您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容主要講解“springboot應用服務啟動事件的監聽怎么實現”,感興趣的朋友不妨來看看。本文介紹的方法操作簡單快捷,實用性強。下面就讓小編來帶大家學習“springboot應用服務啟動事件的監聽怎么實現”吧!
Spring Boot提供了兩個接口:CommandLineRunner、ApplicationRunner,用于啟動應用時做特殊處理,這些代碼會在SpringApplication的run()方法運行完成之前被執行。相對于之前章節為大家介紹的Spring的ApplicationListener接口自定義監聽器、Servlet的ServletContextListener監聽器。使用二者的好處在于,可以方便的使用應用啟動參數,根據參數不同做不同的初始化操作。
實現CommandLineRunner、ApplicationRunner接口。通常用于應用啟動前的特殊代碼執行,比如:
將系統常用的數據加載到內存
應用上一次運行的垃圾數據清理
系統啟動成功后的通知的發送等
如下圖是我實現了CommandLineRunner接口,在應用啟動時將系統內常用的配置數據。從數據庫加載到內存,以后使用該數據的時候只需要調用getSysConfigList方法,不需要每次使用該數據都去數據庫加載。節省系統資源、縮減數據加載時間。
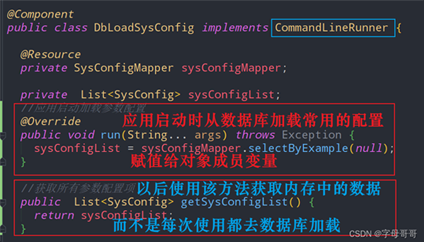
CommandLineRunner:參數是字符串數組
@Slf4j
@Component
public class CommandLineStartupRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
@Override
public void run(String... args){
log.info("CommandLineRunner傳入參數:{}", Arrays.toString(args));
}
}ApplicationRunner:參數被放入ApplicationArguments,通過getOptionNames()、getOptionValues()、getSourceArgs()獲取參數
@Slf4j
@Component
public class AppStartupRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) {
log.info("ApplicationRunner參數名稱: {}", args.getOptionNames());
log.info("ApplicationRunner參數值: {}", args.getOptionValues("age"));
log.info("ApplicationRunner參數: {}", Arrays.toString(args.getSourceArgs()));
}
}這種方式可以指定執行順序,注意前兩個Bean是CommandLineRunner,最后一個Bean是ApplicationRunner 。
@Configuration
public class BeanRunner {
@Bean
@Order(1)
public CommandLineRunner runner1(){
return new CommandLineRunner() {
@Override
public void run(String... args){
System.out.println("BeanCommandLineRunner run1()" + Arrays.toString(args));
}
};
}
@Bean
@Order(2)
public CommandLineRunner runner2(){
return new CommandLineRunner() {
@Override
public void run(String... args){
System.out.println("BeanCommandLineRunner run2()" + Arrays.toString(args));
}
};
}
@Bean
@Order(3)
public ApplicationRunner runner3(){
return new ApplicationRunner() {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args){
System.out.println("BeanApplicationRunner run3()" + Arrays.toString(args.getSourceArgs()));
}
};
}
}可以通過@Order設置執行順序
在IDEA Springboot啟動配置中加入如下參數,保存后啟動應用
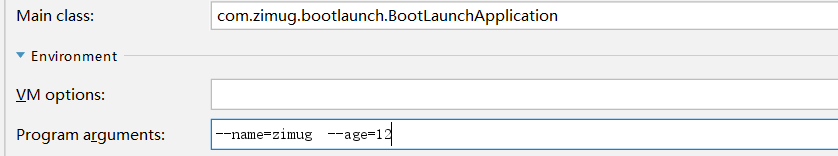
測試輸出結果:
c.z.boot.launch.config.AppStartupRunner : ApplicationRunner參數名稱: [name, age]
c.z.boot.launch.config.AppStartupRunner : ApplicationRunner參數值: [18]
c.z.boot.launch.config.AppStartupRunner : ApplicationRunner參數: [--name=zimug, --age=18]BeanApplicationRunner run3()[--name=zimug, --age=18]
c.z.b.l.config.CommandLineStartupRunner : CommandLineRunner傳入參數:[--name=zimug, --age=18]
BeanCommandLineRunner run1()[--name=zimug, --age=18]
e=18]
BeanCommandLineRunner run2()[--name=zimug, --age=18]
從測試結果上看(筆者目前不敢確定這個優先級順序是不是常態,但從我的多次測試效果,順序一直是這樣的):
ApplicationRunner執行優先級高于CommandLineRunner
以Bean的形式運行的Runner優先級要低于Component注解加implements Runner接口的方式
Order注解只能保證同類的CommandLineRunner或ApplicationRunner的執行順序,不能跨類保證順序
CommandLineRunner、ApplicationRunner的核心用法是一致的,就是用于應用啟動前的特殊代碼執行。ApplicationRunner的執行順序先于CommandLineRunner;ApplicationRunner將參數封裝成了對象,提供了獲取參數名、參數值等方法,操作上會方便一些。
這是筆者在實踐中真實遇到的問題,就是我定義了多個CommandLineRunner的實現。出現奇怪的問題是:當你定義多個CommandLineRunner的實現的時候,其中一個或者幾個將不會執行。
分析一下:下面的代碼是SpringBootApplication啟動項目之后會執行的代碼,大家看代碼中通過一個遍歷來啟動CommandLineRunner或者ApplicationRunner。也就是說,只有上一個CommandLineRunner執行完成之后,才會執行下一個CommandLineRunner,是同步執行的。
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>();
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) {
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {
callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args);
}
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {
callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args);
}
}
}所以,如果在CommandLineRunner某個實現run 方法體中調用了同步阻塞的API或者是一個 while(true) 循環,在遍歷中處于該CommandLineRunner之后的其他實現將不會被執行。
到此,相信大家對“springboot應用服務啟動事件的監聽怎么實現”有了更深的了解,不妨來實際操作一番吧!這里是億速云網站,更多相關內容可以進入相關頻道進行查詢,關注我們,繼續學習!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。