您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹了Java字符串操作的示例分析,具有一定借鑒價值,感興趣的朋友可以參考下,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章之后大有收獲,下面讓小編帶著大家一起了解一下。
字符串內部包含一個字符數組,String 可以和 char[] 相互轉換.
| NO | 方法名稱 | 類型 | 描述 |
| 1 | public String(char value[]) | 構造 | 將字符數組中的所有內容變字符串 |
| 2 | public String(char value[],int offset,int count) | 構造 | 將部分字符數組的內容變為字符串 |
| 3 | public char charAt(int index) | 普通 | 取得指定索引位置的字符串,索引從0開始 |
| 4 | public char[] toChararray() | 普通 | 將字符串變為字符數組返回 |
代碼示例: 獲取指定位置的字符
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello" ;
System.out.println(str.charAt(0));// 下標從 0 開始
System.out.println(str.charAt(1));
System.out.println(str.charAt(2));
System.out.println(str.charAt(3));
}
代碼示例: 字符串與字符數組的轉換
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloworld" ;
// 將字符串變為字符數組
char[] data = str.toCharArray() ;
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
System.out.print(data[i]+" ");
}
}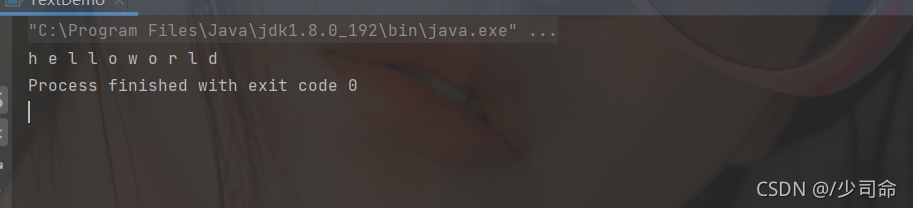
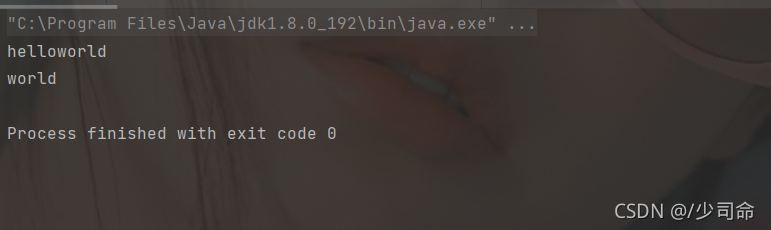
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloworld" ;
// 將字符串變為字符數組
char[] data = str.toCharArray() ;
// 字符數組轉為字符串
System.out.println(new String(data)); // 全部轉換
System.out.println(new String(data,5,5)); // 部分轉換
}
代碼示例: 給定字符串一個字符串, 判斷其是否全部由數字所組成
public static boolean isNumberChar(String s) {
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i);
//判斷某個字符是不是數字
if(c < '0' || c > '9') {
return false;
}
}
return true;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "124567";
System.out.println(isNumberChar(str));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "1d4567";
System.out.println(isNumberChar(str));
}
字節常用于數據傳輸以及編碼轉換的處理之中,String 也能方便的和 byte[] 相互轉換
| NO | 方法名稱 | 類型 | 描述 |
| 1 | public String(byte bytes[]) | 構造 | 將字節數組變為字符串 |
| 2 | public String(byte bytes[],int offset,int length) | 構造 | 將部分字節數組中的內容變為字符串 |
| 3 | public bye[] getBytes() | 普通 | 將字符串以字節數組的形式返回 |
| 4 | public byte[] getBytes(String charsetNAme)throws UnsupportedEncodingException | 普通 | 編碼轉化處理 |
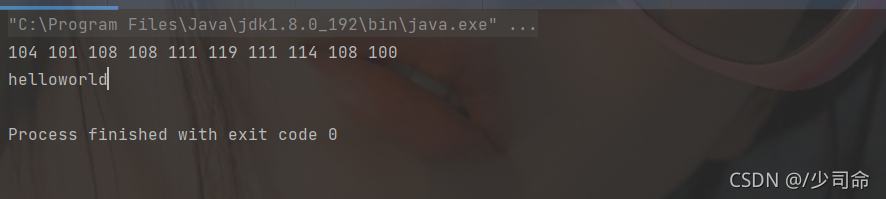
代碼示例: 實現字符串與字節數組的轉換處理
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloworld" ;
// String 轉 byte[]
byte[] data = str.getBytes() ;
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
System.out.print(data[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
// byte[] 轉 String
System.out.println(new String(data));
}
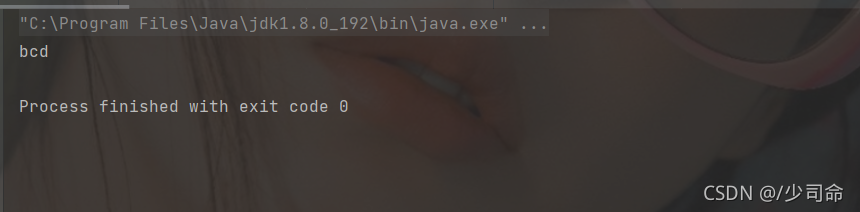
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte[] bytes = {97,98,99,100};
String str = new String(bytes,1,3);
System.out.println(str);
}
????小結
byte[] 是把 String 按照一個字節一個字節的方式處理, 這種適合在網絡傳輸, 數據存儲這樣的場景下使用. 更適合 針對二進制數據來操作.
char[] 是吧 String 按照一個字符一個字符的方式處理, 更適合針對文本數據來操作, 尤其是包含中文的時候.
| No | 方法名稱 | 類型 | 描述 |
| 1 | public boolean equals(Object anObject) | 普通 | 區分大小的比較 |
| 2 | public boolean equalsIanorecase(String anotherString) | 普通 | 不區分大小寫的比較 |
| 3 | public int compareTo(String anotherString) | 普通 | 比較兩個字符串大小關系 |
代碼示例: 不區分大小寫比較
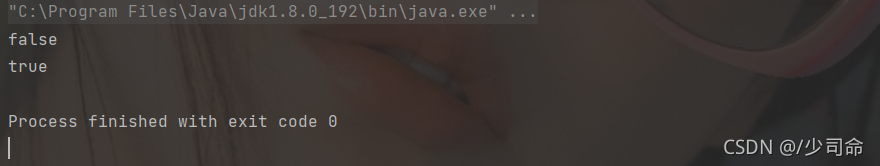
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "hello" ;
String str2 = "Hello" ;
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2)); // false
System.out.println(str1.equalsIgnoreCase(str2)); // true
}
在String類中compareTo()方法是一個非常重要的方法,該方法返回一個整型,該數據會根據大小關系返回三類內容:
1. 相等:返回0.
2. 小于:返回內容小于0.
3. 大于:返回內容大于0。
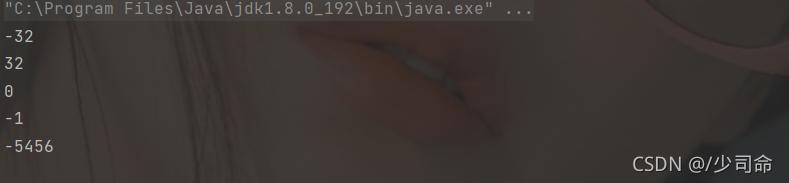
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("A".compareTo("a")); // -32
System.out.println("a".compareTo("A")); // 32
System.out.println("A".compareTo("A")); // 0
System.out.println("AB".compareTo("AC")); // -1
System.out.println("劉".compareTo("楊"));
}
compareTo()是一個可以區分大小關系的方法,是String方法里是一個非常重要的方法。
字符串的比較大小規則, 總結成三個字 "字典序" 相當于判定兩個字符串在一本詞典的前面還是后面. 先比較第一 個字符的大小(根據 unicode 的值來判定), 如果不分勝負, 就依次比較后面的內容
從一個完整的字符串之中可以判斷指定內容是否存在,對于查找方法有如下定義:
| NO | 方法名稱 | 類型 | 描述 |
| 1 | public boolean contains(CharSequence s) | 普通 | 判斷一個子字符串是否存在 |
| 2 | public int indexOf(String str) | 普通 | 從頭開始查找指定字符串的位置,查到了返回位置的開始索引,如果查不到返回-1 |
| 3 | public int indexOf(String str,int fromIndex) | 普通 | 從指定位置查找子字符串位置 |
| 4 | public int LastIndexOf(String str) | 普通 | 從后向前查找子字符串位置 |
| 5 | public int LastIndexOf(String str, int fromIdex) | 普通 | 從指定位置由后向前查找 |
| 6 | public boolean startWith (String prefix) | 普通 | 判斷是否以指定字符串開頭 |
| 7 | public boolean startWith(String prefix, int toffset) | 普通 | 從指定位置開始判斷是否以指定字符串開頭 |
| 8 | public boolean endWith(String suffix) | 普通 | 判斷是否以指定字符串結尾 |
代碼示例: 字符串查找,最好用最方便的就是contains()
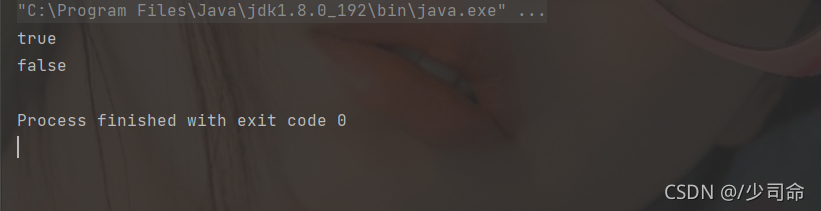
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloworld" ;
System.out.println(str.contains("world"));
System.out.println(str.contains("forld"));
}
代碼示例: 使用indexOf()方法進行位置查找
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloworld" ;
System.out.println(str.indexOf("world")); // 5,w開始的索引
System.out.println(str.indexOf("bit")); // -1,沒有查到
if (str.indexOf("hello") != -1) {
System.out.println("可以查到指定字符串!");
}
}
代碼示例: 使用indexOf()的注意點
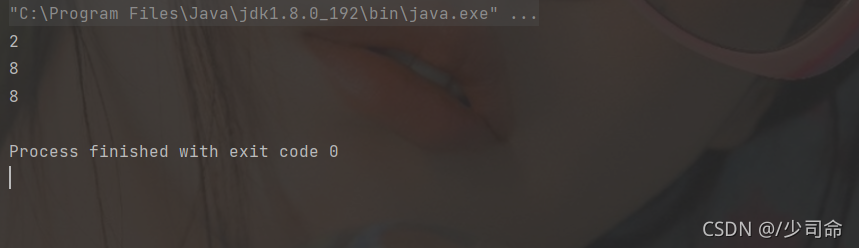
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloworld" ;
System.out.println(str.indexOf("l")); // 2
System.out.println(str.indexOf("l",5)); // 8
System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf("l")); // 8
}
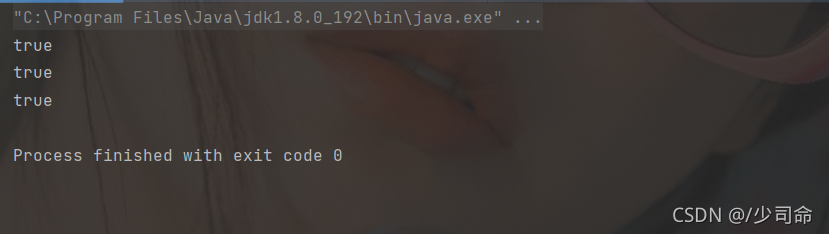
代碼示例: 判斷開頭或結尾
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "**@@helloworld!!" ;
System.out.println(str.startsWith("**")); // true
System.out.println(str.startsWith("@@",2)); // ture
System.out.println(str.endsWith("!!")); // true
}
使用一個指定的新的字符串替換掉已有的字符串數據,可用的方法如下
| No | 方法名稱 | 類型 | 描述 |
| 1 | public String replaceAll(String regex,String replacement) | 普通 | 替換所有指定的內容 |
| 2 | public String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement) | 普通 | 替換首個內容 |
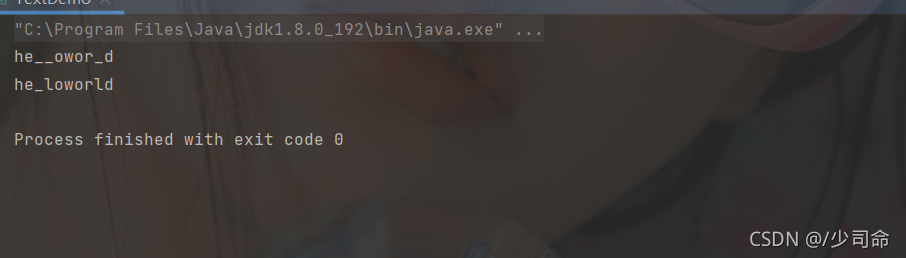
代碼示例: 字符串的替換處理
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloworld" ;
System.out.println(str.replaceAll("l", "_"));
System.out.println(str.replaceFirst("l", "_"));
}
注意事項: 由于字符串是不可變對象 , 替換不修改當前字符串, 而是產生一個新的字符串
可以將一個完整的字符串按照指定的分隔符劃分為若干個子字符串。
| NO | 方法名稱 | 類型 | 描述 |
| 1 | public String[] split(String regex) | 普通 | 將字符串全部拆分 |
| 2 | public String[] split(String regex,int limit) | 普通 | 將字符串部分拆分 |
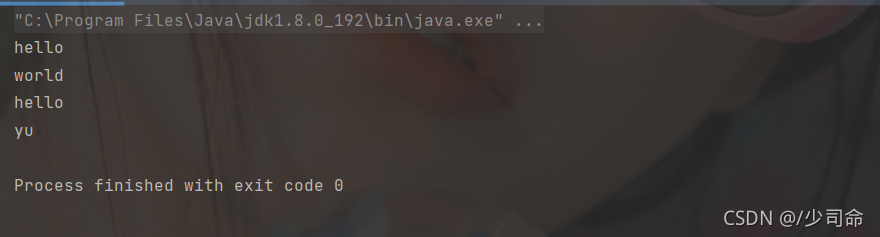
代碼示例: 實現字符串的拆分處理
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello world hello yu" ;
String[] result = str.split(" ") ; // 按照空格拆分
for(String s: result) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
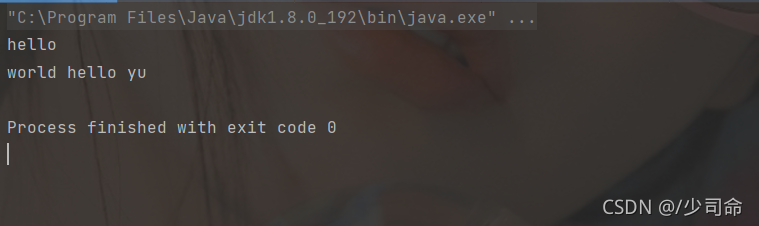
代碼示例: 字符串的部分拆分
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello world hello yu" ;
String[] result = str.split(" ",2) ;
for(String s: result) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
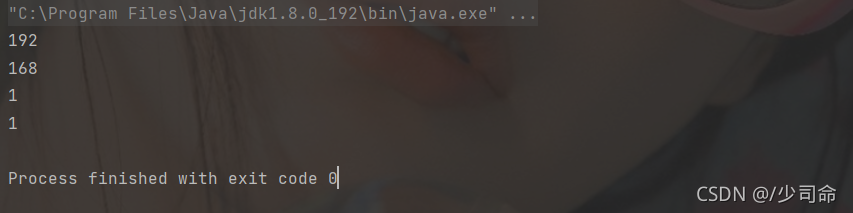
代碼示例: 拆分IP地址
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "192.168.1.1" ;
String[] result = str.split("\\.") ;
for(String s: result) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
注意事項:
1. 字符"|","*","+"都得加上轉義字符,前面加上"\".
2. 而如果是"",那么就得寫成"\\".
3. 如果一個字符串中有多個分隔符,可以用"|"作為連字符
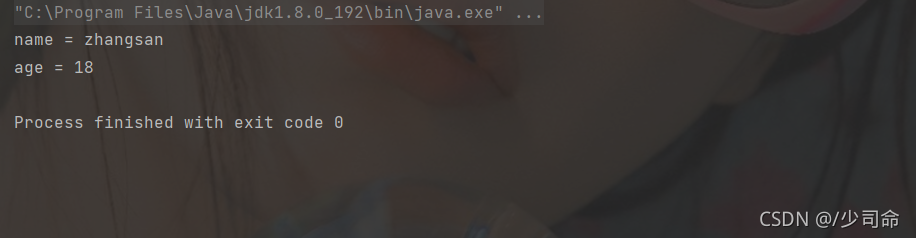
代碼示例: 多次拆分
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "name=zhangsan&age=18" ;
String[] result = str.split("&") ;
for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
String[] temp = result[i].split("=") ;
System.out.println(temp[0]+" = "+temp[1]);
}
}
從一個完整的字符串之中截取出部分內容。可用方法如下:
| NO | 方法名稱 | 類型 | 描述 |
| 1 | public String substring(int beginIndex) | 普通 | 從指定索引截取到結尾 |
| 2 | public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) | 普通 | 截取部分內容 |
代碼示例: 觀察字符串截取
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloworld" ;
System.out.println(str.substring(5));
System.out.println(str.substring(0, 5));
}
注意事項:
1. 索引從0開始
2. 注意前閉后開區間的寫法, substring(0, 5) 表示包含 0 號下標的字符, 不包含 5 號下標
| NO | 方法名稱 | 類型 | 描述 |
| 1 | public String trim() | 普通 | 去掉字符串的左右空格,保留中間空格 |
| 2 | public String toUpperCase() | 普通 | 字符串轉大寫 |
| 3 | public String toLowerCase() | 普通 | 字符串轉小寫 |
| 4 | public native String intern() | 普通 | 字符串入池操作 |
| 5 | public String concat(String str) | 普通 | 字符串連接,等同于+,不入池 |
| 6 | public int length() | 普通 | 取得字符串長度 |
| 7 | public boolean isEmpty | 普通 | 判斷是否為空字符串,但不是null,而是長度0 |
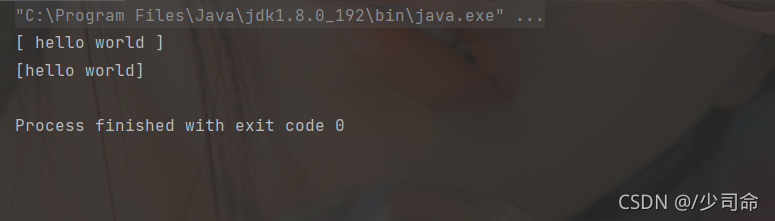
代碼示例: 觀察trim()方法的使用
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = " hello world " ;
System.out.println("["+str+"]");
System.out.println("["+str.trim()+"]");
}
代碼示例: 大小寫轉換
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = " hello%$$%@#$%world 哈哈哈 " ;
System.out.println(str.toUpperCase());
System.out.println(str.toLowerCase());
}
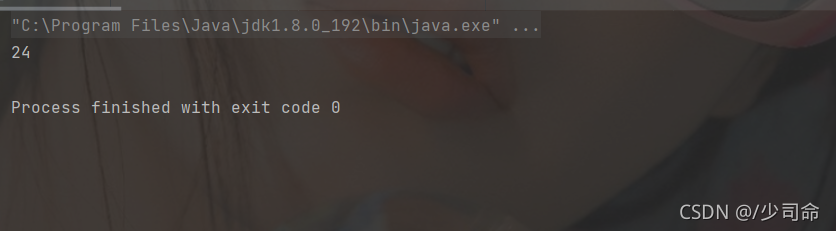
代碼示例: 字符串length()
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = " hello%$$%@#$%world 哈哈哈 " ;
System.out.println(str.length());
}
注意:數組長度使用數組名稱.length屬性,而String中使用的是length()方法
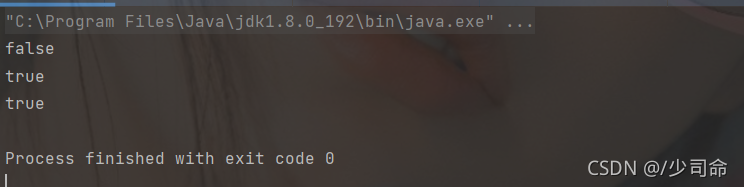
代碼示例: 觀察isEmpty()方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("hello".isEmpty());
System.out.println("".isEmpty());
System.out.println(new String().isEmpty());
}
String類并沒有提供首字母大寫操作,需要自己實現
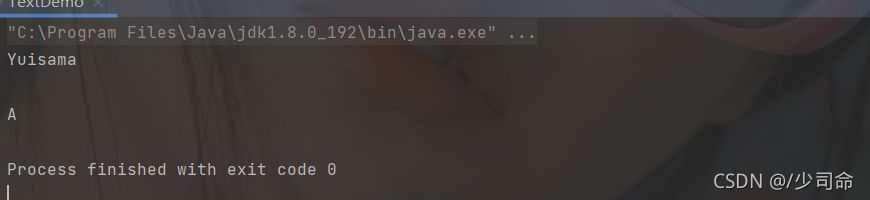
代碼示例: 首字母大寫
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(fistUpper("yuisama"));
System.out.println(fistUpper(""));
System.out.println(fistUpper("a"));
}
public static String fistUpper(String str) {
if ("".equals(str)||str==null) {
return str ;
}
if (str.length()>1) {
return str.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase()+str.substring(1) ;
}
return str.toUpperCase() ;
}
感謝你能夠認真閱讀完這篇文章,希望小編分享的“Java字符串操作的示例分析”這篇文章對大家有幫助,同時也希望大家多多支持億速云,關注億速云行業資訊頻道,更多相關知識等著你來學習!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。