您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
[TOC]
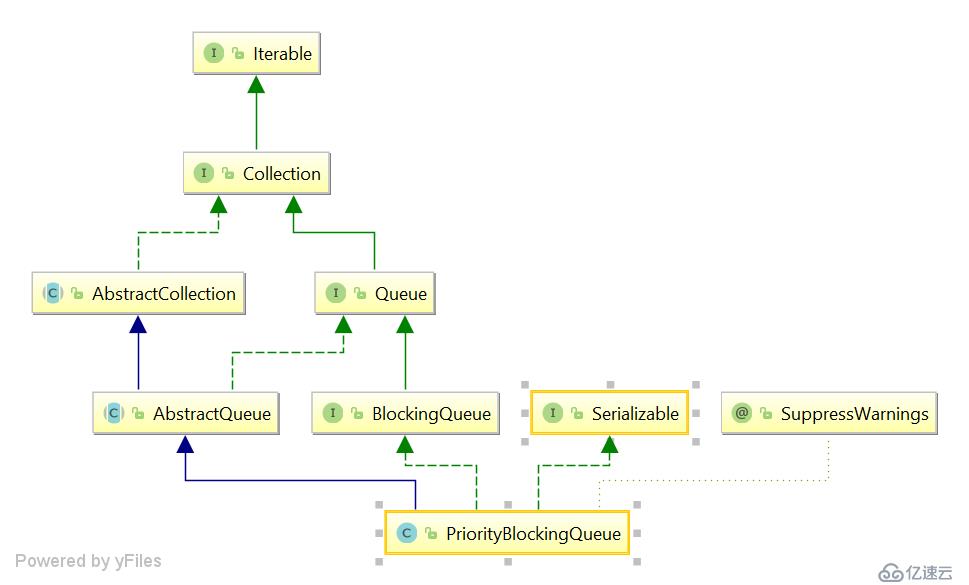
PriorityBlockingQueue 是一個支持優先級的×××阻塞隊列,數據結構采用的是最小堆是通過一個數組實現的,隊列默認采用自然排序的升序排序,如果需要自定義排序,需要在構造隊列時指定Comparetor比較器,隊列也是使用ReentrantLock鎖來實現的同步機制。
// 數組的最大容量 2^31 - 8
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
// 二叉堆數組
private transient Object[] queue;
// 總數
private transient int size;
// /默認比較器
private transient Comparator<? super E> comparator;
// 鎖
private final ReentrantLock lock;
// 為空隊列
private final Condition notEmpty;
// 自旋鎖,在數組擴容時使用
private transient volatile int allocationSpinLock;注意:這里解釋下這個Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8,為什么數組的最大長度是這么多了,這其實和int的最大值有關,最大值就是(1 << 32) -1 ,大家有沒有發現數組的長度類型是int,為什么是int了???我也不知道,我也試了其它數據類型發現數組的長度必須是int類型,哈哈,所以也可以理解為什么是最大值了,至于為什么要減八了,是因為創建數組本身的信息(對象頭,class信息啊)也是需要存儲空間的,所以需要這8位的空間。
public boolean add(E e) {
return offer(e);
}由于是×××隊列所以put方法不會阻塞,也是直接調用了offer方法.
public void put(E e) {
offer(e); // never need to block
} public boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
return offer(e); // never need to block
} // 添加元素
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
int n, cap;
Object[] array;
// size大于等于數組的長度
while ((n = size) >= (cap = (array = queue).length))
// 擴容
tryGrow(array, cap);
try {
Comparator<? super E> cmp = comparator;
if (cmp == null) // 默認排序
siftUpComparable(n, e, array);
else // 自定義排序
siftUpUsingComparator(n, e, array, cmp);
size = n + 1;
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return true;
}這里我們主要分析下offer方法里面的兩個重要方法,擴容和入隊,tryGrow,siftUpComparable方法。
// 擴容方法
private void tryGrow(Object[] array, int oldCap) {
lock.unlock(); // must release and then re-acquire main lock
Object[] newArray = null;
// 只允許一個線程去擴容
if (allocationSpinLock == 0 &&
UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, allocationSpinLockOffset,
0, 1)) {
try {
// oldCap小于64 就加2 ,小于等于64就擴容50%
int newCap = oldCap + ((oldCap < 64) ?
(oldCap + 2) : // grow faster if small
(oldCap >> 1));
// 不可以超過MAX_ARRAY_SIZE
if (newCap - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) { // possible overflow
int minCap = oldCap + 1;
if (minCap < 0 || minCap > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
newCap = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
if (newCap > oldCap && queue == array)
newArray = new Object[newCap];
} finally {
allocationSpinLock = 0;
}
}
if (newArray == null) // back off if another thread is allocating
Thread.yield(); // 擴容獲取鎖失敗的線程,盡量讓出cpu
lock.lock(); // 重新獲取鎖
if (newArray != null && queue == array) {
queue = newArray;
System.arraycopy(array, 0, newArray, 0, oldCap);
}
}分析擴容:
最小堆的構建
// 保證了每條鏈的順序小到大
private static <T> void siftUpComparable(int k, T x, Object[] array) {
Comparable<? super T> key = (Comparable<? super T>) x;
while (k > 0) {
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
Object e = array[parent];
if (key.compareTo((T) e) >= 0)
break;
array[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
array[k] = key;
}分析:
先得解釋下(k - 1) >>> 1,就是求的商,我們來模擬插入五個數吧,默認容量是11.
第一次插入一個1,此時的k是0,x是1,k不大于0,直接插入。
| 索引 | 0 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 值 | 1 |
第二次我們插入一個0,此時的k是1,x是0,parent是0,然后獲取0位置索引的值和現在的比較,現在其實是不大于0的,所以此時交換了位置,array[k] = e; k = parent;parent是0,所以結束循環然后在0的位置設置當前x是1。
| 索引 | 0 | 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 值 | 0 | 1 |
第三次我們插入一個5,此時的k是2,x是5,parent 是0,然后獲取0位置的值和插入值標記,發現是大于0的所以直接插入,在2的位置插入5。
| 索引 | 0 | 1 | 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 值 | 0 | 1 | 5 |
第四次我們插入一個4,此時的k是3,x是4,parent是1,然后獲取1位置的值和插入值比較,發現是大于0的,所以直接插入在3的位置插入。
| 索引 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 值 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 4 |
第五次我們插入一個3,此時的k是4,x是3,parent是1,然后獲取1位置值和插入值做比較,發現大于0的,所以直接在4的位置插入。
| 索引 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 值 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
我們用一個圖來描繪下這個數組,怎么出現的這個圖了,我們發現每次插入的數的索引就是數組的長度,然后通過(i - 1)>>> 2 = n求父節點,通過比較和父節點比較確認自己的位置,左右子節點其實就是2n+1,2n+2,左右子節點就是數組的相鄰元素,我們發現子節點一定比父節點大,這就是最小堆;每次插入一個元素都是從最底層向上冒泡,維護最小堆的次序。
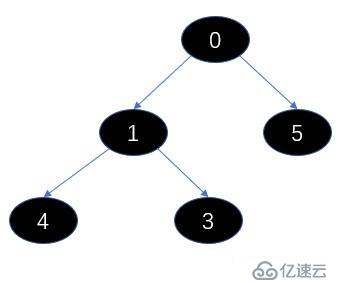
調用了 dequeue方法。
public E poll() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
// 彈出根節點
return dequeue();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 帶超時時間
public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
E result;
try {
while ( (result = dequeue()) == null && nanos > 0)
nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return result;
}也是調用了dequeue方法,這個方法支持線程的中斷。
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
E result;
try {
while ( (result = dequeue()) == null)
notEmpty.await();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return result;
}private E dequeue() {
int n = size - 1;
// 隊列還沒有初始化
if (n < 0)
return null;
else {
Object[] array = queue;
// 獲取根節點
E result = (E) array[0];
// 獲取尾節點
E x = (E) array[n];
// 尾節點置位null
array[n] = null;
Comparator<? super E> cmp = comparator;
// 重新排序最小堆
if (cmp == null)
siftDownComparable(0, x, array, n);
else
siftDownUsingComparator(0, x, array, n, cmp);
size = n;
return result;
}
}其實上面就是返回了根節點,然后獲取尾節點放在根節點的位置調整最小堆請看siftDownComparable方法。
private static <T> void siftDownComparable(int k, T x, Object[] array,
int n) {
// n是數組的最大索引 k開始是0 x就是尾節點的值
if (n > 0) {
// x是最后一個節點的值
Comparable<? super T> key = (Comparable<? super T>)x;
int half = n >>> 1; // 最后一個節點的父節點 // loop while a non-leaf
while (k < half) { // k是頭節點 k> 了 說明到最后了
int child = (k << 1) + 1; // assume left child is least // 左子節點
Object c = array[child]; // 左節點的值
int right = child + 1; // 右子節點
if (right < n && // 左子節點大于由子節點
((Comparable<? super T>) c).compareTo((T) array[right]) > 0)
c = array[child = right]; // c就是右子節點
if (key.compareTo((T) c) <= 0) // 找到了子節點比自己大的
break;
array[k] = c;
k = child;
}
array[k] = key;
}
}分析:
我們上圖的5個元素為例,進行一次出隊操作。
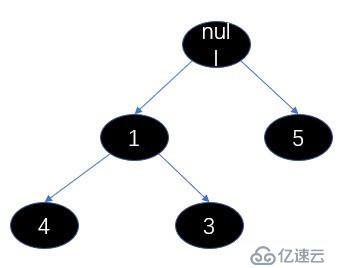
我們調用siftDownComparable 方法調整最小堆,我們看下參數,此時的k是0,x是3,array就是這個數組,n就是4,key就是3,然后算half(half可以理解為堆中父節點最大索引位置,找到這個節點說明已經沒有子節點了),half = 2。
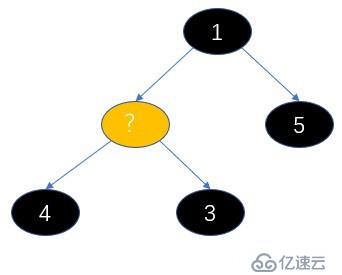
說下調整最小堆的過程,其實就是從根節點開始,重新構建父節點的過程,不過不是每個都需要重新構建,只需要構造子節點小的那邊的的父節點,因為小的節點都去頂替原來的父節點了;我們彈出的是根節點,所以要從他的左右子節點找個根節點(但是要滿足子節點大于父節點的規則),那么左右子節點有一個去當父節點了,它的位置也需要有節點代替,所以又從他的子節點開始找接替的節點,以此類推,直到找到最后一個父節點的位置。
使用了鎖,這個是精確的值。
public int size() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return size;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}PriorityBlockingQueue 是一個wujie的隊列,使用put方法不會阻塞,使用時一定要注意內存溢出的問題;整個隊列的出隊和入隊都是通過最小堆來實現的,理解最小堆是這個隊列的關鍵;這個一個優先級的隊列,適合有優先級的場景。
參考《Java 并發編程的藝術》
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。