您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
shell腳本的基本結構以及如何執行
[root@localhost script]# cat 1.sh #!/bin/bash #The first shell script #Writen by Justin 2015-01-07 date echo "Hello World" [root@localhost script]# ./1.sh -bash: ./1.sh: Permission denied [root@localhost script]# sh 1.sh Wed Jan 7 05:15:38 CST 2015 Hello World [root@localhost script]# chmod +x 1.sh [root@localhost script]# ./1.sh Wed Jan 7 05:15:50 CST 2015 Hello World [root@localhost script]# sh -x 1.sh + date Wed Jan 7 07:29:29 CST 2015 + echo 'Hello World' Hello World [root@localhost script]#
以上為一個簡單的shell腳本和執行,Shell腳本通常都是以.sh 為后綴名,不是說不帶.sh就不是腳本,“#! /bin/bash” 它代表的意思是,該文件使用的是bash語法,其中#表示該行是注釋,嘆號“!”告訴shell運行嘆號之后的命令并用文件的其余部分作為輸入,也就是運行/bin/bash并讓/bin/bash去執行shell程序的內容。后面跟一些該腳本的相關注釋內容以及作者和創建日期或者版本等等,這些注釋并非必須的,可以省略掉,但是不建議省略。因為隨著你工作時間的增加,你寫的shell腳本也會越來越多,如果有一天你回頭查看你寫的某個腳本時,很有可能忘記該腳本是用來干什么的以及什么時候寫的,所以寫上注釋是有必要的。Shell腳本的執行很簡單,直接”sh filename “ 即可,也可以加一個執行權限,直接使用’./filename’ 執行這個腳本。
另外使用sh命令去執行一個shell腳本的時候是可以加-x選項來查看這個腳本執行過程,也可以在腳本里寫上set -x或者set -xv,這樣只執行腳本時候就會顯示執行的每條命令,這樣有利于我們調試這個腳本哪里出了問題。
使用-n可以檢查是否有錯誤
[root@localhost src]# sh -n install-tomcat.sh install-tomcat.sh: line 72: syntax error: unexpected end of file [root@localhost src]#
使用-vx調試腳本
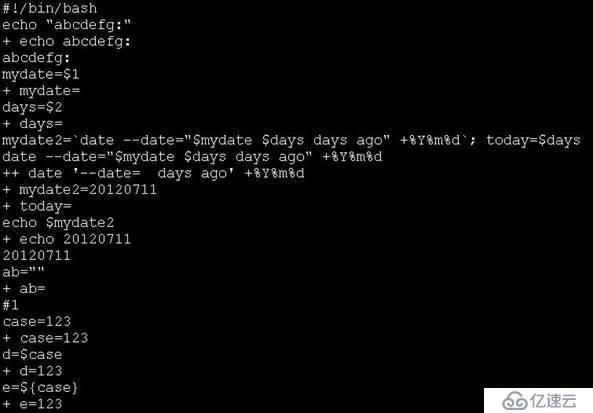
每行代碼原始命令(無+的):-v的效果
代碼執行時的情況(帶+),包括運算結果,邏輯判斷結果,變量賦值等等:-x的效果
syntax error: unexpected end of file:
如果是在windows環境下編寫的shell腳本上傳到linux下需要把dos文件轉換成unix文件格式,否則會出現報錯:syntax error: unexpected end of file:
dos格式文件傳輸到unix系統時,會在每行的結尾多一個^M,而linux下的是沒有的
[root@localhost ~]# cat -A linux.txt linux$ windows$ [root@localhost ~]# cat -A windows.txt windows^M$ linux 最后一行行末沒有換行符; [root@localhost ~]# [root@localhost ~]#
vim windows.txt末尾提示[noeol] 120L, 2532C 信息,'noeol' 就是 'no end-of-line', 即“沒有行末結束符”,vim windows.txt,不做任何修改直接 :wq保存退出換行符已經追加上去,
如果提示 "dos.txt" [dos] 120L, 2532C 字樣,表示是一個[dos]格式文件,如果是MAC系統的,會顯示[MAC],因為文件格式的原因有時會導致我們的unix程序,或者shell程序出現錯誤,那么需要把這些dos文件格式轉換成unix格式,方法是
vi dos.txt
:set fileformat=unix
:w
這樣文件就轉換成unix格式文件了,或者使用dos2unix
yum -y install dos2unix
dos2unix filename.sh
如果還是報錯syntax error: unexpected end of file檢查語法
出現中文亂碼的問題
此問題是因執行定時任務時沒有去獲取系統的環境變量,導致了中文亂碼。在shell腳本開始的時候加下命令:export LANG="en_US.UTF-8"
#!/bin/sh export LANG="en_US.UTF-8"
crontab 里腳本不執行
手動執行腳本正常,加入到crontab里后腳本不執行,這是因為crontab沒有讀取環境變量,腳本中的部分命令不是用的絕對路徑無法找到,可以在腳本開頭讀取環境變量或者所有命令使用絕對路徑
[ -f ~/.bash_profile ] && . ~/.bash_profile [ -f /etc/profile] && . /etc/profile
shell腳本中的變量
$? 是顯示最后命令的退出狀態,0表示沒有錯誤,其他表示有錯誤
$$ Shell本身的PID(ProcessID)
$! Shell最后運行的后臺Process的PID
$- 使用Set命令設定的Flag一覽
$# 是傳給腳本的參數個數
$0 是腳本本身的名字
$1 是傳遞給該shell腳本的第一個參數
$2 是傳遞給該shell腳本的第二個參數
$$ 是腳本運行的當前進程ID號
$* 是以一個單字符串顯示所有向腳本傳遞的參數,與位置變量不同,參數可超過9個
$@:是傳給腳本的所有參數的列表,即被擴展為"$1" "$2" "$3"等;最后一個參數:${@: -1}
$*:是以一個單字符串顯示所有向腳本傳遞的參數,與位置變量不同,參數可超過9個,即被擴展成"$1c$2c$3",其中c是IFS的第一個字符;
${!#}、${@: -1} 輸出最后一個參數
${@:$#-1:1} 倒數第二個參數
[root@localhost script]# cat 2.sh #!/bin/bash #This script,we will use variables. #Write by Justin 2015-01-07 x=`date +%H:%M:%S` echo "the script begin at $x" echo "The script end after 2 seconds" sleep 2 y=`date +%H:%M:%S` echo "The script end at $y" [root@localhost script]# sh 2.sh the script begin at 14:22:08 The script end after 2 seconds The script end at 14:22:10 [root@localhost script]#
腳本中調用了命令date所以使用了反引號,在調用變量時需要加上符號$,這個和在shell中定義變量是一致的。
[root@localhost script]# cat 3.sh #!/bin/bash a=1 b=2 sum=$[$a+$b] echo "sum is $sum" [root@localhost script]# sh 3.sh sum is 3 [root@localhost script]#
數學計算要用’[ ]’括起來并且外頭要帶一個’$’。
[root@localhost script]# cat 4.sh #!/bin/bash echo "please input a number:" read x echo "please input another number:" read y sum=$[$x+$y] echo "The sum of tow number is:$sum" [root@localhost script]# sh 4.sh please input a number: 3 please input another number: 5 The sum of tow number is:8 [root@localhost script]# sh -x 4.sh + echo 'please input a number:' please input a number: + read x 3 + echo 'please input another number:' please input another number: + read y 5 + sum=8 + echo 'The sum of tow number is:8' The sum of tow number is:8 [root@SAMBA1 infa_shared]# echo `date +"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"` > read-only.txt [root@SAMBA1 infa_shared]# cat read-only.txt 2015-11-25 15:56:56 [root@SAMBA1 infa_shared]# y=`date +"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"` [root@SAMBA1 infa_shared]# echo $y 2015-11-25 15:58:27 [root@SAMBA1 infa_shared]#
Shell腳本可以和用戶交互。這就用到了read命令了,它可以從標準輸入獲得變量的值,后跟變量名。”read x”表示x變量的值需要用戶通過鍵盤輸入得到。我們可以直接使用read -p 來代替echo的作用
[root@localhost script]# cat 5.sh #!/bin/bash read -p "please input a number:" x ;x前有個空格 read -p "please input another number:" y sum=$[$x+$y] echo "The sum of tow number is:$sum" [root@localhost script]# sh -x 5.sh + read -p 'please input a number:' x please input a number:3 + read -p 'please input another number:' y please input another number:5 + sum=8 + echo 'The sum of tow number is:8' The sum of tow number is:8 [root@localhost script]#
”/etc/init.d/iptables restart “ 前面的/etc/init.d/iptables 就是一個shell腳本,后面”restart”是了shell腳本的預設變量。上面例子我們可以通過設置預設變量
[root@localhost script]# cat 5.sh #!/bin/bash sum=$[$1+$2] echo "The sum of tow number is:$sum" echo "$0" [root@localhost script]# sh -x 5.sh 3 5 + sum=8 + echo 'The sum of tow number is:8' The sum of tow number is:8 + echo '5.sh' 5.sh [root@localhost script]#
$1和$2就是shell腳本的預設變量,其中$1的值就是在執行的時候輸入的3,而$2的值就是執行的時候輸入的5,一個shell腳本的預設變量是沒有限制的,$0代表的是腳本本身的名字。
set -x與set +x指令
用于腳本調試。set是把它下面的命令打印到屏幕set -x 是開啟 set +x是關閉 set -o是查看 (xtrace),set去追中一段代碼的顯示情況。
set -x /usr/local/bin/sendEmail -s "$SMTP_Server" -xu "$username" -xp "$password" -f "$from_email_address" -t "$to_email_address" -u "$message_subject_utf8" -m "$message_body_utf8" -o message-content-type=text -o message-charset=utf-8
shell腳本中的算術運算
sum=$[$x+$y] sum=$[$x+1] #x y是變量
shell腳本中的邏輯判斷
if判斷語句:
1)不帶else
格式:
if 判斷語句; then
command
fi
[root@localhost script]# cat if1.sh #! /bin/bash read -p "please input your score:" a if ((a<60));then echo "You didn't pass the exam.you score is $a" fi [root@localhost script]# sh if1.sh please input your score:33 You didn't pass the exam.you score is 33 [root@localhost script]#
上面出現了 ((a<60))這樣的形式,這是shell腳本中判斷數值大小特有的格式,用一個小括號或者不用都會報錯,請記住這個格式,在判斷數值大小除了可以用”(( ))”的形式外,還可以使用”[ ]”。但是就不能使用>, < , = ,!=這樣的符號了,要使用 -lt (小于),-gt (大于),-le (小于等于),-ge (大于等于),-eq (等于),-ne (不等于),這種類型在while循環中使用多
常見錯誤:
[ $Sum -ne 0 ]:line 5: [: -ge: unary operator expected
$Sum為空,那么就成了 [ -ge "0"] 了,顯然 [ 和 "0" 不相比較并且缺少了 [ 符號,所以報了這樣的錯誤。
解決辦法:賦值前加declare -i rate=0
declare命令可用來聲明變量并設置變量的屬性,還可以可用來顯示shell函數。
語法:
declare [+/-][rxi][變量名稱=設置值] 或 declare -f
參數說明:
+/- "-"可用來指定變量的屬性,"+"則是取消變量所設的屬性。
-f 函數,declare -f 列出所有在此腳本前面已定義的函數出來;declare -f function_name 列出指定的函數
-F 僅打印函數名字
-r 將變量設置為只讀:declare -r var1
x 指定的變量會成為環境變量,可供shell以外的程序來使用。
-i 聲明變量為整數:declare -i number
-a 聲明變量為數組:declare -a indices
-x 聲明一個變量作為腳本的環境變量而被導出, declare -x var3;declare -x var3=373
declare命令允許在聲明變量類型的時候同時給變量賦值:
declare -i rate=0
rate+=1 #整數聲明后,不需要使用'let'.
let命令用于指定算術運算,即 let expretion,用于執行一個或多個表達式,使用let執行運算時,變量名之前不需要添加$。如果表達式中包含了空格或其他特殊字符,則必須引起來。例如:
a=1
b=2
let result=a+b
echo $result
a=2
let "a+=1"
let ″val=a|b″ 如果不括起來,Shell會把命令行let val=a|b中的“|”看成管道符,將其左右兩邊看成不同的命令,因而無法正確執行
利用(())執行數學運算。使用(())執行算數運算時,變量名之前可以加$,也可不加$。
利[ ]執行數學運算。使用[ ]執行算數運算時,變量名之前可以加$,也可不加$。
let 表達式 支持 ++,-- 的操作,但是不支持 ++a --a 這樣前綴
a = a +1; // 即最普通的寫法,將a的值加1再賦給a
a+=1; // 相當于 a = a+1;
a++; // 是先將a的值賦給一個變量, 再自增,例如:b = a++ 等同于 b = a; a = a + 1;
++a; // 是先自增, 再把a的值給一個變量,例如:b = ++a等同于 a = a + 1; b = a;
2)帶有else
格式:
if 判斷語句 ; then
command
else
command
fi
[root@localhost script]# cat if1.sh #! /bin/bash read -p "please input your score:" a if ((a<60));then echo "You didn't pass the exam.you score is $a" else echo "GOOD! You passed the exam,you score is $a." fi [root@localhost script]# sh if1.sh please input your score:67 GOOD! You passed the exam,you score is 67. [root@localhost script]# sh if1.sh please input your score:33 You didn't pass the exam.you score is 33 [root@localhost script]#
linux-gnv2:/opt/FlashServer/flashserver # cat restart.sh
#!/bin/bash
x=`ps -ef|grep 'flashserver'|grep -v grep|grep -v nohup|awk -F " " '{print $2}'`
y=`ps -ef|grep 'flashserver'|grep -v grep|grep -v nohup|wc -l`
if [ $y -ge 1 ]
then
sudo kill -9 $x
sleep 2
else
echo "no service exist"
fi
nohup ./flashserver >/dev/null &
y=`ps -ef|grep 'flashserver'|grep -v grep|grep -v nohup|wc -l`
sleep 1
if [ $y -ge 1 ]
then
echo "start service success"
else
echo "start service fail"
fi
linux-gnv2:/opt/FlashServer/flashserver #[root@QuoteService Release]# cat RestartQuoteServer.sh #!/bin/bash x=`pgrep QuotePlatform` y=`ps -ef|grep 'QuotePlatform'|grep -v grep|wc -l` z="/usr/local/QuoteService/make/Release" if [ $y -ge 1 ];then kill -9 $x sleep 2 yy=`ps -ef|grep 'QuotePlatform'|grep -v grep|wc -l` #pgrep QuotePlatform是變量,每次應用都需要重新定義變量,不重新定義就是第一次賦予的值 if [ $yy -le 0 ];then echo "QuotePlatform server is not running!" cd $z nohup ./QuotePlatform >/dev/null & sleep 3 yyy=`ps -ef|grep 'QuotePlatform'|grep -v grep|wc -l` if [ $yyy -ge 1 ];then echo "QuotePlatform service successfully started!" else echo "QuotePlatform service startup failed! " fi else echo "Kill QuotePlatform service is failed!" fi else echo "QuotePlatform server is not running!" cd $z nohup ./QuotePlatform >/dev/null & sleep 3 yyyy=`ps -ef|grep 'QuotePlatform'|grep -v grep|wc -l` if [ $yyyy -ge 1 ];then echo "QuotePlatform service successfully started!" else echo "QuotePlatform service startup failed! " fi fi
多判斷條件:同時滿足三個文件大小
[root@localhost src]# cat test.sh
#!/bin/bash
nagiossize=`du -k nagios-plugins-1.4.16.tar.gz|awk '{print $1}'`
nrpesize=`du -k nrpe-2.15.tar.gz|awk '{print $1}'`
zabbixsize=`du -k zabbix-2.2.2.tar.gz|awk '{print $1}'`
if [ $zabbixsize -ge 14200 ] && [ $nagiossize -ge 2000 ] && [ $nrpesize -ge 400 ];then
echo "download is successful"
else
echo "download is failed"
fi
[root@localhost src]# sh test.sh
download is successful
[root@localhost src]#-a 或者 and或者 &&
if (( a > b )) && (( a < c ))
if [ $a > $b ] && [ $a < $c ]]
if [ $a -gt $b -a $a -lt $c ]
-o 或者 or或者||
if (( a > b )) || (( a < c ))
if [ $a > $b ] || [ $a < $c ]
if [ $a -gt $b -o $a -lt $c ]
3)帶有elif
格式:
if [ expression 1 ]
then
Statement(s) to be executed if expression 1 is true
elif [ expression 2 ]
then
Statement(s) to be executed if expression 2 is true
elif [ expression 3 ]
then
Statement(s) to be executed if expression 3 is true
else
Statement(s) to be executed if no expression is true
fi
哪一個 expression 的值為 true,就執行哪個 expression 后面的語句;如果都為 false,那么不執行任何語句。
[root@localhost script]# cat if1.sh #! /bin/bash read -p "please input your score:" a if ((a<60));then echo "You didn't pass the exam.you score is $a" elif ((a>60)) && ((a<85));then echo "GOOD! You passed the exam,you score is $a." else echo "Very Good! You score is $a,it's very hight!" fi [root@localhost script]# sh if1.sh please input your score:33 You didn't pass the exam.you score is 33 [root@localhost script]# sh if1.sh please input your score:77 GOOD! You passed the exam,you score is 77. [root@localhost script]# sh if1.sh please input your score:99 Very Good! You score is 99,it's very hight! [root@localhost script]#
邏輯運算符&& 表示“并且”, || 表示“或者”。
判斷文件(夾)是否存在
注意:單引號和雙引號的區別。單引號告訴shell忽略所有特殊字符,而雙引號忽略大多數,但不包括$、\、`,即雙引號保有變量的內容,但單引號內僅能是 一般字符 ,而不會有特殊符號。
#!/bin/bash myPath="/usr/local/src/dir/test" myFile="/usr/local/src/access.log" #這里的-d參數判斷$myPath是否存在,注意[]前后空格 if [ -d "$myPath" ];then cd "$myPath" tar -cvf myPath.tar * else mkdir -p /usr/local/src/dir/test echo "$myPath is created" touch /usr/local/src/dir/test/1 touch /usr/local/src/dir/test/2 touch /usr/local/src/dir/test/3 fi
#!/bin/bash myPath="/usr/local/src/dir/test" myFile="/usr/local/src/access.log" #這里的-f參數判斷$myPath是否存在 if [ ! -f "$myFile" ];then touch "$myFile" echo "test" > "$myFile" else cat "$myFile" fi
#!/bin/bash #這里的-x參數判斷$myPath是否存在并且有可執行權限 if [ ! -x '/usr/local/src/' ];then chmod +x /usr/local/src/ ll -d /usr/local/src/ else cd "$myPath" && tar -cvf tar.tar /usr/local/src/* tar -tvf tar.tar fi #!/bin/bash MyFile=`command -v ntpdate` if [ ! -x "$MyFile" ];then yum -y install ntp cat >> /var/spool/cron/root << EOF 0 */12 * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate cn.pool.ntp.org EOF /sbin/hwclock --systohc /etc/init.d/crond restart else cat >> /var/spool/cron/root << EOF 0 */12 * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate cn.pool.ntp.org EOF /sbin/hwclock --systohc /etc/init.d/crond restart fi
#!/bin/bash #兩個變量判斷是否相等 if [ "$var1" == "$var2" ]; then echo '$var1 eq $var2' else echo '$var1 not eq $var2' fi
其他參數:
[ -a FILE ] 如果 FILE 存在則為真。
[ -b FILE ] 如果 FILE 存在且是一個塊特殊文件則為真。
[ -c FILE ] 如果 FILE 存在且是一個字特殊文件則為真。
[ -d FILE ] 如果 FILE 存在且是一個目錄則為真。
[ -e FILE ] 如果 FILE 存在則為真。
[ -f FILE ] 如果 FILE 存在且是一個普通文件則為真。
[ -g FILE ] 如果 FILE 存在且已經設置了SGID則為真。
[ -h FILE ] 如果 FILE 存在且是一個符號連接則為真。
[ -k FILE ] 如果 FILE 存在且已經設置了粘制位則為真。
[ -p FILE ] 如果 FILE 存在且是一個名字管道(F如果O)則為真。
[ -r FILE ] 如果 FILE 存在且是可讀的則為真。
[ -s FILE ] 如果 FILE 存在且大小不為o則為真。
[ -t FD ] 如果文件描述符 FD 打開且指向一個終端則為真。
[ -u FILE ] 如果 FILE 存在且設置了SUID (set user ID)則為真。
[ -w FILE ] 如果 FILE 如果 FILE 存在且是可寫的則為真。
[ -x FILE ] 如果 FILE 存在且是可執行的則為真。
[ -O FILE ] 如果 FILE 存在且屬有效用戶ID則為真。
[ -G FILE ] 如果 FILE 存在且屬有效用戶組則為真。
[ -L FILE ] 如果 FILE 存在且是一個符號連接則為真。
[ -N FILE ] 如果 FILE 存在 and has been mod如果ied since it was last read則為真。
[ -S FILE ] 如果 FILE 存在且是一個套接字則為真。
[ FILE1 -nt FILE2 ] 如果 FILE1 has been changed more recently than FILE2, or 如果 FILE1 exists and FILE2 does not則為真。
[ FILE1 -ot FILE2 ] 如果 FILE1 比 FILE2 要老, 或者 FILE2 存在且 FILE1 不存在則為真。
[ FILE1 -ef FILE2 ] 如果 FILE1 和 FILE2 指向相同的設備和節點號則為真。
[ -o OPTIONNAME ] 如果 shell選項 “OPTIONNAME” 開啟則為真。
[ -z STRING ] “STRING” 的長度為零則為真。
[ -n STRING ] “STRING” 的長度為非零o則為真。注意:STRING如果時變量,需要時用雙引號或者使用"[[ ]]",否則當STRING為空值時就變成了[ STRING ],shell會把它當作[ -n ]來處理。
[ STRING1 == STRING2 ] 如果2個字符串相同。 “=” may be used instead of “==” for strict POSIX compliance則為真。
[ STRING1 != STRING2 ] 如果字符串不相等則為真。
[ STRING1 < STRING2 ] 如果 “STRING1” sorts before “STRING2” lexicographically in the current locale則為真。
[ STRING1 > STRING2 ] 如果 “STRING1” sorts after “STRING2” lexicographically in the current locale則為真。
判斷文件是否存在特定字符串grep -q
[root@finchina ~]# cat a.txt nihao nihaooo hello [root@finchina ~]# if grep -q hellooooo a.txt ;then echo 'hello is exist';else echo 'hello is not exist';fi hello is not exist [root@finchina ~]#
case判斷語句
格式:
case 變量 in
value1)
command
;;
value2)
command
;;
value3)
command
;;
*)
command
;;
esac
上面的結構中,不限制value的個數,*則代表除了上面的value外的其他值,case行尾必須為單詞“in”,每一個模式必須以右括號“)”結束。雙分號“;;”表示命令序列結束。匹配模式中可是使用方括號表示一個連續的范圍,如[0-9];使用豎杠符號“|”表示或。最后的“*)”表示默認模式,當使用前面的各種模式均無法匹配該變量時,將執行“*)”后 的命令序列。
[root@localhost script]# cat case.sh #!/bin/bash read -p "please input:" n case $n in [0-9]*) echo "You input a number:$n" ;; [a-z]*|[A-Z]*) echo "You input a letter:$n" ;; *) echo "You input is not a digital or not characters:$n" ;; esac [root@localhost script]# sh case.sh please input:111112222 You input a number:111112222 [root@localhost script]# sh case.sh please input:afdfdaf You input a letter:afdfdaf [root@localhost script]# sh case.sh please input:**(* You input is not a digital or not characters:**(* [root@localhost script]#
case腳本常用于編寫系統服務的啟動腳本,例如/etc/init.d/iptables中就用到了
read命令:
read命令接收標準輸入(鍵盤)的輸入,或其他文件描述符的輸入(后面在說)。得到輸入后,read命令將數據放入一個標準變量中。
語法
read (選項) (參數)
主要參數:
-t 等待時間,eg、read -t 5 -p "please enter your name:" name
read -t 5 -p "please enter your name:" name
-p 允許在read命令行中直接指定一個提示
read -p "Enter your name:" name echo "hello $name, welcome to my program"
-n 計算輸入字符數
read -n1 -p "Do you want to continue [Y/N]?" answer
指示read命令只要接受到一個字符就退出。只要按下一個字符進行回答,read命令立即接受輸入并將其傳給變量。無需按回車鍵
#!/bin/bash read -n1 -p "Do you want to continue [Y/N]?" answer case $answer in Y | y) echo "fine ,continue";; N | n) echo "ok,good bye";; *) echo "error choice";; esac exit 0
-s 選項能夠使read命令中輸入的數據不顯示在監視器上(實際上,數據是顯示的,只是 read命令將文本顏色設置成與背景相同的顏色)。
read -s -p "Enter your password:" pass
shell腳本中的循環
for循環
結構 :
for 變量名 in 循環的條件; do
command
done
或
for ((初始語句;執行條件;增量 ));do
command
done
執行順序:1、初始語句 2、執行條件是否符合? 3、循環體 4、增加增量
初始化語句只在循環開始前執行一次,每次執行循環體時要先判斷是否符合條件,如果循環條件還會true,則執行循環體,在執行迭代語句。
所以對于for循環,循環條件總比循環體多執行一次。
[root@localhost script]# cat for.sh
#!/bin/bash
#for i in `seq 0 5` #這里是反引號
#for i in {0..5}
for i in 0 1 2 3 4 5
do
echo $i
done
[root@localhost script]# sh for.sh
0
1
2
3
4
5
[root@localhost script]# cat for.sh
#!/bin/bash
for i in `tail -5 /etc/passwd`
do
x=`echo $i|awk -F':' '{print $1"\t"$7}'`
echo $x
done
[root@localhost script]# cat for.sh
#!/bin/bash
for i in `cat /etc/passwd`
do
x=`echo $i|awk -F':' '{print $1"\t"$7}'`
echo $x
done
[root@localhost script]# cat for.sh
#!/bin/bash
for i in $(cat /etc/passwd)
do
x=`echo $i|awk -F':' '{print $1"\t"$7}'`
echo $x
done
[root@localhost script]#
[root@localhost script]# sh for.sh
tcpdump /sbin/nologin
[root@localhost script]# cat for.sh #禁止udp對外發包
#!/bin/bash
dns=`grep -i nameserver /etc/resolv.conf|awk '{print $NF}'`
for i in $dns
do
iptables -A OUTPUT -p udp -d $i --dport 53 -j ACCEPT
done
iptables -A OUTPUT -p udp -j DROP
service iptables save
[root@Zabbix ~]# sh for.sh
iptables: Saving firewall rules to /etc/sysconfig/iptables:[ OK ]
[root@Zabbix ~]#seq 0 5 表示從0到5的一個序列,seq默認從0開始,
[root@localhost script]# cat for.sh #!/bin/bash for ((i=1;i<=19;i++)) do if((i%3==0));then echo $i fi done [root@localhost script]# sh for.sh 3 6 9 12 15 18 [root@localhost script]#
for語法循環有點像C語法,但記得雙括號
循環控制break/continue
break和continue都是用來控制循環結構的,主要是停止循環。
break用于完全結束一個循環,跳出循環體,不再執行后面循環,break n表示"從里向外"打斷第n個循環,默認值為 break 1 ,也就是打斷當前的循環。
continue只是跳過當次循環中剩下的語句,但是會繼續執行下一次循環。continue n 表示繼續從哪一層(從里向外計算)的循環,默認值為continue 1 ,也就是繼續當前的循環。
[root@localhost src]# cat for.sh #!/bin/bash for ((i=7000;i<8101;i++)) do if [ $i -ge 7101 ] && [ $i -le 7999 ];then continue else echo $i fi done [root@localhost src]#
這里執行的結果是輸出7000-7100、8000-8100,當循環到7101時候continue會終止這次7101的循環,后面一次類推,如果continue換成break的話只輸出7000-7100,當循環到7101時候if判斷為真,執行break跳出當前循環,如果這里for的外面還有一個循環體系,要跳出該循環體系的話使用break 2;一次類推break 3 ....
while循環
格式:
while 條件; do
command
done
[root@localhost script]# cat while.sh #!/bin/bash min=1 max=20 #while (($min<=$max)) while [ $min -le $max ] ;[后面、]前面有個空格 do echo $min min=$[$min+1] done [root@localhost script]# sh while.sh 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 [root@localhost script]#
.循環控制語句
# break 命令不執行當前循環體內break下面的語句從當前循環退出.
# continue 命令是程序在本循體內忽略下面的語句,從循環頭開始執行
while 逐行讀取文件While read LINE
while循環中執行效率最高,最常用的方法:
While read LINE
do
echo $LINE
done < $FILENAME
}
[root@token1 git]# cat while.sh
#!/bin/bash
ls -l /app/git|grep -v total|awk '{print $NF}' > /tmp/git.txt
while read line
do
cd /app/git/$line
git add .
git commit -am "add new repo $line"
git remote rm origin
git remote add origin git@192.168.100.243:$line.git
git push origin master
done < /tmp/git.txt
[root@token1 git]#或者
[root@token1 git]# cat while.sh
#!/bin/bash
ls -l /app/git|grep -v total|awk '{print $NF}' > /tmp/git.txt
cat /tmp/git.txt|while read line
do
cd /app/git/$line
git add .
git commit -am "add new repo $line"
git remote rm origin
git remote add origin git@192.168.100.243:$line.git
git push origin master
done
[root@token1 git]#對循環重定向的輸入可適用于循環中的所有需要從標準輸入讀取數據的命令;
對循環重定向的輸出可適用于循環中的所有需要向標準輸出寫入數據的命令;
當在循環內部顯式地使用輸入或輸出重定向,內部重定向覆蓋外部重定向。
read通過輸入重定向,把file的第一行所有的內容賦值給變量line,循環體內的命令一般包含對變量line的處理;然后循環處理file的第二行、第三行。。。一直到file的最后一行。還記得while根據其后的命令退出狀態來判斷是否執行循環體嗎?是的,read命令也有退出狀態,當它從文件file中讀到內容時,退出狀態為0,循環繼續驚醒;當read從文件中讀完最后一行后,下次便沒有內容可讀了,此時read的退出狀態為非0,所以循環才會退出。
while read line只讀一行或者最后一行讀不到
[root@Super remote-excet]# cat remote-excet_ipfile.sh for ip in `cat $2` do /usr/local/bin/sshpass -p 123 ssh -n -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -tt root@$ip 'uptime' done [root@Super remote-excet]#
原因是循環里 ssh 進入了另一個進程,導致輸入中斷。while中使用重定向機制,$2文件中的信息都已經讀入并重定向給了整個while語句。所以當我們在while循環中再一次調用read語句,就會讀取到下一條記錄。問題就出在這里,ssh語句正好會讀取輸入中的所有東西,而for就沒這個問題了
Tips:如果腳本你是直接在windows下通過記事本類工具編寫傳到linux上給了執行權限后使用./來執行發現無法執行,而通過sh就可以
[root@localhost src]# chmod +x linux_nagios_client.sh [root@localhost src]# ./linux_nagios_client.sh -bash: ./linux_nagios_client.sh: /bin/bash^M: bad interpreter: No such file or directory [root@localhost src]# sh linux_nagios_client.sh Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, product-id, subscription-manager This system is not registered to Red Hat Subscription Management. You can use subscription-manager to register. Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile Setting up Group Process
出現上面錯誤的原因之一是腳本文件是DOS格式的, 即每一行的行尾以\r\n來標識, 使用vim編輯器打開腳本, 運行:
:set ff?
可以看到DOS或UNIX的字樣. 使用set ff=unix把它強制為unix格式的, 然后存盤退出, 即可.
切換用戶并執行命令
#!/bin/bash su - oracle << EOF salplus / as sysdba startup exit EOF #su - oracle -c "salplus / as sysdba && startup" lsnrctl start
添加腳本運行的日志
有時候腳本運行我們希望看到運行的記錄情況,這時候我們可以在腳本里定義將運行的結果寫入到日志里。
在腳本開頭定義日志信息
#!/bin/bash LOGFILE="/var/log/sendEmail.log" :>"$LOGFILE" exec 1>>"$LOGFILE" exec 2>&1
注意:添加以上行后所有標準輸出信息都重定向到/var/log/sendEmail.log文件中,界面中無法看到輸出信息,如果有交互的操作也無法看到提示信息,此時應避免這種方式
exec 1:0(stdin,標準輸入)、1(stdout,標準輸出)、2(stderr,標準錯誤輸出)
冒號在shell中表示空指令
: >file 清空文件file的內容
設定缺省值(:=): 1.1 未定義時, 生成缺省值,: ${VAR:=DEFAULT} 當變量VAR沒有聲明或者為NULL時,將VAR設置為默認值DEFAULT。如果不在前面加上:命令,那么就會把${VAR:=DEFAULT}本身當做一個命令來執行,報錯是肯定的。
1.2 空值時, 有冒號就生成缺省值;
1.3 有值時, 不覆蓋.
缺省值(:-): 2.1 未定義時, 原變量str不會變; 返回值var可覆蓋;
2.2 空值時, 變量str不會變;
2.3 有值時, 不覆蓋.
覆蓋缺省值(:+): 3.1 未定義時, 原變量str, 返回值var不會變;
3.2 空值時, 原變量str不會變;
3.3 有值時, 覆蓋變量str的缺省值
注意:
1. =, -有值時, 原變量不變, 只有:+才能覆蓋;
2. +, -無值時, 原變量str仍為空.
如果需要把信息打印屏幕同時寫入日志可以使用mkfifo來實現
#!/bin/bash
export LANG="en_US.UTF-8"
error_log='/tmp/error_log.log'
info_log='/tmp/info_log.log'
:>"$error_log"
:>"$info_log"
rm -rf /tmp/info.fifo
rm -rf /tmp/error.fifo
#exec 1>>"$info_log"
#exec 2>>"$error_log"
mkfifo /tmp/info.fifo
mkfifo /tmp/error.fifo
cat /tmp/info.fifo | tee -a "${info_log}" &
exec 1>/tmp/info.fifo
cat /tmp/error.fifo | tee -a "${error_log}" &
exec 2>/tmp/error.fifo
date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" > $error_log
date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" > $info_log
#####################################mkfifo info.fifo
mkfifo error.fifo
#創建管道文件
cat info.fifo | tee -a info.log &
exec 1>info.fifo
#把執行過程輸出到info文件中
cat error.fifo | tee -a error.log &
exec 2>error.fifo
#把報錯輸出到error文件中
printf "\015" #結束從管道文件中獲取信息
自定義函數
當我們要在腳本中多次使用相同一組命令時,可以將這組命令定義成一個函數來調用。
注意:所有函數在使用前必須定義。這意味著必須將函數放在腳本開始部分,直至shell解釋器首次發現它時,才可以使用。調用函數僅使用其函數名即可。
shell中函數的定義格式如下:
函數名(){ #function 函數名(){ 可在函數名前加上關鍵字function
command1
command2
...
commandN
[ return value ]
}例如:
[root@localhost ~]# cat function.sh
#!/bin/bash
function test(){
echo "This is your first shell function!"
}
echo "Function begin..."
test
echo "Function begin..."
[root@localhost ~]# sh function.sh
Function begin...
This is your first shell function!
Function begin...
[root@localhost ~]# echo $?
0
[root@localhost ~]#函數返回值,可以顯示增加return語句;如果不加,則將最后一條命令運行結果作為返回值(一般為0,如果執行失敗則返回錯誤代碼)。 return后跟數值(0-255)。
在Shell中,調用函數時可以向其傳遞參數。在函數體內部,通過 $n 的形式來獲取參數的值,例如,$1表示第一個參數,$2表示第二個參數...當n>=10時,需要使用${n}來獲取參數。
例如:
[root@localhost ~]# cat function.sh
#!/bin/bash
function test(){
echo "This first number is $1"
echo "This second number is $2"
echo "This third number is $3"
return $(($1+$2+$3))
}
test 1 2 3
echo "The sum of Three numbers is $? !"
[root@localhost ~]# sh function.sh
This first number is 1
This second number is 2
This third number is 3
The sum of Three numbers is 6 !
[root@localhost ~]#shell中的函數可以帶參數調用,各個輸入參數直接用空格分隔。
[root@localhost ~]# cat function.sh
#!/bin/bash
function test(){
echo "This first number is $1"
echo "This second number is $2"
echo "This third number is $3"
return $(($1+$2+$3))
}
total=$(test 4 5 6)
echo -e "$total\n return is $? !"
[root@localhost ~]# sh function.sh
This first number is 4
This second number is 5
This third number is 6
return is 15 !
[root@localhost ~]#定義函數可以與系統命令相同,shell搜索命令時候,首先會在當前的shell文件定義好的地方查找,找到直接執行。
[root@localhost ~]# cat function.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo "$(uname)"
function uname(){
echo "This first number is $1"
echo "This second number is $2"
echo "This third number is $3"
return $(($1+$2+$3))
}
total=$(uname 4 5 6)
echo -e "$total\n return is $? !"
[root@localhost ~]# sh function.sh
Linux
This first number is 4
This second number is 5
This third number is 6
return is 15 !
[root@localhost ~]#在函數調用之前定義變量,該變量是全局變量,如果定義的變量只對某個函數定義,可以在函數中定義:local 變量=值 ,這時變量就是內部變量,它的修改,不會影響函數外部相同變量的值 。
[root@localhost ~]# cat function.sh
#!/bin/bash
num=100
function num1(){
local num=10
echo "$num"
}
function num2(){
echo "$num"
}
num1
num2
[root@localhost ~]# sh function.sh
10
100
[root@localhost ~]#shell切換用戶執行命令,執行完切換當前用戶
[root@GIT gitosis-admin]# vim create_repo.sh #!/bin/bash echo -e "Please input repo name \033[031m(Format:dirnam.git)\033[0m:" read name su git << EOF cd /home/gitrepository/; mkdir $name; cd $name; git init --bare; exit; EOF
[root@GIT gitosis-admin]# vim create_repo.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo -e "Please input repo name \033[031m(Format:dirnam.git)\033[0m:"
read name
su git << EOF
cd /home/gitrepository/;
mkdir $name;
cd $name;
git init --bare;
exit;
EOF
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。