您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要講解了“Java怎么使用Condition實現精準喚醒線程”,文中的講解內容簡單清晰,易于學習與理解,下面請大家跟著小編的思路慢慢深入,一起來研究和學習“Java怎么使用Condition實現精準喚醒線程”吧!
Condition是一個接口,創建Condition的實例不能直接new,Java為我們提供一個通過Lock類實例來調用newCondition()的方法來創建。Condition因素出Object監視器方法( wait , notify和notifyAll )到不同的對象,以得到具有多個等待集的每個對象,通過將它們與使用任意的組合的效果Lock個實現。 如果Lock替換了synchronized方法和語句的使用,則Condition將替換Object監視方法的使用。
條件(也稱為條件隊列或條件變量 )為一個線程提供暫停執行(“等待”)的手段,直到另一個線程通知某個狀態條件現在可能為真。 由于對此共享狀態信息的訪問發生在不同的線程中,因此必須對其進行保護,因此某種形式的鎖定與該條件相關聯。 等待條件提供的關鍵屬性是它以原子方式釋放關聯的鎖并掛起當前線程,就像Object.wait一樣。

例子1
package testJUC;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class TestCondition {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Product3 product = new Product3();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
new Producer(product).getProduct();
},"工廠").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
new Consumer(product).saleProduct();
},"學生").start();
}
}
class Product3 {
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition();
private Condition condition2 = lock.newCondition();
private int flag = 1;//標識符
public void getProduct() {
//加鎖
lock.lock();
try {
//使用while循環,可以有效避免線程虛假喚醒
while (flag != 1) {
condition1.await();
}
flag = 2;
//喚醒saleProduct
condition2.signal();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "生產一個產品");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//解鎖
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void saleProduct() {
lock.lock();
try {
while (flag != 2) {
condition2.await();
}
flag = 1;
//喚醒getProduct
condition1.signal();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"消費了一個產品");
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
//實體類
class Producer{
private Product3 product = null;
public Producer(Product3 product) {
this.product = product;
}
public void getProduct(){
product.getProduct();
}
}
class Consumer{
private Product3 product = null;
public Consumer(Product3 product) {
this.product = product;
}
public void saleProduct(){
product.saleProduct();
}
}結果

例子2
package testJUC;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class TestCondition {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Print print = new Print();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
print.printA();
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
print.printB();
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
print.printC();
}).start();
}
}
class Print {
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition();
private Condition condition2 = lock.newCondition();
private Condition condition3 = lock.newCondition();
private int number = 1;
//輸出A的方法
public void printA() {
//加鎖
lock.lock();
try {
//使用while循環,可以有效避免線程虛假喚醒
while (number != 1) {
condition1.await();
}
number = 2;
//喚醒輸出B的方法
condition2.signal();
System.out.println("AAA");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//解鎖
lock.unlock();
}
}
//輸出B的方法
public void printB() {
//加鎖
lock.lock();
try {
while (number != 2) {
condition2.await();
}
System.out.println("BBB");
number = 3;
//喚醒C
condition3.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//喚醒輸出C的方法
lock.unlock();
}
}
//輸出C的方法
public void printC() {
//加鎖
lock.lock();
try {
while (number != 3) {
condition3.await();
}
System.out.println("CCC");
number = 1;
//喚醒輸出A的方法
condition1.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//解鎖
lock.unlock();
}
}
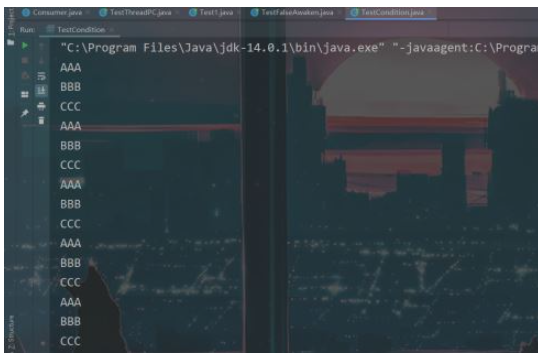
}結果2
感謝各位的閱讀,以上就是“Java怎么使用Condition實現精準喚醒線程”的內容了,經過本文的學習后,相信大家對Java怎么使用Condition實現精準喚醒線程這一問題有了更深刻的體會,具體使用情況還需要大家實踐驗證。這里是億速云,小編將為大家推送更多相關知識點的文章,歡迎關注!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。