您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容介紹了“C語言順序表如何使用”的有關知識,在實際案例的操作過程中,不少人都會遇到這樣的困境,接下來就讓小編帶領大家學習一下如何處理這些情況吧!希望大家仔細閱讀,能夠學有所成!
編程環境為 ubuntu 18.04。
順序表需要連續一片存儲空間,存儲任意類型的元素,這里以存儲 int 類型數據為例。
size 為容量,length 為當前已知數據表元素的個數
typedef struct Vector{
int *data; //該順序表這片連續空間的首地址
int size, length;
} Vec;Vec *init(int n){ //該順序表具有n個存儲單元
Vec *v = (Vec *)malloc(sizeof(Vec)); //在內存棧上開辟一個空間 malloc在內存的堆區,在函數外面也能訪問
v->data = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
v->size = n;
v->length = 0;
return v;
}int insert(Vec *v, int ind, int val) { //ind為插入元素的位置,val為插入元素的值
if(v == NULL) return 0;
if(ind < 0 || ind > v->length) return 0; //判斷要插入的位置是否合法
if(v->length == v->size) {
if(!expand(v)){ //擴容失敗
printf(RED("fail to expand!\n"));
}
printf(GREEN("success to expand! the size = %d\n"),v->size);
}
for(int i = v->length; i > ind; i--){
v->data[i] = v->data[i-1];
}
v->data[ind] = val;
v->length += 1;
return 1;
}為什么需要判斷插入的位置是否合法呢?這是因為順序表是連續一片存儲空間,所以內存是連續的。
下圖以 length = 5,size = 9 為例,我們只能在下標為 0 到 4 之間的數中插入數據。
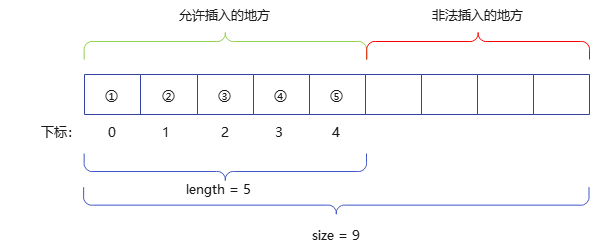
插入一個元素示意圖
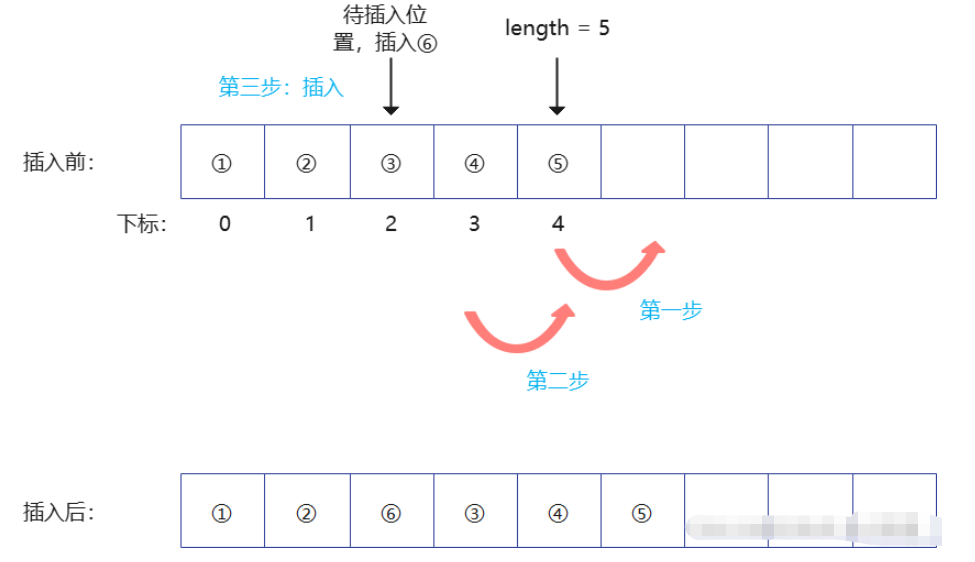
int erase(Vec *v, int ind){ //把下標為ind的元素刪除
if(v == NULL) return 0;
if(ind < 0 || ind >= v->length) return 0;
for(int i = ind + 1; i < v->length; i++){
v->data[i - 1] = v->data[i];
}
v->length -= 1;
return 1;
}判斷需要刪除元素的下標是否合法,與插入元素類似
刪除一個元素示意圖

int expand(Vec *v){
//順序表的擴容
//malloc 動態申請空間,空間不一定干凈 calloc 動態申請空間,并且清空 realloc 重新申請空間
int extr_size = v->size;
int *p;
while(extr_size) {
p = (int *)realloc(v->data, sizeof(int) * (v->size + extr_size));
if(p != NULL) break; //p不為空,說明擴容成功,這個時候直接跳出循環
extr_size >>= 1; //否則就把額外擴容的空間除以2,降低要求
}
if(p == NULL) return 0; //判斷跳出循環究竟是擴容成功還是擴容失敗,如果擴容失敗,那就是p為空地址,找不到符合條件的內存區域
v->size += extr_size;
v->data = p;
return 1;
}注意擴容這里寫的比較巧妙,首先 int extr_size = v->size;表示先將需要擴容的大小設置成原本的大小,然后就判斷能不能找到那么大的空間。 p = (int *)realloc(v->data, sizeof(int) * (v->size + extr_size)); 如果在系統中能找到這么大的容量,那么就返回找到的內存地址的首地址,然后就可以結束跳出循環;要是找不到的話那只能降低要求,把 extr_size 除以 2,看看能不能知道,如果實在找不到,extr_size 為 0,就會跳出循環。然后可以通過判斷 p 是不是空指針來判斷程序是找到能夠擴容的空間退出的還是找不到退出的。
要是對 malloc、calloc 和 realloc 不熟悉的,可以看我這篇博文:C語言深入探索動態內存分配的使用
void clear(Vec *v){ //釋放空間
if(v == NULL) return;
free(v->data);
free(v);
return;
}先釋放數據,再釋放整個順序表。
void output(Vec *v){
if(v == NULL) return ;
printf("[");
for(int i = 0; i < v->length; i++){
i && printf(", ");
printf("%d", v->data[i]);
}
printf("]\n");
return ;
}#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
//#include<windows.h>
#define COLOR(a, b) "\033[" #b "m" a "\033[0m"
#define GREEN(a) COLOR(a, 32)
#define RED(a) COLOR(a, 31)
typedef struct Vector{
int *data; //該順序表這片連續空間的首地址
int size, length;
} Vec;
Vec *init(int n){ //該順序表具有n個存儲單元
Vec *v = (Vec *)malloc(sizeof(Vec)); //在內存棧上開辟一個空間 malloc在內存的堆區,在函數外面也能訪問
v->data = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
v->size = n;
v->length = 0;
return v;
}
int expand(Vec *v){
//順序表的擴容
//malloc 動態申請空間,空間不一定干凈 calloc 動態申請空間,并且清空 realloc 重新申請空間
int extr_size = v->size;
int *p;
while(extr_size) {
p = (int *)realloc(v->data, sizeof(int) * (v->size + extr_size));
if(p != NULL) break; //p不為空,說明擴容成功,這個時候直接跳出循環
extr_size >>= 1; //否則就把額外擴容的空間除以2,降低要求
}
if(p == NULL) return 0; //判斷跳出循環究竟是擴容成功還是擴容失敗,如果擴容失敗,那就是p為空地址,找不到符合條件的內存區域
v->size += extr_size;
v->data = p;
return 1;
}
int insert(Vec *v, int ind, int val) { //ind為插入元素的位置,val為插入元素的值
if(v == NULL) return 0;
if(ind < 0 || ind > v->length) return 0;
if(v->length == v->size) {
if(!expand(v)){
printf(RED("fail to expand!\n"));
}
printf(GREEN("success to expand! the size = %d\n"),v->size);
}
for(int i = v->length; i > ind; i--){
v->data[i] = v->data[i-1];
}
v->data[ind] = val;
v->length += 1;
return 1;
}
int erase(Vec *v, int ind){ //把下標為ind的元素刪除
if(v == NULL) return 0;
if(ind < 0 || ind >= v->length) return 0;
for(int i = ind + 1; i < v->length; i++){
v->data[i - 1] = v->data[i];
}
v->length -= 1;
return 1;
}
void output(Vec *v){
if(v == NULL) return ;
printf("[");
for(int i = 0; i < v->length; i++){
i && printf(", ");
printf("%d", v->data[i]);
}
printf("]\n");
return ;
}
void clear(Vec *v){ //釋放空間
if(v == NULL) return;
free(v->data);
free(v);
return;
}
int main(){
#define MAX_N 20
Vec *v = init(1);
srand(time(0)); //設置種子
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
int op = rand() % 4;
int ind = rand() % (v->length + 3) - 1; //取值范圍[-1, v->length + 1]
int val = rand() % 100; //val為1到99之間的數
switch(op){
case 0:
case 1:
case 2: {
printf("insert %d at %d to the Vector = %d\n", val, ind, insert(v, ind, val));
}break;
case 3:{
printf("erase a item at %d = %d\n",ind,erase(v, ind));
}break;
}
output(v);
printf("\n");
}
#undef MAX_N
clear(v);
return 0;
}輸出結果如下:
insert 82 at 0 to the Vector = 1
[82]
insert 38 at 2 to the Vector = 0
[82]
success to expand! the size = 2
insert 7 at 1 to the Vector = 1
[82, 7]
success to expand! the size = 4
insert 86 at 2 to the Vector = 1
[82, 7, 86]
erase a item at 4 = 0
[82, 7, 86]
erase a item at 4 = 0
[82, 7, 86]
insert 48 at 0 to the Vector = 1
[48, 82, 7, 86]
insert 65 at 5 to the Vector = 0
[48, 82, 7, 86]
success to expand! the size = 8
insert 92 at 4 to the Vector = 1
[48, 82, 7, 86, 92]
erase a item at 2 = 1
[48, 82, 86, 92]
insert 81 at 2 to the Vector = 1
[48, 82, 81, 86, 92]
insert 9 at 0 to the Vector = 1
[9, 48, 82, 81, 86, 92]
insert 99 at 1 to the Vector = 1
[9, 99, 48, 82, 81, 86, 92]
insert 29 at 7 to the Vector = 1
[9, 99, 48, 82, 81, 86, 92, 29]
success to expand! the size = 16
insert 38 at 0 to the Vector = 1
[38, 9, 99, 48, 82, 81, 86, 92, 29]
erase a item at 0 = 1
[9, 99, 48, 82, 81, 86, 92, 29]
erase a item at 8 = 0
[9, 99, 48, 82, 81, 86, 92, 29]
erase a item at 6 = 1
[9, 99, 48, 82, 81, 86, 29]
insert 57 at -1 to the Vector = 0
[9, 99, 48, 82, 81, 86, 29]
insert 32 at 4 to the Vector = 1
[9, 99, 48, 82, 32, 81, 86, 29]
“C語言順序表如何使用”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識可以關注億速云網站,小編將為大家輸出更多高質量的實用文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。