您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容主要講解“Java8自定義CompletableFuture的原理是什么”,感興趣的朋友不妨來看看。本文介紹的方法操作簡單快捷,實用性強。下面就讓小編來帶大家學習“Java8自定義CompletableFuture的原理是什么”吧!
Future 接口 的局限性有很多,其中一個就是需要主動的去詢問是否完成,如果等子線程的任務完成以后,通知我,那豈不是更好?
public class FutureInAction3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Future<String> future = invoke(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(10000L);
return "I am Finished.";
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
return "I am Error";
}
});
future.setCompletable(new Completable<String>() {
@Override
public void complete(String s) {
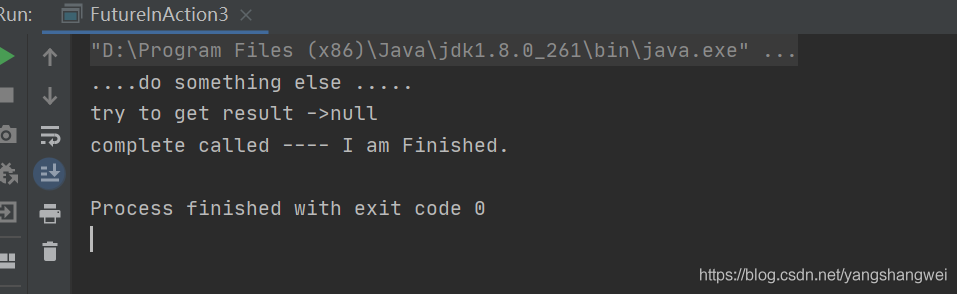
System.out.println("complete called ---- " + s);
}
@Override
public void exception(Throwable cause) {
System.out.println("error");
cause.printStackTrace();
}
});
System.out.println("....do something else .....");
System.out.println("try to get result ->" + future.get());
}
private static <T> Future<T> invoke(Callable<T> callable) {
AtomicReference<T> result = new AtomicReference<>();
AtomicBoolean finished = new AtomicBoolean(false);
Future<T> future = new Future<T>() {
private Completable<T> completable;
@Override
public T get() {
return result.get();
}
@Override
public boolean isDone() {
return finished.get();
}
// 設置完成
@Override
public void setCompletable(Completable<T> completable) {
this.completable = completable;
}
// 獲取
@Override
public Completable<T> getCompletable() {
return completable;
}
};
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
try {
T value = callable.action();
result.set(value);
finished.set(true);
if (future.getCompletable() != null)
future.getCompletable().complete(value);
} catch (Throwable cause) {
if (future.getCompletable() != null)
future.getCompletable().exception(cause);
}
});
t.start();
return future;
}
private interface Future<T> {
T get();
boolean isDone();
// 1
void setCompletable(Completable<T> completable);
// 2
Completable<T> getCompletable();
}
private interface Callable<T> {
T action();
}
// 回調接口
private interface Completable<T> {
void complete(T t);
void exception(Throwable cause);
}
}
Java8 中的 completeFuture 是對 Future 的擴展實現, 主要是為了彌補 Future 沒有相應的回調機制的缺陷.
我們先看看 Java8 之前的 Future 的使用
package demos;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
/**
* @author djh on 2019/4/22 10:23
* @E-Mail 1544579459@qq.com
*/
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService cachePool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Future<String> future = cachePool.submit(() -> {
Thread.sleep(3000);
return "異步任務計算結果!";
});
// 提交完異步任務后, 主線程可以繼續干一些其他的事情.
doSomeThingElse();
// 為了獲取異步計算結果, 我們可以通過 future.get 和 輪詢機制來獲取.
String result;
// Get 方式會導致當前線程阻塞, 這顯然違背了異步計算的初衷.
// result = future.get();
// 輪詢方式雖然不會導致當前線程阻塞, 但是會導致高額的 CPU 負載.
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
while (true) {
if (future.isDone()) {
break;
}
}
System.out.println("輪詢耗時:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
result = future.get();
System.out.println("獲取到異步計算結果啦: " + result);
cachePool.shutdown();
}
private static void doSomeThingElse() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("我的最重要的事情干完了, 我要獲取異步計算結果來執行剩下的事情.");
}
}輸出:
我的最重要的事情干完了, 我要獲取異步計算結果來執行剩下的事情.
輪詢耗時:2000
獲取到異步計算結果啦: 異步任務計算結果!Process finished with exit code 0
從上面的 Demo 中我們可以看出, future 在執行異步任務時, 對于結果的獲取顯的不那么優雅, 很多第三方庫就針對 Future 提供了回調式的接口以用來獲取異步計算結果, 如Google的: ListenableFuture, 而 Java8 所提供的 CompleteFuture 便是官方為了彌補這方面的不足而提供的 API.
package demos;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/**
* @author djh on 2019/5/1 20:26
* @E-Mail 1544579459@qq.com
*/
public class CompleteFutureDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> completableFutureOne = new CompletableFuture<>();
ExecutorService cachePool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
cachePool.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
completableFutureOne.complete("異步任務執行結果");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
// WhenComplete 方法返回的 CompletableFuture 仍然是原來的 CompletableFuture 計算結果.
CompletableFuture<String> completableFutureTwo = completableFutureOne.whenComplete((s, throwable) -> {
System.out.println("當異步任務執行完畢時打印異步任務的執行結果: " + s);
});
// ThenApply 方法返回的是一個新的 completeFuture.
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFutureThree = completableFutureTwo.thenApply(s -> {
System.out.println("當異步任務執行結束時, 根據上一次的異步任務結果, 繼續開始一個新的異步任務!");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return s.length();
});
System.out.println("阻塞方式獲取執行結果:" + completableFutureThree.get());
cachePool.shutdown();
}
}從上面的 Demo 中我們主要需要注意 thenApply 和 whenComplete 這兩個方法, 這兩個方法便是 CompleteFuture 中最具有意義的方法, 他們都會在 completeFuture 調用 complete 方法傳入異步計算結果時回調, 從而獲取到異步任務的結果.
相比之下 future 的阻塞和輪詢方式獲取異步任務的計算結果, CompleteFuture 獲取結果的方式就顯的優雅的多。
到此,相信大家對“Java8自定義CompletableFuture的原理是什么”有了更深的了解,不妨來實際操作一番吧!這里是億速云網站,更多相關內容可以進入相關頻道進行查詢,關注我們,繼續學習!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。