您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
今天就跟大家聊聊有關python版本五子棋的實現,可能很多人都不太了解,為了讓大家更加了解,小編給大家總結了以下內容,希望大家根據這篇文章可以有所收獲。
1、 摘要
機器博弈是人工智能領域的重要分支,它的研究對象多以復雜的棋牌類智力游戲為主,已經得到解決的棋類游戲,幾乎全部都應歸功于機器博弈近半個世紀的發展。計算機解決問題的優勢在于能把不易解析的問題,借助于現代計算機的運算速度優勢枚舉出所有的合理情形而得解;然而,博弈問題的復雜程度決定了它不能過度依賴機器的計算能力。許多待解決的或已經解決的棋類,其狀態空間復雜度或博弈樹復雜度量級都太過龐大,所以我們需要添加約束,并且采用合理的算法進行優化。
五子棋問題是人工智能中的一個經典問題。當今世界,AlphaGo已經執圍棋之牛耳,五子棋領域卻鮮少有人問津。本文根據課堂所學知識結合文獻、博客,基于兩種開發語言實現了一個智能對戰的AI五子棋游戲平臺。
本文所做工作如下:
(1) 五子棋界面實現;
(2) 智能判定棋盤走勢;
(3) 改進了棋盤掃描方式;
(4) 改良了系統評分表評估方式;
(5) 實現了基于點評分表估值找出最佳落子方式。
2、 問題描述、知識表達
2.1 問題描述
五子棋AI問題的最大問題是如何實現智能對弈,即當人落子之后,算法如何解讀當前的棋盤并且對其進行分析解讀,得到電腦方的最佳落子點。其次還有一個問題是如何判斷勝利,這可以作為前面棋盤局勢判定的一個子問題,也可以看做是一個單獨的問題,不過這個問題總體來說較為簡單,所以不做詳細說明。
2.2 知識表達
五子棋的整體知識構建包含以下部分:
(1) 棋盤局面表示法
(2) 棋局勝利判定
(3) 棋型知識庫
(4) 智能博弈流程
對于問題(1),采用數組表示法。棋盤中的各交叉點有三種狀態,不妨令 0表示空(未放置棋子) ,-1 表示有黑子 ,1 表示有白子,數組表示法的基本思想是:以交叉點對應的數組索引值來表達物理位置 ,以交叉點對應的元素值表達狀態(空、 黑子、 白子)。令 V = {0 ,1 ,-1} ,棋盤 的第 i 個交叉點的狀態 Si ∈V ,任何棋局都可以表示成一個 n ×n 的二元組。
對于問題(2), 采用數組表示法時,想知道任意兩個元素 Si 和Sj 是否共線,要通過 i 和 j 之間的數值規律來判斷。從這方面看,數組表示法是一種原始、低效的表示方法,但是對于評分表算法來說其性能損失是可以接受的。要判斷是否有一方已經勝利,只需要對整個棋盤判定當前落子點的縱、橫、正斜、反斜四個方向的最長延伸出四個位置看是否能連成一條同色直線即可。具體的操作可以視為:從落子點出發,向兩個方向延伸,如果遇到同色,那么計數器加一,遇到非同色(空白或者異色)則停止在該方向的延伸,一個計數器記下該方向上的兩頭的連續同色棋子數。等到四個方向都探索完畢,如果四個計數器中有一個計數器達到了5,那么即可判斷出已經有五子連珠了,此局結束。
問題(3)棋型知識庫主要包括各種既定的棋盤形式,有如下幾種:
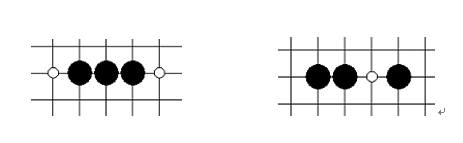
² 活四 :有兩個連五點(即有兩個點可以形成五),圖中白點即為連五點。當活四出現的時候,整個局勢已經無法阻止連五了,活四的歸屬方一定能取得勝利;
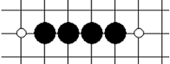
² 沖四 :有一個連五點,如下面三圖,均為沖四棋型。圖中白點為連五點。 相對比活四來說,沖四的威脅性就小了很多,因為這個時候,只要跟著防守在那個唯一的連五點上,沖四就沒法形成連五。
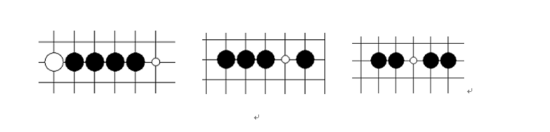
² 活三 :可以形成活四的三,如下圖,代表兩種最基本的活三棋型。圖中白點為活四點。活三棋型是進攻中最常見的一種,因為活三之后,如果對方不以理會,將可以下一手將活三變成活四,而活四是無法防守的。所以,面對活三的時候,需要非常謹慎對待。在沒有更好的進攻手段的情況下,必須對其進行防守,以防止其形成可怕的活四棋型。
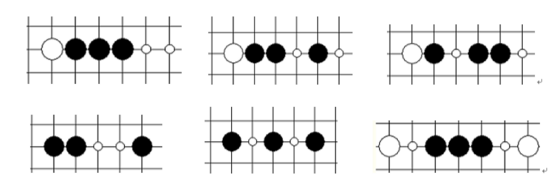
² 眠三: 只能夠形成沖四的三,如下各圖,分別代表最基礎的六種眠三形狀。圖中白點代表沖四點。眠三的棋型與活三的棋型相比,危險系數下降不少,因為眠三棋型即使不去防守,下一手它也只能形成沖四,而對于單純的沖四棋型,是可以很簡單的防守住的。
² 活二 :能夠形成活三的二,如下圖,是三種基本的活二棋型。圖中白點為活三點。
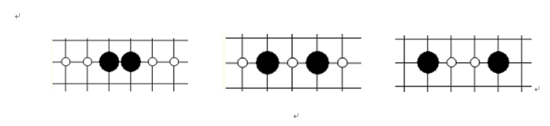
² 眠二 :能夠形成眠三的二。圖中四個為最基本的眠二棋型,細心且喜歡思考的同學會根據眠三介紹中的圖2-13找到與下列四個基本眠二棋型都不一樣的眠二。圖中白點為眠三點。
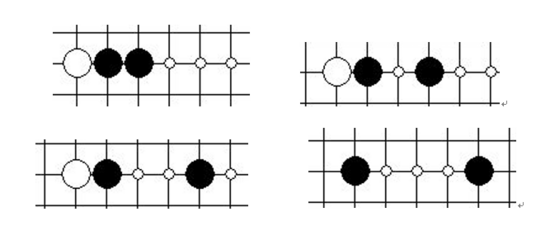
對于上述的棋型,我們主要考慮的是活四、沖四、活三、眠三這幾種主要的進攻棋型的防守與構成,整體棋型遵從以下原則:優先考慮數目,同等數目的情況下考慮是活是眠。評分表算法的設計整體偏向于防守。
對于問題(4),當下棋型的評估分析,算法嚴格遵從以下流程:
當人類方落下一子,算法啟動,掃描全局,得到人類棋子的集合和電腦棋子的集合。全局掃描之后,對當前局勢進行排序、計算。對每個集合的每個空白點位置打分,打分依據是根據這個點周圍四個方向上的同色連續棋子的數量。按照這些最后得到的評分,得出最大值。得到人類方和電腦方的兩個最大值之后,進行比較,如果人類方局勢較好(分數較高),則算法將下一次落子位置設置為人類方得分最高的點,盡力降低人類方的下一步得分;如果電腦方的分數較高,那么則直接在使得分數最高的點落子即可。
3、 開發工具
本次課程設計,一共設計了兩個版本,一個Java版本,為19X19的棋盤,配備簡單的消息提示,基于AWT實現GUI,開發工具IntelliJ IDEA 2018.1
另一個版本是使用Python設計,核心算法相同,但是受限于圖片源文件,為15X15棋盤,基于pygame實現GUI,開發工具是:JetBrains PyCharm 2018.2.4 x64
4、 代碼實現
from time import sleep
import pygame
from pygame.locals import *
from random import randint
level = 15
grade = 10
MAX = 1008611
def Scan(chesspad, color):
shape = [[[0 for high in range(5)] for col in range(15)] for row in range(15)]
# 掃描每一個點,然后在空白的點每一個方向上做出價值評估!!
for i in range(15):
for j in range(15):
# 如果此處為空 那么就可以開始掃描周邊
if chesspad[i][j] == 0:
m = i
n = j
# 如果上方跟當前傳入的顏色參數一致,那么加分到0位!
while n - 1 >= 0 and chesspad[m][n - 1] == color:
n -= 1
shape[i][j][0] += grade
if n-1>=0 and chesspad[m][n - 1] == 0:
shape[i][j][0] += 1
if n-1 >= 0 and chesspad[m][n - 1] == -color:
shape[i][j][0] -= 2
m = i
n = j
# 如果下方跟當前傳入的顏色參數一致,那么加分到0位!
while (n + 1 < level and chesspad[m][n + 1] == color):
n += 1
shape[i][j][0] += grade
if n + 1 < level and chesspad[m][n + 1] == 0:
shape[i][j][0] += 1
if n + 1 < level and chesspad[m][n + 1] == -color:
shape[i][j][0] -= 2
m = i
n = j
# 如果左邊跟當前傳入的顏色參數一致,那么加分到1位!
while (m - 1 >= 0 and chesspad[m - 1][n] == color):
m -= 1
shape[i][j][1] += grade
if m - 1 >= 0 and chesspad[m - 1][n] == 0:
shape[i][j][1] += 1
if m - 1 >= 0 and chesspad[m - 1][n] == -color:
shape[i][j][1] -= 2
m = i
n = j
# 如果右邊跟當前傳入的顏色參數一致,那么加分到1位!
while (m + 1 < level and chesspad[m + 1][n] == color):
m += 1
shape[i][j][1] += grade
if m + 1 < level and chesspad[m + 1][n] == 0:
shape[i][j][1] += 1
if m + 1 < level and chesspad[m + 1][n] == -color:
shape[i][j][1] -= 2
m = i
n = j
# 如果左下方跟當前傳入的顏色參數一致,那么加分到2位!
while (m - 1 >= 0 and n + 1 < level and chesspad[m - 1][n + 1] == color):
m -= 1
n += 1
shape[i][j][2] += grade
if m - 1 >= 0 and n + 1 < level and chesspad[m - 1][n + 1] == 0:
shape[i][j][2] += 1
if m - 1 >= 0 and n + 1 < level and chesspad[m - 1][n + 1] == -color:
shape[i][j][2] -= 2
m = i
n = j
# 如果右上方跟當前傳入的顏色參數一致,那么加分到2位!
while (m + 1 < level and n - 1 >= 0 and chesspad[m + 1][n - 1] == color):
m += 1
n -= 1
shape[i][j][2] += grade
if m + 1 < level and n - 1 >= 0 and chesspad[m + 1][n - 1] == 0:
shape[i][j][2] += 1
if m + 1 < level and n - 1 >= 0 and chesspad[m + 1][n - 1] == -color:
shape[i][j][2] -= 2
m = i
n = j
# 如果左上方跟當前傳入的顏色參數一致,那么加分到3位!
while (m - 1 >= 0 and n - 1 >= 0 and chesspad[m - 1][n - 1] == color):
m -= 1
n -= 1
shape[i][j][3] += grade
if m - 1 >= 0 and n - 1 >= 0 and chesspad[m - 1][n - 1] == 0:
shape[i][j][3] += 1
if m - 1 >= 0 and n - 1 >= 0 and chesspad[m - 1][n - 1] == -color:
shape[i][j][3] -= 2
m = i
n = j
# 如果右下方跟當前傳入的顏色參數一致,那么加分到3位!
while m + 1 < level and n + 1 < level and chesspad[m + 1][n + 1] == color:
m += 1
n += 1
shape[i][j][3] += grade
if m + 1 < level and n + 1 < level and chesspad[m + 1][n + 1] == 0:
shape[i][j][3] += 1
if m + 1 < level and n + 1 < level and chesspad[m + 1][n + 1] == -color:
shape[i][j][3] -= 2
return shape
def Sort(shape):
for i in shape:
for j in i:
for x in range(5):
for w in range(3, x - 1, -1):
if j[w - 1] < j[w]:
temp = j[w]
j[w - 1] = j[w]
j[w] = temp
print("This Time Sort Done !")
return shape
def Evaluate(shape):
for i in range(level):
for j in range(level):
if shape[i][j][0] == 4:
return i, j, MAX
shape[i][j][4] = shape[i][j][0]*1000 + shape[i][j][1]*100 + shape[i][j][2]*10 + shape[i][j][3]
max_x = 0
max_y = 0
max = 0
for i in range(15):
for j in range(15):
if max < shape[i][j][4]:
max = shape[i][j][4]
max_x = i
max_y = j
print("the max is "+ str(max) + " at ( "+ str(max_x)+" , "+str(max_y)+" )")
return max_x, max_y, max
class chess(object):
def __init__(self):
self.a = [[0 for high in range(15)] for col in range(15)]
def fall(self, x, y, color):
if (x < 0 or x > level - 1 or y < 0 or y > level - 1):
return
self.a[x][y] = color
if Judge(x, y, color, self.a, 4):
if color < 0:
print("The Winner is White!!")
else:
print("The Winner is Black!!")
def isEmpty(self, m, n):
if self.a[m][n] != 0:
return False
else:
return True
def Judge(x, y, color, CHESSLOCATION, length):
count1, count2, count3, count4 = 0, 0, 0, 0
# 橫向判斷
i = x - 1
while (i >= 0):
if color == CHESSLOCATION[i][y]:
count1 += 1
i -= 1
else:
break
i = x + 1
while i < level:
if CHESSLOCATION[i][y] == color:
count1 += 1
i += 1
else:
break
# 縱向判斷
j = y - 1
while (j >= 0):
if CHESSLOCATION[x][j] == color:
count2 += 1
j -= 1
else:
break
j = y + 1
while j < level:
if CHESSLOCATION[x][j] == color:
count2 += 1
j += 1
else:
break
# 正對角線判斷
i, j = x - 1, y - 1
while (i >= 0 and j >= 0):
if CHESSLOCATION[i][j] == color:
count3 += 1
i -= 1
j -= 1
else:
break
i, j = x + 1, y + 1
while (i < level and j < level):
if CHESSLOCATION[i][j] == color:
count3 += 1
i += 1
j += 1
else:
break
# 反對角線判斷
i, j = x + 1, y - 1
while (i < level and j >= 0):
if CHESSLOCATION[i][j] == color:
count4 += 1
i += 1
j -= 1
else:
break
i, j = x - 1, y + 1
while (i > 0 and j < level):
if CHESSLOCATION[i][j] == color:
count4 += 1
i -= 1
j += 1
else:
break
if count1 >= length or count2 >= length or count3 >= length or count4 >= length:
return True
else:
return False
def Autoplay(ch, m, n):
a1 = [1,-1,1,-1,1,-1,0,0]
b1 = [1,-1,-1,1,0,0,1,-1]
rand = randint(0,7)
while m+a1[rand]>=0 and m+a1[rand]<level and n+b1[rand]>=0 and n+b1[rand]<level and ch[m+a1[rand]][n+b1[rand]]!=0 :
rand = randint(0,7)
return m + a1[rand], n+b1[rand]
def BetaGo(ch, m, n, color, times):
if times < 2:
return Autoplay(ch, m, n)
else:
shape_P = Scan(ch, -color)
shape_C = Scan(ch,color)
shape_P = Sort(shape_P)
shape_C = Sort(shape_C)
max_x_P, max_y_P, max_P = Evaluate(shape_P)
max_x_C, max_y_C, max_C = Evaluate(shape_C)
if max_P>max_C and max_C<MAX:
return max_x_P,max_y_P
else:
return max_x_C,max_y_C
def satrtGUI(ch):
pygame.init()
bg = 'bg.png'
white_image = 'white.png'
black_image = 'black.png'
screen = pygame.display.set_mode((750, 750), 0, 32)
background = pygame.image.load(bg).convert()
white = pygame.image.load(white_image).convert_alpha()
black = pygame.image.load(black_image).convert_alpha()
white = pygame.transform.smoothscale(white, (int(white.get_width() * 1.5), int(white.get_height() * 1.5)))
black = pygame.transform.smoothscale(black, (int(black.get_width() * 1.5), int(black.get_height() * 1.5)))
screen.blit(background, (0, 0))
font = pygame.font.SysFont("黑體", 40)
pygame.event.set_blocked([1, 4, KEYUP, JOYAXISMOTION, JOYBALLMOTION, JOYBUTTONDOWN, JOYBUTTONUP, JOYHATMOTION])
pygame.event.set_allowed([MOUSEBUTTONDOWN, MOUSEBUTTONUP, 12, KEYDOWN])
dot_list = [(25 + i * 50 - white.get_width() / 2, 25 + j * 50 - white.get_height() / 2) for i in range(level) for
j in range(level)]
color = -1
times = 0
flag = False
while not flag:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == QUIT:
exit()
elif event.type == MOUSEBUTTONDOWN:
x, y = pygame.mouse.get_pos()
if 25 <= x <= 725 and 25 <= y <= 725 and ((x - 25) % 50 <= level or (x - 25) % 50 >= 0) and (
(y - 25) % 50 <= level or (y - 25) % 50 >= 0):
color = -1 * color
m = int(round((x - 25) / 50))
n = int(round((y - 25) / 50))
if not ch.isEmpty(m, n):
print("Black OverWrite~~")
continue
ch.fall(m, n, color)
screen.blit(black, dot_list[level * m + n])
if Judge(m, n, color, ch.a, 4):
screen.blit(font.render('GAME OVER,Black is win!', True, (110, 210, 30)), (80, 650))
break
color = -1 * color
sleep(0.1)
x, y = BetaGo(ch.a, m, n, color, times)
times += 1
print("Predict:" + str(x) + " and " + str(y))
ch.fall(x, y, color)
screen.blit(white, dot_list[level * x + y])
if Judge(x, y, color, ch.a, 4):
screen.blit(font.render('GAME OVER,White is win!', True, (217, 20, 30)), (80, 650))
break
pygame.display.update()
if flag:
sleep(5)
now = chess()
satrtGUI(now)
bg.png
black.png

white.png
看完上述內容,你們對python版本五子棋的實現有進一步的了解嗎?如果還想了解更多知識或者相關內容,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道,感謝大家的支持。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。