶加載
const getComponent = (name: string) => () => import(`./views/${name}.vue`);
Vue.use(Router);
const router = new Router({
routes: [
{
path: '/',
name: 'home',
component: getComponent('home')
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'about',
component: getComponent('about'),
meta: {
auth: true
}
},
{
path: '*',
name: 'not_fount',
component: getComponent('notFount')
}
]
});
/**
* 路由前置檢查
*/
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
// 合法性校驗
if (to.meta.auth) {
console.log('into auth');
next();
}
next();
});
export default router;
api 設計
新建 service 文件夾用于存放api腳本,根據業務模塊來劃分文件,如用戶相關的api一個文件、購買相關的一個文件, api.ts 是各模塊api的集合,如下
// service/api.ts
export { userApi } from './user';
export { buyApi } from './buy';
// service/user.ts
export const userApi = {
/**
* 獲取用戶數據
*/
userInfo: '/node_api/read/userInfo'
};
// service/buy.ts
export const buyApi = {
/**
* 購買
*/
shoping: '/node_api/shop/buy'
};
這么劃分,是為了項目結構和業務結構都足夠清晰,同時可以避免單文件過長的問題。
HTTP請求二次封裝
發送http我使用的是非常流行的 axios ,我在其基礎上,稍微進行簡單的封裝,然后暴露 request 對象供調用。二次封裝主要是為了解決以下幾個問題
根據以上幾點,下面是我封裝的request文件,思路都比較簡單,就不多說啦
import axios from 'axios';
import qs from 'qs';
const Axios = axios.create({
baseURL: '/',
timeout: 10000,
responseType: 'json',
withCredentials: true,
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=utf-8'
}
});
const CancelToken = axios.CancelToken;
const requestMap = new Map();
// 請求前置攔截器
Axios.interceptors.request.use(
config => {
// 防重復提交
const keyString = qs.stringify(Object.assign({}, { url: config.url, method: config.method }, config.data));
if (requestMap.get(keyString)) {
// 取消當前請求
config.cancelToken = new CancelToken((cancel) => {
cancel('Please slow down a little');
});
}
requestMap.set(keyString, true);
Object.assign(config, { _keyString: keyString });
if (config.method === 'post' || config.method === 'put' || config.method === 'delete') {
// 序列化
config.data = qs.stringify(config.data);
}
return config;
},
error => {
return Promise.reject(error);
}
);
// 返回響應攔截器
Axios.interceptors.response.use(
res => {
// 重置requestMap
const config: any = res.config;
requestMap.set(config._keyString, false);
if (res.status === 200) {
return res.data;
}
// todo 彈窗提示等
console.log(`request error:${res}`);
},
error => {
return {
code: -1
};
}
);
/**
* @description
* 請求
* @param url
* @param data
* @param method
*/
const request = (url: string, data = {}, method = 'post') => {
return Axios({
method,
url,
data,
params: method.toUpperCase() === 'GET' && data
});
};
export { request };
vuex狀態管理
這里我根據業務模塊來劃分文件結構,如下圖
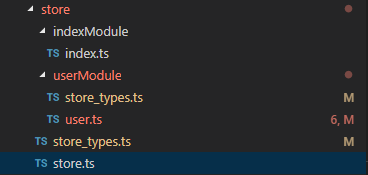
分為首頁模塊和用戶模塊,每個模塊都有自己獨立的 state mutations 等,在 store.ts 中,引入各模塊的文件,如下
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
import index from './indexModule/index';
import user from './userModule/user';
Vue.use(Vuex);
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
user,
index
}
});
大家注意到這里有個 store_types.ts 文件,這個文件主要是為了搭配ts使用的,文件內容如下
export enum UserType {
/**
* 模塊名稱
*/
'MODULE_NAME' = 'user',
/**
* 增加次數
*/
'ADD_COUNT' = 'addCount',
/**
* 計算屬性-獲取十倍的值
*/
'GET_TEM_COUNT' = 'getTenCount'
}
在看下組件中的使用方式:
<script lang="ts">
import { UserType } from '@/store/store_types';
import { Component, Prop, Vue, Watch,Emit } from 'vue-property-decorator';
import {
Action,
Getter,
Mutation,
namespace,
State
} from 'vuex-class';
@Component
export default class Test extends Vue {
@State(state => state[UserType.MODULE_NAME].count) public fff!: number;
@Getter(`${UserType.MODULE_NAME}/${UserType.GET_TEM_COUNT}`) public tenCount!: number;
@Mutation(`${UserType.MODULE_NAME}/${UserType.ADD_COUNT}`) public addCount!: any;
}
</script>
雖然這么寫的確有點繞,但有個好處,我們可以通過注釋清晰知道方法和屬性的說明
小結
以上是我根據自己工作中常見的場景來設計的,希望能對小伙伴能有幫助,其中設計不當的地方,歡迎小伙伴們在留言區一起探討哈~也希望大家多多支持億速云。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。