您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇文章給大家分享的是有關使用java怎么掃描指定包下的類,小編覺得挺實用的,因此分享給大家學習,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后可以有所收獲,話不多說,跟著小編一起來看看吧。
Java主要應用于:1. web開發;2. Android開發;3. 客戶端開發;4. 網頁開發;5. 企業級應用開發;6. Java大數據開發;7.游戲開發等。
首先,比較簡單的是得到我們自己寫的類,我們先來完成這個,
項目的結構圖如下:
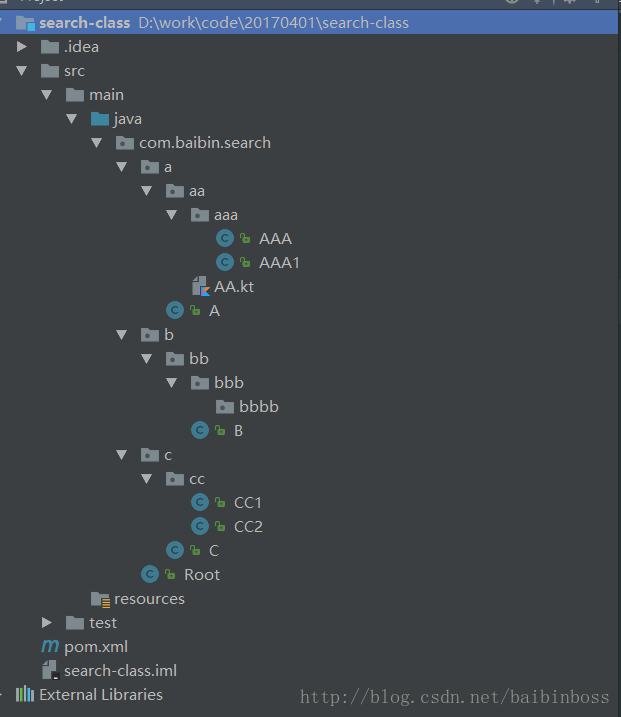
我故意創建了這么個比較復雜的項目結構,現在我們就來獲取com.baibin包下所有的類,并且打印他們,代碼如下:
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
List<String> classPaths = new ArrayList<String>();
@Test
public void searchClass() throws ClassNotFoundException {
//包名
String basePack = "com.baibin";
//先把包名轉換為路徑,首先得到項目的classpath
String classpath = Main.class.getResource("/").getPath();
//然后把我們的包名basPach轉換為路徑名
basePack = basePack.replace(".", File.separator);
//然后把classpath和basePack合并
String searchPath = classpath + basePack;
doPath(new File(searchPath));
//這個時候我們已經得到了指定包下所有的類的絕對路徑了。我們現在利用這些絕對路徑和java的反射機制得到他們的類對象
for (String s : classPaths) {
//把 D:\work\code\20170401\search-class\target\classes\com\baibin\search\a\A.class 這樣的絕對路徑轉換為全類名com.baibin.search.a.A
s = s.replace(classpath.replace("/","\\").replaceFirst("\\\\",""),"").replace("\\",".").replace(".class","");
Class cls = Class.forName(s);
System.out.println(cls);
}
}
/**
* 該方法會得到所有的類,將類的絕對路徑寫入到classPaths中
* @param file
*/
private void doPath(File file) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {//文件夾
//文件夾我們就遞歸
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File f1 : files) {
doPath(f1);
}
} else {//標準文件
//標準文件我們就判斷是否是class文件
if (file.getName().endsWith(".class")) {
//如果是class文件我們就放入我們的集合中。
classPaths.add(file.getPath());
}
}
}
}效果如下:
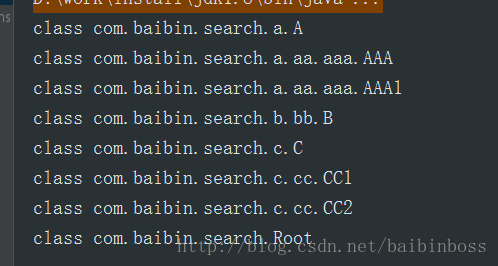
總結:這樣的src下面的都比較容易處理,也很容易想到,但是jar包下面的就沒這么簡單了,
但是還是有辦法的。
jar下的類我們可以通過JarURLConnection類來或者,代碼如下:
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.JarURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.jar.JarEntry;
import java.util.jar.JarFile;
public class JarMain {
@Test
public void searchClass() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
String basePack = "org.junit";
//通過當前線程得到類加載器從而得到URL的枚舉
Enumeration<URL> urlEnumeration = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResources(basePack.replace(".", "/"));
while (urlEnumeration.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urlEnumeration.nextElement();//得到的結果大概是:jar:file:/C:/Users/ibm/.m2/repository/junit/junit/4.12/junit-4.12.jar!/org/junit
String protocol = url.getProtocol();//大概是jar
if ("jar".equalsIgnoreCase(protocol)) {
//轉換為JarURLConnection
JarURLConnection connection = (JarURLConnection) url.openConnection();
if (connection != null) {
JarFile jarFile = connection.getJarFile();
if (jarFile != null) {
//得到該jar文件下面的類實體
Enumeration<JarEntry> jarEntryEnumeration = jarFile.entries();
while (jarEntryEnumeration.hasMoreElements()) {
/*entry的結果大概是這樣:
org/
org/junit/
org/junit/rules/
org/junit/runners/*/
JarEntry entry = jarEntryEnumeration.nextElement();
String jarEntryName = entry.getName();
//這里我們需要過濾不是class文件和不在basePack包名下的類
if (jarEntryName.contains(".class") && jarEntryName.replaceAll("/",".").startsWith(basePack)) {
String className = jarEntryName.substring(0, jarEntryName.lastIndexOf(".")).replace("/", ".");
Class cls = Class.forName(className);
System.out.println(cls);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}通過這兩種方式我們就可以得到指定包名下面所有的類了,這個還是挺有用的,
比如spring中經常用來掃描指定包注解的實現等。
補充:獲取指定包名下的所有類
寫了一個工具類,用于獲取指定包名下的所有類,支持遞歸遍歷,支持注解過濾,可從 classpath (class 文件與 jar 包)中獲取。
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileFilter;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.net.JarURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.jar.JarEntry;
import java.util.jar.JarFile;
public class ClassUtil {
// 獲取指定包名下的所有類
public static List<Class<?>> getClassList(String packageName, boolean isRecursive) {
List<Class<?>> classList = new ArrayList<Class<?>>();
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResources(packageName.replaceAll("\\.", "/"));
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
if (url != null) {
String protocol = url.getProtocol();
if (protocol.equals("file")) {
String packagePath = url.getPath();
addClass(classList, packagePath, packageName, isRecursive);
} else if (protocol.equals("jar")) {
JarURLConnection jarURLConnection = (JarURLConnection) url.openConnection();
JarFile jarFile = jarURLConnection.getJarFile();
Enumeration<JarEntry> jarEntries = jarFile.entries();
while (jarEntries.hasMoreElements()) {
JarEntry jarEntry = jarEntries.nextElement();
String jarEntryName = jarEntry.getName();
if (jarEntryName.endsWith(".class")) {
String className = jarEntryName.substring(0, jarEntryName.lastIndexOf(".")).replaceAll("/", ".");
if (isRecursive || className.substring(0, className.lastIndexOf(".")).equals(packageName)) {
classList.add(Class.forName(className));
}
}
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return classList;
}
// 獲取指定包名下的所有類(可根據注解進行過濾)
public static List<Class<?>> getClassListByAnnotation(String packageName, Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass) {
List<Class<?>> classList = new ArrayList<Class<?>>();
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResources(packageName.replaceAll("\\.", "/"));
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
if (url != null) {
String protocol = url.getProtocol();
if (protocol.equals("file")) {
String packagePath = url.getPath();
addClassByAnnotation(classList, packagePath, packageName, annotationClass);
} else if (protocol.equals("jar")) {
JarURLConnection jarURLConnection = (JarURLConnection) url.openConnection();
JarFile jarFile = jarURLConnection.getJarFile();
Enumeration<JarEntry> jarEntries = jarFile.entries();
while (jarEntries.hasMoreElements()) {
JarEntry jarEntry = jarEntries.nextElement();
String jarEntryName = jarEntry.getName();
if (jarEntryName.endsWith(".class")) {
String className = jarEntryName.substring(0, jarEntryName.lastIndexOf(".")).replaceAll("/", ".");
Class<?> cls = Class.forName(className);
if (cls.isAnnotationPresent(annotationClass)) {
classList.add(cls);
}
}
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return classList;
}
private static void addClass(List<Class<?>> classList, String packagePath, String packageName, boolean isRecursive) {
try {
File[] files = getClassFiles(packagePath);
if (files != null) {
for (File file : files) {
String fileName = file.getName();
if (file.isFile()) {
String className = getClassName(packageName, fileName);
classList.add(Class.forName(className));
} else {
if (isRecursive) {
String subPackagePath = getSubPackagePath(packagePath, fileName);
String subPackageName = getSubPackageName(packageName, fileName);
addClass(classList, subPackagePath, subPackageName, isRecursive);
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static File[] getClassFiles(String packagePath) {
return new File(packagePath).listFiles(new FileFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File file) {
return (file.isFile() && file.getName().endsWith(".class")) || file.isDirectory();
}
});
}
private static String getClassName(String packageName, String fileName) {
String className = fileName.substring(0, fileName.lastIndexOf("."));
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(packageName)) {
className = packageName + "." + className;
}
return className;
}
private static String getSubPackagePath(String packagePath, String filePath) {
String subPackagePath = filePath;
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(packagePath)) {
subPackagePath = packagePath + "/" + subPackagePath;
}
return subPackagePath;
}
private static String getSubPackageName(String packageName, String filePath) {
String subPackageName = filePath;
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(packageName)) {
subPackageName = packageName + "." + subPackageName;
}
return subPackageName;
}
private static void addClassByAnnotation(List<Class<?>> classList, String packagePath, String packageName, Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass) {
try {
File[] files = getClassFiles(packagePath);
if (files != null) {
for (File file : files) {
String fileName = file.getName();
if (file.isFile()) {
String className = getClassName(packageName, fileName);
Class<?> cls = Class.forName(className);
if (cls.isAnnotationPresent(annotationClass)) {
classList.add(cls);
}
} else {
String subPackagePath = getSubPackagePath(packagePath, fileName);
String subPackageName = getSubPackageName(packageName, fileName);
addClassByAnnotation(classList, subPackagePath, subPackageName, annotationClass);
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}以上就是使用java怎么掃描指定包下的類,小編相信有部分知識點可能是我們日常工作會見到或用到的。希望你能通過這篇文章學到更多知識。更多詳情敬請關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。