您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹了C++的程序流程結構是什么的相關知識,內容詳細易懂,操作簡單快捷,具有一定借鑒價值,相信大家閱讀完這篇C++的程序流程結構是什么文章都會有所收獲,下面我們一起來看看吧。
C/C++支持最基本的三種程序運行結構:順序結構、選擇結構、循環結構。

順序結構就是順著寫代碼,不想多說。
作用:執行滿足條件的語句
if語句的三種形式:
單行格式if語句
語法:
if(條件){條件滿足執行的語句}#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//用戶輸入分數,如果分數大于600,視為考上一本大學,在屏幕上輸出
//1.用戶輸入分數
int score = 0;
cout << "請輸入一個分數:" << endl;
cin >> score;
cout << "您輸入的分數為:" << score << endl;
//2.判斷
if (score > 600)
{
cout << "恭喜您考上了一本大學" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}多行格式if語句
語法:
if(條件){條件滿足執行的語句}else{條件不滿足執行的語句}#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//1.用戶輸入分數
int score = 0;
cout << "請輸入一個分數:" << endl;
cin >> score;
cout << "您輸入的分數為:" << score << endl;
//2.判斷
if (score > 600)
{
cout << "恭喜您考上了一本大學" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "您沒有考上一本大學,請再接再厲" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}多條件的if語句
語法:
if(條件1){條件1滿足執行的語句}else if(條件2){條件2滿足執行的語句}... else{都不滿足執行的語句}#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//1.用戶輸入分數
int score = 0;
cout << "請輸入一個分數:" << endl;
cin >> score;
cout << "您輸入的分數為:" << score << endl;
//2.判斷
if (score > 600)
{
cout << "恭喜您考上了一本大學" << endl;
}
else if (score > 500)
{
cout << "恭喜您考上了二本大學" << endl;
}
else if (score > 400)
{
cout << "恭喜您考上了三本大學" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "您沒有考上一本大學,請再接再厲" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}嵌套if語句:在if語句中嵌套使用if語句,達到更精確的條件判斷
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//1.用戶輸入分數
int score = 0;
cout << "請輸入一個分數:" << endl;
cin >> score;
cout << "您輸入的分數為:" << score << endl;
//2.判斷
if (score > 600)
{
if (score > 1000) { cout << "恭喜您考到了地球之外" << endl; }
if (score > 800) { cout << "恭喜您考到了清北" << endl; }
else { cout << "恭喜您考上了普通一本大學" << endl; }
}
else if (score > 500)
{
cout << "恭喜您考上了二本大學" << endl;
}
else if (score > 400)
{
cout << "恭喜您考上了三本大學" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "您沒有考上一本大學,請再接再厲" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num1 = 0;
int num2 = 0;
int num3 = 0;
//用戶輸入
cout << "請輸入小豬A的體重:" << endl;
cin >> num1;
cout << "請輸入小豬B的體重:" << endl;
cin >> num2;
cout << "請輸入小豬C的體重:" << endl;
cin >> num3;
cout << "小豬A的體重為:" << num1 << endl;
cout << "小豬B的體重為:" << num2 << endl;
cout << "小豬C的體重為:" << num3 << endl;
//判斷
if (num1 > num2) //A>B
{
if (num1 > num3) //A>C
{
cout << "\n小豬A最重" << endl;
}
else //C>A
{
cout << "\n小豬C最重" << endl;
}
}
else //B>A
{
if (num2 > num3) //B>C
{
cout << "\n小豬B最重" << endl;
}
else //C>B
{
cout << "\n小豬C最重" << endl;
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}作用:通過三目運算符實現簡單的判斷
語法:
表達式1?表達式2:表達式3
解釋:如果表達式1為真:執行表達式2,并返回表達式2的結果。
如果表達式1為假:執行表達式3,并返回表達式3的結果。
在C++中三目運算符如果后面的表達式是變量,則返回的是變量,并不是變量的值,也就是說可以繼續對變量進行操作。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int b = 50;
int c = 0;
c = (a > b) ? a : b;
cout << "c = " << c << endl;
//在C++中三目運算符如果后面的表達式是變量,則返回的是變量,并不是變量的值,也就是說可以繼續對變量進行操作
(a > b ? a : b) = 100;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}作用:執行多條件分支語句
語法:
switch(表達式){case 結果1 : 執行語句;break; case 結果2 : 執行語句;break; ... default : 執行語句;break;}break可以不加,不加break的時候程序會一直向下執行,即如果執行了結果2的執行語句,那么結果3、結果4...的執行語句都會被執行。switch(表達式)
{case 結果1 : 執行語句;break;
case 結果2 : 執行語句;break;
...
default : 執行語句;break;
}
break可以不加,不加break的時候程序會一直向下執行,即如果執行了結果2的執行語句,那么結果3、結果4...的執行語句都會被執行。優點:結構清晰,執行的效率高;
缺點:case所接的結果必須是整型或者字符型,且不能判斷區間。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int score = 0;
cout << "請給電影打分:" << endl;
cin >> score;
/* 5以下:爛片
5 ~ 6:一般
7 ~ 8:較好
9~ 10:經典
*/
switch (score)
{
case 10:cout << "經典" << endl; break;
case 9:cout << "經典" << endl; break;
case 8:cout << "較好" << endl; break;
case 7:cout << "較好" << endl; break;
case 6:cout << "一般" << endl; break;
case 5:cout << "一般" << endl; break;
default:cout << "爛片" << endl; break;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}如果不加break的時候,執行效果如下:
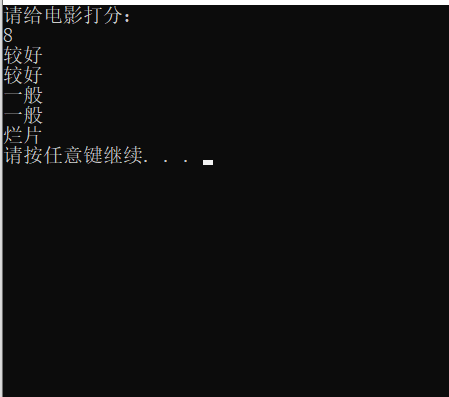
語法:
while(循環條件){循環語句}解釋:只要循環條件的結果為真,就執行循環語句。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//在屏幕上打印0-9這10個數字
int num = 0;
while (num <= 9)
{
cout << num << endl;
num++;
}
system("pause");
return 0;while 循環案例:

隨機數的生成:C++產生隨機數
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib> //可以不輸入此行,iostream間接包含了這里的庫頭文件
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
int main()
{ //srand(0) 不加此行或者使用它時,種子固定,所以產生隨機數固定。
//種子控制產生的隨機數,所以只需要產生隨機種子就可了。
srand((int)time(0)); //利用當前系統時間產生隨機種子,把0換成NULL也行。
int num = rand() % 100 + 1; //rand:偽隨機數,rand()%100生成0-99
//cout << num << endl;
int val = 0;
while (1)
{
cin >> val;
if (val > num)
{
cout << "您猜的數大于此數" << endl;
}
else if (val < num)
{
cout << "您猜的數小于此數" << endl;
}
else
{ cout << "恭喜您猜對了" << endl; break;
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}語法:
do{循環語句} while(循環條件);與while的區別:do…while會先執行一次循環語句,再判斷循環條件。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//死循環,因為先執行了do里面的內容,所以while始終為真。
int num = 0;
do
{
cout << num << endl;
num++;
}
while (num);
system("pause");
return 0;
}do…while 練習案例:

#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num = 100;
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;
do
{
a = num / 100; //百位
b = (num / 10 % 10); //十位
c = num % 10; //個位
if (pow(a, 3) + pow(b, 3) + pow(c, 3) == num)
{
cout << num << endl;
}
num++;
} while (num < 1000);
system("pause");
return 0;
}作用:滿足循環條件,執行循環語句
語法:
for(起始表達式;條件表達式;末尾循環體){循環語句;}#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << i << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}for中的表達式記得加;
for 練習案例

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{ //個位有7,%10==7
//十位有7,/10==7
//7的倍數, %7==0
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++)
{
if ((i % 10 == 7) || (i / 10 == 7) || (i % 7 == 0))
{
cout << "敲桌子" << endl;
}
else { cout << i << endl; }
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}用法:循環中再使用循環
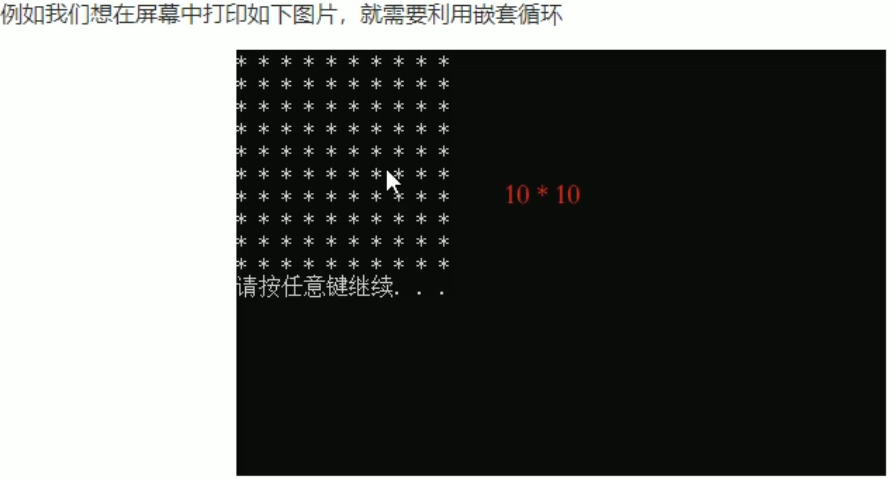
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++)
{
cout << "* " ;
}
cout << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}嵌套循環案例
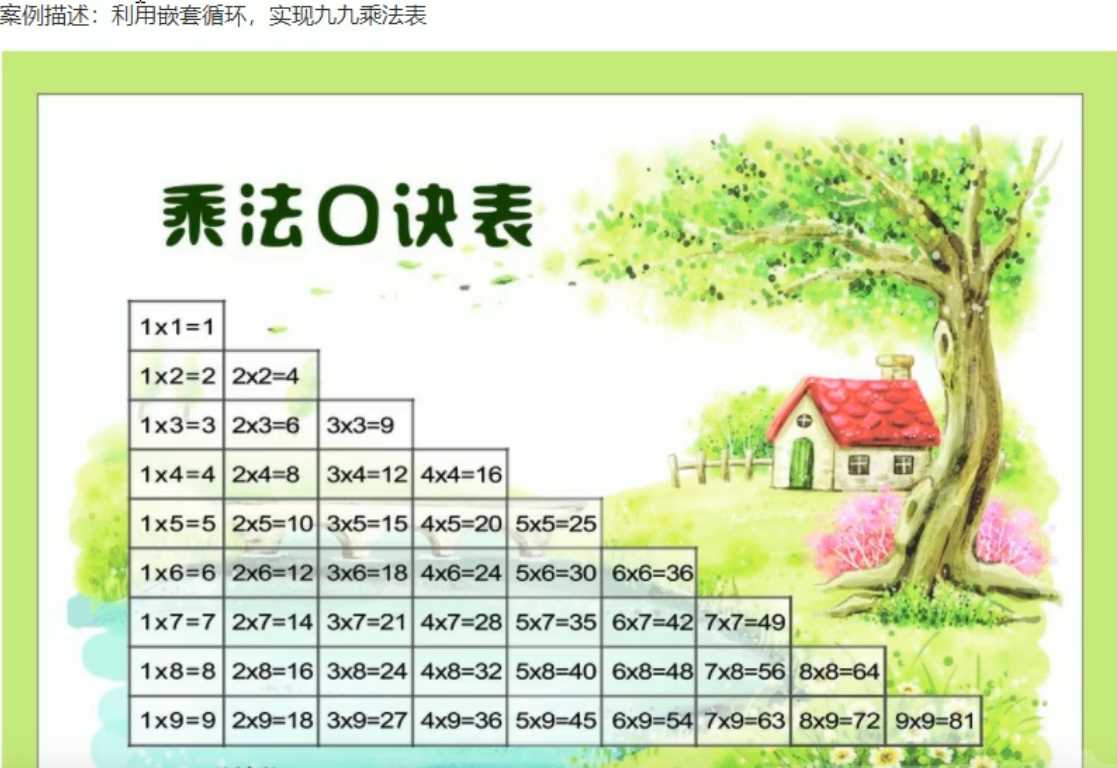
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <=i ; j++)
{
cout << j << "*" << i << "="<< j * i << "\t";
}
cout << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}作用:跳出選擇結構(實際上只有switch語句用得到)或者循環結構。
具體而言也就三種:
出現在switch語句:終止case、跳出switch
出現在循環語句:跳出當前的循環
出現在嵌套循環中:跳出最近的內層循環(此break所屬循環)。
前兩個很簡單,只看第三個情況,對乘法口訣表的代碼稍微進行修改即可:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < 10; j++)
{
cout << j << "×" << i << "=" << j * i << "\t";
if (i == j)
{
break;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}作用:跳過本次循環中余下的執行語句,直接執行下一次循環。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
if (i == 3 || i == 7) { continue; }
cout << i << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}作用:可以無條件跳轉語句
語法:
goto 標記;
解釋;如果標記的名稱存在,執行到goto語句時,會跳轉到標記的位置
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "1.xxxx" << endl;
cout << "2.xxxx" << endl;
goto Flag;
cout << "3.xxxx" << endl;
Flag: cout << "4.xxxx" << endl;
cout << "5.xxxx" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}一般不建議使用goto,因為標記太多,會導致代碼及其混亂。
關于“C++的程序流程結構是什么”這篇文章的內容就介紹到這里,感謝各位的閱讀!相信大家對“C++的程序流程結構是什么”知識都有一定的了解,大家如果還想學習更多知識,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。