您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
怎么在Android應用中實現一個抽屜效果?很多新手對此不是很清楚,為了幫助大家解決這個難題,下面小編將為大家詳細講解,有這方面需求的人可以來學習下,希望你能有所收獲。
實現原理
其實單就一個SwipeLayout的實現原理來講的話,還是很簡單的,實際上單個SwipeLayout隱藏抽屜狀態時,應該是這樣的:
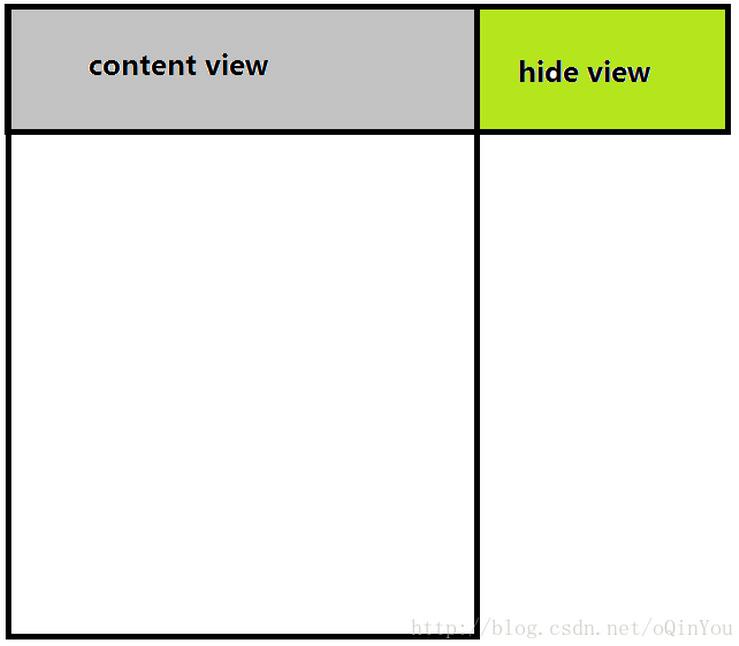
也就是說,最初的隱藏狀態,實際上是將hide view區域layout到conten view的右邊,達到隱藏效果,而后顯示則是根據拖拽的x值變化來動態的layout 2個view,從而達到一個滑動抽屜效果。
當然,直接重寫view的onTouchEvent來動態的layout 2個view是可以實現我們需要的效果的,但是有更好的方法來實現,就是同過ViewDragHelper。
ViewDragHelper是google官方提供的一個專門用于手勢分析處理的類,關于ViewDragHelper的基本使用,網上有一大堆的資源。具體的ViewDragHelper介紹以及基本使用方法,本文就不重復造輪子了,此處推薦鴻洋大神的一篇微博:Android ViewDragHelper完全解析 自定義ViewGroup神器。
具體實現
下面我們開始具體的實現。
布局比較簡單,這里就不貼代碼了,最后會貼上本demo的完整代碼地址。
首先我們實現一個繼承FrameLayout的自定義SwipeLauout,重寫onFinishInflate方法:
這里我們只允許SwipeLayout設置2個子View,ContentLayout是繼承LinearLayout的自定義layout,后面會講到這個,此處先略過;
@Override
protected void onFinishInflate() {
super.onFinishInflate();
if (getChildCount() != 2) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Must 2 views in SwipeLayout");
}
contentView = getChildAt(0);
hideView = getChildAt(1);
if (contentView instanceof ContentLayout)
((ContentLayout) contentView).setSwipeLayout(this);
else {
throw new IllegalStateException("content view must be an instanceof FrontLayout");
}
}接著重寫onSizeChanged,onLayout,onInterceptTouchEvent方法:
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
hideViewHeight = hideView.getMeasuredHeight();
hideViewWidth = hideView.getMeasuredWidth();
contentWidth = contentView.getMeasuredWidth();
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right,
int bottom) {
// super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom);
contentView.layout(0, 0, contentWidth, hideViewHeight);
hideView.layout(contentView.getRight(), 0, contentView.getRight()
+ hideViewWidth, hideViewHeight);
}
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
boolean result = viewDragHelper.shouldInterceptTouchEvent(ev);
// Log.e("SwipeLayout", "-----onInterceptTouchEvent-----");
return result;
}然后是比較關鍵的,重寫onTouchEvent方法以及ViewDragHelper.Callback回調,我們定了一個enum來判斷SwipeLayout的三種狀態。在onViewPositionChanged中,有2種方法實現content view和hide view的伴隨移動,一種是直接offset view的橫向變化量,還有一種就是直接通過layout的方式,兩種方式都可以。
public enum SwipeState {
Open, Swiping, Close;
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
// Log.e("SwipeLayout", "-----onTouchEvent-----");
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
downX = event.getX();
downY = event.getY();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
// 1.獲取x和y方向移動的距離
float moveX = event.getX();
float moveY = event.getY();
float delatX = moveX - downX;// x方向移動的距離
float delatY = moveY - downY;// y方向移動的距離
if (Math.abs(delatX) > Math.abs(delatY)) {
// 表示移動是偏向于水平方向,那么應該SwipeLayout應該處理,請求listview不要攔截
this.requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(true);
}
// 更新downX,downY
downX = moveX;
downY = moveY;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
break;
}
viewDragHelper.processTouchEvent(event);
return true;
}
private ViewDragHelper.Callback callback = new ViewDragHelper.Callback() {
@Override
public boolean tryCaptureView(View child, int pointerId) {
return child == contentView || child == hideView;
}
@Override
public int getViewHorizontalDragRange(View child) {
return hideViewWidth;
}
@Override
public int clampViewPositionHorizontal(View child, int left, int dx) {
if (child == contentView) {
if (left > 0)
left = 0;
if (left < -hideViewWidth)
left = -hideViewWidth;
} else if (child == hideView) {
if (left > contentWidth)
left = contentWidth;
if (left < (contentWidth - hideViewWidth))
left = contentWidth - hideViewWidth;
}
return left;
}
@Override
public void onViewPositionChanged(View changedView, int left, int top,
int dx, int dy) {
super.onViewPositionChanged(changedView, left, top, dx, dy);
if (changedView == contentView) {
// 如果手指滑動deleteView,那么也要講橫向變化量dx設置給contentView
hideView.offsetLeftAndRight(dx);
} else if (changedView == hideView) {
// 如果手指滑動contentView,那么也要講橫向變化量dx設置給deleteView
contentView.offsetLeftAndRight(dx);
}
// if (changedView == contentView) {
// // 手動移動deleteView
// hideView.layout(hideView.getLeft() + dx,
// hideView.getTop() + dy, hideView.getRight() + dx,
// hideView.getBottom() + dy);
// } else if (hideView == changedView) {
// // 手動移動contentView
// contentView.layout(contentView.getLeft() + dx,
// contentView.getTop() + dy, contentView.getRight() + dx,
// contentView.getBottom() + dy);
// }
//實時更新當前狀態
updateSwipeStates();
invalidate();
}
@Override
public void onViewReleased(View releasedChild, float xvel, float yvel) {
super.onViewReleased(releasedChild, xvel, yvel);
//根據用戶滑動速度處理開關
//xvel: x方向滑動速度
//yvel: y方向滑動速度
// Log.e("tag", "currentState = " + currentState);
// Log.e("tag", "xvel = " + xvel);
if (xvel < -200 && currentState != SwipeState.Open) {
open();
return;
} else if (xvel > 200 && currentState != SwipeState.Close) {
close();
return;
}
if (contentView.getLeft() < -hideViewWidth / 2) {
// 打開
open();
} else {
// 關閉
close();
}
}
};open(),close()實現
public void open() {
open(true);
}
public void close() {
close(true);
}
/**
* 打開的方法
*
* @param isSmooth 是否通過緩沖動畫的形式設定view的位置
*/
public void open(boolean isSmooth) {
if (isSmooth) {
viewDragHelper.smoothSlideViewTo(contentView, -hideViewWidth,
contentView.getTop());
ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(SwipeLayout.this);
} else {
contentView.offsetLeftAndRight(-hideViewWidth);//直接偏移View的位置
hideView.offsetLeftAndRight(-hideViewWidth);//直接偏移View的位置
// contentView.layout(-hideViewWidth, 0, contentWidth - hideViewWidth, hideViewHeight);//直接通過坐標擺放
// hideView.layout(contentView.getRight(), 0, hideViewWidth, hideViewHeight);//直接通過坐標擺放
invalidate();
}
}
/**
* 關閉的方法
*
* @param isSmooth true:通過緩沖動畫的形式設定view的位置
* false:直接設定view的位置
*/
public void close(boolean isSmooth) {
if (isSmooth) {
viewDragHelper.smoothSlideViewTo(contentView, 0, contentView.getTop());
ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(SwipeLayout.this);
} else {
contentView.offsetLeftAndRight(hideViewWidth);
hideView.offsetLeftAndRight(hideViewWidth);
invalidate();
//contentView.layout(0, 0, contentWidth, hideViewHeight);//直接通過坐標擺放
//hideView.layout(contentView.getRight(), 0, hideViewWidth, hideViewHeight);//直接通過坐標擺放
}
}此上基本實現了單個SwipeLayout的抽屜滑動效果,但是將此SwipeLayout作為一個item布局設置給一個listView的時候,還需要做許多的判斷。
由于listView的重用機制,我們這里并未針對listview做任何處理,所以一旦有一個item的SwipeLayout的狀態是打開狀態,不可避免的其它也必然有幾個是打開狀態,所以我們這里需要根據檢測listView的滑動,當listView滑動時,關閉SwipeLayout。既然需要在外部控制SwipeLayout的開關,我們先定義一個SwipeLayoutManager用于管理SwipeLayout的控制。
public class SwipeLayoutManager {
//記錄打開的SwipeLayout集合
private HashSet<SwipeLayout> mUnClosedSwipeLayouts = new HashSet<SwipeLayout>();
private SwipeLayoutManager() {
}
private static SwipeLayoutManager mInstance = new SwipeLayoutManager();
public static SwipeLayoutManager getInstance() {
return mInstance;
}
/**
* 將一個沒有關閉的SwipeLayout加入集合
* @param layout
*/
public void add(SwipeLayout layout) {
mUnClosedSwipeLayouts.add(layout);
}
/**
* 將一個沒有關閉的SwipeLayout移出集合
* @param layout
*/
public void remove(SwipeLayout layout){
mUnClosedSwipeLayouts.remove(layout);
}
/**
* 關閉已經打開的SwipeLayout
*/
public void closeUnCloseSwipeLayout() {
if(mUnClosedSwipeLayouts.size() == 0){
return;
}
for(SwipeLayout l : mUnClosedSwipeLayouts){
l.close(true);
}
mUnClosedSwipeLayouts.clear();
}
/**
* 關閉已經打開的SwipeLayout
*/
public void closeUnCloseSwipeLayout(boolean isSmooth) {
if(mUnClosedSwipeLayouts.size() == 0){
return;
}
for(SwipeLayout l : mUnClosedSwipeLayouts){
l.close(isSmooth);
}
mUnClosedSwipeLayouts.clear();
}
}這樣就可以監聽listView的滑動,然后在listView滑動的時候,關閉所有的抽屜View。
listView.setOnScrollListener(new OnScrollListener() {
@Override
public void onScrollStateChanged(AbsListView view, int scrollState) {
swipeLayoutManager.closeUnCloseSwipeLayout();
}
@Override
public void onScroll(AbsListView view, int firstVisibleItem, int visibleItemCount, int totalItemCount) {
}
});考慮到大多數時候,在我們打開抽屜View和關閉抽屜View的時候,外部需要知道SwipeLayout的狀態值,所以我們需要在SwipeLayout中增加幾個接口,告訴外部當前SwipeLayout的狀態值:
SwipeLayout.java
----------------
private void updateSwipeStates() {
SwipeState lastSwipeState = currentState;
SwipeState swipeState = getCurrentState();
if (listener == null) {
try {
throw new Exception("please setOnSwipeStateChangeListener first!");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return;
}
if (swipeState != currentState) {
currentState = swipeState;
if (currentState == SwipeState.Open) {
listener.onOpen(this);
// 當前的Swipelayout已經打開,需要讓Manager記錄
swipeLayoutManager.add(this);
} else if (currentState == SwipeState.Close) {
listener.onClose(this);
// 說明當前的SwipeLayout已經關閉,需要讓Manager移除
swipeLayoutManager.remove(this);
} else if (currentState == SwipeState.Swiping) {
if (lastSwipeState == SwipeState.Open) {
listener.onStartClose(this);
} else if (lastSwipeState == SwipeState.Close) {
listener.onStartOpen(this);
//hideView準備顯示之前,先將之前打開的的SwipeLayout全部關閉
swipeLayoutManager.closeUnCloseSwipeLayout();
swipeLayoutManager.add(this);
}
}
} else {
currentState = swipeState;
}
}
/**
* 獲取當前控件狀態
*
* @return
*/
public SwipeState getCurrentState() {
int left = contentView.getLeft();
// Log.e("tag", "contentView.getLeft() = " + left);
// Log.e("tag", "hideViewWidth = " + hideViewWidth);
if (left == 0) {
return SwipeState.Close;
}
if (left == -hideViewWidth) {
return SwipeState.Open;
}
return SwipeState.Swiping;
}
private OnSwipeStateChangeListener listener;
public void setOnSwipeStateChangeListener(
OnSwipeStateChangeListener listener) {
this.listener = listener;
}
public View getContentView() {
return contentView;
}
public interface OnSwipeStateChangeListener {
void onOpen(SwipeLayout swipeLayout);
void onClose(SwipeLayout swipeLayout);
void onStartOpen(SwipeLayout swipeLayout);
void onStartClose(SwipeLayout swipeLayout);
}然后接下來是寫一個為listView設置的SwipeAdapter
SwipeAdapter.java
------------
public class SwipeAdapter extends BaseAdapter implements OnSwipeStateChangeListener {
private Context mContext;
private List<String> list;
private MyClickListener myClickListener;
private SwipeLayoutManager swipeLayoutManager;
public SwipeAdapter(Context mContext) {
super();
this.mContext = mContext;
init();
}
private void init() {
myClickListener = new MyClickListener();
swipeLayoutManager = SwipeLayoutManager.getInstance();
}
public void setList(List<String> list){
this.list = list;
notifyDataSetChanged();
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return list.size();
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
return list.get(position);
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
return position;
}
@Override
public View getView(final int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
if (convertView == null) {
convertView = UIUtils.inflate(R.layout.list_item_swipe);
}
ViewHolder holder = ViewHolder.getHolder(convertView);
holder.tv_content.setText(list.get(position));
holder.tv_overhead.setOnClickListener(myClickListener);
holder.tv_overhead.setTag(position);
holder.tv_delete.setOnClickListener(myClickListener);
holder.tv_delete.setTag(position);
holder.sv_layout.setOnSwipeStateChangeListener(this);
holder.sv_layout.setTag(position);
holder.sv_layout.getContentView().setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
ToastUtils.showToast("item click : " + position);
swipeLayoutManager.closeUnCloseSwipeLayout();
}
});
return convertView;
}
static class ViewHolder {
TextView tv_content, tv_overhead, tv_delete;
SwipeLayout sv_layout;
public ViewHolder(View convertView) {
tv_content = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_content);
tv_overhead = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_overhead);
tv_delete = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_delete);
sv_layout = (SwipeLayout) convertView.findViewById(R.id.sv_layout);
}
public static ViewHolder getHolder(View convertView) {
ViewHolder holder = (ViewHolder) convertView.getTag();
if (holder == null) {
holder = new ViewHolder(convertView);
convertView.setTag(holder);
}
return holder;
}
}
class MyClickListener implements View.OnClickListener {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Integer position = (Integer) v.getTag();
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.tv_overhead:
//ToastUtils.showToast("position : " + position + " overhead is clicked.");
}
break;
case R.id.tv_delete:
//ToastUtils.showToast("position : " + position + " delete is clicked.");
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
@Override
public void onOpen(SwipeLayout swipeLayout) {
//ToastUtils.showToast(swipeLayout.getTag() + "onOpen.");
}
@Override
public void onClose(SwipeLayout swipeLayout) {
//ToastUtils.showToast(swipeLayout.getTag() + "onClose.");
}
@Override
public void onStartOpen(SwipeLayout swipeLayout) {
// ToastUtils.showToast("onStartOpen.");
}
@Override
public void onStartClose(SwipeLayout swipeLayout) {
// ToastUtils.showToast("onStartClose.");
}
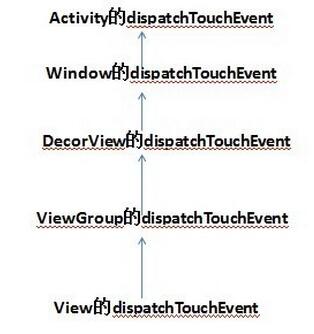
}此時已經基本實現了我們需要的大部分功能了,但是當我們滑動的時候,又發現新的問題,我們的SwipeLayout和listview滑動判斷有問題。由于前面我們僅僅是將touch攔截事件簡簡單單的丟給了viewDragHelper.shouldInterceptTouchEvent(ev)來處理,導致SwipeLayout和listview攔截touch事件時的處理存在一定的問題,這里我們要提到一個知識點:Android view事件的傳遞。
(1)首先由Activity分發,分發給根View,也就是DecorView(DecorView為整個Window界面的最頂層View)
(2)然后由根View分發到子的View
view事件攔截如下圖所示:
view事件的消費如下圖所示:
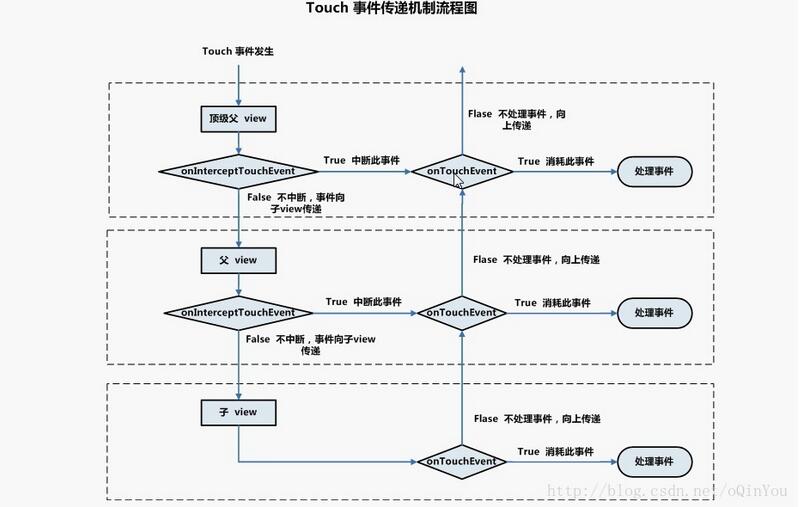
注:以上2張圖借鑒網上總結的比較經典的圖
所以這里我們就要談到一開始出現的ContentLayout,主要重寫了onInterceptTouchEvent和onTouchEvent。
public class ContentLayout extends LinearLayout {
SwipeLayoutInterface mISwipeLayout;
public ContentLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public ContentLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public ContentLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
public void setSwipeLayout(SwipeLayoutInterface iSwipeLayout) {
this.mISwipeLayout = iSwipeLayout;
}
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
// Log.e("ContentLayout", "-----onInterceptTouchEvent-----");
if (mISwipeLayout.getCurrentState() == SwipeState.Close) {
return super.onInterceptTouchEvent(ev);
} else {
return true;
}
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
// Log.e("ContentLayout", "-----onTouchEvent-----");
if (mISwipeLayout.getCurrentState() == SwipeState.Close) {
return super.onTouchEvent(ev);
} else {
if (ev.getActionMasked() == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP) {
mISwipeLayout.close();
}
return true;
}
}
}另外由于在ContentLayout中需要拿到父View SwipeLayout的開關狀態以及控制SwipeLayout的關閉,因此在再寫一個接口,用于ContentLayout獲取SwipeLayout的開關狀態以及更新SwipeLayout。
public interface SwipeLayoutInterface {
SwipeState getCurrentState();
void open();
void close();
}然后接著的是完善SwipeLayout的onInterceptTouchEvent,我們在這里增加一個GestureDetectorCompat處理手勢識別:
private void init(Context context) {
viewDragHelper = ViewDragHelper.create(this, callback);
mGestureDetector = new GestureDetectorCompat(context, mOnGestureListener);
swipeLayoutManager = SwipeLayoutManager.getInstance();
}
private SimpleOnGestureListener mOnGestureListener = new SimpleOnGestureListener() {
@Override
public boolean onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float distanceX, float distanceY) {
// 當橫向移動距離大于等于縱向時,返回true
return Math.abs(distanceX) >= Math.abs(distanceY);
}
};
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
boolean result = viewDragHelper.shouldInterceptTouchEvent(ev) & mGestureDetector.onTouchEvent(ev);
// Log.e("SwipeLayout", "-----onInterceptTouchEvent-----");
return result;
}如此下來,整個View不管是上下拖動,還是SwipeLayout的開關滑動,都已經實現完成了。最后增加對應overhead,delete以及item的點擊事件,此處完善SwipeAdapter的代碼之后如下。
class MyClickListener implements View.OnClickListener {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Integer position = (Integer) v.getTag();
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.tv_overhead:
//ToastUtils.showToast("position : " + position + " overhead is clicked.");
swipeLayoutManager.closeUnCloseSwipeLayout(false);
if(onSwipeControlListener != null){
onSwipeControlListener.onOverhead(position, list.get(position));
}
break;
case R.id.tv_delete:
//ToastUtils.showToast("position : " + position + " delete is clicked.");
swipeLayoutManager.closeUnCloseSwipeLayout(false);
if(onSwipeControlListener != null){
onSwipeControlListener.onDelete(position, list.get(position));
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
private OnSwipeControlListener onSwipeControlListener;
public void setOnSwipeControlListener(OnSwipeControlListener onSwipeControlListener){
this.onSwipeControlListener = onSwipeControlListener;
}
/**
* overhead 和 delete點擊事件接口
*/
public interface OnSwipeControlListener{
void onOverhead(int position, String itemTitle);
void onDelete(int position, String itemTitle);
}最后貼上MainActivity代碼,此處通過OnSwipeControlListener接口回調實現item的刪除和置頂:
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnSwipeControlListener {
private ListView listView;
private List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
private SwipeLayoutManager swipeLayoutManager;
private SwipeAdapter swipeAdapter;
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initData();
initView();
}
private void initData() {
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
list.add("content - " + i);
}
}
private void initView() {
swipeLayoutManager = SwipeLayoutManager.getInstance();
swipeAdapter = new SwipeAdapter(this);
swipeAdapter.setList(list);
listView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.list_view);
listView.setAdapter(swipeAdapter);
listView.setOnScrollListener(new OnScrollListener() {
@Override
public void onScrollStateChanged(AbsListView view, int scrollState) {
swipeLayoutManager.closeUnCloseSwipeLayout();
}
@Override
public void onScroll(AbsListView view, int firstVisibleItem, int visibleItemCount, int totalItemCount) {
}
});
swipeAdapter.setOnSwipeControlListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onOverhead(int position, String itemTitle) {
setItemOverhead(position, itemTitle);
}
@Override
public void onDelete(int position, String itemTitle) {
removeItem(position, itemTitle);
}
/**
* 設置item置頂
*
* @param position
* @param itemTitle
*/
private void setItemOverhead(int position, String itemTitle) {
// ToastUtils.showToast("position : " + position + " overhead.");
ToastUtils.showToast("overhead ---" + itemTitle + "--- success.");
String newTitle = itemTitle;
list.remove(position);//刪除要置頂的item
list.add(0, newTitle);//根據adapter傳來的Title數據在list 0位置插入title字符串,達到置頂效果
swipeAdapter.setList(list);//重新給Adapter設置list數據并更新
UIUtils.runOnUIThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
listView.setSelection(0);//listview選中第0項item
}
});
}
/**
* 刪除item
*
* @param position
* @param itemTitle
*/
private void removeItem(int position, String itemTitle) {
// ToastUtils.showToast("position : " + position + " delete.");
ToastUtils.showToast("delete ---" + itemTitle + "--- success.");
list.remove(position);
swipeAdapter.setList(list);//重新給Adapter設置list數據并更新
}
}至此整個demo基本完成,本次完成的功能基本能夠直接放到項目中使用。其實最麻煩的地方就在于view的touch事件攔截和處理,不過將本demo的log打開看一下對比之后,也就能夠理解整個傳遞過程了。
看完上述內容是否對您有幫助呢?如果還想對相關知識有進一步的了解或閱讀更多相關文章,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道,感謝您對億速云的支持。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。