您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章給大家分享的是有關java代碼中init method和destroy method怎么使用的內容。小編覺得挺實用的,因此分享給大家做個參考,一起跟隨小編過來看看吧。
在java的實際開發過程中,我們可能常常需要使用到init method和destroy method,比如初始化一個對象(bean)后立即初始化(加載)一些數據,在銷毀一個對象之前進行垃圾回收等等。
周末對這兩個方法進行了一點學習和整理,倒也不是專門為了這兩個方法,而是在鞏固spring相關知識的時候提到了,然后感覺自己并不是很熟悉這個,便好好的了解一下。
根據特意的去了解后,發現實際上可以有三種方式來實現init method和destroy method。
要用這兩個方法,自然先要知道這兩個方法究竟是干嘛用的。而從字面意思就很容易理解,一個是加載,一個是銷毀。
下邊就正式代碼演示三種創建方式:
一、@Bean注解方式:
首先要創建一個至少擁有兩個方法的類,一個方法充當init method,另一個充當destroy method。
package springTest2;
public class Test1 {
public void init() {
System.out.println("this is init method1");
}
public Test1() {
super();
System.out.println("構造函數1");
}
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("this is destroy method1");
}
}這里很顯然只是一個普通的java類,擁有一個無參構造和另外兩個方法。
需要注意的是,這里的init和destroy兩個方法名實際上是可以隨意取得,不叫這個也沒有問題,只不過算是一種約定俗稱,一般都是這樣叫。
另外我們也知道,這個構造方法也是可以不要的,因為會隱式的自動創建,但是為了更清楚的看到init和destroy是什么時候執行,我們就顯示的寫出來。
創建好了這個類,我們就可以使用@Bean注解的方式指定兩個方法,以讓他們生效。
package springTest2;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("springTest2")
public class ConfigTest {
@Bean(initMethod = "init", destroyMethod = "destroy")
Test1 test1() {
return new Test1();
}
}這里邊的@Configguration注解是告訴spring這個類是一個配置類,相當于我們的xml文件,@ComponentScan則是指定需要spring來掃描的包,相當于xml中的context:component-scan屬性。
而@Bean后邊的initMethod和destroyMethod就是在聲明這是一個baen的同時指定了init和destroy方法,方法名從功能實現上來說可以隨意。
到這里我們就已經用第一種方式寫好了,為了驗證成功與否,再寫一個main方法驗證一下:
package springTest2;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ConfigTest.class);
System.out.println("#################################");
context.close();
}
}運行之后結果如圖:
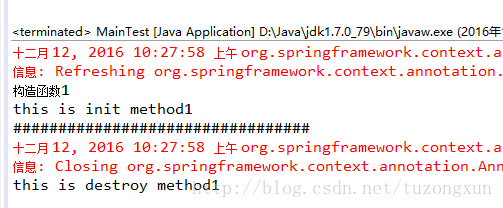
根據打印順序可以看到,首先是構造函數,也就是創建了bean,緊接著執行了init,然后再context.close要銷毀bean之前又執行了destroy。
二、JSR-250注解的方式(需要導入jsr250-api的jar包):
首先依然是創建一個擁有構造方法在內的三個方法的java類:
package springTest2;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
public class Test2 {
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("this is init method2");
}
public Test2() {
super();
System.out.println("構造函數2");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("this is destroy method2");
}
}很顯然,這里和上一個類不同的是,在init和destroy方法上加入了兩個注解,@PostConstruct和上邊@Bean后的initMethod相同,而@PreDestroy則是和destroyMethod做用相同。
既然這里有了區別,已經指定了init method和destroy method,那么后邊聲明bean的時候自然也會有不同,也就不需要再指定一遍:
package springTest2;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("springTest2")
public class ConfigTest {
@Bean
Test2 test2() {
return new Test2();
}
}所以,如上代碼中只需要簡單的聲明這是一個bean就可以了,類上邊的兩個注解和上一個例子中的意思相同。
再測試一下:
package springTest2;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ConfigTest.class);
System.out.println("#################################");
context.close();
}
}結果如下:
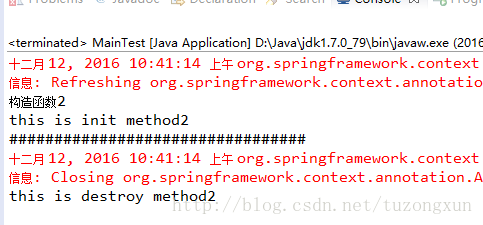
三、xml配置的方式:
這種方式實際上是和第一種對應的,只不過細節上略有改變而已,首先,創建的java類完全一樣:
package springTest2;
public class Test3 {
public void init() {
System.out.println("this is init method3");
}
public Test3() {
super();
System.out.println("構造函數3");
}
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("this is destroy method3");
}
public void test() {
System.out.println("testttttttt");
}
}不同的地方就在于,第一個例子中是使用注解告訴spring這個類相當于一個配置文件,而這里則是實實在在的配置文件spring.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="initOrDestroyTest" class="springTest2.Test3" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"> </bean> </beans>
這個配置大概也能算是spring.xml中最簡單的一個配置了吧,除開必要的文件頭,就只有一個bean,而且bean里邊也只有id,calss和init以及destroy方法。
因為簡單,所以一目了然,id只是為了其他地方引用,class是指定這個bean對應的類,而后邊兩個屬性則和用@Bean聲明時一模一樣。
因為這里聲明bean和指定兩個方法是用的xml配置,因此在測試的時候也就需要稍微有一點點改變:
package springTest2;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context1 = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
System.out.println("#################################");
context1.close();
}
}區別在于這里直接加載了配置文件,而不是java類,使用的是ClassPathxXmlApplicationContext而不是AnnotationConfigApplicationContext。
結果如下:
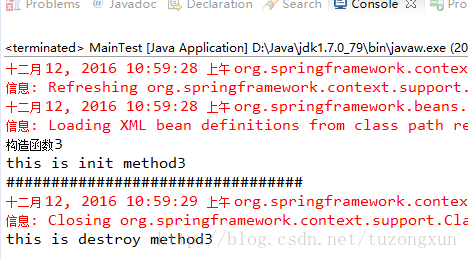
這里需要說明的一點是,在實際的web應用使用時,可以在web.xml中使用類似下邊的配置來加載bean,實現init method:
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:spring.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
然后啟動tomcat結果如下:
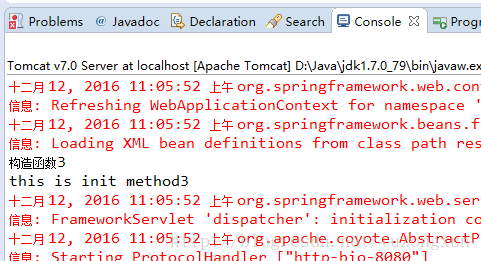
這里邊沒有調用destroy method,原因是spring本身代碼就需要我們手動調用銷毀bean的方法,像前邊的幾個例子中的context.close就是。
如果不手動調用這個方法,bean就不會被銷毀,也就不會去調用destroy method,這也就是為何這里在web.xml中配置后,啟動tomcat 只打印了構造函數和init方法中的內容。
例子都是很簡單的,而通過簡單的例子對比可能能更進一步理解相關的知識,理解了才能在實際應用中更好的進行選擇和集成。
感謝各位的閱讀!關于“java代碼中init method和destroy method怎么使用”這篇文章就分享到這里了,希望以上內容可以對大家有一定的幫助,讓大家可以學到更多知識,如果覺得文章不錯,可以把它分享出去讓更多的人看到吧!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。