您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
locate
find
壓縮與歸檔
locate
主要用途
查詢系統上預建的文件索引數據庫
locate - find files by namelocate [OPTION]... PATTERN...
locate查詢文件時,會去搜索/var/lib/mlocate/mlocage.db, 這個數據庫會在系統空閑時自動周期性進行,一般一天一次更新,手動更新命令為updatedb, 索引的構建需要遍歷整個根文件系統,比較消耗資源。但locate有如下特性:
1. 模糊查找,速度快 2. 非實時查找,搜索的是文件的全路徑,而非文件名 3. 可能只搜索用戶具有讀取與執行權限的目錄
常用參數
-d: --database, 指定數據庫所在的目錄
-i: --ignore-case, 搜索時忽略大小寫
-n N: 只列舉前N個匹配項目
-r: --regexp, 搜索時支持正則表達式
使用示例
查找/etc/目錄下以sh開頭的文件:
[root@centos7 ~#]locate /etc/sh /etc/shadow /etc/shadow- /etc/shells [root@centos7 ~#]locate -r "/etc/\<sh" # 正則,錨定詞首 /etc/shadow /etc/shadow- /etc/shells [root@centos7 ~#]
更新數據庫
[root@centos7 ~#]locate ~/a /root/anaconda-ks.cfg [root@centos7 ~#]updatedb [root@centos7 ~#]locate ~/a /root/a.sh /root/anaconda-ks.cfg [root@centos7 ~#]
忽略字符大小寫
[root@centos7 ~#]locate -i ~/d /root/Desktop/root/Documents/root/Downloads /root/d1 /root/dd /var/lib/pcp/pmdas/root/domain.h [root@centos7 ~#]
find
主要用途
實時查找文件
find - search for files in a directory hierarchy find [-H] [-L] [-P] [-D debugopts] [-Olevel] [path...] [expression]
find命令是一個實時查找工具,通過遍歷指定路徑而完成對文件的查找;在使用該命令時,如果不選定參數,則在當前目錄下查找子目錄與文件并顯示之;另外,任何位于參數之前的字符串,都將視為欲查找的目錄名。由于是實時遍歷查找,find有如下特性:
精確實時查找,速度慢 可能只搜索用戶具備讀取和執行權限的目錄
find語法:
find [OPTION]... [查找路徑] [查找條件] [處理動作]查找路徑:指定具體目標路徑,默認為當前目錄 查找條件:指定的查找標準,可以是文件名、大小、類型、權限等標準進行;默認為找出指定路徑下的所有文件 處理動作:對符合條件的文件做操作,默認輸出至屏幕
查找條件
1. 根據文件名和inode查找 2. 根據屬主、屬組查找 3. 根據文件類型查找 4. 根據邏輯組合條件查找 5. 根據文件大小來查找 6. 根據時間戳來查找 7. 根據權限來查找
處理動作
1. -print: 默認動作,顯示至屏幕
2. -ls: 類似于對查找到的文件執行 ls -l 命令
3. -delete: 刪除查找到的文件
4. -fls file: 查找到的所有長格式的信息保存至指定文件中
5. -ok COMMMAND {} \; 對查找到的每個文件執行由COMMAND指定的命令,且都會交互式要求用戶確認
6. -exec COMMAND {} \; 對查找到的每個文件執行由COMMAND指定的命令;
7. {}: 用于引用查找至的文件名稱自身
8. find 傳遞查找到的文件至后面指定的命令時,查找到所有符號條件的文件一次性傳遞給后面的命令
9. 有些命令不能接受過多的參數,此時命令執行可能會失敗,用 xargs 來規避此問題
find |xargs COMMAND常用參數
文件名和inode類:
-name "文件名稱": 支持使用glob, *, ?, [], [^]
-iname "文件名稱": 不區分字母大小寫
-inum n: 按inode號查找
-somefile name: 相同的inode號文件
-links n: 鏈接數為n的文件
-regex "PATTERN": 以PATTERN匹配整個文件路徑字符串,而不僅僅是文件名稱
屬主屬組類:
-user USERNAME: 查找屬主為指定用戶(UID)的文件
-group GROUPNAME: 查找屬組為指定組(GID)的文件
-uid UserID: 查找屬主為指定的UID號的文件
-gid GroupID: 查找屬組為指定的GID號的文件
-nouser: 查找沒有屬主的文件
-nogroup: 查找沒有屬組的文件
文件類型類:
b block (buffered) special c character (unbuffered) special d directory p named pipe (FIFO)f regular file l symbolic link s socket
邏輯組合條件類:
組合條件: 與:-a 或:-o 非:-not, ! 摩根定律: (非P) 或(非Q) = 非(P且Q) (非P) 且 (非Q) = 非(P或Q) 示例: !A -o !B = !(A -a B) !A -a !B = !(A -o B)
文件大小類:
-size [+|-]#UNIT 常用單位:k,M,G #UNIT: (#-1,#] 如:5M 表示 (4M,5M] -#UNIT: [0,#-1] 如:-5M 表示 [0,5M] +#UNIT: (#,oo) 如:+5M 表示 (6M,oo)
關于文件大小類的解釋:為什么-size 5M 還是找精確的5M而是表示(4M,5M], 試想文件的大小指什么?是指文件數據的大小還是包括了元數據后的大小,那你找元數據的大小有意義嗎?但文件的大小肯定是包含元數據大小的,而我們一般以文件大小找文件時往往考慮的是文件數據的大小;另外,精確查找一定大小的文件意義不大;所以這里的大小會有1個單位的浮動。
時間戳類:
以”天”為單位: -atime [+|-]# #: [#,#+1) +#: [#+1,oo) -#: [0,#) -mtime -ctime 以“分鐘”為單位: -amin -mmin -cmin
關于時間戳類的解釋:為什么-atime 3 表示的是 [3,4),這個就很好解釋了,我們這兒所說的時間是指時間段而非時刻,一“天”與一“分鐘”都是指一個時間段,只有[3,4)這個半閉半開的區間才能完整地表示第三天。
權限類:
-perm [/|-]MODE MODE: 精確匹配權限 /MODE: 任何一類(u,g,o)對象的權限中只要能一位匹配即可,屬于或關系。以前用'+',CentOS 7以'/'替代之 -MODE: 每一類對象都必須同時擁有指定權限,屬于與關系 0:表示不關注 示例: find -perm 644 表示要嚴格匹配644的文件 find -perm +222 表示u,g,o任何一類用戶有寫權限即匹配 find -perm -222 表示僅嚴格匹配寫權限,即每個用戶必須要有寫權限 find -perm -002 表示僅嚴格匹配other用戶的寫權限
使用示例
1.將配置文件備份到指定目錄下并添加擴展名.org
[root@centos7 ~#]find -name "*.conf" -exec cp -r {} /testdir/{}.org \;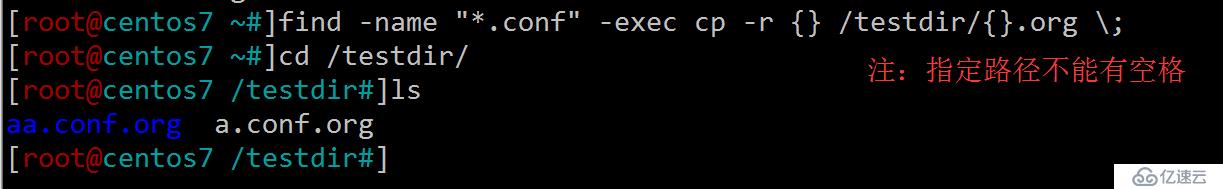
2.提示刪除存在時間超過3天以上的liansir的臨時文件
[root@centos7 ~#]find /tmp -ctime +3 -user liansir -ok rm {} \;3.在主目錄中查找可被其它用戶寫入的文件
[root@centos7 ~#]find ~ -perm -002 -exec chmod o-w {} \;4.查找/var目錄下屬主為root,且屬組為mail的所有文件
[root@centos7 ~#]find /var/ -user root -group mail -ls 402656342 4 drwxrwxr-x 2 root mail 4096 Aug 15 22:56 /var/spool/mail 407540491 4 -rw------- 1 root mail 2878 Aug 14 00:25 /var/spool/mail/root [root@centos7 ~#]
5.查找/var目錄下不屬于root、lp、gdm的所有文件
[root@centos7 ~#]find /var/ ! -user root ! -user lp ! -user gdm
6.查找/var目錄下最近一周內其內容修改過,同時屬主不為root,也不是postfix的文件
[root@centos7 ~#]find /var/ -ctime -7 ! -user root ! -user postfix
7.查找當前系統上沒有屬主或屬組,且最近一個周內曾被訪問過的文件
[root@centos7 ~#]find / -nouser -nogroup -atime -7 | wc -l find: ‘/proc/7562/task/7562/fd/6’: No such file or directory find: ‘/proc/7562/task/7562/fdinfo/6’: No such file or directory find: ‘/proc/7562/fd/6’: No such file or directory find: ‘/proc/7562/fdinfo/6’: No such file or directory 15 [root@centos7 ~#]
8.查找/etc目錄下大于1M且類型為普通文件的所有文件
[root@centos7 ~#]find /etc/ -type f -size +1M /etc/udev/hwdb.bin /etc/selinux/targeted/policy/policy.29 /etc/brltty/zh-tw.ctb [root@centos7 ~#]
9.查找/etc目錄下所有用戶都沒有寫權限的文件
[root@centos7 ~#]find /etc/ ! -perm /222
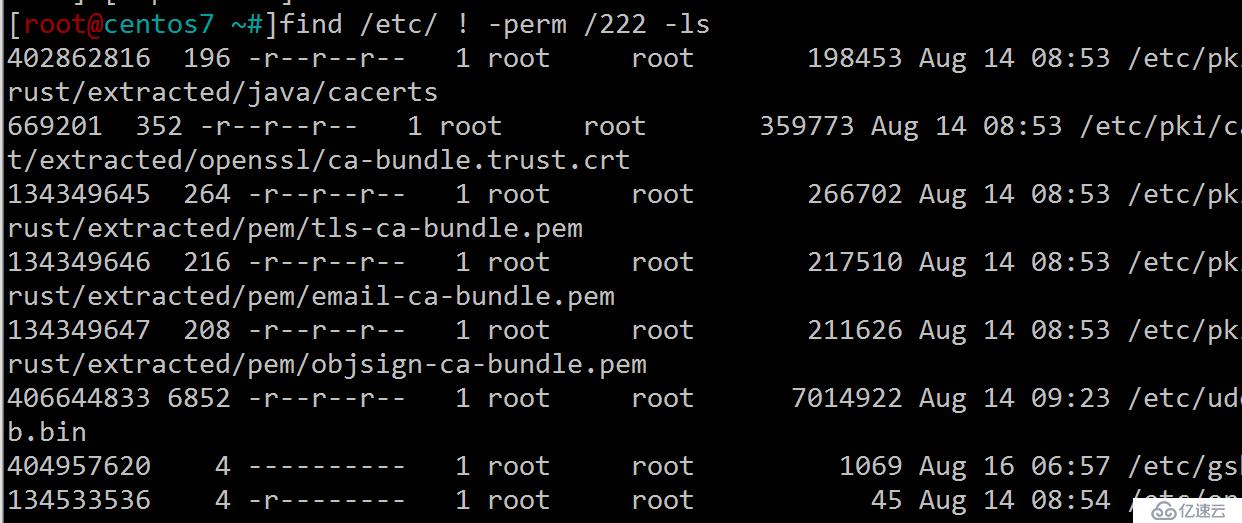
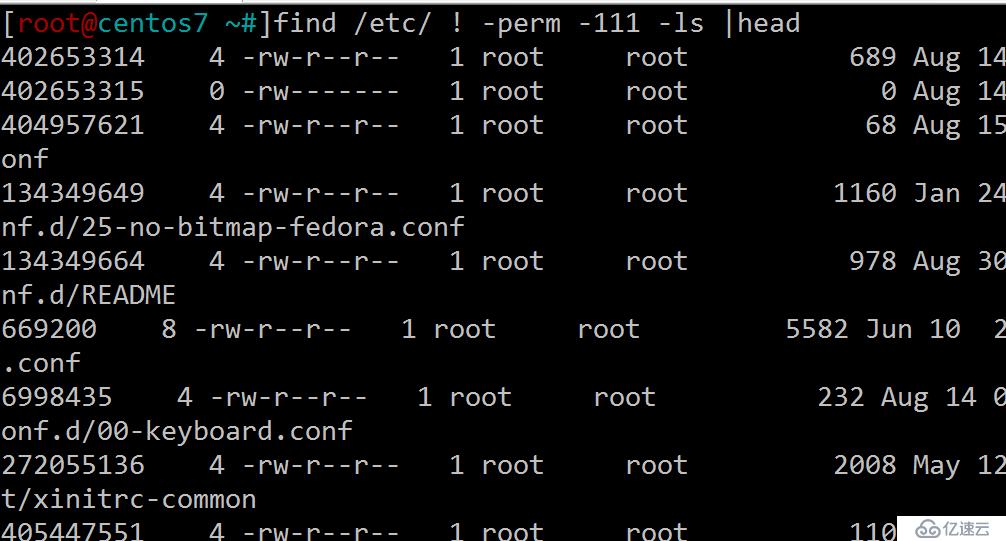
10.查找/etc目錄下至少有一類用戶沒有執行權限的文件
[root@centos7 ~#]find /etc/ ! -perm -111 # 至少有一類用戶沒用就是所有用戶都沒有
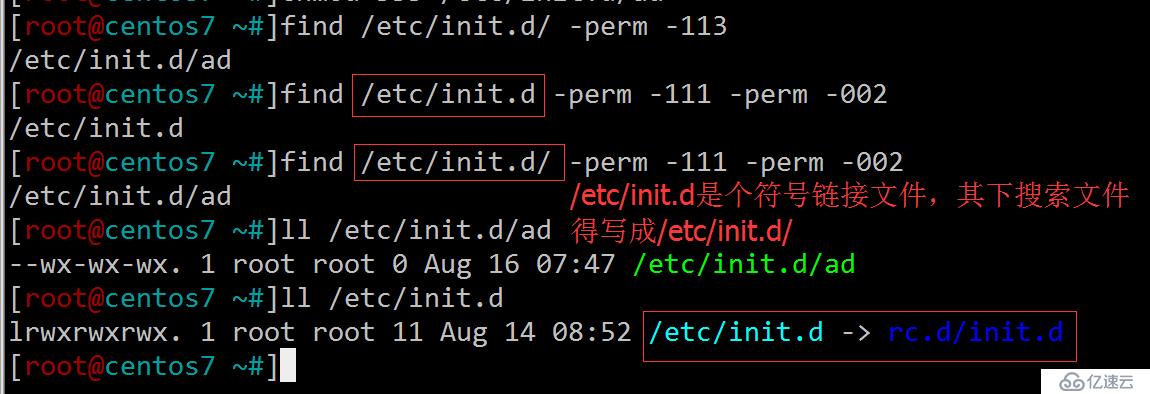
11.查找/etc/init.d目錄下,所有用戶都有執行權限,且其它用戶有寫權限的文件
[root@centos7 ~#]find /etc/init.d/ -perm -113 或 [root@centos7 ~#]find /etc/init.d/ -perm -111 -perm -002
12.摩根定律
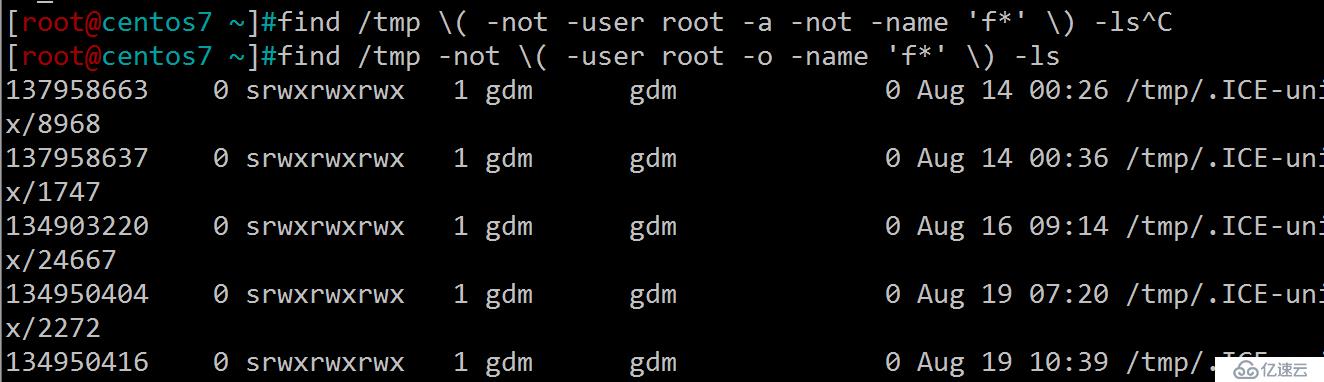
找出/tmp目錄下,屬主不是root,且文件名不以f開頭的文件
[root@centos7 ~]#find /tmp \( -not -user root -a -not -name 'f*' \) -ls 即 [root@centos7 ~]#find /tmp -not \( -user root -o -name 'f*' \) -ls
13.排除目錄
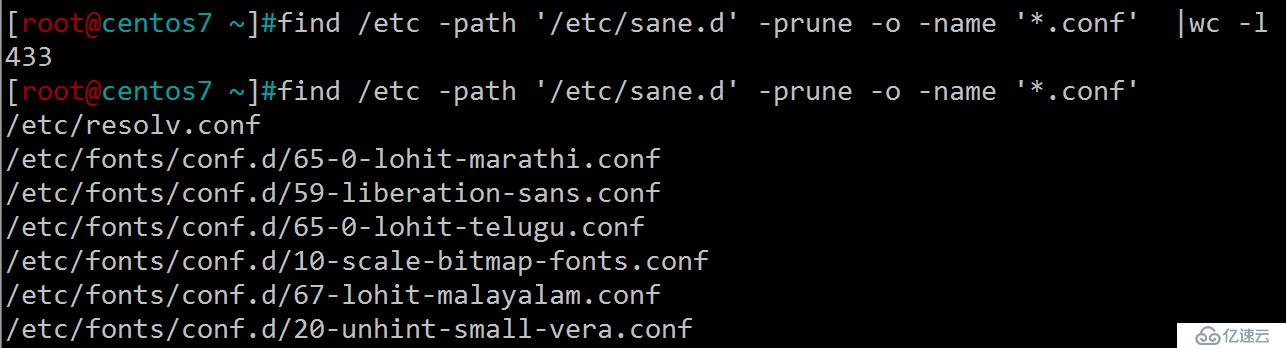
查找/etc/下,除/etc/sane.d目錄的其它所有.conf后綴的文件
[root@centos7 ~]#find /etc -path '/etc/sane.d' -prune -o -name '*.conf'
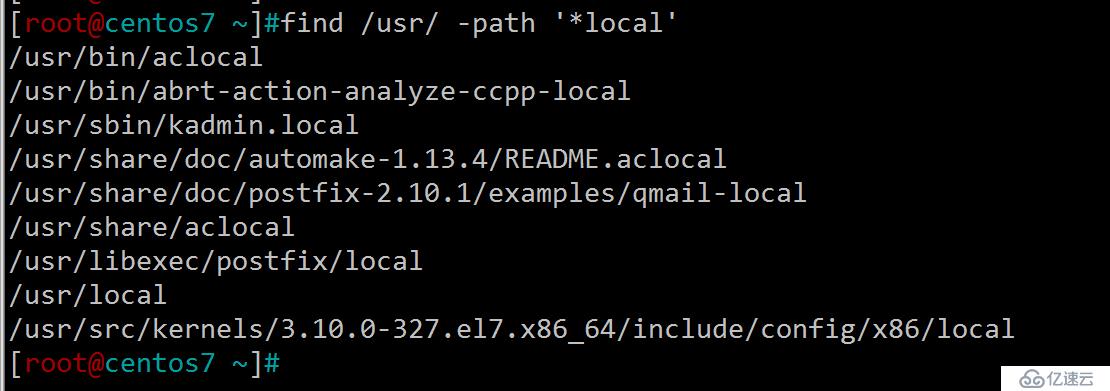
14.匹配文件路徑或文件
[root@centos7 ~]#find /usr/ -path '*local'
15.基于正則表達式匹配文件路徑
[root@centos7 ~]#find . -regex "\(.*\.txt | \.cfg\)$"
壓縮與歸檔
數據壓縮,就是在不丟失數據信息的前提下減少數據量的一種技術。
compress
compress是一個古老的壓縮工具,其壓縮文件后綴為.Z,zcat命令可查看.Z的文件,但并不解壓。
-d: 解壓縮-c: 結果輸出至標準輸出,不刪除原文件-v: 顯示詳情
使用示例
[root@centos7 /testdir]#compress passwd # 壓縮 [root@centos7 /testdir]#ls passwd.Z [root@centos7 /testdir]#compress -d passwd # 解壓 [root@centos7 /testdir]#ls passwd [root@centos7 /testdir]# [root@centos7 /testdir]#zcat passwd.Z > passwd [root@centos7 /testdir]#lspasswd passwd.Z [root@centos7 /testdir]#
gzip
gzip壓縮后的文件后綴為.gz,如果壓縮的是tar備份文件,則擴展名為.tar.gz
gzip, gunzip, zcat - compress or expand files -d: 解壓縮,相當于unzip -c: 將壓縮或解壓縮的結果輸出至標準輸出 -#:1-9,指定壓縮比zcat: 不顯示解壓縮的前提下查看文本文件內容
使用示例
[root@centos7 /testdir]#gzip passwd [root@centos7 /testdir]#ls passwd.gz passwd.Z [root@centos7 /testdir]# [root@centos7 /testdir]#zcat passwd.gz > passwd [root@centos7 /testdir]#ls passwd.gz passwd passwd.Z [root@centos7 /testdir]#
bzip2
bzipw2壓縮的文件的擴展名為.bz2
-k: keep,保留原文件 -d: 解壓縮 -#:1-9,壓縮比,默認為6bzcat: 不顯示解壓縮的前提下查看文件文件內容
使用示例
[root@centos7 /testdir]#bzip2 passwd [root@centos7 /testdir]#ls passwd.gz passwd.bz2 passwd.Z[ root@centos7 /testdir]#bzcat passwd.bz2 > passwd [root@centos7 /testdir]#ls passwd.gz passwd passwd.bz2 passwd.Z [root@centos7 /testdir]#
xz
xz壓縮后的文件擴展名為.xz
-k: keep,保留原文件 -d: 解壓縮 -#:1-9,壓縮比,默認為6xzcat: 不顯示解壓縮的前提下查看文件文件內容
[root@centos7 /testdir]#xz passwd [root@centos7 /testdir]#ls passwd.bz2 passwd.gz passwd.xz passwd.Z [root@centos7 /testdir]# [root@centos7 /testdir]#xzcat passwd.xz > passwd [root@centos7 /testdir]#ls passwd passwd.bz2 passwd.gz passwd.xz passwd.Z [root@centos7 /testdir]#
zip: 打包壓縮
文件經zip壓縮后會另外生成.zip的文件而不刪除原文件。
zip - package and compress (archive) files -r: 遞歸處理,將指定目錄下的所有文件與子目錄一并處理 -q: 不顯示執行過程
使用示例
[root@centos7 /testdir]#zip -q passwd ./passwd [root@centos7 /testdir]#ls passwd passwd.bz2 passwd.gz passwd.xz passwd.Z passwd.zip [root@centos7 /testdir]#
看看大概的壓縮情況:
[root@centos7 /testdir]#ll total 192 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 164065 Aug 19 09:06 message.zip -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 4129 Aug 19 08:46 passwd -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1526 Aug 19 08:30 passwd.bz2 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1539 Aug 19 08:39 passwd.gz -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1540 Aug 19 08:45 passwd.xz -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2151 Aug 19 08:16 passwd.Z -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1676 Aug 19 09:02 passwd.zip [root@centos7 /testdir]#
tar
tar [OPTION...] [FILE]... EXAMPLES tar -cf archive.tar foo bar # Create archive.tar from files foo and bar. tar -tvf archive.tar # List all files in archive.tar verbosely. tar -xf archive.tar # Extract all files from archive.tar.
tar命令可為文件或目錄創建檔案(備份文件),tar命令可將很多文件打包成一個文件,從而可結合壓縮工具實現歸檔并壓縮了。
常用參數
-c: --creat, 創建新的備份文件
-f: --file=ARCHIVE, 指定備份文件
-x: --extract, --get, 從備份文件中還原文件
-t: --list, 列出備份文件的內容
-v: --verbose
tar用法小結:
(1) 創建歸檔 tar -c -f /PATH/TO/SOMEFILE.tar FILE... tar cf/PATH/TO/SOMEFILE.tar FILE... (2) 查看歸檔文件中的文件列表 tar -t -f /PATH/TO/SOMEFILE.tar(3) 展開歸檔 tar -x -f /PATH/TO/SOMEFILE.tar tar -x -f /PATH/TO/SOMEFILE.tar -C /PATH/ (4) 結合壓縮工具實現:歸檔并壓縮 -j: bzip2, -z: gzip, -J: xz 打包成tar包: tar -cvf passwd.tar passwd 僅打包,不壓縮 tar -zcvf passwd.tar.gz passwd 打包并以gzip壓縮 tar -jcvf passwd.tar.bz2 passwd 打包并以bzip2壓縮 tar -Jcvf passwd.tar.xz passwd 打包并以xz壓縮
使用示例
[root@centos7 /testdir]#tar -cf passwd.tar passwd [root@centos7 /testdir]#ls passwd passwd.tar [root @centos7 /testdir]#tar -zcf passwd.tar.gz passwd [root@centos7 /testdir]#ls passwd passwd.tar passwd.tar.gz [root@centos7 /testdir]#tar -jcf passwd.tar.bz2 passwd [root@centos7 /testdir]#ls passwd passwd.tar passwd.tar.bz2 passwd.tar.gz [root@centos7 /testdir]#tar -Jcf passwd.tar.xz passwd [root@centos7 /testdir]#ls passwd passwd.tar passwd.tar.bz2 passwd.tar.gz passwd.tar.xz [root@centos7 /testdir]# [root@centos7 /testdir]#tar -tvf passwd.tar # 查詢 -rw-r--r-- root/root 10240 2016-08-19 09:27 passwd [root@centos7 /testdir]#tar -tvf passwd.tar.gz -rw-r--r-- root/root 10240 2016-08-19 09:27 passwd [root@centos7 /testdir]# [root@centos7 /testdir]#tar xf passwd.tar # 解壓 [root@centos7 /testdir]#ls passwd passwd.tar passwd.tar.bz2 passwd.tar.gz passwd.tar.xz [root@centos7 /testdir]#tar xf passwd.tar.gz [root@centos7 /testdir]#ls passwd passwd.tar passwd.tar.bz2 passwd.tar.gz passwd.tar.xz [root@centos7 /testdir]# [root@centos7 /testdir]#ll total 44 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 10240 Aug 19 09:27 passwd -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 20480 Aug 19 10:52 passwd.tar -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 116 Aug 19 10:53 passwd.tar.bz2 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 120 Aug 19 10:52 passwd.tar.gz -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 180 Aug 19 10:53 passwd.tar.xz
cpio
cpio命令是通過重定向的方式將文件進行打包備份,還原恢復的工具,它可以解壓以.cpio或者.tar結尾的文件;換言之,cpio可以復制文件到歸檔包中,或者從歸檔包中復制文件。
cpio - copy files to and from archives cpio[選項] > 文件名或者設備名 cpio[選項] < 文件名或者設備名 EXAMPLES % ls | cpio -ov > directory.cpio % find . -print -depth | cpio -ov > tree.cpio % cpio -iv < directory.cpio % cpio -idv < tree.cpio % find . -depth -print0 | cpio --null -pvd new-dir
常用參數
-o: --create,Run in copy-out mode,將文件拷貝打包成文件或者將文件輸出到設備上
-i: --extract,Run in copy-in mode,解包,將打包文件解壓或將設備上的備份還原到系統
-t: 預覽,查看文件內容或者輸出到設備上的文件內容
-v: 顯示打包過程中的文件名稱。
-d: 解包生成目錄,在cpio還原時,自動的建立目錄
-c: 一種較新的存儲方式
使用示例
[root@centos7 /]#find ./etc |cpio -o > etc.cpio # 備份/etc目錄
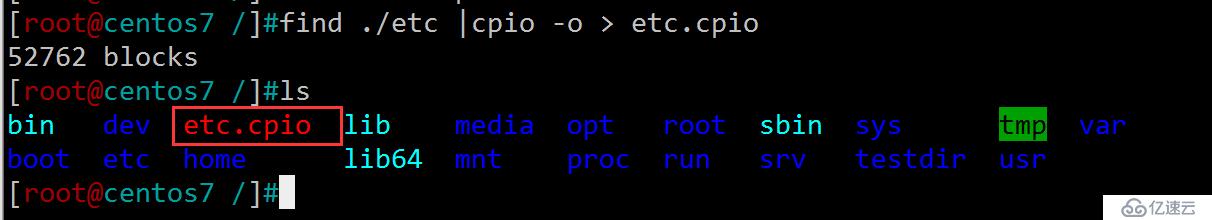
[root@centos7 /testdir]#find /etc/issue |cpio -o >issue.cpio1 block [root@centos7 /testdir]#lsissue.cpio [root@centos7 /testdir]#cpio -tv <issue.cpio # 顯示預覽 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 23 Dec 9 2015 /etc/issue1 block [root@centos7 /testdir]#
cpio在打包備份時用的是絕對路徑,且cpio無法直接讀取文件,它需要每個文件或目錄的完整路徑名才能讀取識別,故cpio命令一般與find配合使用。
本文主要講解了文件查找與壓縮,文件查找命令主要有locate與find; 常見的壓縮工具有gzip, bzip2, xz, zip還有tar這個打包壓縮歸檔命令。
止戰
2016.8.19
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。