您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹“Android怎么自定義View”,在日常操作中,相信很多人在Android怎么自定義View問題上存在疑惑,小編查閱了各式資料,整理出簡單好用的操作方法,希望對大家解答”Android怎么自定義View”的疑惑有所幫助!接下來,請跟著小編一起來學習吧!
Android系統內置的View不滿足我們的業務需求
onMeasure:決定著View的大小
onLayout:決定View在ViewGroup中的位置
onDraw:決定繪制什么樣的View
通常情況下:
自定義View只需要重寫onMeasure和onDraw這兩個方法
自定義ViewGroup只需要重寫onMeasure和onLayout這兩個方法
在values文件中創建attr文件,然后使用< declare-styleable >為自定義View添加屬性,在xml中設置相應的屬性值,然后再自定義View的構造方法中獲取屬性值(AtrributeSet),將獲取到的屬性值應用到View中去
1、每一個Activity都有一個Window,Window用于顯示我們的界面,Activity負責管理Window
2、每個Window都有一個根View->DecorView,Window本身不能顯示界面,需要依托于View
3、DecorView是一個FrameLayout,它主要由兩部分組成,一部分是ActionBar,一部分是一個id為android.R.content的FrameLayout,我們寫好的Activity的根部局的View就是被添加到這里去了,通過setContentView()方法
4、在往下就是一個樹形結構的視圖結構,ViewGroup中嵌套ViewGroup和View
FrameLayout rootView = findViewById(android.R.id.content); RelativeLayout relativeLayout = (LinearLayout) rootView.getChildAt(0);//獲取Activity的根部局
注意:無論是measure過程還是layout過程還是draw過程,永遠都是從View樹的根節點往下樹形遞歸的開始測量或者計算。
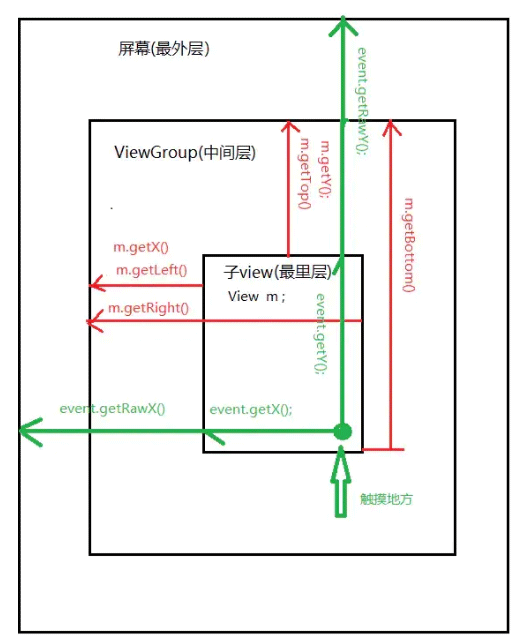
注意:
1、當view沒有發生動畫偏移的時候,getX()和getLeft()相等,如果由translation的時候,getX() = getLeft() + getTranslationX()
2、getLeft()等獲取的值是相對父容器而言的
View樹的繪制是交給ViewRootImpl去負責的,入口在 ViewRootImpl.setView() --> requestLayout()方法中進行的,最終調用到了一個叫做performTraversals()方法里面,這里面就開始了真正的繪制流程工作,平時寫的onDraw、onMeasure、onLayout也都在這里邊。
1、系統為什么需要measure過程
因為我們在寫布局的時候要針對不同的機型做適配,不能寫死view的高度和寬度,經常使用wrap_content這種形式,為了適配這種自適應布局的機制,所以系統需要進行measure測量
2、measure過程做了什么事情
確定每個view在屏幕上顯示的時候所需要的真實的寬度和高度
3、ViewGroup如何向子View傳遞限制信息
通過MeasureSpec,從名字上來看叫做測量規格,它封裝了父容器對子View的布局上的限制,內部提供了寬高的信息(SpecMode、SpecSize),SpecSize是指在某種情況下SpecMode下的參考尺寸。
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int width = 0;//最終確定的寬度
int height = 0;//最終確定的高度
//1、首先測量自身
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//2、為每個子view計算測量的限制信息Mode/Size
int widthMeasureSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthMeasureSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMeasureSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightMeasureSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
//3、測量子View;把上一步確定的限制信息,傳遞給每一個子View,然后子View開始measure自己的尺寸
int childCount = getChildCount();
for(int i=0;i<childCount;i++){
View child = getChildAt(i);
measureChild(child,widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec);//這個方法就是確定子view的測量大小
}
//4、根據子View的測量尺寸以及自身的SpecMode計算自己的尺寸
switch (widthMeasureSpecMode) {
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY://如果是確定值,則使用確定值
width = widthMeasureSpecSize;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST://如果是根據內容定的大小
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED://一般可以不用單獨處理
for(int i=0;i<childCount;i++){
View child = getChildAt(i);
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();//這一步只有當measureChild方法執行完之后才能拿到
width = Math.max(childWidth,width);
}
default:break;
}
switch (heightMeasureSpecMode) {
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY://如果是確定值,則使用確定值
height = heightMeasureSpecSize;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST://如果是根據內容定的大小
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
for(int i=0;i<childCount;i++){
View child = getChildAt(i);
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();//這一步只有當measureChild方法執行完之后才能拿到
height+=childHeight;
}
default:break;
}
//保存自身測量后的寬和高
setMeasuredDimension(width,height);
}要明確一點,重寫自定義ViewGroup的onMeasure方法是為了確定這個View的真正的寬度和高度,很明顯這與它的子View脫離不了干系。
onMeasure()方法中的兩個參數,是這個自定義ViewGroup的父View給出的參考值,具體怎么給出的呢,可以參考ViewGroup的measureChild()方法,這個方法我們在重寫onMeasure時也用到了,看這個方法的第一個參數好像是View,看起來好像跟我們自定義ViewGroup沒啥關系,但別忘了,ViewGroup也是一個View,所以,我們的自定義ViewGroup的onMeasure()方法中的兩個參數就是由下面的方法產生的,具體來講就是下面的 childWidthMeasureSpec和childHeightMeasureSpec。
總結一句話就是:子View(包括子ViewGroup)的WidthMeasureSpec和HeightMeasureSpec的確定是由子View本身的LayoutParams以及父View(包括父ViewGroup)的WidthMeasureSpec和HeightMeasureSpec確定的。這一段邏輯是ViewGroup#getChildMeasureSpec()。有個表格
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}知道了自身的MeasureSpec參數,下面就好辦了,那么直接調用view.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec)完成自身的測量。
關鍵來了, 在View的measure方法里面會調用onMeasure方法,如果當前View是一個普通的View,則直接執行這里的方法,完成普通View的測量過程,但是, 如果當前View是一個ViewGroup就會調用自身重寫好的onMeasure方法,也就是我們重寫的方法。
對于自定義ViewGroup重寫的onMeasure方法需要結合子View的寬度和高度,以及自身的LayOutParams的模式來確定最終的寬度和高度
那么對于普通View是否就不需要重寫onMeasure了呢,源碼不是已經寫好了嗎?
看一下代碼:
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}發現,無論是精確模式,還是wrap_content模式最后值都是之前由子View本身的LayoutParams以及父View(包括父ViewGroup)的WidthMeasureSpec和HeightMeasureSpec確定的measureSpecSize值大小,通過查表可知,如果當普通的自定義View的寬度或者高度被設置成了為了wrap_content的話,它的效果跟mathch_parent效果一樣,所以普通的自定義View需要對wrap_content這一情況進行完善,參考TextView
onLayout的中后四個參數,指的是,當前自定義ViewGroup在它的父布局中的上下左右坐標,通過這個坐標可以得到當前自定義ViewGroup的測量寬度和高度,不過一般也不需要用到這個四個參數,因為可以直接通過 getMeasuredWidth() 方法得到
所以onLayout的核心目的就是計算每一個控件的left、top、right、bottom坐標,然后通過 child.layout()方法set進去就行了,所以onLayout主要工作就在于如何確定這四個參數。
追蹤child.layout()方法進去看看:
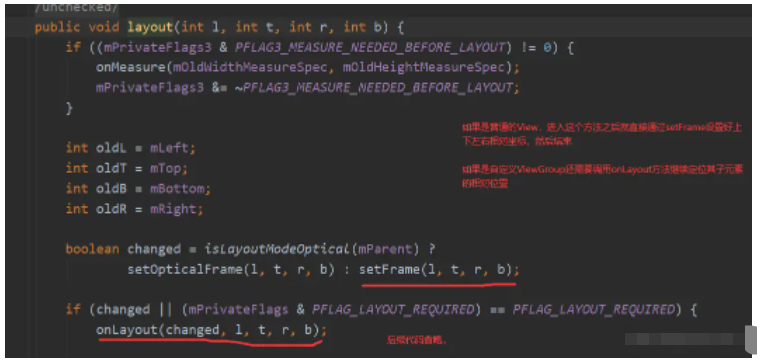
流布局:
package com.example.materialdesign.selfView;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Build;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import androidx.annotation.RequiresApi;
public class FlowLayout extends ViewGroup {
public FlowLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@RequiresApi(api = Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP)
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int lineWidth = 0;//記錄每一行的寬度,最終的寬度是由所有行中的最大值
int lineHeight = 0;//記錄每一行的高度,取決于每一行中最高的那個組件
int resH = 0;//最終的高度
int resW = 0;//最終的寬度
//1、首先測量自身
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//2、為每個子view計算測量的限制信息Mode/Size
int widthMeasureSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthMeasureSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMeasureSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightMeasureSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
//3、測量每個子view的寬度和高度
int childCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int childMeasuredWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
int childMeasuredHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.bottomMargin + lp.topMargin;
if (lineWidth + childMeasuredWidth > widthMeasureSpecSize) {//當前行的的寬度已經加上當前view的寬度已經大于建議值寬度了
//需要換行
resW = Math.max(resW, lineWidth);
resH += lineHeight;
//重新賦值
lineWidth = childMeasuredWidth;
lineHeight = childMeasuredHeight;
} else {//不需要換行則累加
lineWidth += childMeasuredWidth;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight,childMeasuredHeight);//取最高的那個
}
if (i == childCount - 1) {//別忘了單獨處理最后一行的最后一個元素的情況
resH += lineHeight;
resW = Math.max(resW, lineWidth);
}
}
setMeasuredDimension((widthMeasureSpecMode==MeasureSpec.EXACTLY)?widthMeasureSpecSize:resW,
(heightMeasureSpecMode==MeasureSpec.EXACTLY)?heightMeasureSpecSize:resH);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int count = getChildCount();
int lineWidth = 0;//累加當前行的行寬
int lineHeight = 0;//累加當前行的行高
int top = 0, left = 0;//當前控件的left坐標和top坐標
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int childMeasuredWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
int childMeasuredHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.bottomMargin + lp.topMargin;
//根據是否要換行,來計算當前控件的top坐標和Left坐標,是否換行是需要考慮margin的
if (childMeasuredWidth + lineWidth > getMeasuredWidth()) {
top += lineHeight;
left = 0;
lineHeight = childMeasuredHeight;
lineWidth = childMeasuredWidth;
} else {
lineWidth += childMeasuredWidth;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childMeasuredHeight);
}
//在已知left和top情況下計算當前View的上下左右坐標,在真正給當前View定位置時候需要考慮margin的
int lc = left + lp.leftMargin;
int tc = top + lp.topMargin;
int rc = lc + child.getMeasuredWidth();//注意在layout的時候沒有算上margin
int bc = tc + child.getMeasuredHeight();
child.layout(lc, tc, rc, bc);
left += childMeasuredWidth;//下一起點算上margin
}
}
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(LayoutParams p) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(p);
}
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(),attrs);
}
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
return new MarginLayoutParams(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
}
}注意:上述代碼實際上可能不符合業務預期,在于 measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);這一句,我們直接調用系統的方法去獲得子View的MeasureSpec,但實際上獲取到的值不一定是我們想要的,即下圖的值不一定符合我們的業務,所以在真正測量子View的時候,需要針對子View的match_parent情況或者wrap_content情況進行特殊處理

一般情況下是針對子View是match_parent的情況做處理,比如我們自定義的FlowLayout,如果FlowLayout是match_parent、子View是match_parent的話,就需要特殊處理了,根據模式表子View所占的空間將充滿整個父View的剩余空間,這一點符合代碼邏輯但是可能不會符合業務需求
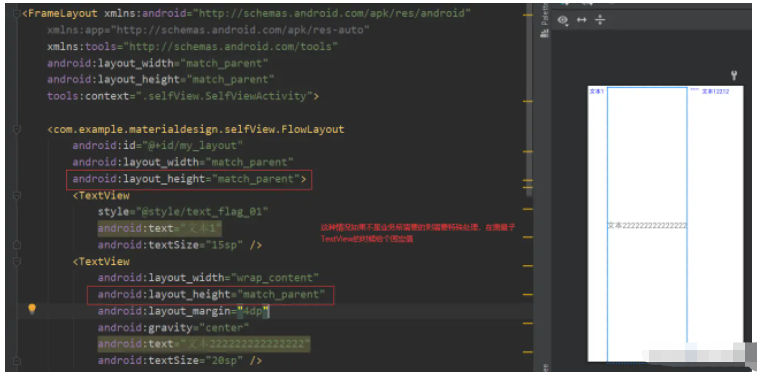
1、getMeasuredWidth和getWidth的區別
getMeasuredWidth是在measure的過程結束后就可以獲得到的View測量寬度值;而getWidth是在layout過程結束后通過mRight-mLeft得到的;一般情況下,二者是相等的,但有可能不相等,getWidth取決于layout過程中怎么算的四點坐標值。
2、onDraw、onMeasure以及onLayout會多次調用,所以這里面盡量不要頻繁的new 對象
3、調用view.invalidate()以及requestLayout()有什么區別:
這個方法是用來刷新整個視圖的,當視圖的內容,可見性發生變化,onDraw(Canvas canvas)方法會被調用。 調用invalidate()方法不會導致measure和layout方法被調用。
requestLayout()是在view的布局發生變化時調用,布局的變化包含位置,大小。重新觸發measure,layout,draw
注意:
1.這個方法不能在正在布局的時候調用
2.調用這個方法,會導致布局重繪,調用measure,layout,draw的過程。
到此,關于“Android怎么自定義View”的學習就結束了,希望能夠解決大家的疑惑。理論與實踐的搭配能更好的幫助大家學習,快去試試吧!若想繼續學習更多相關知識,請繼續關注億速云網站,小編會繼續努力為大家帶來更多實用的文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。