您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹“Flutter runApp GestureBinding如何使用”,在日常操作中,相信很多人在Flutter runApp GestureBinding如何使用問題上存在疑惑,小編查閱了各式資料,整理出簡單好用的操作方法,希望對大家解答”Flutter runApp GestureBinding如何使用”的疑惑有所幫助!接下來,請跟著小編一起來學習吧!
想去了解一個類最好的方法無外乎去閱讀它的注釋,我們可以從它的注釋中去了解它是為了做什么,做了些什么, 能夠做什么.
| 原文 | 漢譯 |
|---|---|
| A binding for the gesture subsystem. ## Lifecycle of pointer events and the gesture arena ### [PointerDownEvent] When a [PointerDownEvent] is received by the [GestureBinding] (from [dart:ui.PlatformDispatcher.onPointerDataPacket], as interpreted by the [PointerEventConverter]), a [hitTest] is performed to determine which [HitTestTarget] nodes are affected. (Other bindings are expected to implement [hitTest] to defer to [HitTestable] objects. For example, the rendering layer defers to the [RenderView] and the rest of the render object hierarchy.) The affected nodes then are given the event to handle ([dispatchEvent] calls [HitTestTarget.handleEvent] for each affected node). If any have relevant [GestureRecognizer]s, they provide the event to them using [GestureRecognizer.addPointer]. This typically causes the recognizer to register with the [PointerRouter] to receive notifications regarding the pointer in question. Once the hit test and dispatching logic is complete, the event is then passed to the aforementioned [PointerRouter], which passes it to any objects that have registered interest in that event. Finally, the [gestureArena] is closed for the given pointer ([GestureArenaManager.close]), which begins the process of selecting a gesture to win that pointer. ### Other events A pointer that is [PointerEvent.down] may send further events, such as [PointerMoveEvent], [PointerUpEvent], or [PointerCancelEvent]. These are sent to the same [HitTestTarget] nodes as were found when the [PointerDownEvent] was received (even if they have since been disposed; it is the responsibility of those objects to be aware of that possibility). Then, the events are routed to any still-registered entrants in the [PointerRouter]'s table for that pointer. When a [PointerUpEvent] is received, the [GestureArenaManager.sweep] method is invoked to force the gesture arena logic to terminate if necessary. | 手勢子系統的綁定。 ## 指針事件和手勢競技場的生命周期 ### [PointerDownEvent] 當 [GestureBinding] 接收到 [PointerDownEvent](來自[dart:ui.PlatformDispatcher.onPointerDataPacket],由[PointerEventConverter]), 執行[hitTest]以確定哪個[HitTestTarget] 節點受到影響。 (其他Bindings預計實現 [hitTest] 以推遲到 [HitTestable] 對象。例如,渲染層遵從 [RenderView] 和渲染對象的其余部分。) 然后給受影響的節點處理事件([dispatchEvent] 調用每個受影響節點的 [HitTestTarget.handleEvent])。如有相關[GestureRecognizer]s,他們使用[GestureRecognizer.addPointer]。這通常會導致識別器向 [PointerRouter] 注冊以接收有關有問題的指針。 一旦命中測試和調度邏輯完成,事件就會發生傳遞給前面提到的 [PointerRouter],它將它傳遞給任何對象已經注冊了對該事件的興趣。 最后,[gestureArena] 為給定的指針關閉([GestureArenaManager.close]),它開始選擇一個贏得該指針的手勢。 ### 其他事件 [PointerEvent.down] 的指針可能會發送更多事件,例如[PointerMoveEvent]、[PointerUpEvent] 或 [PointerCancelEvent]。這些是發送到相同的 [HitTestTarget] 節點 [PointerDownEvent] 已收到(即使它們已被處置;它是這些對象有責任意識到這種可能性)。 然后,事件被路由到[PointerRouter] 的指針表。 當接收到 [PointerUpEvent] 時,[GestureArenaManager.sweep] 方法被調用以強制手勢競技場邏輯在必要時終止。 |
了解完GestureBinding大致是做什么的, 我們再了解一下它有哪些方法.
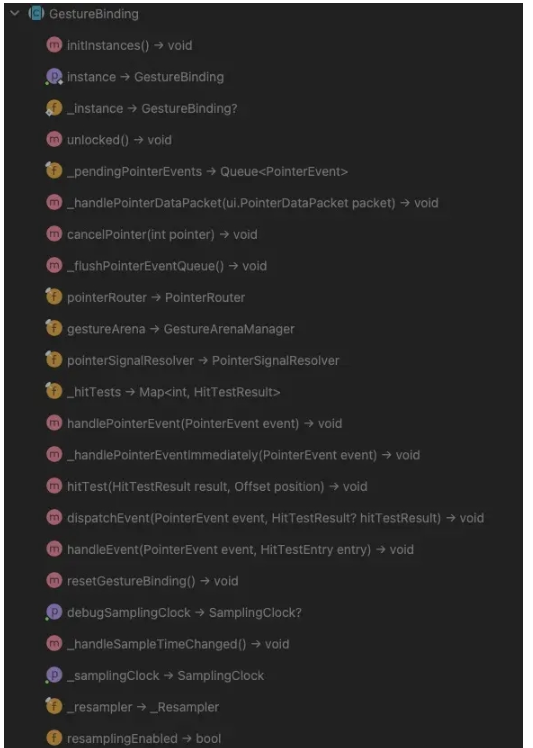
其中initInstances()不知道大家有沒有印象, 在BindingBase的構造方法中有調用這個方法, 那自然在初始的時候會調用這個方法.
{
// 保存實例
_instance = this;
// 平臺分發, 這里接受native傳來的手勢信息作分發
platformDispatcher.onPointerDataPacket = _handlePointerDataPacket;
}實際上也就是在開始的時候注冊了手勢的接收分發.那么手勢是如何分發的呢?我們不如看一下_handlePointerDataPacket 的具體實現:
{
// 這里會將指針數據轉換為邏輯像素,同時保存
_pendingPointerEvents.addAll(PointerEventConverter.expand(packet.data,
window.devicePixelRatio));
// 首先,我們要了解下locked是從什么地方來的,
// 可以看到它最終的改變地只有*lockEvents()*方法中,而*lockEvents()*方法
// 由*reassembleApplication()*或scheduleWarmUpFrame()調用,
// 前者屬于例如熱重載之類時調用, 而后者我們在runApp時也有過介紹.
// 這里看起來更像是一個異步回調的鎖.也就是在重啟界面的時候不用去刷新指針隊列
if (!locked) _flushPointerEventQueue();
}這里又引出來一個_flushPointerEventQueue()的概念,這里會真正的去分發手勢事件:
{
// 只有我們接收到了手勢隊列中還有對象就會持續運行
while (_pendingPointerEvents.isNotEmpty){
// 這里刪除了第一個元素并返回第一個元素,也就是隊列的fifo.
// 我們會依次處理接受到的手勢事件
handlePointerEvent(_pendingPointerEvents.removeFirst());
}
}那么,*handlePointerEvent()*做了什么呢?
// 斷言之類代碼已經去掉
{
// 如果這個開關打開,我們可以獲取更平滑到手勢事件,
// 比如90hz、120hz的屏幕. 我們在一些界面處理上就可以打開這個開關,
// 同樣這個值也是可以動態開關的
if (resamplingEnabled) {
// 重采樣這里不過多介紹,有興趣可以自行探索一下哦!
_resampler.addOrDispatch(event);
_resampler.sample(samplingOffset, _samplingClock);
return;
}
_resampler.stop();
// 這里去處理指針事件,從名字上來看是非常迫切了,hhh
_handlePointerEventImmediately(event);
}// 這里會對每一個指針事件進行判斷,是否點中widget或者說命中了哪個widget
{
HitTestResult? hitTestResult;
if (event is PointerDownEvent || event is PointerSignalEvent || event is PointerHoverEvent) {
hitTestResult = HitTestResult();
hitTest(hitTestResult, event.position);
if (event is PointerDownEvent) {
_hitTests[event.pointer] = hitTestResult;
}
} else if (event is PointerUpEvent || event is PointerCancelEvent) {
hitTestResult = _hitTests.remove(event.pointer);
} else if (event.down) {
hitTestResult = _hitTests[event.pointer];
}
if (hitTestResult != null ||
event is PointerAddedEvent ||
event is PointerRemovedEvent) {
dispatchEvent(event, hitTestResult);
}
}這里的代碼比較簡單, 如果事件是down、signal或者hover之中的任何事件,則會通過hitTest()添加到HitTestResult中,假如是down事件還需要增加到_hitTests結果中.如果是up或者cancel事件,那說明用戶取消了當時到滑動事件,我們自然而然需要去除相應的事件.最后去分發手勢.
void dispatchEvent(PointerEvent event, HitTestResult? hitTestResult) {
if (hitTestResult == null) {
try {
// 分發指針時, 會把所有通過條件的event都注冊到手勢路由里面
pointerRouter.route(event);
} catch (exception, stack) {
...
}
return;
}
for (final HitTestEntry entry in hitTestResult.path) {
try {
// 這里回調一下結果判斷有沒有命中
entry.target.handleEvent(event.transformed(entry.transform), entry);
} catch (exception, stack) {
...
}
}
}到此,關于“Flutter runApp GestureBinding如何使用”的學習就結束了,希望能夠解決大家的疑惑。理論與實踐的搭配能更好的幫助大家學習,快去試試吧!若想繼續學習更多相關知識,請繼續關注億速云網站,小編會繼續努力為大家帶來更多實用的文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。