您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本文小編為大家詳細介紹“Java怎么用EasyExcel解析動態表頭并導出”,內容詳細,步驟清晰,細節處理妥當,希望這篇“Java怎么用EasyExcel解析動態表頭并導出”文章能幫助大家解決疑惑,下面跟著小編的思路慢慢深入,一起來學習新知識吧。
const download = () => {
axios({
method: 'GET',
url: config.http.baseUrl + '/templateDownload',
responseType: 'blob',
})
.then(function (res) {
const content = res.data
const blob = new Blob([content], { type: "application/application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet" })
const downloadElement = document.createElement("a");
const href = window.URL.createObjectURL(blob);
downloadElement.href = href;
downloadElement.download = decodeURI(res.headers['filename']);
document.body.appendChild(downloadElement);
downloadElement.click();
document.body.removeChild(downloadElement); // 下載完成移除元素
window.URL.revokeObjectURL(href); // 釋放掉blob對象
})
}excel文件導入功能,常常需要進行模板下載,在springboot項目中,程序是以jar包的形式運行的,所以有很多小伙伴常常
遇到在本地開發中能夠實現下載功能,但部署到服務器的時候,找不到模板文件的問題。
@Override
public void templateDownload(HttpServletResponse response, HttpServletRequest request) {
//獲取要下載的模板名稱
String fileName = "批量導入模板.xlsx";
//獲取文件下載路徑
String filePath = "/template/template.xlsx";
TemplateDownloadUtil.download(response, request, fileName, filePath);
}import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.URLEncoder;
/**
* 模板文件下載工具類
* @author
* @date 2021/05/20 9:20
*/
@Slf4j
public class TemplateDownloadUtil {
public static void download(HttpServletResponse response, HttpServletRequest request,String fileName,String filePath){
try {
response.setContentType("application/application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
// 這里URLEncoder.encode可以防止中文亂碼 當然和easyexcel沒有關系
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment; filename=" + URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "UTF-8"));
response.setHeader("filename", URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "UTF-8"));
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Expose-Headers", "filename,Content-Disposition");
//獲取文件的路徑,此方式本地開發可以運行,服務器無法獲取文件
// String filePath = getClass().getResource("/template/template.xlsx").getPath();
// FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(filePath);
//在服務器中能夠讀取到模板文件
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(filePath);
InputStream input = resource.getInputStream();
OutputStream out = response.getOutputStream();
byte[] b = new byte[2048];
int len;
while ((len = input.read(b)) != -1) {
out.write(b, 0, len);
}
//修正 Excel在“xxx.xlsx”中發現不可讀取的內容。是否恢復此工作薄的內容?如果信任此工作簿的來源,請點擊"是"
// response.setHeader("Content-Length", String.valueOf(input.getChannel().size()));
input.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("下載模板失敗 :", e);
}
}
}EasyExcel簡單的讀文件,官網中已經有詳細的說明,本文不再贅述。
本文主要針對筆者遇到的復雜表頭及動態表頭進行講解。
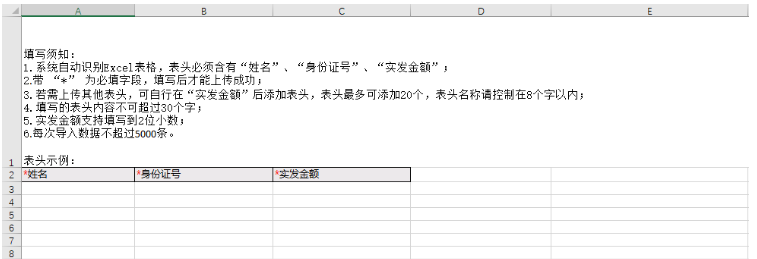
模板示例
解析
import com.alibaba.excel.context.AnalysisContext;
import com.alibaba.excel.event.AnalysisEventListener;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* 發薪單上傳excel讀取類
*
* @author yupf
* @description Listener 不能被spring管理,要每次讀取excel都要new,然后里面用到spring可以構造方法傳進去
*/
@Slf4j
@Data
public class BatchReadListener extends AnalysisEventListener<Map<Integer, String>> {
/**
* 每隔500條存儲數據庫,然后清理list ,方便內存回收
*/
private static final int BATCH_COUNT = 500;
//Excel數據緩存結構
private List<Map<Integer, Map<Integer, String>>> list = new ArrayList<>();
//Excel表頭(列名)數據緩存結構
private Map<Integer, String> headTitleMap = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 假設這個是一個DAO,當然有業務邏輯這個也可以是一個service。當然如果不用存儲這個對象沒用。
*/
private DbFileBatchService dbFileBatchService;
private DbFileContentService dbFileContentService;
private FileBatch fileBatch;
private int total = 0;
/**
* 如果使用了spring,請使用這個構造方法。每次創建Listener的時候需要把spring管理的類傳進來
*/
public BatchReadListener(DbFileBatchService dbFileBatchService, DbFileContentService dbFileContentService, FileBatch fileBatch) {
this.dbFileBatchService = dbFileBatchService;
this.dbFileContentService = dbFileContentService;
this.fileBatch = fileBatch;
}
/**
* 這個每一條數據解析都會來調用
*
* @param data one row value. Is is same as {@link AnalysisContext#readRowHolder()}
* @param context
*/
@Override
public void invoke(Map<Integer, String> data, AnalysisContext context) {
log.info("解析到一條數據:{}", JSON.toJSONString(data));
total++;
Map<Integer, Map<Integer, String>> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(context.readRowHolder().getRowIndex(), data);
list.add(map);
// 達到BATCH_COUNT了,需要去存儲一次數據庫,防止數據幾萬條數據在內存,容易OOM
if (list.size() >= BATCH_COUNT) {
saveData();
// 存儲完成清理 list
list.clear();
}
}
/**
* 所有數據解析完成了 都會來調用
*
* @param context
*/
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext context) {
// 這里也要保存數據,確保最后遺留的數據也存儲到數據庫
saveData();
log.info("所有數據解析完成!");
}
/**
* 解析表頭數據
**/
@Override
public void invokeHeadMap(Map<Integer, String> headMap, AnalysisContext context) {
log.info("表頭數據:{}", JSONObject.toJSONString(headMap));
headTitleMap = headMap;
}
/**
* 加上存儲數據庫
*/
private void saveData() {
log.info("{}條數據,開始存儲數據庫!", list.size());
FileContent fileContent = null;
List<FileContent> fileContentList = list.stream().flatMap(
integerMap -> integerMap.entrySet().stream().map(entrySet -> {
//entrySet.getKey()獲取的是內容的RowIndex,實際的行數需要根據表頭數進行處理
Integer rowIndex = entrySet.getKey();
Map<Integer, String> value = entrySet.getValue();
log.info(JSONObject.toJSONString(value));
fileContent = new FileContent();
fileContent.setBatchId(fileBatch.getId());
fileContent.setBatchNo(fileBatch.getBatchNo());
//固定字段入庫
fileContent.setName(value.get(0) != null ? value.get(0).trim() : "");
fileContent.setCertNo(value.get(1) != null ? value.get(1).trim() : "");
fileContent.setRealAmount(value.get(2) != null ? value.get(2).trim() : "");
//所有動態表頭數據轉為JSON串入庫
fileContent.setFieldsValue(JSONObject.toJSONString(value));
//取實際的內容rowIndex
fileContent.setRowNum(rowIndex + 1);
fileContent.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
return xcSalaryFileContent;
}
)).collect(Collectors.toList());
log.info(JSONObject.toJSONString(fileContentList));
dbFileContentService.saveBatch(fileContentList);
log.info("存儲數據庫成功!");
}
} BatchReadListener listener = new BatchReadListener(dbFileBatchService, dbFileContentService, fileBatch);
try {
//注:headRowNumber默認為1,現賦值為2,即從第三行開始讀取內容
EasyExcel.read(fileInputStream, listener).headRowNumber(2).sheet().doRead();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.info("EasyExcel解析文件失敗,{}", e);
throw new CustomException("文件解析失敗,請重新上傳");
}
//獲取表頭信息進行處理
Map<Integer, String> headTitleMap = listener.getHeadTitleMap();
//獲取動態表頭信息
List<String> headList = headTitleMap.keySet().stream().map(key -> {
String head = headTitleMap.get(key);
log.info(head);
return head == null ? "" : head.replace("*", "");
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
//可以對表頭進行入庫保存,方便后續導出綜上,動態表頭即可完成解析。
導出示例
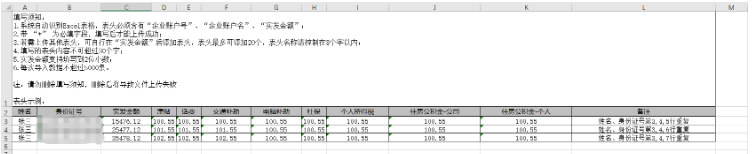
獲取動態頭
private List<List<String>> getFileHeadList( FileBatch fileBatch) {
String head = fileBatch.getFileHead();
List<String> headList = Arrays.asList(head.split(","));
List<List<String>> fileHead = headList.stream().map(item -> concatHead(Lists.newArrayList(item))).collect(Collectors.toList());
fileHead.add(concatHead(Lists.newArrayList("備注")));
return fileHead;
} /**
* 填寫須知
* @param headContent
* @return
*/
private List<String> concatHead(List<String> headContent) {
String remake = "填寫須知: \n" +
"1.系統自動識別Excel表格,表頭必須含有“企業賬戶號”、“企業賬戶名”、“實發金額”;\n" +
"2.帶 “*” 為必填字段,填寫后才能上傳成功;\n" +
"3.若需上傳其他表頭,可自行在“實發金額”后添加表頭,表頭最多可添加20個,表頭名稱請控制在8個字以內;\n" +
"4.填寫的表頭內容不可超過30個字;\n" +
"5.實發金額支持填寫到2位小數;\n" +
"6.每次導入數據不超過5000條。\n" +
"\n" +
"注:請勿刪除填寫須知,刪除后將導致文件上傳失敗\n" +
"\n" +
"表頭示例:";
headContent.add(0, remake);
return headContent;
}獲取數據
List<FileContent> fileContentList = dbFileContentService.list(
Wrappers.<FileContent>lambdaQuery()
.eq(FileContent::getBatchId, fileBatch.getId())
.orderByAsc(FileContent::getRowNum)
);
List<List<Object>> contentList = fileContentList.stream().map(fileContent -> {
List<Object> rowList = new ArrayList<>();
String fieldsValue = fileContent.getFieldsValue();
JSONObject contentObj = JSONObject.parseObject(fieldsValue);
for (int columnIndex = 0 , length = headList.size(); columnIndex < length; columnIndex++) {
Object content = contentObj.get(columnIndex);
rowList.add(content == null ? "" : content);
}
rowList.add(fileContent.getCheckMessage());
return rowList;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());單元格格式設置
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.data.DataFormatData;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.data.WriteCellData;
import com.alibaba.excel.write.handler.context.CellWriteHandlerContext;
import com.alibaba.excel.write.metadata.style.WriteCellStyle;
import com.alibaba.excel.write.metadata.style.WriteFont;
import com.alibaba.excel.write.style.HorizontalCellStyleStrategy;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.BorderStyle;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.HorizontalAlignment;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.IndexedColors;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 設置表頭和填充內容的樣式
*/
public class CellStyleStrategy extends HorizontalCellStyleStrategy {
private final WriteCellStyle headWriteCellStyle;
private final WriteCellStyle contentWriteCellStyle;
/**
* 操作列
*/
private final List<Integer> columnIndexes;
public CellStyleStrategy(List<Integer> columnIndexes,WriteCellStyle headWriteCellStyle, WriteCellStyle contentWriteCellStyle) {
this.columnIndexes = columnIndexes;
this.headWriteCellStyle = headWriteCellStyle;
this.contentWriteCellStyle = contentWriteCellStyle;
}
//設置頭樣式
@Override
protected void setHeadCellStyle( CellWriteHandlerContext context) {
// 獲取字體實例
WriteFont headWriteFont = new WriteFont();
headWriteFont.setFontName("宋體");
//表頭不同處理
if (columnIndexes.get(0).equals(context.getRowIndex())) {
headWriteCellStyle.setFillForegroundColor(IndexedColors.WHITE.getIndex());
headWriteCellStyle.setHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.LEFT);
headWriteFont.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 12);
headWriteFont.setBold(false);
headWriteFont.setFontName("宋體");
}else{
headWriteCellStyle.setFillForegroundColor(IndexedColors.GREY_25_PERCENT.getIndex());
headWriteCellStyle.setHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER);
headWriteFont.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 11);
headWriteFont.setBold(false);
headWriteFont.setFontName("微軟雅黑");
}
headWriteCellStyle.setWriteFont(headWriteFont);
DataFormatData dataFormatData = new DataFormatData();
dataFormatData.setIndex((short)49);
headWriteCellStyle.setDataFormatData(dataFormatData);
if (stopProcessing(context)) {
return;
}
WriteCellData<?> cellData = context.getFirstCellData();
WriteCellStyle.merge(headWriteCellStyle, cellData.getOrCreateStyle());
}
//設置填充數據樣式
@Override
protected void setContentCellStyle(CellWriteHandlerContext context) {
WriteFont contentWriteFont = new WriteFont();
contentWriteFont.setFontName("宋體");
contentWriteFont.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 11);
//設置數據填充后的實線邊框
contentWriteCellStyle.setWriteFont(contentWriteFont);
contentWriteCellStyle.setBorderLeft(BorderStyle.THIN);
contentWriteCellStyle.setBorderTop(BorderStyle.THIN);
contentWriteCellStyle.setBorderRight(BorderStyle.THIN);
contentWriteCellStyle.setBorderBottom(BorderStyle.THIN);
DataFormatData dataFormatData = new DataFormatData();
dataFormatData.setIndex((short)49);
contentWriteCellStyle.setDataFormatData(dataFormatData);
contentWriteCellStyle.setHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER);
WriteCellData<?> cellData = context.getFirstCellData();
WriteCellStyle.merge(contentWriteCellStyle, cellData.getOrCreateStyle());
}
}行高設置
import com.alibaba.excel.write.style.row.AbstractRowHeightStyleStrategy;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
/**
* 設置表頭的自動調整行高策略
*/
public class CellRowHeightStyleStrategy extends AbstractRowHeightStyleStrategy {
@Override
protected void setHeadColumnHeight(Row row, int relativeRowIndex) {
//設置主標題行高為17.7
if(relativeRowIndex == 0){
//如果excel需要顯示行高為15,那這里就要設置為15*20=300
row.setHeight((short) 3240);
}
}
@Override
protected void setContentColumnHeight(Row row, int relativeRowIndex) {
}
}列寬度自適應
如果是簡單表頭,可以使用EasyExcel中的LongestMatchColumnWidthStyleStrategy()來實現。
EasyExcel.write(fileName, LongestMatchColumnWidthData.class)
.registerWriteHandler(new LongestMatchColumnWidthStyleStrategy()).sheet("模板").doWrite(dataLong());如果是復雜表頭,就需要自己來實現,代碼如下:
import com.alibaba.excel.enums.CellDataTypeEnum;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Head;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.data.CellData;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.data.WriteCellData;
import com.alibaba.excel.write.metadata.holder.WriteSheetHolder;
import com.alibaba.excel.write.style.column.AbstractColumnWidthStyleStrategy;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.collections.CollectionUtils;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author yupf
* @description
* @date 2022/9/7 18:48
*/
@Slf4j
public class CellWidthStyleStrategy extends AbstractColumnWidthStyleStrategy {
private Map<Integer, Map<Integer, Integer>> CACHE = new HashMap<>();
@Override
protected void setColumnWidth(WriteSheetHolder writeSheetHolder, List<WriteCellData<?>> cellDataList, Cell cell, Head head, Integer relativeRowIndex, Boolean isHead) {
Map<Integer, Integer> maxColumnWidthMap = CACHE.get(writeSheetHolder.getSheetNo());
if (maxColumnWidthMap == null) {
maxColumnWidthMap = new HashMap<>();
CACHE.put(writeSheetHolder.getSheetNo(), maxColumnWidthMap);
}
if (isHead) {
if(relativeRowIndex.intValue() == 1){
Integer length = cell.getStringCellValue().getBytes().length;
Integer maxColumnWidth = maxColumnWidthMap.get(cell.getColumnIndex());
if (maxColumnWidth == null || length > maxColumnWidth) {
maxColumnWidthMap.put(cell.getColumnIndex(), length);
writeSheetHolder.getSheet().setColumnWidth(cell.getColumnIndex(), length * 300);
}
}
}else{
Integer columnWidth = this.dataLength(cellDataList, cell, isHead);
if (columnWidth >= 0) {
if (columnWidth > 255) {
columnWidth = 255;
}
Integer maxColumnWidth = maxColumnWidthMap.get(cell.getColumnIndex());
if (maxColumnWidth == null || columnWidth > maxColumnWidth) {
maxColumnWidthMap.put(cell.getColumnIndex(), columnWidth);
writeSheetHolder.getSheet().setColumnWidth(cell.getColumnIndex(), columnWidth * 256);
}
}
}
}
private Integer dataLength(List<WriteCellData<?>> cellDataList, Cell cell, Boolean isHead) {
if (isHead) {
return cell.getStringCellValue().getBytes().length;
} else {
CellData cellData = cellDataList.get(0);
CellDataTypeEnum type = cellData.getType();
if (type == null) {
return -1;
} else {
switch (type) {
case STRING:
return cellData.getStringValue().getBytes().length;
case BOOLEAN:
return cellData.getBooleanValue().toString().getBytes().length;
case NUMBER:
return cellData.getNumberValue().toString().getBytes().length;
default:
return -1;
}
}
}
}
}寫入文件
EasyExcel.write(response.getOutputStream()) .head(head) .registerWriteHandler(new CellRowHeightStyleStrategy()) //設置行高的策略 .registerWriteHandler(new CellStyleStrategy(Arrays.asList(0,1),new WriteCellStyle(), new WriteCellStyle())) .registerWriteHandler(new CellWidthStyleStrategy()) .sheet(sheetName) .doWrite(list);
讀到這里,這篇“Java怎么用EasyExcel解析動態表頭并導出”文章已經介紹完畢,想要掌握這篇文章的知識點還需要大家自己動手實踐使用過才能領會,如果想了解更多相關內容的文章,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。