您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹“Java多線程并發ReentrantLock怎么使用”的相關知識,小編通過實際案例向大家展示操作過程,操作方法簡單快捷,實用性強,希望這篇“Java多線程并發ReentrantLock怎么使用”文章能幫助大家解決問題。
在 Java 中實現線程安全的傳統方式是 synchronized 關鍵字,雖然它提供了一定的同步能力,但它在使用上是嚴格的互斥同步實現:一個線程只能獲取一次鎖,沒有給其他線程提供等待隊列等機制,以至于當一個鎖被釋放后,任意線程都有可能獲取到鎖,沒有線程等待的優先級順序,會導致重要的線程在沒有爭用到鎖的情況下,長時間阻塞。為了解決 synchronized 的痛點,Java 提供了 ReentrantLock 可重入鎖來提供更豐富的能力和靈活性。
ReentrantLock 是一種可重入互斥鎖,其基本能力與使用 synchronized 關鍵字相同,但拓展了一些功能。它實現了 Lock 接口,在訪問共享資源時提供了同步的方法。操作共享資源的代碼被加鎖和解鎖方法的調用之間,從而確保當前線程在調用加鎖方法后,阻止其他線程試圖訪問共享資源。
ReentrantLock 由上次成功鎖定的但尚未解鎖的線程持有;當鎖不被任何線程擁有時,調用 lock 方法的線程將獲取到這個 ReentrantLock,如果當前線程已經擁有 ReentrantLock ,lock 方法會立即返回。
ReentrantLock 允許線程多次進入資源鎖。當線程第一次進入鎖時,保持計數設置為 1。在解鎖之前,線程可以再次重新進入鎖定狀態,并且每次保持計數加一。對于每個解鎖請求,保持計數減一,當保持計數為 0 時,資源被解鎖。
ReentrantLock 的構造器接收一個可選的 fairness 參數(Boolean 類型)。當設置為 true 時,在線程爭用時,鎖優先授予等待時間最長的線程訪問。否則,此鎖不保證任何特定的順序。但是請注意,鎖的公平性不能保證線程調度的公平性。
可重入鎖還提供了一個公平參數,通過該參數,鎖將遵循鎖請求的順序,即在線程解鎖資源后,鎖將轉到等待時間最長的線程。這種公平模式是通過將 true 傳遞給鎖的構造函數來設置的。
ReentrantLock 實現了 Lock 接口,所以分析源碼先從 Lock 接口開始:
public interface Lock {
void lock();
void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException;
boolean tryLock();
boolean tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException;
void unlock();
Condition newCondition();
}Lock 接口定義了更靈活和更廣泛的鎖定操作。synchronized 關鍵字是 JVM 底層提供了 monitor 指令的形式加鎖,這導致了獲取多個鎖時,需要按獲取順序的倒序解鎖。Lock 就是為了解決這種不夠靈活的問題而出現的。Lock 接口的實現通過允許在不同范圍內獲取和釋放鎖以及允許多個鎖按任意順序的獲取和釋放。隨著這種靈活性的增加,額外的職責也就隨之而來,synchronized 關鍵字以代碼塊的結構加鎖,執行完成鎖會自動釋放,而 Lock 的實現則需要手動釋放鎖,大多數情況下,
應該使用下面的語句實現:
Lock l = ...;
l.lock();
try {
// access the resource protected by this lock
} finally {
l.unlock();
}當鎖定和解鎖發生在不同的作用域時,必須注意確保所有在持有鎖時執行的代碼都受到 try-finally 或 try-catch 的保護,以確保在必要時釋放鎖。
Lock 接口中定義的方法可以劃分為三部分:
加鎖操作
解鎖操作
newCondition
加鎖操作提供了四個方法:
// 獲取鎖,如果鎖不可用,則當前線程將被禁用以用于線程調度目的并處于休眠狀態,直到獲取到鎖為止。 void lock(); void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException; boolean tryLock(); boolean tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException;
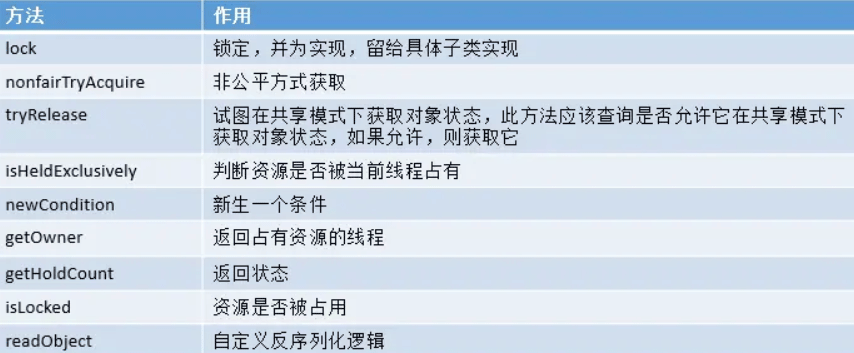
lock():獲取鎖,如果無法獲取到,則當前線程進入阻塞狀態,直到獲取到鎖為止。
lockInterruptibly():除非當前線程被中斷,否則去獲取鎖。如果獲取到了鎖,則立即返回。如果沒有爭用到鎖,則當前線程阻塞,直到發生下面兩種情況之一:
如果當前線程:
以上兩種情況都會拋出 InterruptedException ,并清除當前線程的中斷狀態。
當前線程獲取到了鎖
其他線程中斷了當前線程
在進入此方法時,設置了中斷狀態
在獲取鎖的過程中被中斷
tryLock()
僅當鎖處于空閑狀態時,才獲取鎖。獲取到鎖立即返回 true,如果鎖被其他線程持有,則此方法立即返回 false 。
此方法的典型用法是:
Lock lock = ...;
if (lock.tryLock()) {
try {
// manipulate protected state
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
} else {
// perform alternative actions
}這種用法確保鎖在獲得時解鎖,并且在未獲得鎖時不嘗試解鎖。
tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit)
如果在給定時間內鎖處于空閑狀態,且當前線程沒有被中斷,則獲取鎖。
如果當前線程成功獲取到了鎖,則此方法立即返回 true ;如果當前線程無法獲取到鎖,則當前線程會進入阻塞狀態直到發生下面三種情況之一:
如果進入此方法時當前線程處于中斷狀態或獲取鎖的過程中已進入中斷狀態,以上兩種情況都會拋出 InterruptedException ,并清除當前線程的中斷狀態。
此外,如果 time 參數小于等于 0 ,該方法不會等待。
鎖被當前線程成功獲取
指定時間超時
其他線程中斷了當前線程
解鎖操作:
解鎖操作只提供了 unlock() 方法。
newCondition:
返回綁定到此 Lock 的 Condition 實例。
ReentrantLock 有三個內部類,分別是 Sync、NonfairSync、FairSync 。
它們的繼承關系是:
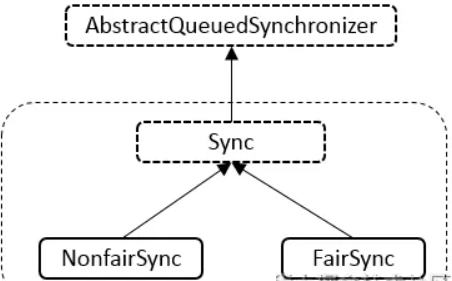
這個類是 AQS 的直接實現,它為公平鎖實現 FairSync 和非公平鎖實現 NonfairSync 提供了共同的基礎能力。
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
@ReservedStackAccess
final boolean tryLock()
abstract boolean initialTryLock();
@ReservedStackAccess
final void lock()
@ReservedStackAccess
final void lockInterruptibly()
@ReservedStackAccess
final boolean tryLockNanos(long nanos)
@ReservedStackAccess
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases)
protected final boolean isHeldExclusively()
final ConditionObject newCondition()
final Thread getOwner()
final int getHoldCount()
final boolean isLocked()
}下面是一些重點的方法講解。
這個方法執行了一個不公平的嘗試加鎖操作:
@ReservedStackAccess
final boolean tryLock() {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); // 獲取當前線程
int c = getState(); // 從 AQS 中獲取狀態
if (c == 0) { // 當前鎖的狀態為未被持有
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1)) { // CAS 更新狀態為加鎖狀態 1
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); // 設置當前持有的線程
return true; // 獲取鎖成功,return true
}
} else if (getExclusiveOwnerThread() == current) { // 如果當前持有鎖的線程是當前線程
if (++c < 0) // overflow // c 即是狀態也是計數器,可重入計數 + 1
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(c); // 更新狀態
return true; // 重入成功,return true
}
return false; // 嘗試獲取鎖失敗。
}為什么說它是不公平的,因為這個方法沒有按照公平等待原則,讓等待時間最久的線程優先獲取鎖資源。
這是一個抽象方法,用來在 lock 前執行初始化工作。
@ReservedStackAccess
final void lock() {
if (!initialTryLock())
acquire(1);
}先根據 initialTryLock() 進行判斷,然后調用 acquire(1) ,acquire 方法在 AQS 中:
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg))
acquire(null, arg, false, false, false, 0L);
}這個方法會讓當前線程去嘗試獲取鎖資源,并忽略中斷。通過調用 tryAcquire 至少一次來實現,如果失敗,則去等待隊列排隊,可能會導致阻塞。
@ReservedStackAccess
final void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (!initialTryLock())
acquireInterruptibly(1);
}這個方法相當于在 lock 方法前首先進行了線程中斷檢查,如果沒有被中斷,也是通過 initialTryLock() 判斷是否需要執行嘗試獲取鎖的操作。與 lock 方法不同,這里調用的是 (1):
public final void acquireInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted() || (!tryAcquire(arg) && acquire(null, arg, false, true, false, 0L) < 0))
throw new InterruptedException();
}對線程中斷進行了檢查,如果線程被中斷則中止當前操作,至少調用 1 次 tryAcquire 嘗試去獲取鎖資源。否則線程去隊列排隊,此方法可能會導致阻塞,直到調用 tryAcquire 成功或線程被中斷。
final boolean tryLockNanos(long nanos) throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
return initialTryLock() || tryAcquireNanos(1, nanos);
} public final boolean tryAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout)
throws InterruptedException {
if (!Thread.interrupted()) {
if (tryAcquire(arg))
return true;
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L)
return false;
int stat = acquire(null, arg, false, true, true,
System.nanoTime() + nanosTimeout); // 多了一個超時時間
if (stat > 0)
return true;
if (stat == 0)
return false;
}
throw new InterruptedException();
}本質上調用 acquire ,多設置了一個 time 參數。
@ReservedStackAccess
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases;
if (getExclusiveOwnerThread() != Thread.currentThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = (c == 0); // c = 0 說明成功釋放鎖資源
if (free)
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
setState(c);
return free;
}可以看出,tryRelease 方法最終更新了 State ,進一步說明了 AQS 的實現,本質上都是通過原子 int 來表示同步狀態的。
final ConditionObject newCondition() {
return new ConditionObject();
}這里的 newCondition 返回的是 AQS 的內部類 ConditionObject 的實例。
Sync 中的方法與其含義:
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
final boolean initialTryLock() {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1)) { // 比較并設置狀態成功,狀態0表示鎖沒有被占用
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); // 設置當前線程為持有鎖的線程
return true;
} else if (getExclusiveOwnerThread() == current) { // 重入情況
int c = getState() + 1;
if (c < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(c);
return true;
} else
return false;
}
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
if (getState() == 0 && compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
return true;
}
return false;
}
}NonfairSync 實現了 initialTryLock() ,其中主要是為當前對象設置持有線程;如果是重入的情況,則 state 計數 + 1 。這個方法中的邏輯和 tryLock 方法十分相似,他們都是不公平的。每次嘗試獲取鎖,都不是按照公平等待的原則,讓等待時間最久的線程獲得鎖,所以這是不公平鎖。
static final class FairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3000897897090466540L;
/**
* 僅在可重入或隊列為空時獲取。
*/
final boolean initialTryLock() {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) { // 鎖處于可用狀態
if (!hasQueuedThreads() && compareAndSetState(0, 1)) { // 查詢是否有線程正在等待獲取此鎖
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
} else if (getExclusiveOwnerThread() == current) {
if (++c < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(c);
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 僅當線程是隊列頭節點或為空時獲取。
*/
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
if (getState() == 0 && !hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
return true;
}
return false;
}
}公平鎖依賴兩個判斷條件實現:
hasQueuedThreads 用來查詢是否有其他線程正在等待獲取此鎖。
hasQueuedPredecessors 是用來查詢是否有其他線程比當前線程等待的時間更長。
當存在其他線程等待時間更久時,當前線程的 tryAcquire 會直接返回 false 。
ReentrantLock 有兩個構造函數:
public ReentrantLock() {
sync = new NonfairSync();
}
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
}其中一個帶有 boolean 參數的構造方法,用來根據參數 fair 實現公平鎖或非公平鎖,無參構造方法默認實現是非公平鎖。
private final Sync sync;
從構造方法中就可以看出,ReentrantLock 的 sync 屬性,代表了鎖的策略(公平 or 非公平)。
sync 是一個 Sync 類型的對象,繼承自 AQS ,ReentrantLock 對外暴露的方法,內部實際上就是調用 Sync 對應的方法實現的:
public class ReentrantLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {
// ...
public void lock() {
sync.lock();
}
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
sync.lockInterruptibly();
}
public boolean tryLock() {
return sync.tryLock();
}
public boolean tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
return sync.tryLockNanos(unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
public Condition newCondition() {
return sync.newCondition();
}
public int getHoldCount() {
return sync.getHoldCount();
}
public boolean isHeldByCurrentThread() {
return sync.isHeldExclusively();
}
public boolean isLocked() {
return sync.isLocked();
}
public final boolean isFair() {
return sync instanceof FairSync;
}
protected Thread getOwner() {
return sync.getOwner();
}
// ...
}ReentrantLock 看起來就像是 Sync 的代理類,當調用 ReentrantLock 對外暴露的方法時,會根據 sync 對象的不同的類型調用不同的實現 。
比如,下圖就是一個公平鎖的調用過程:
ReentrantLock.lock -> FairSync.lock -> AQS.acquire -> FairSync.tryAcquire -> AQS.hasQueuedPredecessors -> AQS.setExclusiveOwnerThread
關于“Java多線程并發ReentrantLock怎么使用”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識,可以關注億速云行業資訊頻道,小編每天都會為大家更新不同的知識點。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。