您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
怎樣進行MySQL的學習,相信很多沒有經驗的人對此束手無策,為此本文總結了問題出現的原因和解決方法,通過這篇文章希望你能解決這個問題。
| 對比 | MyISAM | InnoDB |
|---|---|---|
| 主外鍵 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 事務 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 行表鎖 | 表鎖,操作時即使操作一條記錄也會鎖住一整張表,不適合高并發的操作 | 行鎖,操作時只鎖住某一行,不會影響到其他行,適合高并發 |
| 緩存 | 只緩存索引,不緩存其他數據 | 緩存索引和真實數據,對內存要求較高,而且內存大小對性能有影響 |
| 表空間 | 小 | 大 |
| 關注點 | 性能 | 事務 |
| 默認安裝 | Y | Y |
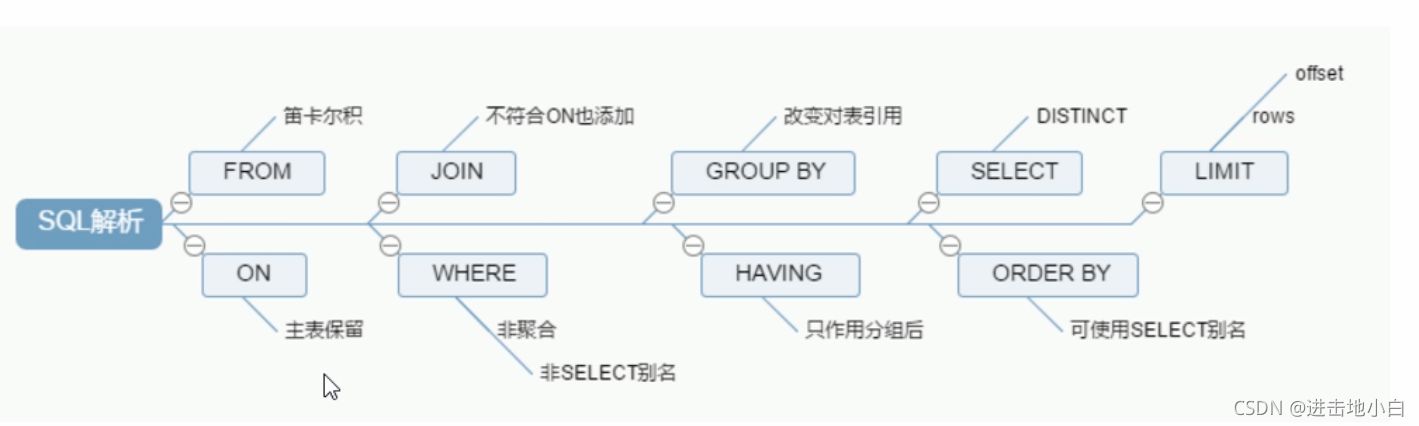
查詢語句寫的差
索引失效
關聯查詢太多join (設計缺陷或不得已的需求)
服務器調優及各個參數設置(緩沖,線程參數)
手寫
機讀先從from開始
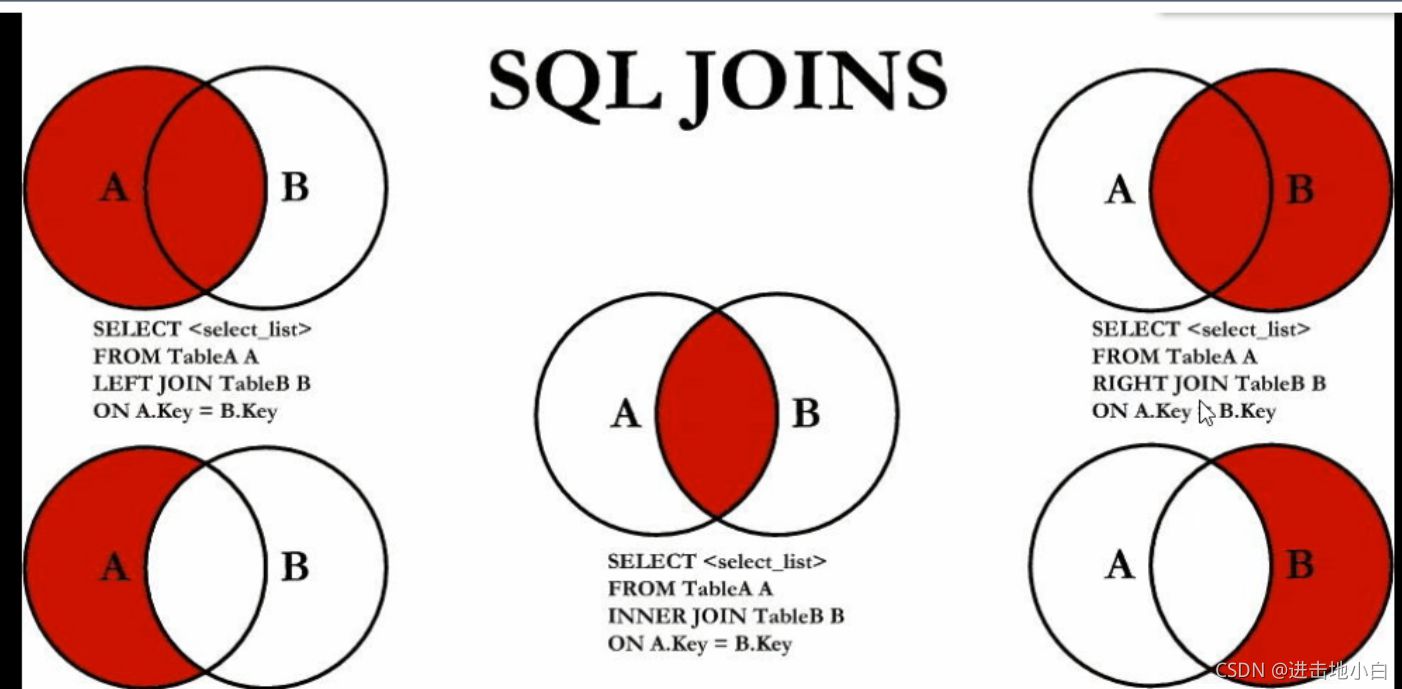
a表
mysql> select * from tbl_dept; +----+----------+--------+ | id | deptName | locAdd | +----+----------+--------+ | 1 | RD | 11 | | 2 | HR | 12 | | 3 | MK | 13 | | 4 | MIS | 14 | | 5 | FD | 15 | +----+----------+--------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
b表
+----+------+--------+ | id | name | deptId | +----+------+--------+ | 1 | z3 | 1 | | 2 | z4 | 1 | | 3 | z5 | 1 | | 4 | w5 | 2 | | 5 | w6 | 2 | | 6 | s7 | 3 | | 7 | s8 | 4 | | 8 | s9 | 51 | +----+------+--------+ 8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql不支持全連接
使用以下方式可以實現全連接
mysql> select * from tbl_dept a right join tbl_emp b on a.id=b.deptId -> union -> select * from tbl_dept a left join tbl_emp b on a.id=b.deptId; +------+----------+--------+------+------+--------+ | id | deptName | locAdd | id | name | deptId | +------+----------+--------+------+------+--------+ | 1 | RD | 11 | 1 | z3 | 1 | | 1 | RD | 11 | 2 | z4 | 1 | | 1 | RD | 11 | 3 | z5 | 1 | | 2 | HR | 12 | 4 | w5 | 2 | | 2 | HR | 12 | 5 | w6 | 2 | | 3 | MK | 13 | 6 | s7 | 3 | | 4 | MIS | 14 | 7 | s8 | 4 | | NULL | NULL | NULL | 8 | s9 | 51 | | 5 | FD | 15 | NULL | NULL | NULL | +------+----------+--------+------+------+--------+ 9 rows in set (0.00 sec)
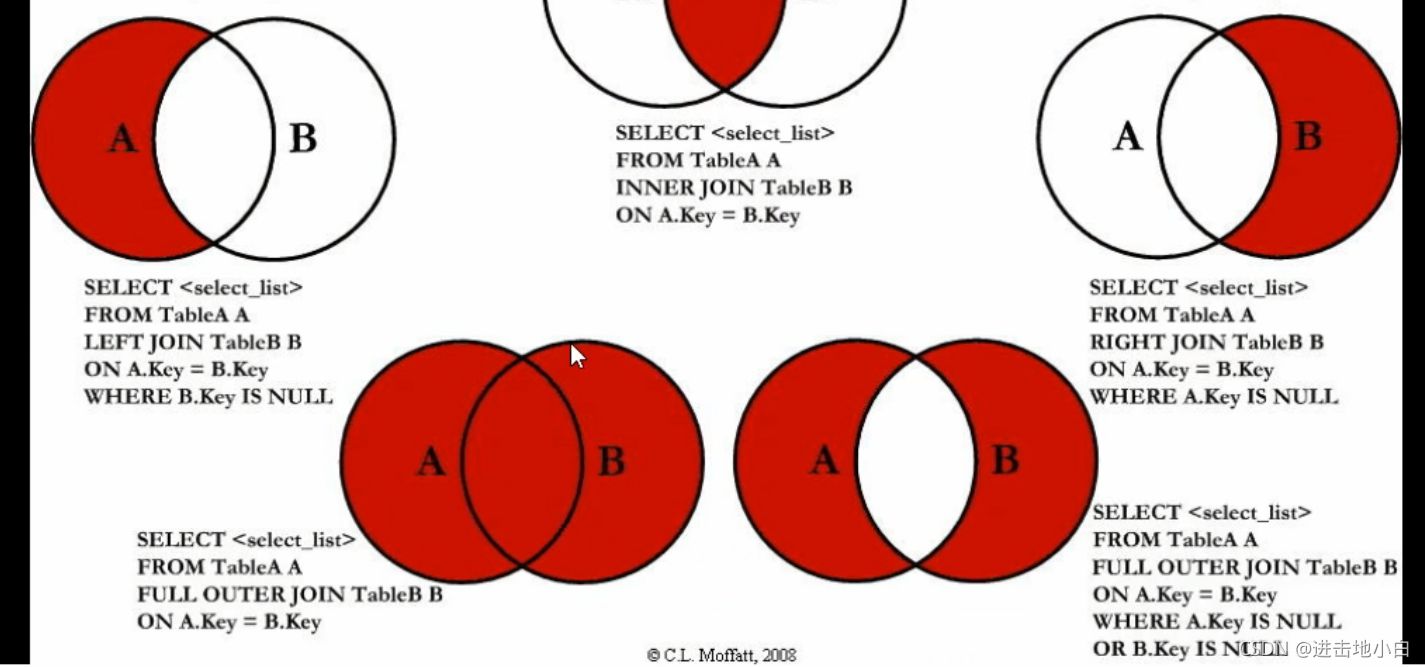
a的獨有和b的獨有
mysql> select * from tbl_dept a left join tbl_emp b on a.id=b.deptId where b.id is null -> union -> select * from tbl_dept a right join tbl_emp b on a.id=b.deptId where a.id is null; +------+----------+--------+------+------+--------+ | id | deptName | locAdd | id | name | deptId | +------+----------+--------+------+------+--------+ | 5 | FD | 15 | NULL | NULL | NULL | | NULL | NULL | NULL | 8 | s9 | 51 | +------+----------+--------+------+------+--------+ 2 rows in set (0.01 sec)
索引的定義:
索引是幫助SQL高效獲取數據的數據結構,索引的本質:數據結構
可以簡單的理解為:排好序的快速查找數據結構
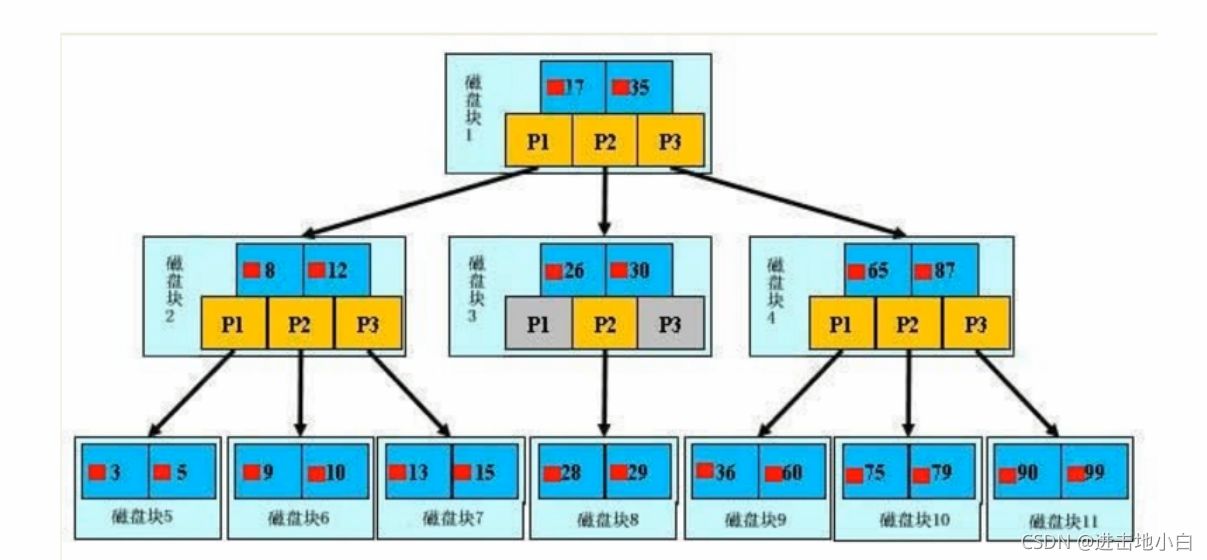
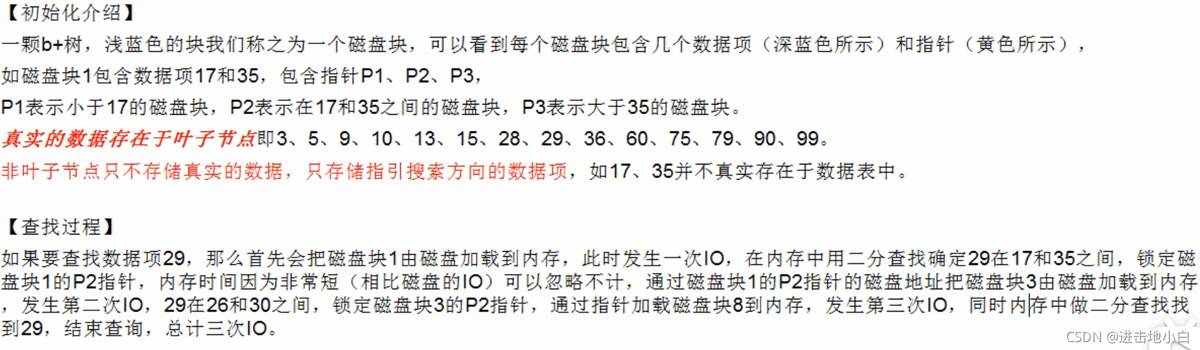
在數據之外,數據庫系統還維護著滿足特定查找算法的數據結構,這些數據結構以某種方式(引用)指向數據,這樣就可以在這些數據結構上實現高級查找算法。這種數據結構,就是索引,下圖就是一種示例:
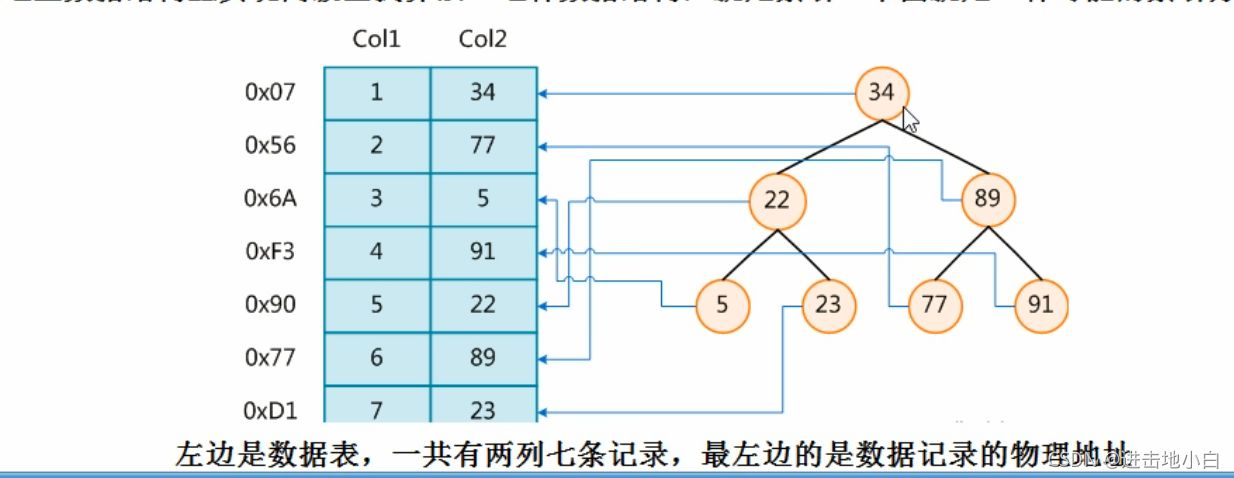
一般來說索引也很大,因此索引往往以索引文件的方式存儲在磁盤上
我們平常所說的索引,如果沒有特別指明,一般都是指B樹(多路搜索樹,不一定是二叉的)結構組織的索引,
其中聚集索引,次要索引,復合索引,前綴索引,唯一索引默認都是使用B+樹索引,統稱索引,當然除了B+樹這種類型的索引之外,還有哈希索引。
類似大學圖書館圖書編號建索引,提高了數據檢索的效率,降低數據庫的IO成本
通過索引對數據進行排序,降低數據排序的成本,降低了CPU的消耗
實際上索引也是一張表,該表保存了主鍵與存在索引的字段,并指向實體表的記錄,所以索引列也是占用空間的
雖然索引大大提高了查詢速度,但是會降低更新表的速度,比如 update,insert,delete操作,因為更新表時,MySQL不僅要數據也要保存索引文件每次更新添加了索引的字段,都會調整因為更新所帶來的鍵值變化后的索引信息
索引只是提高效率的一個因素,在一個大數據量的表上,需要建立最為優秀的索引或者寫優秀的查詢語句,而不是加了索引就能提高效率
單值索引
唯一索引
復合索引
基本語法:
create [unique] index indexName on mytable(cloumnname(length));
alter mytable add [unique] index [indexName] on (columnname(length));
drop index [indexName] on mytable
show index from table_name\G
有四種方式來添加數據表的索引

BTree索引
Hash索引
full-text全文索引
R-Tree

主鍵自動建立唯一索引
頻繁作為查詢條件的字段應該創建索引
查詢中與其他表相關聯的字段,外鍵關系建立索引
頻繁更新的字段不適合創建索引,因為每次更新不單單更新了記錄還更新了索引
where條件里用不到的字段不要創建索引
單鍵/組合索引的選擇問題 who?(高并發下建議組合索引)
查詢中排序的字段,排序字段若通過索引去訪問將大大提高排序速度
查詢中統計或分組字段
表記錄少
經常操作dml語句的表
數據重復且平均分布的表字段,因此只為最經常查詢和最經常排序的數據列建立索引,注意,如果某個數據列包含許多重復的內容,為它建立索引就沒有太大的實際效果
explian重點

表的讀取順序
數據讀取操作的操作類型
哪些索引可以被使用
哪些索引被實際使用
表之間的引用
每張表有多少行被優化器查詢
id 相同,執行順序由上至下
id不同,如果是子查詢,id序號遞增,id越大優先級越高
id相同不同 ,同時存在
SIMPLE 簡單查詢
PRIMARY 主查詢 (最外層的查詢)
SUBQUERY 子查詢
DERIUED 某個查詢的子查詢的臨時表
UNION 聯合查詢
UNION RESULT 聯合查詢結果
type顯示的是訪問類型排列,是較為重要的一個指標

從最好到最差依次是:
system > const > eq_ref> ref > range > index > ALL;
一般來說,得保證查詢至少達到range級別,最好ref
----------------------------------------------type類型-------------------------------------------------------
system:表只有一行記錄(等于系統表) 這是const類型的特列 一般不會出現,可忽略不計
const:表示通過索引一次就查詢到了,const用來比較primary key或者unique索引。因為只匹配一行數據,所以很快,如將主鍵置于where列表中,Mysql就能將該查詢轉換為一個常量
eq_ref:唯一性索引掃描,表中只有一條記錄與之匹配,常用于主鍵或唯一索引掃描(兩個表是多對一或者一對一的關系,被連接的表是一的情況下,他的查詢是eq_ref)
ref:非唯一性索引掃描,返回匹配某個單獨值的所有行,本質上也是一種索引訪問,它返回匹配某個單獨值的所有行,然而他可能會找到多個復合條件的行,屬于查找和掃描的結合體
range:只檢索給定范圍的行,使用一個索引來選擇行,key列顯示使用了哪個索引,一般where語句里出現了betweent,<,>,in等的查詢,這種范圍掃描索引比全表掃描好
index:index與ALL的區別,index只遍歷索引樹,索引文件通常比數據文件小
ALL:全表掃描
----------------------------------------------type類型-------------------------------------------------------
possible_keys:顯示可能應用的的索引(理論上)
key:實際使用的索引,查詢中若使用了覆蓋索引,則該索引僅僅出現在key中
key_len:表示索引中使用的字節數,在不損失精度的情況下越短越好,kenlen顯示的值為索引字段的最大可能長度,并非實際使用長度,kenlen是根據表定義計算而得,而不是通過表內檢索出的
key_len長度:13是因為char(4)*utf8(3)+允許為null(1)=13
ref:顯示索引的哪一列被使用了,如果可能的話是一個常數,哪些列或常量被用于查找索引列上的值

rows:根據表統計信息及索引選用情況,大致計算出找到所需的記錄所需要讀取的行數
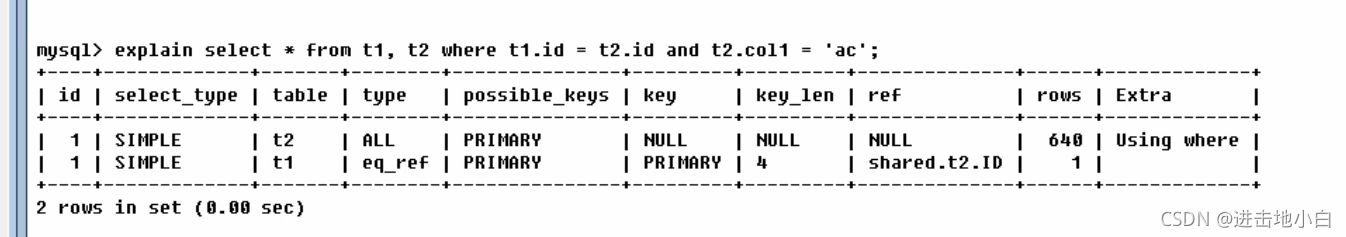
沒建立索引時查詢t1 t2表 t1表對應t2表的id t2表 col1的值要為'ac'
對于Id這個字段t1表對t2表相當于 一對多
t1表的type為 eq_ref代表唯一性索引掃描,表中只有一條記錄與之匹配,t2表對應t1的這個id對應的col值只有一個,根據t2表的主鍵id索引查詢,t1表讀取了一行,t2表讀取了640行
建立索引后
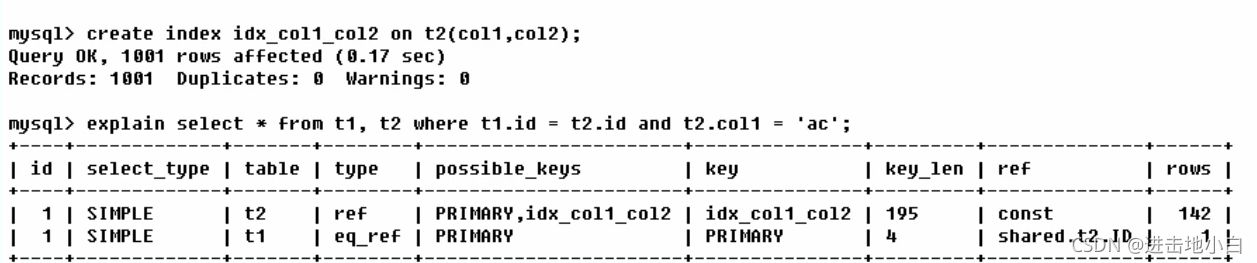
t1讀取一行,t2讀取142行,ref非唯一性索引掃描,返回匹配某個單獨值的所有行,返回t2對應id的col所有行,而t1對應id的col只有一行,所以type為eq_ref
包含不適合在其他列展現但十分重要的信息
\G :豎直顯示排序
Using filesort:說明mysql會對數據使用一個外部的索引排序,而不是按照表內的索引順序進行讀取,mysql中無法利用索引完成排序的操作稱為文件排序未被方框框住的圖建立了復合索引,但是直接使用col3進行排序導致空中樓閣,mysql不得已只能進行filesoft
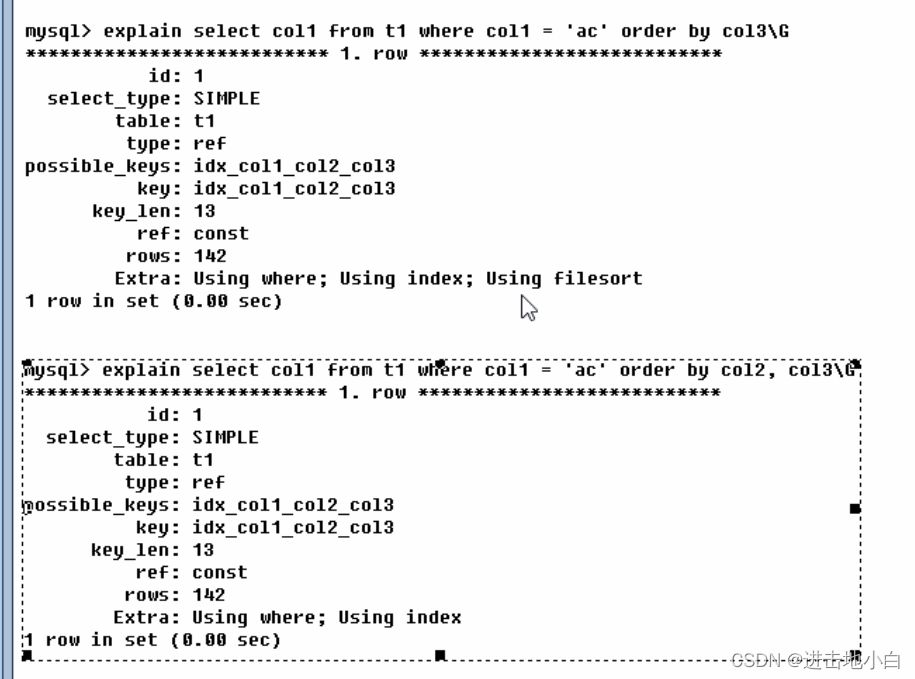
Using temporary:使用了臨時表保存中間中間結果,MySQL在對查詢結果排序時使用臨時表。常見于order by排序和group by分組上表中建立了復合索引 col1_col2 但是直接通過col2進行分組導致了mysql不得已只能進行filesoft和建立臨時表
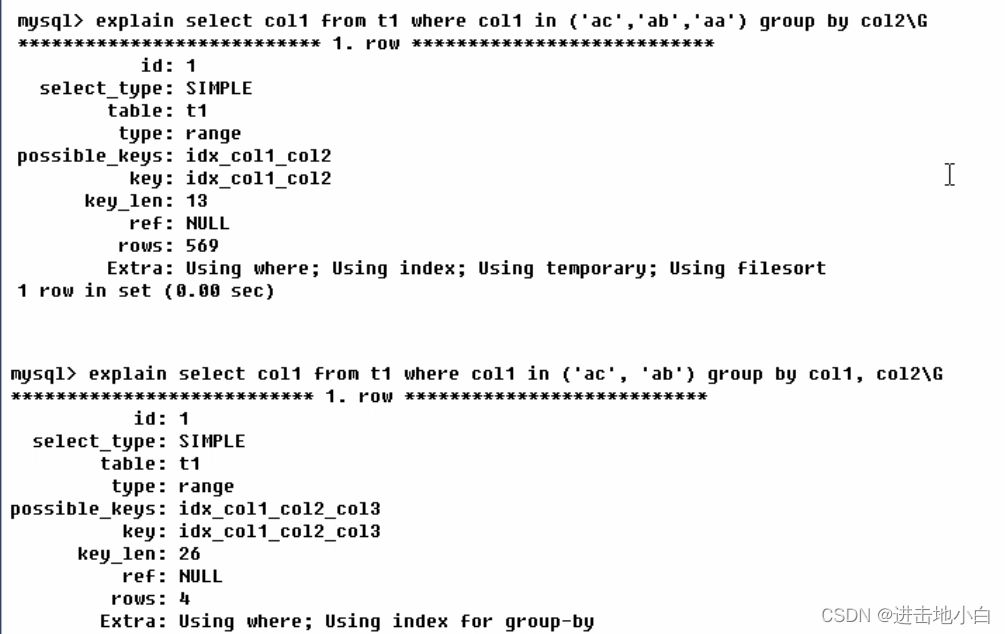
using index 表示相應的select操作中使用了覆蓋索引,避免訪問了表的數據行,如果同時出現using where 表示索引被用來執行索引鍵值的查找,沒有usingwhere表示索引用來讀取數據而非執行查找動作
using where 表示使用了 where過濾
using join buffer 私用了鏈接緩存
impossible buffer where子句的值總是false 不能用來獲取任何元組
select tables optimized away 在沒有group by子句的情況下,基于索引優化min/max操作,或者對myisam存儲引擎執行count(*)操作,不必等到執行操作進行,查詢執行計劃生成的階段即完成優化
distinct 優化distinct操作,在找到第一匹配的元組后立即停止查找同樣值的操作
案例
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `article`( `id` INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, `author_id` INT (10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL, `category_id` INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL , `views` INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL , `comments` INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL, `title` VARBINARY(255) NOT NULL, `content` TEXT NOT NULL ); INSERT INTO `article`(`author_id`,`category_id` ,`views` ,`comments` ,`title` ,`content` )VALUES (1,1,1,1,'1','1'), (2,2,2,2,'2','2'), (1,1,3,3,'3','3'); SELECT * FROM ARTICLE; mysql> select id,author_id from article where category_id = 1 and comments > 1 order by views desc limit 1; +----+-----------+ | id | author_id | +----+-----------+ | 3 | 1 | +----+-----------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select author_id from article where category_id = 1 and comments > 1 order by views desc li imit 1; +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | article | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 33.33 | Using where; Using filesort | +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
可以看出雖然查詢出來了 但是 type是all,Extra里面出現了using filesort證明查詢效率很低
需要優化
建立索引
create index idx_article_ccv on article(category_id,comments,views);
查詢
mysql> explain select author_id from article where category_id = 1 and comments > 1 order by views desc limit 1; +----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+------+------+----------+---------------------------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+------+------+----------+---------------------------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | article | NULL | range | inx_article_ccv | inx_article_ccv | 8 | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | Using index condition; Using filesort | +----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+------+------+----------+---------------------------------------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
這里發現type 變為了 range 查詢全表變為了 范圍查詢 優化了一點
但是 extra 仍然 有 using filesort 證明 索引優化并不成功

所以我們刪除索引
drop index idx_article_ccv on article;
建立新的索引,排除掉range
create index idx_article_cv on article(category_id,views); mysql> explain select author_id from article where category_id = 1 and comments > 1 order by views desc limit 1; +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+----------------+----------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+----------------+----------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | article | NULL | ref | idx_article_cv | idx_article_cv | 4 | const | 2 | 33.33 | Using where | +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+----------------+----------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec) 這時候會發現 優化成功 type 變為了ref extra變為了 using where 在這次實驗中我又加入了一次試驗 發現當建立索引時comments放在最后也是可行的 mysql> create index idx_article_cvc on article(category_id,views,comments); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec) Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> explain select author_id from article where category_id = 1 and comments > 1 order by views desc limit 1; +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | article | NULL | ref | idx_article_cvc | idx_article_cvc | 4 | const | 2 | 33.33 | Using where | +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
這時候會發現 優化成功 type 變為了ref extra變為了 using where
在這次實驗中我又加入了一次試驗 發現當建立索引時comments放在最后也是可行的
這里發現了 type仍然是ref,extra也是usingwhere,而只是把索引建立的位置換了一換,把范圍查詢的字段挪到了最后!!!!
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `class`( `id` INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, `card` INT (10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL ); CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `book`( `bookid` INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, `card` INT (10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL ); INSERT INTO class(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); mysql> create index Y on book(card); explain select * from book left join class on book.card=class.card; +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | book | NULL | index | NULL | Y | 4 | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | Using index | | 1 | SIMPLE | class | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop) | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+ 2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
會發現并無多大區別 還是全表查詢 這是因為倆表查詢左連接把左表必須全查詢 這時候只有對右表建立索引才有用
相反的右鏈接必須對左表建立索引才有用
對右表建立索引
create index Y on class; explain select * from book left join class on book.card=class.card; +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+----------------+------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+----------------+------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | book | NULL | index | NULL | Y | 4 | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | Using index | | 1 | SIMPLE | class | NULL | ref | Y | Y | 4 | db01.book.card | 1 | 100.00 | Using index | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+----------------+------+----------+-------------+ 2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
會發現 右表只查詢了一次。。type為ref
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `phone`( `phoneid` INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, `card` INT (10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL )ENGINE = INNODB; INSERT INTO phone(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card)VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20)));
先刪除所有索引
drop index Y on book; drop index Y on class; explain select * from class left join book on class.card=book.card left join phone on book.card=phone.card; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | class | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | NULL | | 1 | SIMPLE | book | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop) | | 1 | SIMPLE | phone | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop) | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+ 3 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
建立索引
create index y on book(card); create index z on phone(card); explain select * from class left join book on class.card=book.card left join phone on book.card=phone.card; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+-----------------+------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+-----------------+------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | class | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | NULL | | 1 | SIMPLE | book | NULL | ref | y | y | 4 | db01.class.card | 1 | 100.00 | Using index | | 1 | SIMPLE | phone | NULL | ref | z | z | 4 | db01.book.card | 1 | 100.00 | Using index | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+-----------------+------+----------+-------------+ 3 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
會發現索引建立的非常成功。。 但是left join 最左表必須全部查詢 建立索引
create index x on class(card); explain select * from class left join book on class.card=book.card left join phone on book.card=phone.card; +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+-----------------+------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+-----------------+------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | class | NULL | index | NULL | x | 4 | NULL | 20 | 100.00 | Using index | | 1 | SIMPLE | book | NULL | ref | y | y | 4 | db01.class.card | 1 | 100.00 | Using index | | 1 | SIMPLE | phone | NULL | ref | z | z | 4 | db01.book.card | 1 | 100.00 | Using index | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+-----------------+------+----------+-------------+ 3 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
結果仍然一樣
建立表
CREATE TABLE staffs(
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` VARCHAR(24)NOT NULL DEFAULT'' COMMENT'姓名',
`age` INT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT'年齡',
`pos` VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT'' COMMENT'職位',
`add_time` TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT'入職時間'
)CHARSET utf8 COMMENT'員工記錄表';
INSERT INTO staffs(`name`,`age`,`pos`,`add_time`) VALUES('z3',22,'manager',NOW());
INSERT INTO staffs(`name`,`age`,`pos`,`add_time`) VALUES('July',23,'dev',NOW());
INSERT INTO staffs(`name`,`age`,`pos`,`add_time`) VALUES('2000',23,'dev',NOW());
建立索引
ALTER TABLE staffs ADD INDEX index_staffs_nameAgePos(`name`,`age`,`pos`);1.帶頭大哥不能死,中間兄弟不能斷:當建立復合索引時,必須帶上頭索引,不能跳過中間索引直接使用后面的索引,使用后面的索引必須加上中間的索引(可以先使用后面的索引再使用中間的索引,但是不能直接使用后面的索引而跳過中間索引)(針對where)
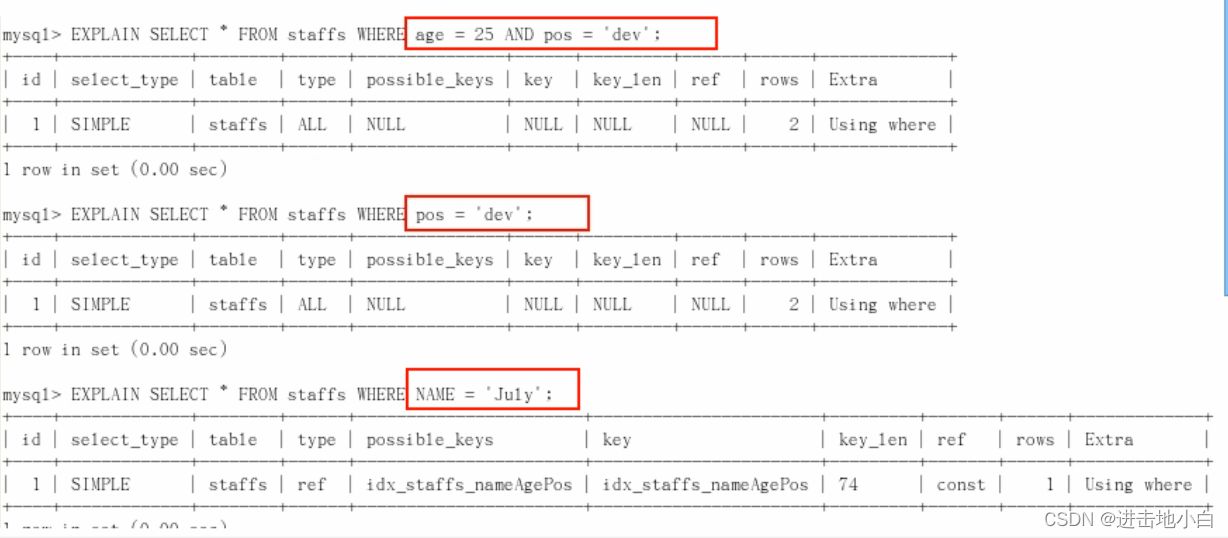
可以從上圖看出 跳過name的都用不了索引
mysql> explain select * from staffs where name='july'; +----+-------------+--------+------------+------+-------------------------+-------------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+--------+------------+------+-------------------------+-------------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | staffs | NULL | ref | index_staffs_nameAgePos | index_staffs_nameAgePos | 74 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+--------+------------+------+-------------------------+-------------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select * from staffs where name='july' and pos='dev'; +----+-------------+--------+------------+------+-------------------------+-------------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+--------+------------+------+-------------------------+-------------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | staffs | NULL | ref | index_staffs_nameAgePos | index_staffs_nameAgePos | 74 | const | 1 | 33.33 | Using index condition | +----+-------------+--------+------------+------+-------------------------+-------------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
可以從語句中看出跳過中間的索引后 key_len 不變 證明第索引pos沒有被用到
2.不能對索引列進行任何操作(計算,類型轉換 等等)
3.存儲引擎不能使用索引中范圍條件右邊的列(索引列上少計算)
4.盡量使用覆蓋索引,即是只訪問索引的查詢減少select *的用法
5.少使用(!=,<>,<,>) is not null ,is null;
6.like以 '%'開頭會導致索引失效(使用覆蓋索引課避免索引失效)覆蓋索引:(建立的索引與查詢的字段順序數量盡量一致)
7.字符串不加單引號會導致索引失效(mysql會將字符串類型強制轉換 導致索引失效)
8.少用or,用它連接會失效
假設index(a,b,c)
Y代表索引全部使用了 N全沒使用
| where語句 | 索引是否被使用 |
|---|---|
| where a=3 and c=5 | (中間b斷掉了)使用了a 沒使用c |
| where a=3 and b=4 andc=5 | Y |
| where a=3 and c=5 and b=4 | Y這里mysql自動做了優化對語句排序 |
| where a=3 and b>4 and c=5 | a,b被使用 |
| where a=3 and b like 'k%' and c=5 | Y like后面常量開頭索引全用 |
| where b=3 and c=4 | N |
| where a=3 and c>5 and b=4 | Y:mysql自動做了優化對語句排序 范圍c之后索引才會失效 |
| where b=3 and c=4 and a=2 | Y :mysql自動做了優化對語句排序 |
| where c=5 and b=4 and a=3 | Y :mysql自動做了優化對語句排序 |
假設index(a,b,c, d)
create table test03( id int primary key not null auto_increment, a int(10), b int(10), c int(10), d int(10), insert into test03(a,b,c,d) values (3,4,5,6); insert into test03(a,b,c,d) values (3,4,5,6); insert into test03(a,b,c,d) values (3,4,5,6); insert into test03(a,b,c,d) values (3,4,5,6); create index idx_test03_abcd on test03(a,b,c,d);
###
| where a=3 and b>4 and c=5 | 使用了a和b ,b后面的索引全失效 |
|---|---|
| where a=3 and b=4 and d=6 order by c | 使用了a和b,c其實也用了但是是用在排序,沒有統計到mysql中 |
| where a=3 and b=4 order by c | 使用了a和b,c其實也用了但是是用在排序,沒有統計到mysql中 |
| where a=3 and b=4 order by d | 使用了a和b, 這里跳過c 會導致using filesort |
| where a=3 and d=6 order by b ,c | 使用了a, 排序用到了b,c索引 |
| where a=3 and d=6 order by c ,b | 使用了 a,會產生using filesort,因為跳過了b對c進行排序 |
| where a=3 and b=4 order by b ,c | Y 全使用 |
| where a=3 and b=4 and d&##61;6 order by c , b | 使用了a,b,不會產生using filesort 因為在對c,b排序前對b進行了查詢,查詢時b已經確定了(常量),這樣就沒有跳過b對c進行排序了,而是相當于直接對c排序 相當于第三格的查詢語句 |
group by 更嚴重group by先分組再排序 把order by換為 group by 甚至會產生using temporary,與order by差不多,但是更嚴重 而且與group by產生的效果差不多就不做演示了
| orderBy 條件 | Extra |
|---|---|
| where a>4 order by a | using where using index |
| where a>4 order by a,b | using where using index |
| where a>4 order by b | using where, using index ,using filesort(order by 后面帶頭大哥不在) |
| where a>4 order by b,a | using where, using index ,using filesort(order by 后面順序) |
| where a=const order by b,c | 如果where使用索引的最左前綴定義為常量,則order by能使用索引 |
| where a=const and b=const order by c | where使用索引的最左前綴定義為常量,則order by能使用索引 |
| where a=const and b>3 order by b c | using where using index |
| order by a asc, b desc ,c desc | 排序不一致 升降機 |


select a.* from A a where exists(select 1 from B b where a.id=b.id)
以上查詢使用了exists語句,exists()會執行A.length次,它并不緩存exists()結果集,因為exists()結果集的內容并不重要,重要的是結果集中是否有記錄,如果有則返回true,沒有則返回false. 它的查詢過程類似于以下過程
List resultSet=[]; Array A=(select * from A)
for(int i=0;i<A.length;i++) { if(exists(A[i].id) { //執行select 1 from B b where b.id=a.id是否有記錄返回 resultSet.add(A[i]); } } return resultSet;
當B表比A表數據大時適合使用exists(),因為它沒有那么遍歷操作,只需要再執行一次查詢就行. 如:A表有10000條記錄,B表有1000000條記錄,那么exists()會執行10000次去判斷A表中的id是否與B表中的id相等. 如:A表有10000條記錄,B表有100000000條記錄,那么exists()還是執行10000次,因為它只執行A.length次,可見B表數據越多,越適合exists()發揮效果. 再如:A表有10000條記錄,B表有100條記錄,那么exists()還是執行10000次,還不如使用in()遍歷10000*100次,因為in()是在內存里遍歷比較,而exists()需要查詢數據庫,我們都知道查詢數據庫所消耗的性能更高,而內存比較很快.show VARIABLES like '%slow_query_log%';
顯示是否開啟mysql慢查詢日志
set global slow_query_log=0;
關閉mysql慢查詢日志
set global slow_query_log=1;
開啟mysql慢查詢日志
show VARIABLES like '%long_query_time%';
顯示超過多長時間即為 慢查詢
set global long_quert_time=10;
修改慢查詢時間為10秒,當查詢語句時間超過10秒即為慢查詢
show global status like '%Slow_queries%';
顯示一共有幾條慢查詢語句
[root@iZ0jlh2zn42cgftmrf6p6sZ data]# cat mysql-slow.log
linux查詢慢sql
CREATE TABLE dept( id INT UNSIGNED PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, deptno MEDIUMINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT 0, dname VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '', loc VARCHAR(13) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' )ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=GBK; CREATE TABLE emp( id INT UNSIGNED PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, empno MEDIUMINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT 0, #編號 enname VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '', #名字 job VARCHAR(9) NOT NULL DEFAULT '', #工作 mgr MEDIUMINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT 0, #上級編號 hiredate DATE NOT NULL, #入職時間 sal DECIMAL(7,2) NOT NULL, #薪水 comm DECIMAL(7,2) NOT NULL, #紅利 deptno MEDIUMINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 #部門編號 )ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=GBK;
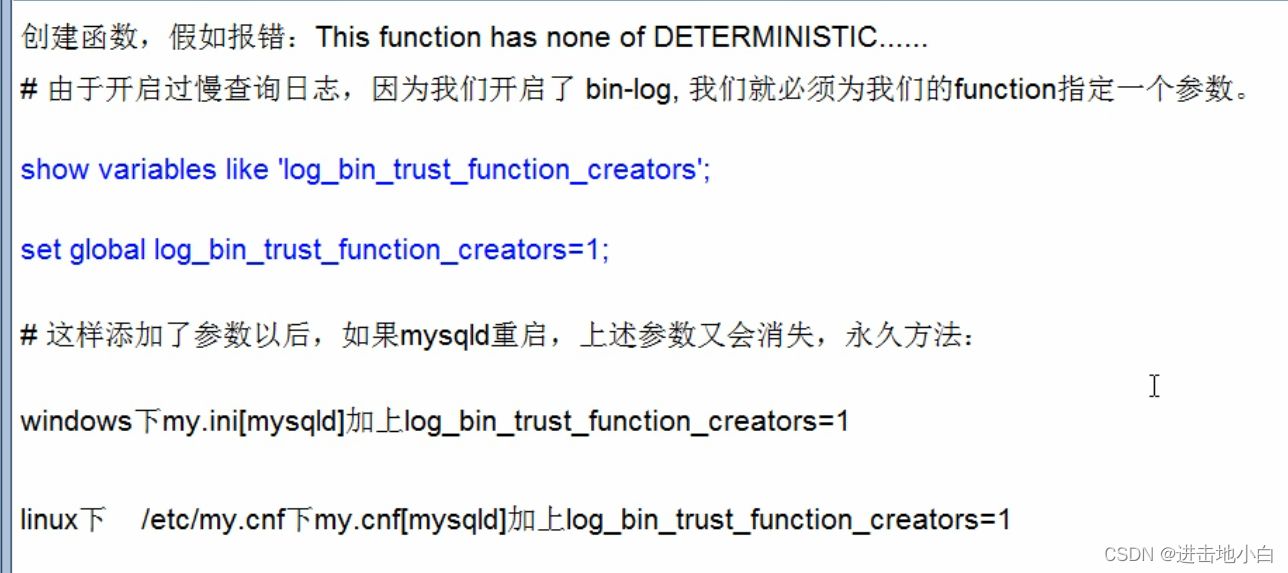
show variables like 'log_bin_trust_function_creators'; set global log_bin_trust_function_creators=1;
創建函數:隨機產生部門編號 隨機產生字符串
DELIMITER $$是因為sql都是;進行結尾但是創建函數過程要多次使用;所以改變sql執行結束的條件為輸入$$,相當于代替了分號' ;'
//定義函數1 DELIMITER $$ CREATE FUNCTION rand_string(n INT) RETURNS VARCHAR(255) BEGIN DECLARE chars_set VARCHAR(100) DEFAULT 'abcdefghigklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIGKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'; DECLARE return_str VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT ''; DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 0; WHILE i < n DO SET return_str = CONCAT(return_str,SUBSTRING(chars_set,FLOOR(1 + RAND()*52),1)); SET i = i + 1; END WHILE; RETURN return_str; END $$ //定義函數2 DELIMITER $$ CREATE FUNCTION rand_num() RETURNS INT(5) BEGIN DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 0; SET i = FLOOR(100 + RAND()*10); RETURN i; END $$ //定義存儲過程1 DELIMITER $$ CREATE PROCEDURE insert_emp(IN start INT(10), IN max_num INT(10)) BEGIN DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 0; SET autocommit = 0; REPEAT SET i = i + 1; INSERT INTO emp(empno, enname, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno) VALUES((start + i),rand_string(6),'SALESMAN',0001,CURDATE(),2000,400,rand_num()); UNTIL i = max_num END REPEAT; COMMIT; END $$ //定義存儲過程2 DELIMITER $$ CREATE PROCEDURE insert_dept(IN start INT(10), IN max_num INT(10)) BEGIN DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 0; SET autocommit = 0; REPEAT SET i = i + 1; INSERT INTO dept(deptno,dname,loc) VALUES((start + i),rand_string(10),rand_string(8)); UNTIL i = max_num END REPEAT; COMMIT; END $$ //開始插入數據 DELIMITER ; call insert_dept(100,10); call insert_emp(100001,500000); show Profile分析sql mysql> show variables like 'profiling'; +---------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +---------------+-------+ | profiling | OFF | +---------------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> set profiling=on; Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec) mysql> show variables like 'profiling'; +---------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +---------------+-------+ | profiling | ON | +---------------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.01 sec) ————————————————
隨便寫幾條插入語句‘
顯示查詢操作語句的速度
mysql> show profiles; +----------+------------+----------------------------------------------------------------+ | Query_ID | Duration | Query | +----------+------------+----------------------------------------------------------------+ | 1 | 0.00125325 | show variables like 'profiling' | | 2 | 0.00018850 | select * from dept | | 3 | 0.00016825 | select * from tb1_emp e inner join tbl_dept d on e.deptId=d.id | | 4 | 0.00023900 | show tables | | 5 | 0.00031125 | select * from tbl_emp e inner join tbl_dept d on e.deptId=d.id | | 6 | 0.00024775 | select * from tbl_emp e inner join tbl_dept d on e.deptId=d.id | | 7 | 0.00023725 | select * from tbl_emp e inner join tbl_dept d on e.deptId=d.id | | 8 | 0.00023825 | select * from tbl_emp e left join tbl_dept d on e.deptId=d.id | | 9 | 0.35058075 | select * from emp group by id%10 limit 15000 | | 10 | 0.35542250 | select * from emp group by id%10 limit 15000 | | 11 | 0.00024550 | select * from tbl_emp e left join tbl_dept d on e.deptId=d.id | | 12 | 0.36441850 | select * from emp group by id%20 order by 5 | +----------+------------+----------------------------------------------------------------+ 12 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
顯示查詢過程 sql生命周期
mysql> show profile cpu,block io for query 3; +----------------------+----------+----------+------------+--------------+---------------+ | Status | Duration | CPU_user | CPU_system | Block_ops_in | Block_ops_out | +----------------------+----------+----------+------------+--------------+---------------+ | starting | 0.000062 | 0.000040 | 0.000021 | 0 | 0 | | checking permissions | 0.000004 | 0.000003 | 0.000001 | 0 | 0 | | checking permissions | 0.000015 | 0.000006 | 0.000003 | 0 | 0 | | Opening tables | 0.000059 | 0.000039 | 0.000020 | 0 | 0 | | query end | 0.000004 | 0.000002 | 0.000001 | 0 | 0 | | closing tables | 0.000002 | 0.000001 | 0.000000 | 0 | 0 | | freeing items | 0.000014 | 0.000010 | 0.000005 | 0 | 0 | | cleaning up | 0.000009 | 0.000006 | 0.000003 | 0 | 0 | +----------------------+----------+----------+------------+--------------+---------------+ 8 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec) mysql> show profile cpu,block io for query 12; +----------------------+----------+----------+------------+--------------+---------------+ | Status | Duration | CPU_user | CPU_system | Block_ops_in | Block_ops_out | +----------------------+----------+----------+------------+--------------+---------------+ | starting | 0.000063 | 0.000042 | 0.000021 | 0 | 0 | | checking permissions | 0.000006 | 0.000003 | 0.000002 | 0 | 0 | | Opening tables | 0.000013 | 0.000009 | 0.000004 | 0 | 0 | | init | 0.000028 | 0.000017 | 0.000008 | 0 | 0 | | System lock | 0.000007 | 0.000004 | 0.000002 | 0 | 0 | | optimizing | 0.000004 | 0.000002 | 0.000002 | 0 | 0 | | statistics | 0.000014 | 0.000010 | 0.000004 | 0 | 0 | | preparing | 0.000008 | 0.000005 | 0.000003 | 0 | 0 | | Creating tmp table | 0.000028 | 0.000018 | 0.000009 | 0 | 0 | | Sorting result | 0.000003 | 0.000002 | 0.000001 | 0 | 0 | | executing | 0.000002 | 0.000002 | 0.000001 | 0 | 0 | | Sending data | 0.364132 | 0.360529 | 0.002426 | 0 | 0 | | Creating sort index | 0.000053 | 0.000034 | 0.000017 | 0 | 0 | | end | 0.000004 | 0.000002 | 0.000002 | 0 | 0 | | query end | 0.000007 | 0.000005 | 0.000002 | 0 | 0 | | removing tmp table | 0.000005 | 0.000003 | 0.000002 | 0 | 0 | | query end | 0.000003 | 0.000002 | 0.000001 | 0 | 0 | | closing tables | 0.000006 | 0.000004 | 0.000002 | 0 | 0 | | freeing items | 0.000023 | 0.000016 | 0.000007 | 0 | 0 | | cleaning up | 0.000012 | 0.000007 | 0.000004 | 0 | 0 | +----------------------+----------+----------+------------+--------------+---------------+ 20 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
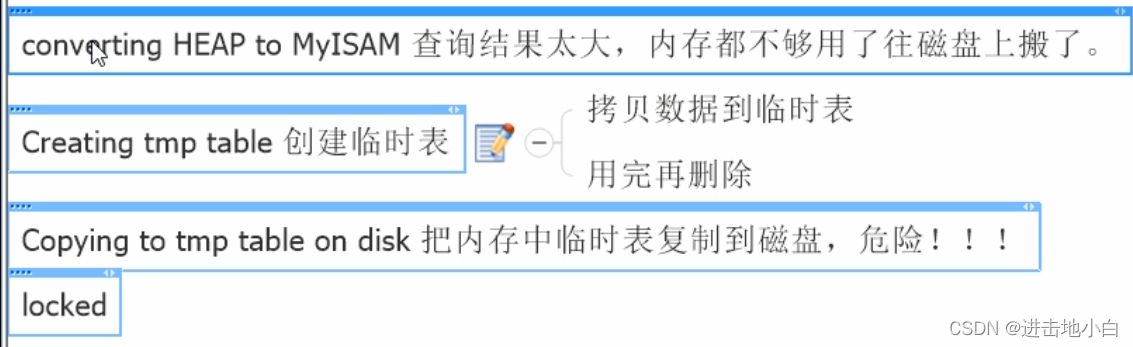
如果出現以上這四個 中的任何一個就需要 優化查詢語句
set global general_log=1; set global log_output='TABLE';
此后你編寫的sql語句將會記錄到mysql庫里的general_log表,可以用下面的命令查看
select * from mysql.general_log; mysql> select * from mysql.general_log; +----------------------------+---------------------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+---------------------------------+ | event_time | user_host | thread_id | server_id | command_type | argument | +----------------------------+---------------------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+---------------------------------+ | 2021-12-06 11:53:53.457242 | root[root] @ localhost [] | 68 | 1 | Query | select * from mysql.general_log | +----------------------------+---------------------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+---------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
讀鎖(共享鎖):針對同一份數據,多個讀操作可以同時進行而不會互相影響
寫鎖(排它鎖):當前寫操作沒有完成時,它會阻斷其他寫鎖和讀鎖
行鎖:偏向InnoDB引擎,開銷大,加鎖慢,會出現死鎖:鎖定粒度最小,發生鎖沖突的概率最低,并發量高
表鎖:偏向myisam引擎,開銷小,加鎖快;鎖定粒度大,發生鎖沖突的概率最高,并發度最低
在下面進行表鎖的測試
use big_data;
create table mylock (
id int not null primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20) default ''
) engine myisam;
insert into mylock(name) values('a');
insert into mylock(name) values('b');
insert into mylock(name) values('c');
insert into mylock(name) values('d');
insert into mylock(name) values('e');
select * from mylock;lock table mylock read,book write;## 讀鎖鎖mylock 寫鎖鎖book show open tables; ##顯示哪些表被加鎖了 unlock tables;##取消鎖
##添加讀鎖后不可修改 mysql> lock table mylock read;##1 Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from mylock;##1 +----+------+ | id | name | +----+------+ | 1 | a | | 2 | b | | 3 | c | | 4 | d | | 5 | e | +----+------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> update mylock set name='a2' where id=1; ##1 ERROR 1099 (HY000): Table 'mylock' was locked with a READ lock and can't be updated ##改不了當前讀鎖鎖住的表 ##讀不了其他表 mysql> select * from book;##1 ERROR 1100 (HY000): Table 'book' was not locked with LOCK TABLES
為了區分兩個命令 把1當作原有的mysql命令終端上的操作,2當作新建的mysql終端
新建一個mysql終端命令操作
##新建一個mysql終端命令操作 mysql> update mylock set name='a3' where id=1; ##2
發現會出現阻塞操作
在原有的mysql命令終端上取消鎖
unlock tables;##1 Query OK, 1 row affected (2 min 1.46 sec) ##2 Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0 ##2
會發現阻塞了兩分鐘多
總結 :當讀鎖鎖表mylock之后:1.查詢操作:當前client(終端命令操作1)可以進行查詢表mylock
其他client(終端命令操作2)也可以查詢表mylock 2.DML操作(增刪改)當前client會失效報錯 ERROR 1099 (HY000): Table 'mylock' was locked with a READ lock and can't be updated 其他client進行DML操作會讓mysql陷入阻塞狀態直到當前session釋放鎖
mysql> lock table mylock write; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) 給當前session mylock表加上寫鎖 mysql> update mylock set name='a4'where id=1 ; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0 mysql> select * from mylock; +----+------+ | id | name | +----+------+ | 1 | a4 | | 2 | b | | 3 | c | | 4 | d | | 5 | e | +----+------+ mysql> select * from book; ERROR 1100 (HY000): Table 'book' was not locked with LOCK TABLES
會發現無法操其他表但是可以操作加上鎖的表
再開啟一個新的客戶端測試被鎖住的表
mysql> select * from mylock; 5 rows in set (2 min 30.92 sec)
發現新的客戶端上操作(增刪改查)被寫鎖鎖住的表會陷入阻塞狀態
作
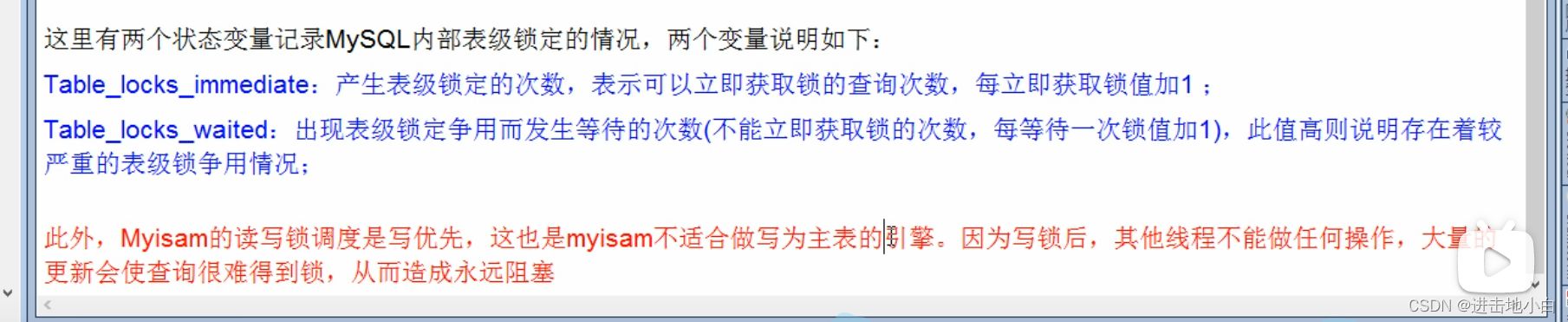
分析表鎖定
mysql> show status like 'table%'; +----------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +----------------------------+-------+ | Table_locks_immediate | 194 | | Table_locks_waited | 0 | | Table_open_cache_hits | 18 | | Table_open_cache_misses | 2 | | Table_open_cache_overflows | 0 | +----------------------------+-------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
InnoDB 的行鎖模式
InnoDB 實現了以下兩種類型的行鎖。
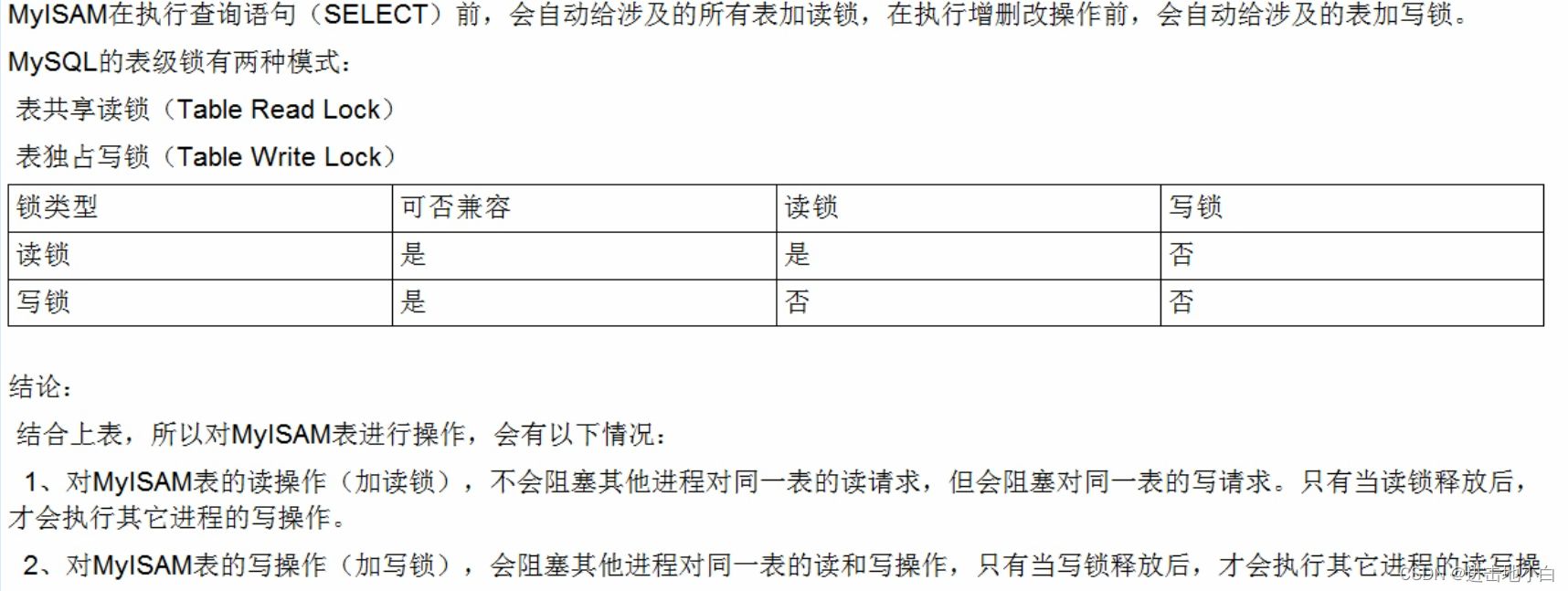
共享鎖(S):又稱為讀鎖,簡稱S鎖,共享鎖就是多個事務對于同一數據可以共享一把鎖,都能訪問到數據,但是只能讀不能修改。
排他鎖(X):又稱為寫鎖,簡稱X鎖,排他鎖就是不能與其他鎖并存,如一個事務獲取了一個數據行的排他鎖,其他事務就不能再獲取該行的其他鎖,包括共享鎖和排他鎖,但是獲取排他鎖的事務是可以對數據就行讀取和修改。
對于UPDATE、DELETE和INSERT語句,InnoDB會自動給涉及數據集加排他鎖(X);
對于普通SELECT語句,InnoDB不會加任何鎖;
可以通過以下語句顯示給記錄集加共享鎖或排他鎖 。
共享鎖(S):SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE ... LOCK IN SHARE MODE 排他鎖(X) :SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE ... FOR UPDATE
由于行鎖支持事務,在此復習一下
事務是一組由SQL語句組成的邏輯處理單元,事務具有四個屬性:ACID
原子性(Atomicity):事務是一個原子操作單元,其對數據的操作要么全部執行,要么全不執行。
一致性(Consistent):在事務開始和完成時,數據都必須保持一致狀態。這意味著所有相關的數據都必須應用于事務的修改,以保持數據的完整性;事務結束時,所有的內部數據結構(如B樹索引或雙向鏈表)也都必須是正確的。
隔離性(Isolation):數據庫提供一定的隔離機制,保證事務在不受外部并發操作影響的"獨立"環境執行。這意味著事務處理過程的中間狀態對外部都是不可見的,反之亦然。
持久性(Durable):事務完成后,它對數據的操作是永久性的,哪怕出現系統故障也能維持
并發事務帶來的問題:
更新丟失,臟讀,不可重復讀,幻讀
| ACID屬性 | 含義 |
|---|---|
| 原子性(Atomicity) | 事務是一個原子操作單元,其對數據的修改,要么全部成功,要么全部失敗。 |
| 一致性(Consistent) | 在事務開始和完成時,數據都必須保持一致狀態。 |
| 隔離性(Isolation) | 數據庫系統提供一定的隔離機制,保證事務在不受外部并發操作影響的 “獨立” 環境下運行。 |
| 持久性(Durable) | 事務完成之后,對于數據的修改是永久的。 |
并發事務處理帶來的問題
| 問題 | 含義 |
|---|---|
| 丟失更新(Lost Update) | 當兩個或多個事務選擇同一行,最初的事務修改的值,會被后面的事務修改的值覆蓋。 |
| 臟讀(Dirty Reads) | 當一個事務正在訪問數據,并且對數據進行了修改,而這種修改還沒有提交到數據庫中,這時,另外一個事務也訪問這個數據,然后使用了這個數據。 |
| 不可重復讀(Non-Repeatable Reads) | 一個事務在讀取某些數據后的某個時間,再次讀取以前讀過的數據,卻發現和以前讀出的數據不一致。 |
| 幻讀(Phantom Reads) | 一個事務按照相同的查詢條件重新讀取以前查詢過的數據,卻發現其他事務插入了滿足其查詢條件的新數據。 |
事務隔離級別
為了解決上述提到的事務并發問題,數據庫提供一定的事務隔離機制來解決這個問題。數據庫的事務隔離越嚴格,并發副作用越小,但付出的代價也就越大,因為事務隔離實質上就是使用事務在一定程度上“串行化” 進行,這顯然與“并發” 是矛盾的。
數據庫的隔離級別有4個,由低到高依次為Read uncommitted、Read committed、Repeatable read、Serializable,這四個級別可以逐個解決臟寫、臟讀、不可重復讀、幻讀這幾類問題。
| 隔離級別 | 丟失更新 | 臟讀 | 不可重復讀 | 幻讀 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Read uncommitted | × | √ | √ | √ |
| Read committed | × | × | √ | √ |
| Repeatable read(默認) | × | × | × | √ |
| Serializable | × | × | × | × |
備注 : √ 代表可能出現 , × 代表不會出現 。
Mysql 的數據庫的默認隔離級別為 Repeatable read , 查看方式:
show variables like 'tx_isolation';
行鎖測試建表, 案例準備工作
create table test_innodb_lock( id int(11), name varchar(16), sex varchar(1) )engine = innodb default charset=utf8; insert into test_innodb_lock values(1,'100','1'); insert into test_innodb_lock values(3,'3','1'); insert into test_innodb_lock values(4,'400','0'); insert into test_innodb_lock values(5,'500','1'); insert into test_innodb_lock values(6,'600','0'); insert into test_innodb_lock values(7,'700','0'); insert into test_innodb_lock values(8,'800','1'); insert into test_innodb_lock values(9,'900','1'); insert into test_innodb_lock values(1,'200','0'); create index idx_test_innodb_lock_id on test_innodb_lock(id); create index idx_test_innodb_lock_name on test_innodb_lock(name);
還是開倆個終端測試,關閉事自動事務提交,因為自動事務提交會自動加鎖釋放鎖;
mysql> set autocommit=0; mysql> set autocommit=0;
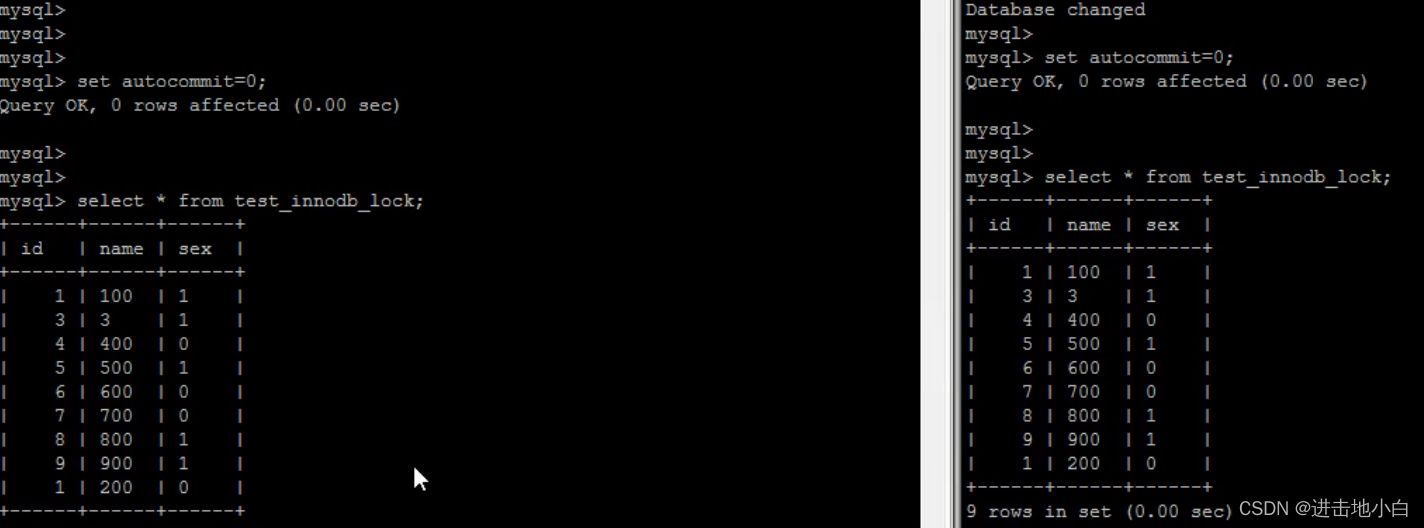
會發現查詢無影響
對左邊進行更新操作
mysql> update test_innodb_lock set name='100' where id=3; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) Rows matched: 1 Changed: 0 Warnings: 0
對左邊進行更新操作
對右邊進行更新操作后停止操作
mysql> update test_innodb_lock set name='340' where id=3; ERROR 1205 (HY000): Lock wait timeout exceeded; try restarting transaction
會發現進行阻塞了 直到鎖釋放或者提交事務(commit)為止
對于innodb引擎來說,對某一行數據進行DML(增刪改)操作會對操作的那行添加排它鎖
別的事務就不能執行這行語句了,但是可以操作其他行的數據
無索引行鎖會升級成表鎖:如果不通過索引條件檢索數據,那么innodb會對表中所有記錄加鎖,實際效果和表鎖一樣
記住進行操作時使用索引:innodb引擎索引失效時時行鎖會升級為表鎖
mysql> update test_innodb_lock set sex='2' where name=400; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) Rows matched: 2 Changed: 0 Warnings: 0
注意這里name沒有加單引號 索引失效
mysql> update test_innodb_lock set sex='3' where id=3; Query OK, 1 row affected (23.20 sec) Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
發現了對其他行操作也陷入了阻塞狀態,這是沒加索引導致的行鎖升級為表鎖
本來只對一行數據加鎖 但是由于忘記給name字段加單引號導致索引失效給全表都加上了鎖;
當我們使用范圍條件而不是想等條件進行檢索數據,并請求共享或排它鎖,在那個范圍條件中有不存在的記錄,叫做間隙,innodb也會對這個間隙進行加鎖,這種鎖機制就叫做間隙鎖
mysql> select * from test_innodb_lock; +------+------+------+ | id | name | sex | +------+------+------+ | 1 | 100 | 2 | | 3 | 100 | 3 | | 4 | 400 | 0 | | 5 | 500 | 1 | | 6 | 600 | 0 | | 7 | 700 | 3 | | 8 | 800 | 1 | | 9 | 900 | 2 | | 1 | 200 | 0 | +------+------+------+ 沒有id為2的數據

行鎖征用情況查看
mysql> show status like 'innodb_row_lock%'; +-------------------------------+--------+ | Variable_name | Value | +-------------------------------+--------+ | Innodb_row_lock_current_waits | 0 | | Innodb_row_lock_time | 284387 | | Innodb_row_lock_time_avg | 21875 | | Innodb_row_lock_time_max | 51003 | | Innodb_row_lock_waits | 13 | +-------------------------------+--------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec) Innodb_row_lock_current_waits: 當前正在等待鎖定的數量 Innodb_row_lock_time: 從系統啟動到現在鎖定總時間長度 Innodb_row_lock_time_avg:每次等待所花平均時長 Innodb_row_lock_time_max:從系統啟動到現在等待最長的一次所花的時間 Innodb_row_lock_waits: 系統啟動后到現在總共等待的次數
InnoDB存儲引擎由于實現了行級鎖定,雖然在鎖定機制的實現方面帶來了性能損耗可能比表鎖會更高一些,但是在整體并發處理能力方面要遠遠由于MyISAM的表鎖的。當系統并發量較高的時候,InnoDB的整體性能和MyISAM相比就會有比較明顯的優勢。
但是,InnoDB的行級鎖同樣也有其脆弱的一面,當我們使用不當的時候,可能會讓InnoDB的整體性能表現不僅不能比MyISAM高,甚至可能會更差。
優化建議:
盡可能讓所有數據檢索都能通過索引來完成,避免無索引行鎖升級為表鎖。
合理設計索引,盡量縮小鎖的范圍
盡可能減少索引條件,及索引范圍,避免間隙鎖
盡量控制事務大小,減少鎖定資源量和時間長度
盡可使用低級別事務隔離(但是需要業務層面滿足需求)
看完上述內容,你們掌握怎樣進行MySQL的學習的方法了嗎?如果還想學到更多技能或想了解更多相關內容,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道,感謝各位的閱讀!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。