溫馨提示×
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
點擊 登錄注冊 即表示同意《億速云用戶服務條款》
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
[TOC]
行式數據庫:
可以簡單的理解為類似傳統的rdbmspaint這些數據,存放的數據都是結構化的數據。
行式數據庫,是有利于全表數據的掃描,不利于只查詢個別字段列式數據庫:
對行式數據庫的一個改進,將部分列(或者說有關聯的一些列)存放到單獨的文件中,其他列存在其它多個文件中,
我們在進行查詢的時候,只需要讀取出這些常用列即可完成工作,這樣,減少了文件IO的讀寫,提高讀寫的效率(
不用再想行式數據庫進行全表掃描,然后過濾相關字段)
在行式數據庫里面,大數據領域有一個非常著名的產品——HBase,其有別于傳統的RDBMS,被稱之為列式數據庫,
或者是NoSQL(Not Only SQL,是一類數據庫的統稱,常見的有Hbase、Redis、mechache、mongodb。。。。)中的一塊數據。
能夠滿足對hdfs上面海量數據的告訴數據讀寫。是一個高可靠性、高性能、面向列、可伸縮的分布式存儲系統,
利用HBase技術可在廉價PC Server上搭建起大規模結構化存儲集群。
HBase利用Hadoop HDFS作為其文件存儲系統,利用Hadoop MapReduce來處理HBase中的海量數據,
利用Zookeeper作為協調工具。特點:
高可靠性
高性能
面向列
可伸縮
表的特點
縱向擴展
橫向擴展
部署上來說:
分布式集群
HBase設計初衷,是為了企業中的大表,面向上百萬列,上百億條記錄設計的數據庫。
可以分布式存儲海量的數據
具有容錯能力強,數據高可靠的特點
HBase是一個列式NoSQL數據庫
數據存儲的結構是按照列進行存儲。按照列進行存儲的數據庫產品,一般都有行鍵的概念。
使用行鍵,可以標示一行數據。理解行鍵的時候,可以簡單的認為是RDBMS中的PK。
Hbase存儲數據的物理結構是key-value形式。key就是行鍵。
同時可以非常方便的進行橫向擴展(scale out,縱向擴展scale up)。安裝前需要保證hadoop、zookeeper、java已經安裝好。
解壓 ~]$ tar -zxf /home/uplooking/soft/hbase-1.1.5-bin.tar.gz -C /home/uplooking/app
重命名 ~]$ mv /home/uplooking/app/hbase-1.1.5 /home/uplooking/app/hbase
添加至環境變量 export HBASE_HOME=/home/uplooking/app/hbase
配置 $HBASE_HOME/conf/hbase-env.sh、hbase-site.xml
$HBASE_HOME/conf/hbase-env.sh
export JAVA_HOME=/opt/jdk
export HBASE_MANAGES_ZK=false
$HBASE_HOME/conf/hbase-site.xml
<property>
<name>hbase.rootdir</name>
<value>hdfs://ns1/hbase</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hbase.cluster.distributed</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hbase.zookeeper.quorum</name>
<value>uplooking01,uplooking02,uplooking03</value>
</property>
啟動
sh $HBASE_HOME/bin/start-hbase.sh
使用jps命令,當有HMaster、HQuorumPeer(使用hbase自帶的zk)、HRegionServer三個進程啟動的時候,說明hbase服務已經啟動成功
停止
sh $HBASE_HOME/bin/stop-hbase.sh
單進程啟動
HMaster hbase-daemon.sh start master
HRegionserver hbase-daemon.sh start regionserver
訪問:
web http://<ip>:16010
cli bin/hbase shell在上述的基礎之上,只需要再配置一個conf/regionservers,添加兩行內容:
uplooking02
uplooking03
注意:
如果已經配置過單機版,需要將hbase在hdfs上面的目錄、以及hbase在zk中的目錄清除,以免和集群版本操作沖突
zk
rmr /hbase
hdfs
hdfs dfs -rm -R /hbase
拷貝master上面的數據到uplooking02和uplooking03
scp -r app/hbase uplooking@uplooking02:/home/uplooking/app/
scp -r app/hbase uplooking@uplooking03:/home/uplooking/app/
同樣在slave01和slave02上面添加相關環境變量
scp ~/.bash_profile uplooking@uplooking02:/home/uplooking/
scp ~/.bash_profile uplooking@uplooking02:/home/uplooking/
讓其生效
source ~/.bash_profile
啟動hbase集群
sh $HBASE_HOME/bin/start-hbase.sh
這個時候在master機器上面,有一個進程HMaster,在uplooking02和uplooking03上面分別有一個HRegionServer啟動hbase出現如下問題:
Caused by: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: java.net.UnknownHostException: ns1
at org.apache.hadoop.security.SecurityUtil.buildTokenService(SecurityUtil.java:373)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.NameNodeProxies.createNonHAProxy(NameNodeProxies.java:258)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.NameNodeProxies.createProxy(NameNodeProxies.java:153)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.DFSClient.<init>(DFSClient.java:602)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.DFSClient.<init>(DFSClient.java:547)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.DistributedFileSystem.initialize(DistributedFileSystem.java:139)
at org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem.createFileSystem(FileSystem.java:2591)
at org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem.access$200(FileSystem.java:89)
at org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem$Cache.getInternal(FileSystem.java:2625)
at org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem$Cache.get(FileSystem.java:2607)
at org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem.get(FileSystem.java:368)
at org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path.getFileSystem(Path.java:296)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.FSUtils.getRootDir(FSUtils.java:1002)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.HRegionServer.<init>(HRegionServer.java:566)
... 10 more
Caused by: java.net.UnknownHostException: ns1解決方案:
第一種方式:
source一下環境變量文件
第二種方式:
將hdfs對應的hdfs-site.xml和core-site.xml交給hbase管理另外需要注意的是,如果原來已經安裝了單機版,如果再安裝集群版本時,需要把原來相關的數據刪除。
邏輯結構:
表(table)
劃分數據集合的概念,和傳統的db中的表的概念是一樣的。
行健(RowKey):
一行數據的唯一標示,要想操作(read/write)一條數據,必須通過行健,其在hbase底層都是使用字節數組進行存放,
所以方便我們使用rk進行排序,
行鍵是字節數組, 任何字符串都可以作為行鍵;表中的行根據行鍵進行排序,數據按照Row key的字節序(byte order)排序存儲;
所有對表的訪問都要通過行鍵 (單個RowKey訪問,或RowKey范圍訪問,或全表掃描)。
列族(columnFamily)
簡單的認為是一系列“列”的集合。列族是以單獨的文件進行存儲。
列限定符(column Qualifier)
或者叫列。列里面的數據定位通過列限定符 每個CF可以有一個或多個列成員(ColumnQualifier),
列成員不需要在表定義時給出,新的列族成員可以隨后按需、動態加入。時間戳(version)
在單元格中可以存放多個版本的數據。
單元格(cell)
Cell 由行鍵,列族:限定符,時間戳唯一決定,Cell中的數據是沒有類型的,全部以字節碼形式存貯,主要用來存儲數據。單元格的圖示如下:

物理結構: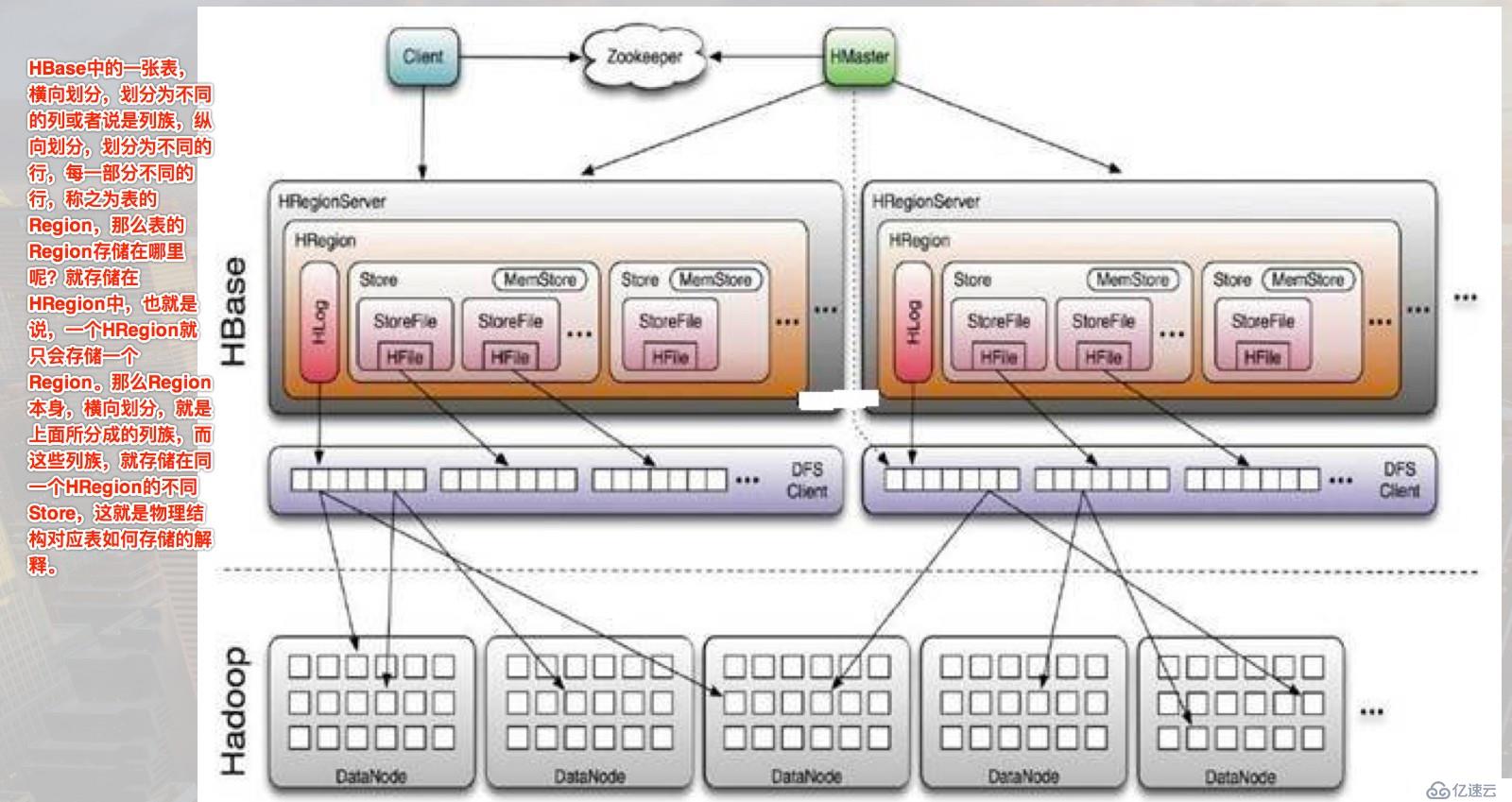
HMaster ----->NameNode
管理節點
HRegionServer----->DataNode
存放Region的服務器
HRegion
存放hbase中數據的一個概念,可以簡單的理解為表,存放一張表中的一部分數據,當該region中的數據超過一定量的時候,會自動進行分裂,
分裂成兩個region(一份為二),從這個角度上而言,Region是對hbase中表的一個橫向的劃分。
HFile
在hdfs上存放數據之前的一個物理結構,用于接收從客戶端提交過來的數據。
一個集群中有多個HRegionServer
|-----一個HLog
|-----多個HRegion
|---多個Store
|----一個CFHBase的物理結構圖示如下:
CLI(Command Line interface):
使用bin/hbase shell來進入命令終端
命令:
list查看當前命名空間下的所有的表,也可以查看特定命名空間下的表
list 'ns:abc.*' --->查看命名空間ns下面的所有的以表名以abc開頭的表的列表
創建一張表
create 't1', 'cf1' --->在默認的命名空間下創建一張表名為t1,只有一個列族,列族名為cf1
查看一張表的所有內容:scan
scan 't1'或者scan 'ns1:t1'
往表中增加一條記錄:put
put 't1', '1'(rowkey), 'cf1:name', 'zhangsan'
查看其中一個具體的值
get 't1', '1', 'cf1:name'
查看表的屬性信息:
describe/desc 't1'
刪除記錄:delete
delete 't1', '1', 'cf1:age' -->刪除某一個rowkey對應的cf1:age對應的單元格
deleteall 't1', '2' -->刪除rowkey=2對應的所有的單元格
刪除一張表:
注意:刪除表之前,需要先確認表狀態是否為disable,如果不是,需要disable '表名'
disable 't1'
drop 't1'練習:
rk column column cf
name grad course
math art |column
1 Tom 5 97 87
2 Jim 4 89 80
創建表
create 'stu','name', 'grad','course' --->創建了表stu,有三個列族,name、grad、course
增加數據:
put 'stu', '1', ':name', 'Tom' 直接寫成'name'也是可以的,也就是說name這個列族下面沒有多列
put 'stu', '1', ':grad', '5'
put 'stu', '1', 'course:art', '97'
put 'stu', '1', 'course:math', '88'
刪除name="Jim"的art成績
delete 'stu', '2', 'name', 'Jim', "course:art" --->錯誤的
delete 'stu', '2',"course:art" 因為每次操作,只能操作的是單一單元格,hbase的原子性操作是基于單元格的
而一個單元格的確定是由rk、cf、col、ts(timestamp)
刪除name="JIM"所在的行的而所有單元格
deleteall 'stu', '2'
查看當前表有多少條記錄:select count(1) from t;
count package com.uplooking.bigdata.hbase;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.*;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.*;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.filter.CompareFilter;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.filter.Filter;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.filter.FilterList;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.filter.SingleColumnValueFilter;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
/**
* HBase Java API 學習
*/
public class HBaseAPIOps {
private Connection connection;
private Admin admin;
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(conf);
admin = connection.getAdmin();
}
/*
list 'default:t.*'
TABLE
t1
t2
*/
@Test
public void testList() throws IOException {
TableName[] tblNames = admin.listTableNames("default:t.*");
for (TableName tblName : tblNames) {
System.out.println(tblName.getNamespaceAsString() + ":" + tblName.getNameAsString());
}
}
@Test
public void testCreate() throws IOException {
HTableDescriptor desc = new HTableDescriptor(TableName.valueOf("t3"));
HColumnDescriptor family = new HColumnDescriptor("cf");
desc.addFamily(family);
admin.createTable(desc);
}
@Test
public void testAddRecord() throws IOException {
Table t3 = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf("t3"));
byte[] cf = "cf".getBytes();
byte[] nameBytes = "name".getBytes();
byte[] ageBytes = "age".getBytes();
List<Put> puts = new ArrayList<Put>();
/*Put put1 = new Put("1".getBytes());
put1.addColumn(cf, nameBytes, "xiaofazeng".getBytes());
put1.addColumn(cf, ageBytes, "13".getBytes());
puts.add(put1);
Put put2 = new Put("2".getBytes());
put2.addColumn(cf, nameBytes, "xiaoshihao".getBytes());
put2.addColumn(cf, ageBytes, "15".getBytes());*/
// puts.add(put2);
for (int i = 1000; i <= 10000; i++) {
Put put = new Put((i + "").getBytes());
put.addColumn(cf, nameBytes, ("xiaohuihui" + i).getBytes());
put.addColumn(cf, ageBytes, ("" + (i % 99 + 1)).getBytes());
puts.add(put);
}
t3.put(puts);
t3.close();
}
@Test
public void testGetRecord() throws IOException {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf("t3"));
List<Get> gets = Arrays.asList(
new Get("1".getBytes()),
new Get("2".getBytes()).addColumn("cf".getBytes(), "name".getBytes())
);
Result[] results = table.get(gets);
for (Result result : results) {
CellScanner cs = result.cellScanner();
while(cs.advance()) {
System.out.println("=======================================================");
Cell cell = cs.current();
String value = new String(cell.getValueArray(), cell.getValueOffset(), cell.getValueLength());
String cf = new String(cell.getFamilyArray(), cell.getFamilyOffset(), cell.getFamilyLength());
String qualifier = new String(cell.getQualifierArray(), cell.getQualifierOffset(), cell.getQualifierLength());
String rk = new String(cell.getRowArray(), cell.getRowOffset(), cell.getRowLength());
long timestamp = cell.getTimestamp();
System.out.println(rk + "\t" + cf + ":" + qualifier + "\t" + timestamp + "\t" + value);
System.out.println("cell.getValueArray() == cell.getFamilyArray()? " + (cell.getValueArray() == cell.getFamilyArray()));
System.out.println("cell.getValueArray() == cell.getQualifierArray()? " + (cell.getValueArray() == cell.getQualifierArray()));
System.out.println("cell.getValueArray() == cell.getRowArray()? " + (cell.getValueArray() == cell.getRowArray()));
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------");
int rowOffset = cell.getRowOffset();
short rowLength = cell.getRowLength();
int fOffset = cell.getFamilyOffset();
byte fLength = cell.getFamilyLength();
int qOffset = cell.getQualifierOffset();
int qLength = cell.getQualifierLength();
int vOffset = cell.getValueOffset();
int vLength = cell.getValueLength();
byte typeByte = cell.getTypeByte();
System.out.println("rowOffset: " + rowOffset + ", rowLength: " + rowLength);
System.out.println("fOffset: " + fOffset + ", fLength: " + fLength);
System.out.println("qOffset: " + qOffset + ", qLength: " + qLength);
System.out.println("vOffset: " + vOffset + ", vLength: " + vLength);
System.out.println("typeByte: " + typeByte);
}
}
table.close();
}
@Test
public void testScan() throws IOException {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf("t3"));
Scan scan = new Scan();
ResultScanner resultScanner = table.getScanner(scan);
/* for (Result result : resultScanner) {
String name = new String(result.getValue("cf".getBytes(), "name".getBytes()));
int age = Integer.valueOf(new String(result.getValue("cf".getBytes(), "age".getBytes())));
String rowKey = new String(result.getRow());
System.out.println(rowKey + "\t" + "cf:name-->" + name + ", cf:age-->" + age);
}*/
resultScanner.forEach(result -> {
String name = new String(result.getValue("cf".getBytes(), "name".getBytes()));
int age = Integer.valueOf(new String(result.getValue("cf".getBytes(), "age".getBytes())));
String rowKey = new String(result.getRow());
System.out.println(rowKey + "\t" + "cf:name-->" + name + ", cf:age-->" + age);
});
table.close();
}
/**
* 條件查詢
* 其實說白了就是sql中的where條件,給hbase程序添加過濾器
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void testQueryByCondtion() throws IOException {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf("t3"));
Scan scan = new Scan();
Filter filter1 = new SingleColumnValueFilter("cf".getBytes(),
"age".getBytes(),
CompareFilter.CompareOp.GREATER_OR_EQUAL,
"13".getBytes());
Filter filter2 = new SingleColumnValueFilter("cf".getBytes(),
"age".getBytes(),
CompareFilter.CompareOp.LESS_OR_EQUAL,
"18".getBytes());
FilterList filterList = new FilterList();
filterList.addFilter(filter1);
filterList.addFilter(filter2);
scan.setFilter(filterList);
ResultScanner resultScanner = table.getScanner(scan);
resultScanner.forEach(result -> {
String name = new String(result.getValue("cf".getBytes(), "name".getBytes()));
int age = Integer.valueOf(new String(result.getValue("cf".getBytes(), "age".getBytes())));
String rowKey = new String(result.getRow());
System.out.println(rowKey + "\t" + "cf:name-->" + name + ", cf:age-->" + age);
});
table.close();
}
@After
public void cleanUp() throws IOException {
admin.close();
connection.close();
}
}<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<hive-api.version>2.1.0</hive-api.version>
<hadoop-api.version>2.6.4</hadoop-api.version>
<hadoop-core.version>1.2.1</hadoop-core.version>
<hbase-version>1.1.5</hbase-version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
<!-- HBase的maven依賴-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase-client</artifactId>
<version>${hbase-version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase-server</artifactId>
<version>${hbase-version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hive</groupId>
<artifactId>hive-hbase-handler</artifactId>
<version>${hive-api.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<!-- compiler插件, 設定JDK版本 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.3.2</version>
<configuration>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<showWarnings>true</showWarnings>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-assembly-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<descriptorRefs>
<descriptorRef>jar-with-dependencies</descriptorRef>
</descriptorRefs>
<archive>
<manifest>
<mainClass>com.uplooking.bigdata.hbase.HBase2HDFSOps</mainClass>
</manifest>
</archive>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>make-assembly</id>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>single</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。