您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要講解了“Java鏈表怎么應用”,文中的講解內容簡單清晰,易于學習與理解,下面請大家跟著小編的思路慢慢深入,一起來研究和學習“Java鏈表怎么應用”吧!
刪除鏈表中等于給定值val的所有節點。【OJ鏈接】
定義兩個指針prev、cur,cur指向頭節點的下一個節點,prev始終指向cur的前一個結點(方便刪除節點)。通過cur指針去遍歷鏈表,和val值比較,相同就刪除這個節點。最后再來比較頭節點。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if(head==null){
return null;
}
ListNode prev=head;
ListNode cur=head.next;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val==val){
prev.next=cur.next;
cur=cur.next;
}else{
prev=cur;
cur=cur.next;
}
}
if(head.val==val){
head=head.next;
}
return head;
}
}反轉一個鏈表。【OJ鏈接】
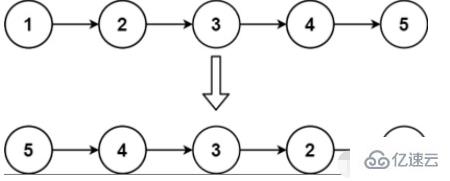
在遍歷鏈表時,將當前節點的 指針改為指向前一個節點。由于節點沒有引用其前一個節點,因此必須事先存儲其前一個節點。在更改引用之前,還需要存儲后一個節點。最后返回新的頭引用。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null){
return null;
}
ListNode cur=head.next;
head.next=null;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode curNext=cur.next;
cur.next=head;
head=cur;
cur=curNext;
}
return head;
}
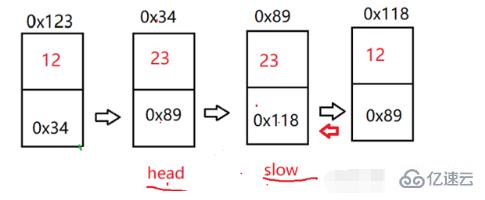
}給定一個帶有頭節點的非空單鏈表,返回鏈表的中間節點。如果有兩個中間節點,則返回第二個中間節點。【OJ鏈接】
我們可以定義兩個快慢指針(fast、slow),都指向頭節點。快指針每次走兩步,慢指針每次走一步。鏈表有偶數個節點時,fast=null時slow為中間節點;鏈表有奇數個節點時,fast.next=null時slow為中間節點。
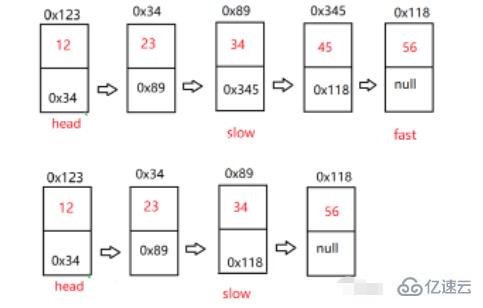
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
if(head==null){
return null;
}
ListNode slow=head;
ListNode fast=head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}輸入一個鏈表,返回該鏈表中倒數第K個節點。【OJ鏈接】
這個題和找中間節點的思路相似。定義兩個指針(fast、slow)。在K合理的前提下,我們可以讓快指針先走K-1步,然后快慢指針同時向后走,當fast到達鏈表結尾時,slow就指向倒數第K個節點。
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
if(k<=0||head==null){
return null;
}
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while(k-1>0){
if(fast.next==null){
return null;
}
fast=fast.next;
//先讓快節點走k-1步
k--;
}
while(fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}將兩個有序鏈表合并為一個有序鏈表并返回。新鏈表是通過拼接給定的兩個鏈表的所有節點組成的。【OJ鏈接】
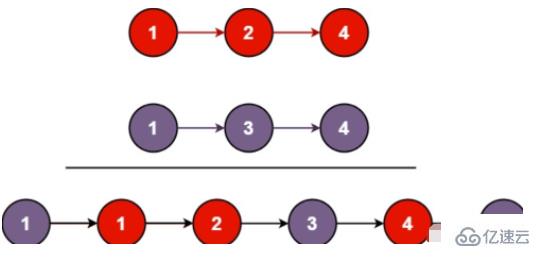
解這個題,需要定義虛假節點來充當新鏈表的頭節點。通過兩個鏈表的頭節點去遍歷兩個節點,去比較兩個鏈表對應節點的值,將值小的節點連接到新鏈表的后面,知道兩個鏈表遍歷完,當其中一個鏈表為空時,直接將另一個鏈表連接到新鏈表后面即可。
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1==null){
return list2;
}
if(list2==null){
return list1;
}
//創建虛擬節點,充當新鏈表的頭節點,值不代表任何意義
ListNode node=new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur=node;
while(list1!=null&&list2!=null){
if(list1.val<list2.val){
cur.next=list1;
list1=list1.next;
}else{
cur.next=list2;
list2=list2.next;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
if(list1==null){
cur.next=list2;
}else{
cur.next=list1;
}
return node.next;
}
}將一個鏈表按照給定值X劃分為兩部分,所有小于X的節點排在大于或等于X的節點之前。不改變節點原來的順序。【OJ鏈接】
首先我們需要定義四個指針(bs、be、as、ae)分別表示小于X部分鏈表的頭節點和尾節點、大于X部分鏈表的頭節點和尾節點。通過頭節點遍歷鏈表,將鏈表分為兩部分。最后將兩個鏈表連接起來即可。需要特別注意,當小于X部分鏈表不為空時,我們需要手動將ae.next置為空。
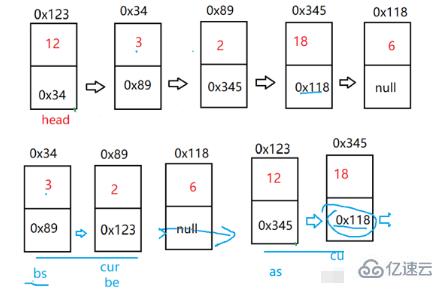
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Partition {
public ListNode partition(ListNode pHead, int x) {
if(pHead==null){
return null;
}
ListNode bs=null;
ListNode be=null;
ListNode as=null;
ListNode ae=null;
ListNode cur=pHead;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val<x){
if(bs==null){
bs=cur;
be=cur;
}else{
be.next=cur;
be=cur;
}
}else{
if(as==null){
as=cur;
ae=cur;
}else{
ae.next=cur;
ae=cur;
}
}
cur=cur.next;
}
if(bs==null){
return as;
//如果小于X部分為空,則直接返回大于X部分即可。此時ae.next一定為null
}
be.next=as;//否則連接小于X和大于X部分
if(as!=null){
ae.next=null;
//當小于X部分不為空時,ae.next可能不為null,需要手動置為null
}
return bs;
}
}判斷鏈表是不是回文鏈表。【OJ鏈接】
首先我們需要找到鏈表的中間節點,然后將后半段鏈表反轉。最后通過兩邊來逐步比較即可。特別注意,當鏈表結點個數為偶數時,因為中間節點的緣故,兩邊遍歷時,無法相遇,需要特殊處理。
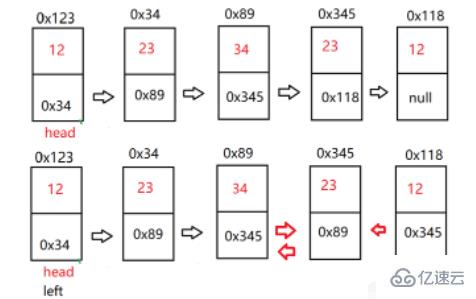
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class PalindromeList {
public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode A) {
if(A==null){
return false;
}
if(A.next==null){
return true;
}
//求鏈表的中間節點
ListNode slow=A;
ListNode fast=A;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
//反轉后半段鏈表
ListNode cur=slow.next;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode curNext=cur.next;
cur.next=slow;
slow=cur;
cur=curNext;
}
//判斷回文鏈表
while(slow!=A){
if(slow.val!=A.val){
return false;
}
if(A.next==slow){
return true;
}
slow=slow.next;
A=A.next;
}
return true;
}
}輸入兩個鏈表,輸出兩個鏈表的第一個公共節點。沒有返回NULL。【OJ鏈接】
兩個鏈表相交呈現Y字型。那么兩個鏈表長度的差肯定是未相交前兩個鏈表節點的差。我們需要求出兩個鏈表的長度。定義兩個指針(pl、ps),讓pl指向長的鏈表,ps指向短的鏈表。求出兩個鏈表的長度差len。讓pl想走len步。這樣兩個鏈表的剩余長度就相同。此時兩個指針同時遍歷連個鏈表,如果其指向一致,則兩個鏈表相交,否則,兩個鏈表不相交。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
//求鏈表長度
public int len(ListNode head){
int len=0;
while(head!=null){
head=head.next;
len++;
}
return len;
}
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA==null||headB==null){
return null;
}
ListNode pl=headA;
ListNode ps=headB;
int lenA=len(headA);
int lenB=len(headB);
int len=lenA-lenB;
if(len<0){
//pl指向長的鏈表,ps指向短的鏈表
pl=headB;
ps=headA;
len=-len;
}
while(len--!=0){
pl=pl.next;
}
while(pl!=null){
if(pl==ps){
return pl;
}
pl=pl.next;
ps=ps.next;
}
return null;
}
}判斷鏈表中是否有環。【OJ鏈接】
還是快慢指針。慢指針一次走一步,快指針一次走兩步。兩個指針從鏈表起始位置開始運行。如果鏈表帶環則一定會在環中相遇,否則快指針率先走到鏈表的末尾。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null||head.next==null){
return false;//鏈表為空或者只有一個節點時,沒有環
}
ListNode slow=head;
ListNode fast=head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
if(fast==slow){
return true;
//如果快慢節點可以相遇,表示鏈表有環
}
}
return false;
}
}給定一個鏈表,判斷鏈表是否有環并返回入環的節點。如果沒有環,返回NULL。【OJ鏈接】
讓一個指針從鏈表的其實在位置開始遍歷,同時另一個指針從上題中兩只真相與的位置開始走,兩個指針再次相遇時的位置肯定為環的入口
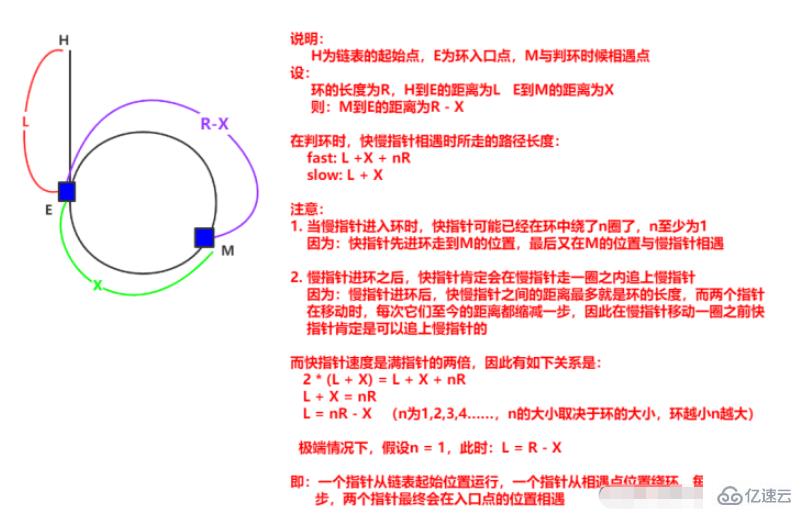
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
//判斷鏈表是否有環,并返回第一次快慢節點相交的位置
public ListNode hasCycle(ListNode head){
if(head==null||head.next==null){
return null;
}
ListNode slow=head;
ListNode fast=head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next.next;
if(slow==fast){
return slow;
}
}
return null;
}
//當返回的結點與頭節點再次相交時,為環的入口
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode node=hasCycle(head);
if(node==null){
return null;
}else{
while(head!=node){
head=head.next;
node=node.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}感謝各位的閱讀,以上就是“Java鏈表怎么應用”的內容了,經過本文的學習后,相信大家對Java鏈表怎么應用這一問題有了更深刻的體會,具體使用情況還需要大家實踐驗證。這里是億速云,小編將為大家推送更多相關知識點的文章,歡迎關注!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。