您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
今天小編給大家分享一下Android怎么使用RecyclerView實現瀑布流界面的相關知識點,內容詳細,邏輯清晰,相信大部分人都還太了解這方面的知識,所以分享這篇文章給大家參考一下,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后有所收獲,下面我們一起來了解一下吧。
最早采用此布局的網站是Pinterest,逐漸在國內流行開來。國內大多數做的好的大廠的APP都是這種布局、尤以UGC(UGC它的中文意思是用戶生產內容的意思,簡稱為UGC)為主的APP采用此布局最多像:知乎上的精品貼、推薦貼、小紅書種草等都是這種風格。
瀑布流布局的優點為:
1.吸引用戶,當用戶在瀏覽瀑布流式布局的時候(這里拋開懶加載),用戶會產生一種錯覺,就是信息是不停的在更新的,這會激發用戶的好奇心,使用戶不停的往下滑動。
2.良好視覺體驗,采用瀑布流布局的方式可以打破常規網站布局排版,給用戶眼前一亮的新鮮感,用戶在瀏覽內容時會感到很有新鮮感,帶來良好的視覺體驗。
3.更好的適應移動端,由于移動設備屏幕比電腦小,一個屏幕顯示的內容不會非常多,因此可能要經常翻頁。而在建網站時使用瀑布流布局,用戶則只需要進行滾動就能夠不斷瀏覽內容。(這一點和懶加載有一點像)
網上有一些第三方控件使用了瀑布流,但是這些第三方控件都已經廢棄或者是停更了。這些第三方控件本人都用過,不是有各種BUG就是把問題搞了很復雜。這東西其實很簡單,一天內就可以做出生產級別的應用了,哪有這么難。
難就是難在太多初學者為了趕項目或者說很多人急功近利,只想著copy paste,因此搞了一堆其實無用的代碼還把問題“混攪”了。
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView android:id="@+id/rv" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> </androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView>
這是一個使用androidx的基于mvvm的工程。
至于如何把一個工程變成androidx和mvvm此處就不再贅述了,在我前面的博客中已經寫了很詳細了。

activity_main.xml布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"> <data> </data> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView android:id="@+id/rv" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> </androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView> </LinearLayout> </layout>
瀑布流中具體的明細布局-rv_item.xml
在明細布局里,整體瀑布流墻就兩個元素,一個是照片的url另一個是文本框,實現很簡單。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto">
<data>
<variable
name="item"
type="org.mk.android.demo.demo.staggerdrecyclerview.RVBean" />
</data>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<androidx.cardview.widget.CardView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="8dp"
app:cardCornerRadius="8dp"
app:cardElevation="4dp">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/rvImageView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:adjustViewBounds="true"
android:scaleType="fitXY"
app:url="@{item.url}" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/rvTextView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAlignment="center"
android:layout_margin="4dp"
android:text="@{item.text}" />
</LinearLayout>
</androidx.cardview.widget.CardView>
</LinearLayout>
</layout>現在就來看我們的代碼。
RVBean.java
package org.mk.android.demo.demo.staggerdrecyclerview;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import androidx.databinding.BindingAdapter;
import com.bumptech.glide.Glide;
import java.util.Objects;
public class RVBean {
private String url;
private String text;
private final static String TAG = "DemoStaggerdRecyclerView";
@BindingAdapter("url")
public static void loadImg(ImageView imageView, String url) {
Glide.with(imageView).load(url).into(imageView);
}
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getText() {
return text;
}
public void setText(String text) {
this.text = text;
}
public RVBean(String url, String text) {
this.url = url;
this.text = text;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
//Log.i(TAG, ">>>>>>this==o return true");
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
//Log.i(TAG, ">>>>>>o==null||getClass()!=o.getClass() is false");
return false;
}
RVBean rvBean = (RVBean) o;
if (rvBean.url.length() != url.length() || rvBean.text.length() != text.length()) {
//Log.i(TAG, ">>>>>>target length()!=existed url length");
return false;
}
if(url.equals(rvBean.url)&&text.equals(rvBean.text)){
//Log.i(TAG,">>>>>>url euqlas && text equals");
return true;
}else{
//Log.i(TAG,">>>>>>not url euqlas && text equals");
return false;
}
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int hashCode = Objects.hash(url, text);
//Log.i(TAG, ">>>>>>hashCode->" + hashCode);
return hashCode;
}
}代碼中它定義了兩個元素,一個為文本框,一個為用于加載網絡圖片的url,網絡圖片我用的是我另一臺VM上的Nginx做的靜態圖片資源服務。
RVAdapter.java
package org.mk.android.demo.demo.staggerdrecyclerview;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.TextView;
import androidx.annotation.NonNull;
import androidx.databinding.DataBindingUtil;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView;
import com.bumptech.glide.Glide;
import org.mk.android.demo.demo.staggerdrecyclerview.databinding.RvItemBinding;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Locale;
public class RVAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<RVAdapter.VH> {
private Context context;
private List<RVBean> rvBeans;
private final static String TAG = "DemoStaggerdRecyclerView";
public RVAdapter(Context context, List<RVBean> rvBeans) {
this.context = context;
this.rvBeans = rvBeans;
}
@Override
public int getItemViewType(int position) {
return position;
}
@NonNull
@Override
public VH onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
return new VH(DataBindingUtil.inflate(
LayoutInflater.from(context), R.layout.rv_item, parent, false).getRoot());
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull VH holder, int position) {
//try {
RvItemBinding binding = DataBindingUtil.bind(holder.itemView);
//binding.rvTextView.setText(rvBeans.get(position).getText());
binding.setItem(rvBeans.get(position));
/*
//Set size
BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options();
options.inJustDecodeBounds = true;//這個參數設置為true才有效,
Bitmap bmp = BitmapFactory.decodeFile(rvBeans.get(position).getUrl(), options);
//這里的bitmap是個空
int outHeight = options.outHeight;
int outWidth = options.outWidth;
Glide.with(context).load(rvBeans.get(position).getUrl()).override(outWidth,
outHeight).into(binding.rvImageView);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, ">>>>>>onbindViewHolder error: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
*/
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return rvBeans.size();
}
public class VH extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
public VH(@NonNull View itemView) {
super(itemView);
}
}
//增加外部調用增加一條記錄
public void refreshDatas(List<RVBean> datas) {
int pc=0;
if (datas != null && datas.size() > 0) {
int oldSize = rvBeans.size();
//List<RVBean> refreshedData = new ArrayList<RVBean>();
boolean isItemExisted = false;
for (Iterator<RVBean> newData = datas.iterator(); newData.hasNext(); ) {
RVBean a = newData.next();
for (Iterator<RVBean> existedData = rvBeans.iterator(); existedData.hasNext(); ) {
RVBean b = existedData.next();
if (b.equals(a)) {
{
isItemExisted = true;
//Log.i(TAG, b.getText() + " -> " + b.getUrl() + " is existed");
break;
}
}
}
if (!isItemExisted) {
pc+=1;
rvBeans.add(a);
}
}
Log.i(TAG,">>>>>>pc->"+pc);
if(pc>0){
notifyItemRangeChanged(oldSize,rvBeans.size());
}
}
}
}核心代碼導讀
1.這個adapter用的正是mvvm設計模式做的adapter;
2.這個adapter和網上那些錯誤、有坑的例子最大的不同在于getItemViewType方法內必須返回position,否則你的瀑布流在上劃加載新數據時會產生界面內對照片重新進行左右切換、重排、或者把照片底部留出很大一塊空白如:左邊垂直排3張,右邊一大邊空白或者反之亦然的情況;
3.必須使用notifyItemRangeChanged來通知刷新新數據,網上很多例子用的是notifyDataSetChange或者是其它相關的notify,它們都是錯的,這是因為RecyclerViewer在上劃下劃時會導致整個瀑布流重新布局、而RecyclerView里用的是Glide異步加載網絡圖片的,這會導致組件看到有一個組片就去開始計算它的高度而實際這個照片還未加載好因此才會導致RecyclerView在上劃下劃時整體布局重新刷新和重布局。一定記得這個notifyItemRangeChanged,同時這個方法在使用前加載所有的圖片(list數據),傳參有兩個參數,參數1:加載新數據前原數據行.size(),參數2:新加載數據.size();
有了adapter我們來看我們的應用了。
應用前先別急,我們自定義了一個StaggeredGridLayoutManager。
自定義FullyStaggeredGridLayoutManager
這邊先說一下,為什么要自定義這個StaggeredGridLayoutManager?
public class FullyStaggeredGridLayoutManager extends StaggeredGridLayoutManager {大家可以認為,這個類是一個策略。這也是網上絕大部分教程根本不說的,這個策略就是從根本上避免RecyclerViewer在上劃下劃時不要進行左右切換、重新布局、圖片閃爍以及“解決Scrollview中嵌套RecyclerView實現瀑布流時無法顯示的問題,同時修復了子View顯示時底部多出空白區域的問題”用的,我在代碼中也做了注釋。
此處要敲一下黑板了。因此整個RecyclerView要做到類淘寶、抖音的這種用戶體驗必須是adapter里的代碼和這個自定義StaggeredGridLayoutManager結合起來才能做到。
因此我們下面就來看在MainActivity里如何把adapter結合著這個自定義的StaggeredGridLayoutManager的應用吧。
先上我們自定義的這個StaggeredGridLayoutManager-我們在此把它命名叫做:FullyStaggeredGridLayoutManager的全代碼。
FullyStaggeredGridLayoutManager.java代碼
package org.mk.android.demo.demo.staggerdrecyclerview;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.StaggeredGridLayoutManager;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
/**
* @descride 解決Scrollview中嵌套RecyclerView實現瀑布流時無法顯示的問題,同時修復了子View顯示時底部多出空白區域的問題
*/
public class FullyStaggeredGridLayoutManager extends StaggeredGridLayoutManager {
private static boolean canMakeInsetsDirty = true;
private static Field insetsDirtyField = null;
private static final int CHILD_WIDTH = 0;
private static final int CHILD_HEIGHT = 1;
private static final int DEFAULT_CHILD_SIZE = 100;
private int spanCount = 0;
private final int[] childDimensions = new int[2];
private int[] childColumnDimensions;
private int childSize = DEFAULT_CHILD_SIZE;
private boolean hasChildSize;
private final Rect tmpRect = new Rect();
public FullyStaggeredGridLayoutManager(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr,
int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
public FullyStaggeredGridLayoutManager(int spanCount, int orientation) {
super(spanCount, orientation);
this.spanCount = spanCount;
}
public static int makeUnspecifiedSpec() {
return View.MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(0, View.MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED);
}
@Override
public void onMeasure(RecyclerView.Recycler recycler, RecyclerView.State state, int widthSpec,
int heightSpec) {
final int widthMode = View.MeasureSpec.getMode(widthSpec);
final int heightMode = View.MeasureSpec.getMode(heightSpec);
final int widthSize = View.MeasureSpec.getSize(widthSpec);
final int heightSize = View.MeasureSpec.getSize(heightSpec);
final boolean hasWidthSize = widthMode != View.MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
final boolean hasHeightSize = heightMode != View.MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
final boolean exactWidth = widthMode == View.MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
final boolean exactHeight = heightMode == View.MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
final int unspecified = makeUnspecifiedSpec();
if (exactWidth && exactHeight) {
// in case of exact calculations for both dimensions let's use default "onMeasure" implementation
super.onMeasure(recycler, state, widthSpec, heightSpec);
return;
}
final boolean vertical = getOrientation() == VERTICAL;
initChildDimensions(widthSize, heightSize, vertical);
int width = 0;
int height = 0;
// it's possible to get scrap views in recycler which are bound to old (invalid) adapter entities. This
// happens because their invalidation happens after "onMeasure" method. As a workaround let's clear the
// recycler now (it should not cause any performance issues while scrolling as "onMeasure" is never
// called whiles scrolling)
recycler.clear();
final int stateItemCount = state.getItemCount();
final int adapterItemCount = getItemCount();
childColumnDimensions = new int[adapterItemCount];
// adapter always contains actual data while state might contain old data (f.e. data before the animation is
// done). As we want to measure the view with actual data we must use data from the adapter and not from the
// state
for (int i = 0; i < adapterItemCount; i++) {
if (vertical) {
if (!hasChildSize) {
if (i < stateItemCount) {
// we should not exceed state count, otherwise we'll get IndexOutOfBoundsException. For such items
// we will use previously calculated dimensions
measureChild(recycler, i, widthSize, unspecified, childDimensions);
} else {
logMeasureWarning(i);
}
}
childColumnDimensions[i] = childDimensions[CHILD_HEIGHT];
//height += childDimensions[CHILD_HEIGHT];
if (i == 0) {
width = childDimensions[CHILD_WIDTH];
}
if (hasHeightSize && height >= heightSize) {
break;
}
} else {
if (!hasChildSize) {
if (i < stateItemCount) {
// we should not exceed state count, otherwise we'll get IndexOutOfBoundsException. For such items
// we will use previously calculated dimensions
measureChild(recycler, i, unspecified, heightSize, childDimensions);
} else {
logMeasureWarning(i);
}
}
width += childDimensions[CHILD_WIDTH];
if (i == 0) {
height = childDimensions[CHILD_HEIGHT];
}
if (hasWidthSize && width >= widthSize) {
break;
}
}
}
int[] maxHeight = new int[spanCount];
for (int i = 0; i < adapterItemCount; i++) {
int position = i % spanCount;
if (i < spanCount) {
maxHeight[position] += childColumnDimensions[i];
} else if (position < spanCount) {
int mixHeight = maxHeight[0];
int mixPosition = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < spanCount; j++) {
if (mixHeight > maxHeight[j]) {
mixHeight = maxHeight[j];
mixPosition = j;
}
}
maxHeight[mixPosition] += childColumnDimensions[i];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < spanCount; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < spanCount - i - 1; j++) {
if (maxHeight[j] < maxHeight[j + 1]) {
int temp = maxHeight[j];
maxHeight[j] = maxHeight[j + 1];
maxHeight[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
height = maxHeight[0];//this is max height
if (exactWidth) {
width = widthSize;
} else {
width += getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight();
if (hasWidthSize) {
width = Math.min(width, widthSize);
}
}
if (exactHeight) {
height = heightSize;
} else {
height += getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom();
if (hasHeightSize) {
height = Math.min(height, heightSize);
}
}
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
}
private void logMeasureWarning(int child) {
if (BuildConfig.DEBUG) {
Log.w("LinearLayoutManager", "Can't measure child #"
+ child
+ ", previously used dimensions will be reused."
+ "To remove this message either use #setChildSize() method or don't run RecyclerView animations");
}
}
private void initChildDimensions(int width, int height, boolean vertical) {
if (childDimensions[CHILD_WIDTH] != 0 || childDimensions[CHILD_HEIGHT] != 0) {
// already initialized, skipping
return;
}
if (vertical) {
childDimensions[CHILD_WIDTH] = width;
childDimensions[CHILD_HEIGHT] = childSize;
} else {
childDimensions[CHILD_WIDTH] = childSize;
childDimensions[CHILD_HEIGHT] = height;
}
}
@Override public void setOrientation(int orientation) {
// might be called before the constructor of this class is called
//noinspection ConstantConditions
if (childDimensions != null) {
if (getOrientation() != orientation) {
childDimensions[CHILD_WIDTH] = 0;
childDimensions[CHILD_HEIGHT] = 0;
}
}
super.setOrientation(orientation);
}
public void clearChildSize() {
hasChildSize = false;
setChildSize(DEFAULT_CHILD_SIZE);
}
public void setChildSize(int childSize) {
hasChildSize = true;
if (this.childSize != childSize) {
this.childSize = childSize;
requestLayout();
}
}
private void measureChild(RecyclerView.Recycler recycler, int position, int widthSize,
int heightSize, int[] dimensions) {
final View child;
try {
child = recycler.getViewForPosition(position);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
if (BuildConfig.DEBUG) {
Log.w("LinearLayoutManager",
"LinearLayoutManager doesn't work well with animations. Consider switching them off",
e);
}
return;
}
final RecyclerView.LayoutParams p = (RecyclerView.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int hPadding = getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight();
final int vPadding = getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom();
final int hMargin = p.leftMargin + p.rightMargin;
final int vMargin = p.topMargin + p.bottomMargin;
// we must make insets dirty in order calculateItemDecorationsForChild to work
makeInsetsDirty(p);
// this method should be called before any getXxxDecorationXxx() methods
calculateItemDecorationsForChild(child, tmpRect);
final int hDecoration = getRightDecorationWidth(child) + getLeftDecorationWidth(child);
final int vDecoration = getTopDecorationHeight(child) + getBottomDecorationHeight(child);
final int childWidthSpec =
getChildMeasureSpec(widthSize, hPadding + hMargin + hDecoration, p.width,
canScrollHorizontally());
final int childHeightSpec =
getChildMeasureSpec(heightSize, vPadding + vMargin + vDecoration, p.height,
canScrollVertically());
child.measure(childWidthSpec, childHeightSpec);
dimensions[CHILD_WIDTH] = getDecoratedMeasuredWidth(child) + p.leftMargin + p.rightMargin;
dimensions[CHILD_HEIGHT] = getDecoratedMeasuredHeight(child) + p.bottomMargin + p.topMargin;
// as view is recycled let's not keep old measured values
makeInsetsDirty(p);
recycler.recycleView(child);
}
private static void makeInsetsDirty(RecyclerView.LayoutParams p) {
if (!canMakeInsetsDirty) {
return;
}
try {
if (insetsDirtyField == null) {
insetsDirtyField = RecyclerView.LayoutParams.class.getDeclaredField("mInsetsDirty");
insetsDirtyField.setAccessible(true);
}
insetsDirtyField.set(p, true);
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
onMakeInsertDirtyFailed();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
onMakeInsertDirtyFailed();
}
}
private static void onMakeInsertDirtyFailed() {
canMakeInsetsDirty = false;
if (BuildConfig.DEBUG) {
Log.w("LinearLayoutManager",
"Can't make LayoutParams insets dirty, decorations measurements might be incorrect");
}
}
}MainActivity.java
從這兒開始我們要進入正題了,這邊要說真正的RecyclerView的應用了。
在此演示代碼塊里為了同時便于初學者和正在尋找RecyclerView上劃下劃時錯位過大、重新布局影響體驗的老手同時閱讀和查詢問題時方便,我要說一下整個Demo代碼運行的設計思路如下:
1.上手先加載12條數據;
2.對上劃(手指按住屏幕向上拉),一直拉、拉、拉,拉到第12條,觸發了RecyclerView的onScrollStateChanged中的“往上拉拉不動”事件后開始再加載6條數據,以模擬實際項目中的“翻頁時走一下后臺API取新數據”的過程;
package org.mk.android.demo.demo.staggerdrecyclerview;
import androidx.annotation.NonNull;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import androidx.databinding.DataBindingUtil;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.DefaultItemAnimator;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.SimpleItemAnimator;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.StaggeredGridLayoutManager;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import org.mk.android.demo.demo.staggerdrecyclerview.databinding.ActivityMainBinding;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private ActivityMainBinding binding;
private List<RVBean> rvBeanList = new ArrayList<>();
private RVAdapter adapter;
private final static String TAG = "DemoStaggerdRecyclerView";
private final static String CDN_URL="http://172.16.4.249/mkcdn";
private FullyStaggeredGridLayoutManager slm=null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
binding = DataBindingUtil.inflate(LayoutInflater.from(this), R.layout.activity_main, null, false);
setContentView(binding.getRoot());
slm=new FullyStaggeredGridLayoutManager(2,
FullyStaggeredGridLayoutManager.VERTICAL);
binding.rv.setLayoutManager(slm);
((SimpleItemAnimator)binding.rv.getItemAnimator()).setSupportsChangeAnimations(false);
((DefaultItemAnimator) binding.rv.getItemAnimator()).setSupportsChangeAnimations(false);
binding.rv.getItemAnimator().setChangeDuration(0);
binding.rv.setHasFixedSize(true);
initData();
}
private void initData() {
rvBeanList.add(new RVBean(CDN_URL+"/img/recommend/recom_13.jpeg", "1"));
rvBeanList.add(new RVBean(CDN_URL+"/img/recommend/recom_14.jpeg", "2"));
rvBeanList.add(new RVBean(CDN_URL+"/img/recommend/recom_15.jpeg", "3"));
rvBeanList.add(new RVBean(CDN_URL+"/img/recommend/recom_16.jpeg", "4"));
rvBeanList.add(new RVBean(CDN_URL+"/img/recommend/recom_17.jpeg", "5"));
rvBeanList.add(new RVBean(CDN_URL+"/img/recommend/recom_18.jpeg", "6"));
rvBeanList.add(new RVBean(CDN_URL+"img/recommend/recom_19.jpeg", "7"));
rvBeanList.add(new RVBean(CDN_URL+"/img/recommend/recom_20.jpeg", "8"));
rvBeanList.add(new RVBean(CDN_URL+"/img/recommend/recom_21.jpeg", "9"));
rvBeanList.add(new RVBean(CDN_URL+"/img/recommend/recom_22.jpeg", "10"));
rvBeanList.add(new RVBean(CDN_URL+"/img/recommend/recom_23.jpeg", "11"));
rvBeanList.add(new RVBean(CDN_URL+"/img/recommend/recom_24.jpeg", "12"));
adapter = new RVAdapter(this, rvBeanList);
//主要就是這個LayoutManager,就是用這個來實現瀑布流的,2表示有2列(垂直)或3行(水平),我們這里用的垂直VERTICAL
//binding.rv.addItemDecoration(new SpaceItemDecoration(2, 20));
binding.rv.addOnScrollListener(new RecyclerView.OnScrollListener() {
@Override
public void onScrollStateChanged(@NonNull RecyclerView recyclerView, int newState) {
super.onScrollStateChanged(recyclerView, newState);
if (!recyclerView.canScrollVertically(1) && newState == RecyclerView.SCROLL_STATE_IDLE) {
Log.i(TAG, "上拉拉不動時觸發加載新數據");
rvBeanList = new ArrayList<>();
rvBeanList.add(new RVBean(CDN_URL+"/img/recommend/recom_25.jpeg", "13"));
rvBeanList.add(new RVBean(CDN_URL+"/img/recommend/recom_26.jpeg", "14"));
rvBeanList.add(new RVBean(CDN_URL+"/img/recommend/recom_27.jpeg", "15"));
rvBeanList.add(new RVBean(CDN_URL+"/img/recommend/recom_28.jpeg", "16"));
rvBeanList.add(new RVBean(CDN_URL+"/img/recommend/recom_29.jpeg", "17"));
rvBeanList.add(new RVBean(CDN_URL+"/img/recommend/recom_30.jpeg", "18"));
adapter.refreshDatas(rvBeanList);
}
if (!recyclerView.canScrollVertically(-1) && newState == RecyclerView.SCROLL_STATE_IDLE) {
Log.i(TAG, "下拉拉不動時觸發加載新數據");
}
}
@Override
public void onScrolled(RecyclerView recyclerView, int dx, int dy) {
super.onScrolled(recyclerView, dx, dy);
slm.invalidateSpanAssignments();//防止第一行到頂部有空白
}
});
//((SimpleItemAnimator)RecyclerView.getItemAnimator()).setSupportsChangeAnimations(false);
binding.rv.setAdapter(adapter);
}
}核心代碼導讀:
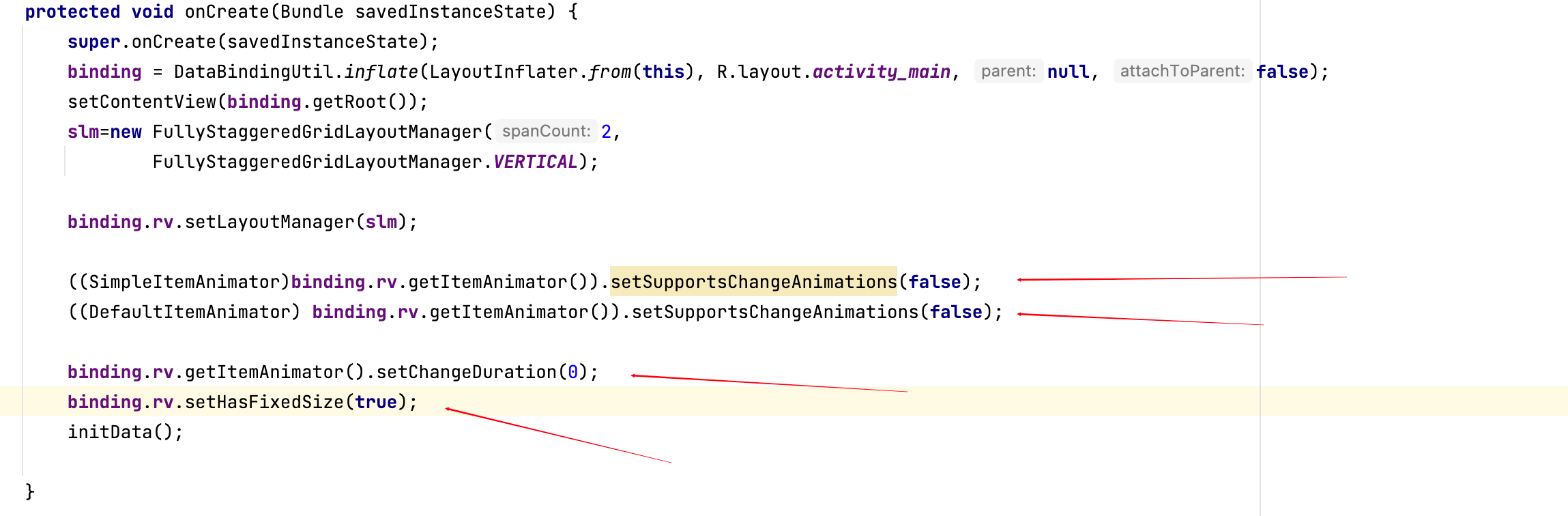
以下這一陀就是我說的使用自定義的StaggeredGridLayoutManager+adapter中的事件覆蓋一起實現了著名的RecyclerView上劃下劃時重新布局、翻頁的梗。
同時,一定要記得覆蓋RecyclerView的onScrolled事件,在事件中加入這樣的代碼
@Override
public void onScrolled(RecyclerView recyclerView, int dx, int dy) {
super.onScrolled(recyclerView, dx, dy);
slm.invalidateSpanAssignments();//防止第一行到頂部有空白
}因此這邊總結一下共有5個點,做到這5個點才能真正避免網上一堆的關于RecyclerView快速上劃下劃時整個界面產生了春左右列切換、重新布局、布局不合理如:左邊垂直排了3-4個圖片而把右邊留出一大塊空白的梗的綜合手段:
1.必須使用一個自定義的StaggeredGridLayoutManager,你可以直接使用我博客中的代碼,它來自于我正在制作的上生產的mao-sir.com的app中的代碼,這是我的個人的一個開源中臺產品;
2.必須要設置上面代碼截圖中的4個屬性即:
SimpleItemAnimator里的setSupportsChangeAnimations(false);
DefaultItemAnimator里的setSupportsChangeAnimations(false);
setChangeDuration(0);
setHasFixedSize(true);
3.必須要覆蓋RecyclerView的onScrolled方法,在方法里設置防止第一行到頂部有空白的操作;
4.必須要在adapter里覆蓋getItemViewType,在方法內返回position;
5.必須要在adapter里刷新數據時使用:notifyItemRangeChanged;
這邊我說網上絕大部分示例是錯的可能是客氣了點,因該說可以搜到的全是錯的。我們也來總結一下,希望各位不要再去踩這種坑了。
1.把圖片的尺寸預先存在后臺、每次接口取圖片時后臺把這個尺寸返回給到RecyclerView的adapter。。。這是得有多。。。無聊的做法,覆蓋一個getItemViewType不就同樣實現了這樣的手法?
2.setGapStrategy(StaggeredGridLayoutManager.GAP_HANDLING_NONE)的做法是錯的,設完后圖片要么在一開始進入界面時顯示不出要么顯示不全,我不知道這個問題最早是誰想出的解決辦法?怎么自己也不去驗證一下對不對?
3.網上還有一種手法也是錯的離譜,就是在onBindViewHolder方法里通過BitMap+GLIDE重設圖片的尺寸,這種方法根本無效;
下面我們來感受一下使用了網上錯誤的手法后,這個瀑布流會變成什么樣,大家就能感受到我說的這種:體驗問題了。這種體驗問題在APP上如果沒有做好會直接要了你這家企業的“口碑的命”。
以上就是“Android怎么使用RecyclerView實現瀑布流界面”這篇文章的所有內容,感謝各位的閱讀!相信大家閱讀完這篇文章都有很大的收獲,小編每天都會為大家更新不同的知識,如果還想學習更多的知識,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。