您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容主要講解“vue-roter有哪些模式”,感興趣的朋友不妨來看看。本文介紹的方法操作簡單快捷,實用性強。下面就讓小編來帶大家學習“vue-roter有哪些模式”吧!
vue-roter有3種模式:1、hash模式,用URL hash值來做路由,支持所有瀏覽器;該模式實現的路由,在通過鏈接后面添加““#”+路由名字”。2、history模式,由h6提供的history對象實現,依賴H5 History API和服務器配置。3、abstract模式,支持所有JS運行環境,如Node服務器端,如果發現沒有瀏覽器的API,路由會自動強制進入該模式。

本教程操作環境:windows7系統、vue3版,DELL G3電腦。
Vue-router 是vue框架的路由插件。
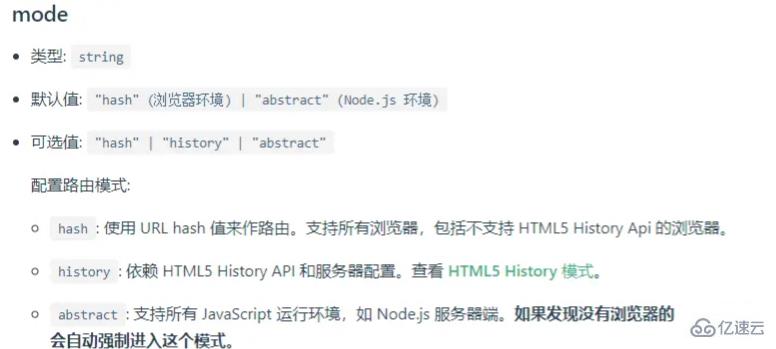
根據vue-router官網,我們可以明確看到vue-router的mode值有3種
hash
history
abstract
其中,hash 和 history 是 SPA 單頁應用程序的基礎。
先說結論: spa應用路由有2種模式,hash 和 history,vue路由有3種模式,比 spa 多了一個 abstract。
在vue-router中通過mode這個參數修改路由的模式:
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'history',
routes: [...]
})具體怎么實現的呢,首先我們下載 vue-router 的源碼
抽離出來對mode的處理
class vueRouter {
constructor(options) {
let mode = options.mode || 'hash'
this.fallback =
mode === 'history' && !supportsPushState && options.fallback !== false
if (this.fallback) {
mode = 'hash'
}
if (!inBrowser) {
mode = 'abstract'
}
this.mode = mode
switch (mode) {
case 'history':
this.history = new HTML5History(this, options.base)
break
case 'hash':
this.history = new HashHistory(this, options.base, this.fallback)
break
case 'abstract':
this.history = new AbstractHistory(this, options.base)
break
default:
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
assert(false, `invalid mode: ${mode}`)
}
}
}
}可以看到默認使用的是 hash 模式,當設置為 history 時,如果不支持 history 方法,也會強制使用 hash 模式。 當不在瀏覽器環境,比如 node 中時,直接強制使用 abstract 模式。
閱讀這部分源碼前,我們先來了解下 hash 的基礎: 根據MDN上的介紹,Location 接口的 hash 屬性返回一個 USVString,其中會包含URL標識中的 '#' 和 后面URL片段標識符,'#' 和后面URL片段標識符被稱為 hash。 它有這樣一些特點:
在第一個#后面出現的任何字符,都會被瀏覽器解讀為位置標識符。這意味著,這些字符都不會被發送到服務器端。
單單改變#后的部分,瀏覽器只會滾動到相應位置,不會重新加載網頁。
每一次改變#后的部分,都會在瀏覽器的訪問歷史中增加一個記錄,使用"后退"按鈕,就可以回到上一個位置。
可通過window.location.hash屬性讀取 hash 值,并且 window.location.hash 這個屬性可讀可寫。
使用 window.addEventListener("hashchange", fun) 可以監聽 hash 的變化
了解了這些基本知識后,我們繼續來看 vue-router 源碼對 /src/history/hash.js 的處理
const handleRoutingEvent = () => {
const current = this.current
if (!ensureSlash()) {
return
}
this.transitionTo(getHash(), route => {
if (supportsScroll) {
handleScroll(this.router, route, current, true)
}
if (!supportsPushState) {
replaceHash(route.fullPath)
}
})
}
const eventType = supportsPushState ? 'popstate' : 'hashchange'
window.addEventListener(
eventType,
handleRoutingEvent
)
this.listeners.push(() => {
window.removeEventListener(eventType, handleRoutingEvent)
})首先也是使用 window.addEventListener("hashchange", fun) 監聽路由的變化,然后使用 transitionTo 方法更新視圖
push (location: RawLocation, onComplete?: Function, onAbort?: Function) {
const { current: fromRoute } = this
this.transitionTo(
location,
route => {
pushHash(route.fullPath)
handleScroll(this.router, route, fromRoute, false)
onComplete && onComplete(route)
},
onAbort
)
}
replace (location: RawLocation, onComplete?: Function, onAbort?: Function) {
const { current: fromRoute } = this
this.transitionTo(
location,
route => {
replaceHash(route.fullPath)
handleScroll(this.router, route, fromRoute, false)
onComplete && onComplete(route)
},
onAbort
)
}vue-router 的2個主要API push 和 replace 也是簡單處理了下 hash , 然后調用 transitionTo 方法更新視圖
老規矩,先來了解下 HTML5History 的的基本知識: 根據MDN上的介紹,History 接口允許操作瀏覽器的曾經在標簽頁或者框架里訪問的會話歷史記錄。 使用 back(), forward()和 go() 方法來完成在用戶歷史記錄中向后和向前的跳轉。 HTML5引入了 history.pushState() 和 history.replaceState() 方法,它們分別可以添加和修改歷史記錄條目。 稍微了解下 history.pushState():
window.onpopstate = function(e) {
alert(2);
}
let stateObj = {
foo: "bar",
};
history.pushState(stateObj, "page 2", "bar.html");這將使瀏覽器地址欄顯示為 mozilla.org/bar.html ,但并不會導致瀏覽器加載 bar.html ,甚至不會檢查bar.html 是否存在。
也就是說,雖然瀏覽器 URL 改變了,但不會立即重新向服務端發送請求,這也是 spa應用 更新視圖但不 重新請求頁面的基礎。
接著我們繼續看 vue-router 源碼對 /src/history/html5.js 的處理:
const handleRoutingEvent = () => {
const current = this.current
// Avoiding first `popstate` event dispatched in some browsers but first
// history route not updated since async guard at the same time.
const location = getLocation(this.base)
if (this.current === START && location === this._startLocation) {
return
}
this.transitionTo(location, route => {
if (supportsScroll) {
handleScroll(router, route, current, true)
}
})
}
window.addEventListener('popstate', handleRoutingEvent)
this.listeners.push(() => {
window.removeEventListener('popstate', handleRoutingEvent)
})處理邏輯和 hash 相似,使用 window.addEventListener("popstate", fun) 監聽路由的變化,然后使用 transitionTo 方法更新視圖。 push 和 replace 等方法就不再詳細介紹。
最后我們直接來看一下對 /src/history/abstract.js 的處理:
constructor (router: Router, base: ?string) {
super(router, base)
this.stack = []
this.index = -1
}首先定義了2個變量,stack 來記錄調用的記錄, index 記錄當前的指針位置
push (location: RawLocation, onComplete?: Function, onAbort?: Function) {
this.transitionTo(
location,
route => {
this.stack = this.stack.slice(0, this.index + 1).concat(route)
this.index++
onComplete && onComplete(route)
},
onAbort
)
}
replace (location: RawLocation, onComplete?: Function, onAbort?: Function) {
this.transitionTo(
location,
route => {
this.stack = this.stack.slice(0, this.index).concat(route)
onComplete && onComplete(route)
},
onAbort
)
}push 和 replac方法 也是通過 stack 和 index 2個變量,模擬出瀏覽器的歷史調用記錄。
到此,相信大家對“vue-roter有哪些模式”有了更深的了解,不妨來實際操作一番吧!這里是億速云網站,更多相關內容可以進入相關頻道進行查詢,關注我們,繼續學習!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。