您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容主要講解“Java Servlet響應httpServletResponse過程是什么”,感興趣的朋友不妨來看看。本文介紹的方法操作簡單快捷,實用性強。下面就讓小編來帶大家學習“Java Servlet響應httpServletResponse過程是什么”吧!
設置響應狀態碼 如果沒有調用這個方法,默認返回200狀態碼(前提:正常執行,沒有異常) 如果出現異常,返回500
前端代碼:
<body>
<h4>設置響應頭</h4>
<input type="text" id="status">
<br>
<button onclick="setStatus()">提交</button>
</body>
<script>
function setStatus(){
//js中發送請求:(1)ajax(2)直接修改url
let status = document.querySelector("#status");
//后端會設置文本框輸入的值為響應狀態碼:嚴格來做需要驗證(省略)
window.location.href = "response?status="+status.value;
}
</script>后端代碼:
@WebServlet("/response")
public class ResponseStudyServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//獲取請求發送的queryString數據:status=xxx
String status = req.getParameter("status");
resp.setStatus((Integer.parseInt(status)));
resp.getWriter().write("設置響應狀態碼成功");
}
}前端顯示:

提交后fiddler抓包:
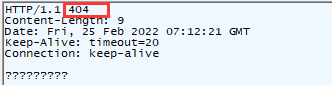
設置響應頭
響應頭name鍵已有,會覆蓋原有的鍵值對
前端代碼:
<h4>設置響應頭</h4> <a href="response" rel="external nofollow" >設置</a>
后端代碼:
//設置響應頭的鍵值對,鍵可以是標準的http響應頭的鍵,也可以是自定義的
//響應狀態碼是301,302,307,響應頭有Location字段,才是重定向
resp.setHeader("Location","http://www.baidu.com");
resp.setHeader("username","張三");fiddler抓包結果:
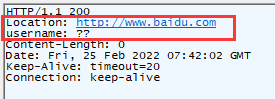
設置響應頭
響應頭name鍵已有,不會影響,添加一個新的
這兩個了解即可
設置響應頭Content-Type的值,等同于setHeader(“Content-Type”,String type) 因為Content-Type是標識body的數據格式,所以還需要設置body的內容
1.響應一個網頁
//響應html:設置響應的Content-Type
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf-8");可以返回靜態和動態網頁
兩種方式展示:
前端代碼:
<body>
<h4>返回響應正文為簡單的html</h4>
<a href="html?type=1" rel="external nofollow" >查看</a>
<h4>返回響應正文為復雜的html(動態變化的)</h4>
<input type="text" id="username" placeholder="輸入姓名">
<br>
<button onclick="toWelcome()">跳轉</button>
</body>
<script>
function toWelcome(){
let username = document.querySelector("#username");
window.location.href = "html?type=2&username="+username.value;
}
</script>后端代碼:
@WebServlet("/html")
public class HTMLTypeServlet extends HttpServlet {
//html?type=...
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//響應html:設置響應的Content-Type
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter pw = resp.getWriter();
//獲取queryString中,type的值
String type = req.getParameter("type");
if("1".equals(type)){//返回簡單的html
pw.println("<h4>獲取網頁成功</h4>");
}else if("2".equals(type)){//返回復雜的動態html
//html?type=2&username=xxx
String username = req.getParameter("username");
pw.println("<p>");
pw.println("歡迎你,"+username);
pw.println("</p>");
}
}
}簡單:
前端顯示:

點擊“查看”:

動態:
前端顯式:

點擊“跳轉”:

關于動態網頁:在Java的代碼中,寫很多html的代碼
耦合性太強(兩個完全不同的編程語言,放在一起來開發)、維護性、擴展性很差
解決方式:
模板技術
這種方式還存在一些問題,進一步發展就有了ajax技術的產生
返回已有的一個網頁
(1)重定向:
特點:url地址欄會變,發起兩次請求
原理:
第一次返回301/302/307響應狀態碼,及響應頭Location:網頁的地址
第二次:瀏覽器自動的跳轉到Location設置的地址
還是比較常用的:比如登錄成功(其實也可以在js代碼中跳轉)后,跳轉到某個首頁
(2)轉發:
特點:url地址欄不變,只有一次請求
原理:當次請求Servlet時,由Servlet獲取到轉發路徑的html,把這個路徑的內容設置到響應正文
前端代碼:
<h4>重定向到hello.html</h4> <a href="goto?type=1" rel="external nofollow" >跳轉</a> <h4>轉發到hello.html</h4> <a href="goto?type=2" rel="external nofollow" >跳轉</a>
后端代碼:
@WebServlet("/goto")
public class GoToServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//goto?type=xxx
String type = req.getParameter("type");
if("1".equals(type)){//重定向
// resp.setStatus(301);
// resp.setHeader("Location","hello.html");
//以上代碼可以簡化為sendRedirect
resp.sendRedirect("hello.html");
}else if("2".equals(type)){//轉發
req.getRequestDispatcher("hello.html")
.forward(req,resp);
}
}
}設置一下Content-Type,然后把文件的二進制數據放在響應正文就可以
前端代碼:
<h4>獲取一個圖片(渲染展示)</h4> <img src="file?type=photo&show=1"> <h4>獲取一個音樂(渲染展示)</h4> <audio src="file?type=music&show=1" controls></audio> <h4>獲取一個圖片(下載)</h4> <a href="file?type=photo&show=0" rel="external nofollow" >下載</a> <h4>獲取一個音樂(下載)</h4> <audio src="file?type=music&show=0" controls></audio>
后端代碼:
@WebServlet("/file")
public class FileServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//<img src="file?type=photo&show=1">
//獲取響應對象的字節輸出流
OutputStream os = resp.getOutputStream();
//返回的文件類型:1.圖片 2.音樂
String type = req.getParameter("type");
//返回時的操作:1.渲染 2.下載
String show = req.getParameter("show");
File file = null;
byte[] data = null;
//<img src="file?type=photo&show=1">
if("photo".equals(type)){//返回圖片
if("1".equals(show)){
resp.setContentType("image/jpeg");//jpg格式
}else{
//這樣只是沒有設置下載的文件名,有興趣可以自行擴展完成
resp.setContentType("application/octet-stream");
}
file =new File("D:\\java\\servlet-study\\src\\main\\resources\\cui.jpg");
//<audio src="file?type=music&show=1" controls></audio>
}else if("music".equals(type)){//返回音樂
if("1".equals(show)){
resp.setContentType("audio/mp3");//mp3格式
}else{
resp.setContentType("application/octet-stream");
}
file = new File("D:\\java\\servlet-study\\src\\main\\resources\\這世界有那么多人.mp3");
}//其他格式可以自行擴展完成
//返回一個文件類型:Content-Length,body
data = Files.readAllBytes(file.toPath());
resp.setContentLength(data.length);//setHeader("Content-Length",xxx)
os.write(data);
}
}問題:圖片、音樂、視頻是靜態文件,直接放在web應用webapp下,就可以直接訪問,那還需要Servlet來返回么?是否多此一舉?
如果文件總的大小非常大,放在web應用的webapp下就不合適了:打包就比較費勁,使用Servlet去讀取本地其他地方的文件,來返回,就比較適合
常用于ajax請求,返回一些數據,用于動態的填充網頁
前端代碼:
<body>
<h4>獲取ajax響應數據,動態生成網頁內容</h4>
<button onclick="gen()">試試</button>
<div id="content"></div>
</body>
<script>
function gen(){
let content = document.querySelector("#content");
ajax({
url: "ajax-response",
method: "get",
callback: function(status,resp){
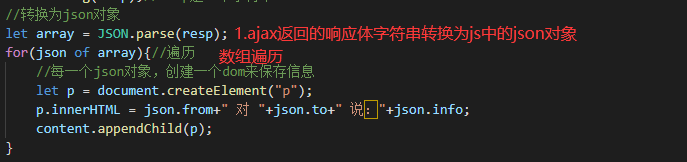
console.log(resp);//resp是一個字符串
//轉換為json對象
let array = JSON.parse(resp);
for(json of array){//遍歷
//每一個json對象,創建一個dom來保存信息
let p = document.createElement("p");
p.innerHTML = json.from+" 對 "+json.to+" 說:"+json.info;
content.appendChild(p);
}
}
});
}
function ajax(args){//var ajax = function(){}
let xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
//設置回調函數
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
//4:客戶端接收到響應后回調
if(xhr.readyState == 4){
// 回調函數可能需要使用響應的內容,作為傳入參數
args.callback(xhr.status,xhr.responseText);
}
}
xhr.open(args.method,args.url);
// 如果args中,Content-Type屬性有內容,就設置Content-Type請求頭
if(args.contentType){//js中,除了判斷boolean值,還可以判斷字符串,對象等,有值就為true
xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-Type",args.contentType);
}
//如果args中,設置了body請求正文,調用send(body)
if(args.body){
xhr.send(args.body);
}else{//如果沒有設置,調用send()
xhr.send();
}
}
</script>后端代碼:
@WebServlet("/ajax-response")
public class AjaxJsonServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
List<Message> messages = new ArrayList<>();
Message m1 = new Message("汪汪","喵喵","我喜歡你");
Message m2 = new Message("喵喵","汪汪","我喜歡你");
messages.add(m1);
messages.add(m2);
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
//把Java對象,轉換為一個json字符串,list和數組會轉換為[],一個對象{成員變量名:值}
String json = mapper.writeValueAsString(messages);
//[{"from":"汪汪","to":"喵喵","info":"我喜歡你"},{"from":"喵喵","to":"汪汪","info":"我喜歡你"}]
System.out.println("轉換的json字符串"+json);
//設置json可以不設置Content-Length,tomcat會設置
resp.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf-8");
resp.getWriter().println(json);
}
static class Message{
private String from;//誰
private String to;//對誰
private String info;//說了什么
public Message(String from, String to, String info) {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.info = info;
}
public String getFrom() {
return from;
}
public void setFrom(String from) {
this.from = from;
}
public String getTo() {
return to;
}
public void setTo(String to) {
this.to = to;
}
public String getInfo() {
return info;
}
public void setInfo(String info) {
this.info = info;
}
}
}點擊“試試”:

具體過程:
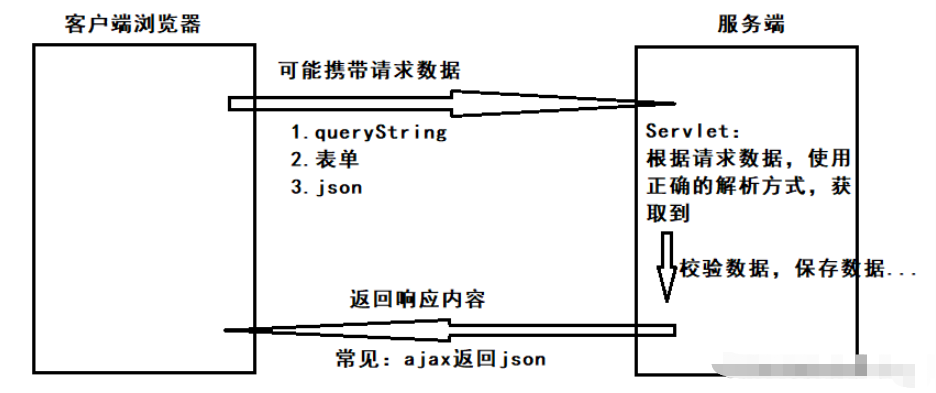
對應可以使用的數據格式:

到此,相信大家對“Java Servlet響應httpServletResponse過程是什么”有了更深的了解,不妨來實際操作一番吧!這里是億速云網站,更多相關內容可以進入相關頻道進行查詢,關注我們,繼續學習!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。