您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹“怎么通過Python實現批量數據提取”,在日常操作中,相信很多人在怎么通過Python實現批量數據提取問題上存在疑惑,小編查閱了各式資料,整理出簡單好用的操作方法,希望對大家解答”怎么通過Python實現批量數據提取”的疑惑有所幫助!接下來,請跟著小編一起來學習吧!
1.ImageMagick
2.tesseract-OCR
3.Python3.7
4.from PIL import Image as PI
5.import io
6.import os
7.import pyocr.builders
8.from cnocr import CnOcr
9.import xlwt

分析上圖發現票據金額為“貳拾萬元整”,數據金額為大寫中文,因此在導入Excel之前我們需要將金額票據的數據轉換成數字的格式,基于此,我們需要首先完成大寫漢字和數字的轉換。
def chineseNumber2Int(strNum: str): result = 0 temp = 1 # 存放一個單位的數字如:十萬 count = 0 # 判斷是否有chArr cnArr = ['壹', '貳', '叁', '肆', '伍', '陸', '柒', '捌', '玖'] chArr = ['拾', '佰', '仟', '萬', '億'] for i in range(len(strNum)): b = True c = strNum[i] for j in range(len(cnArr)): if c == cnArr[j]: if count != 0: result += temp count = 0 temp = j + 1 b = False break if b: for j in range(len(chArr)): if c == chArr[j]: if j == 0: temp *= 10 elif j == 1: temp *= 100 elif j == 2: temp *= 1000 elif j == 3: temp *= 10000 elif j == 4: temp *= 100000000 count += 1 if i == len(strNum) - 1: result += temp return result
通過上述代碼即可實現大寫字母與數字的轉換,例如輸入“貳拾萬元整”即可導出“200000”,再將其轉換成數字后即可極大地簡化表格的操作,也可以在完成表格操作的同時有利于數據歸檔。
接下來,我們需要分析發票的內部內容,分析下圖可知,我們需要獲取以下幾個數據內容:“出票日期”、“匯票到賬日期”、“票據號碼”、“收款人”、“票據金額”、“出票人”,可以通過畫圖軟件獲取精準定位。

如圖,小黑點即鼠標所在地,畫圖軟件左下角即他的坐標。
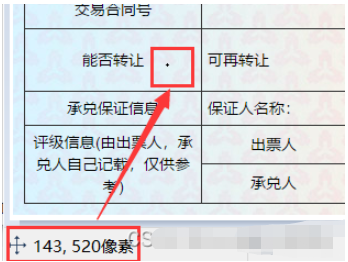
def text1(new_img): #提取出票日期 left = 80 top = 143 right = 162 bottom = 162 image_text1 = new_img.crop((left, top, right, bottom)) #展示圖片 #image_text1.show() txt1 = tool.image_to_string(image_text1) print(txt1) return str(txt1)
def text2(new_img):
#提取金額
left = 224
top = 355
right = 585
bottom = 380
image_text2 = new_img.crop((left, top, right, bottom))
#展示圖片
#image_text2.show()
image_text2.save("img/tmp.png")
temp = ocr.ocr("img/tmp.png")
temp="".join(temp[0])
txt2=chineseNumber2Int(temp)
print(txt2)
return txt2def text3(new_img):
#提取出票人
left = 177
top = 207
right = 506
bottom = 231
image_text3 = new_img.crop((left, top, right, bottom))
#展示圖片
#image_text3.show()
image_text3.save("img/tmp.png")
temp = ocr.ocr("img/tmp.png")
txt3="".join(temp[0])
print(txt3)
return txt3def text4(new_img):
#提取付款行
left = 177
top = 274
right = 492
bottom = 311
image_text4 = new_img.crop((left, top, right, bottom))
#展示圖片
#image_text4.show()
image_text4.save("img/tmp.png")
temp = ocr.ocr("img/tmp.png")
txt4="".join(temp[0])
print(txt4)
return txt4def text5(new_img): #提取匯票到日期 left = 92 top = 166 right = 176 bottom = 184 image_text5 = new_img.crop((left, top, right, bottom)) #展示圖片 #image_text5.show() txt5 = tool.image_to_string(image_text5) print(txt5) return txt5
def text6(new_img): #提取票據號碼 left = 598 top = 166 right = 870 bottom = 182 image_text6 = new_img.crop((left, top, right, bottom)) #展示圖片 #image_text6.show() txt6 = tool.image_to_string(image_text6) print(txt6) return txt6
在將數據全部提取完成之后,即進入設置環節,我們需要首先將所有賬單文件進行提取,獲取他們的文件名和路徑。
ocr=CnOcr() tool = pyocr.get_available_tools()[0] filePath='img' img_name=[] for i,j,name in os.walk(filePath): img_name=name
在獲取完整后,即可進行數據導入Excel的操作。
count=1
book = xlwt.Workbook(encoding='utf-8',style_compression=0)
sheet = book.add_sheet('test',cell_overwrite_ok=True)
for i in img_name:
img_url = filePath+"/"+i
with open(img_url, 'rb') as f:
a = f.read()
new_img = PI.open(io.BytesIO(a))
## 寫入csv
col = ('年份','出票日期','金額','出票人','付款行全稱','匯票到日期','備注')
for j in range(0,7):
sheet.write(0,j,col[j])
book.save('1.csv')
shijian=text1(new_img)
sheet.write(count,0,shijian[0:4])
sheet.write(count,1,shijian[5:])
sheet.write(count,2,text2(new_img))
sheet.write(count,3,text3(new_img))
sheet.write(count,4,text4(new_img))
sheet.write(count,5,text5(new_img))
sheet.write(count,6,text6(new_img))
count = count + 1至此,完整流程結束。
from wand.image import Image
from PIL import Image as PI
import pyocr
import io
import re
import os
import shutil
import pyocr.builders
from cnocr import CnOcr
import requests
import xlrd
import xlwt
from openpyxl import load_workbook
def chineseNumber2Int(strNum: str):
result = 0
temp = 1 # 存放一個單位的數字如:十萬
count = 0 # 判斷是否有chArr
cnArr = ['壹', '貳', '叁', '肆', '伍', '陸', '柒', '捌', '玖']
chArr = ['拾', '佰', '仟', '萬', '億']
for i in range(len(strNum)):
b = True
c = strNum[i]
for j in range(len(cnArr)):
if c == cnArr[j]:
if count != 0:
result += temp
count = 0
temp = j + 1
b = False
break
if b:
for j in range(len(chArr)):
if c == chArr[j]:
if j == 0:
temp *= 10
elif j == 1:
temp *= 100
elif j == 2:
temp *= 1000
elif j == 3:
temp *= 10000
elif j == 4:
temp *= 100000000
count += 1
if i == len(strNum) - 1:
result += temp
return result
def text1(new_img):
#提取出票日期
left = 80
top = 143
right = 162
bottom = 162
image_text1 = new_img.crop((left, top, right, bottom))
#展示圖片
#image_text1.show()
txt1 = tool.image_to_string(image_text1)
print(txt1)
return str(txt1)
def text2(new_img):
#提取金額
left = 224
top = 355
right = 585
bottom = 380
image_text2 = new_img.crop((left, top, right, bottom))
#展示圖片
#image_text2.show()
image_text2.save("img/tmp.png")
temp = ocr.ocr("img/tmp.png")
temp="".join(temp[0])
txt2=chineseNumber2Int(temp)
print(txt2)
return txt2
def text3(new_img):
#提取出票人
left = 177
top = 207
right = 506
bottom = 231
image_text3 = new_img.crop((left, top, right, bottom))
#展示圖片
#image_text3.show()
image_text3.save("img/tmp.png")
temp = ocr.ocr("img/tmp.png")
txt3="".join(temp[0])
print(txt3)
return txt3
def text4(new_img):
#提取付款行
left = 177
top = 274
right = 492
bottom = 311
image_text4 = new_img.crop((left, top, right, bottom))
#展示圖片
#image_text4.show()
image_text4.save("img/tmp.png")
temp = ocr.ocr("img/tmp.png")
txt4="".join(temp[0])
print(txt4)
return txt4
def text5(new_img):
#提取匯票到日期
left = 92
top = 166
right = 176
bottom = 184
image_text5 = new_img.crop((left, top, right, bottom))
#展示圖片
#image_text5.show()
txt5 = tool.image_to_string(image_text5)
print(txt5)
return txt5
def text6(new_img):
#提取票據號碼
left = 598
top = 166
right = 870
bottom = 182
image_text6 = new_img.crop((left, top, right, bottom))
#展示圖片
#image_text6.show()
txt6 = tool.image_to_string(image_text6)
print(txt6)
return txt6
ocr=CnOcr()
tool = pyocr.get_available_tools()[0]
filePath='img'
img_name=[]
for i,j,name in os.walk(filePath):
img_name=name
count=1
book = xlwt.Workbook(encoding='utf-8',style_compression=0)
sheet = book.add_sheet('test',cell_overwrite_ok=True)
for i in img_name:
img_url = filePath+"/"+i
with open(img_url, 'rb') as f:
a = f.read()
new_img = PI.open(io.BytesIO(a))
## 寫入csv
col = ('年份','出票日期','金額','出票人','付款行全稱','匯票到日期','備注')
for j in range(0,7):
sheet.write(0,j,col[j])
book.save('1.csv')
shijian=text1(new_img)
sheet.write(count,0,shijian[0:4])
sheet.write(count,1,shijian[5:])
sheet.write(count,2,text2(new_img))
sheet.write(count,3,text3(new_img))
sheet.write(count,4,text4(new_img))
sheet.write(count,5,text5(new_img))
sheet.write(count,6,text6(new_img))
count = count + 1到此,關于“怎么通過Python實現批量數據提取”的學習就結束了,希望能夠解決大家的疑惑。理論與實踐的搭配能更好的幫助大家學習,快去試試吧!若想繼續學習更多相關知識,請繼續關注億速云網站,小編會繼續努力為大家帶來更多實用的文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。