您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要講解了“怎么理解java.lang.Runtime.exec的流輸入和流讀取”,文中的講解內容簡單清晰,易于學習與理解,下面請大家跟著小編的思路慢慢深入,一起來研究和學習“怎么理解java.lang.Runtime.exec的流輸入和流讀取”吧!
首先我們要明確一點,什么是Java.lang.Runtime? 我們來看官方[->link<-]的描述:
" Every Java application has a single instance of class Runtime that allows the application to interface with the environment in which the application is running. The current runtime can be obtained from the getRuntime method.
An application cannot create its own instance of this class. "
也就是說,Runtime是每個java-application運行時有且僅有一個的當前實例.允許Application接入當前運行環境.
我們再來看看Runtime的exec()方法:
" Executes the specified command in a separate process. "
這個方法可以讓我們在一個進程中執行指定的命令.其返回類型是Process類.
那么我們還需要來看一下Process類:
什么是Java.lang.Process? 我們來看官方[->link<-]的描述:
"The class Process provides methods for performing input from the process, performing output to the process, waiting for the process to complete, checking the exit status of the process, and destroying (killing) the process."
也就是說這個類提供控制線程的方法.
我們再來看看Process提供的獲取輸入流和輸出流的方法:
public abstract InputStream getInputStream()
"Returns the input stream connected to the normal output of the subprocess.
The stream obtains data piped from the standard output of the process represented by this Process object."
public abstract OutputStream getOutputStream()
"Returns the output stream connected to the normal input of the subprocess.
Output to the stream is piped into the standard input of the process represented by this Process object."public abstract InputStream getErrorStream()
"Returns the input stream connected to the error output of the subprocess.
The stream obtains data piped from the error output of the process represented by this Process object."
到這里,我們就明白里其中的因果>從exec()返回的Process的對象中調用獲取流的方法.從而達到目的!
在需要使用exec()去執行命令并獲取返回值的時候,具體的做法是什么呢?
僅僅圍繞這個思路:"從exec()返回的Process的對象中調用獲取流的方法getXStream"
String s = null;
Process p = Runtime
.getRuntime()
.exec(
new String[]{"/bin/sh",
"-c",
"java HelloWorld"},null,dir);
BufferedReader stdInput = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(p.getInputStream()));
BufferedReader stdError = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(p.getErrorStream()));
//打印出輸出結果
log.info("標準輸出命令");
while ((s = stdInput.readLine()) != null) {
log.info(s);
}
log.info("標準錯誤的輸出命令");
while ((s = stdError.readLine()) != null) {
log.info(s);
}其中
dir 是我的HelloWorld.class的存放目錄,只能這樣用,請參照這篇
HelloWorld.java 的內容是Sysotem.out.println打印幾行Hello World,此處沒有編譯,使用時應注意.
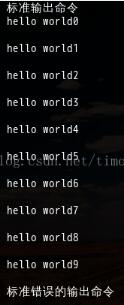
到此,大功告成!
該類java.lang.Runtime具有一個稱為的靜態方法getRuntime(),該方法檢索當前的Java Runtime Environment。這是獲得對該Runtime對象的引用的唯一方法。使用該參考,您可以通過調用Runtime類的exec()方法來運行外部程序。開發人員經常調用此方法來啟動瀏覽器,以顯示HTML的幫助頁面。
該exec()命令有四個重載版本:
public Process exec(String command); public Process exec(String [] cmdArray); public Process exec(String command, String [] envp); public Process exec(String [] cmdArray, String [] envp);
對于這些方法中的每一個,命令(可能還有一組參數)都傳遞給特定于操作系統的函數調用。隨后,這將參考Process返回給Java VM的類來創建特定于操作系統的進程(正在運行的程序)。所述Process類是一個抽象類,因為一個特定的子類Process存在于每個操作系統。
您可以將三個可能的輸入參數傳遞給這些方法:
一個字符串,代表要執行的程序和該程序的所有參數
字符串數組,用于將程序與其參數分開
一組環境變量
以形式傳遞環境變量name=value。如果exec()對程序及其參數使用單個字符串的版本,請注意,通過StringTokenizer類使用空格作為分隔符來解析該字符串。
要執行Java VM外部的進程,我們使用exec()方法。要查看外部進程返回的值,我們exitValue()。
如果外部過程尚未完成,則該exitValue()方法將拋出IllegalThreadStateException;。這就是該程序失敗的原因。盡管文檔中說明了這一事實,但為什么不能等到此方法可以給出有效答案呢?
對該Process類中可用的方法進行更徹底的研究,就會發現waitFor()可以做到這一點的方法。實際上,waitFor()還會返回退出值,這意味著您將不會使用exitValue()和waitFor()彼此結合,而是會選擇一個或另一個。你會使用的唯一可能的時間exitValue(),而不是waitFor()會當你不希望你的程序阻止等待外部過程中可能永遠不會完成。與其使用該waitFor()方法,不如將一個被調用的布爾參數waitFor傳入該exitValue()方法以確定當前線程是否應等待。布爾值會更有利,因為exitValue()是此方法的更合適的名稱,兩個方法在不同條件下不必執行相同的功能。這種簡單的條件判別是輸入參數的領域。
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class BadExecJavac
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
try
{
Runtime rt = Runtime.getRuntime();
Process proc = rt.exec("javac");
int exitVal = proc.exitValue();
System.out.println("Process exitValue: " + exitVal);
} catch (Throwable t)
{
t.printStackTrace();
}
}
}import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class BadExecJavac2
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
try
{
Runtime rt = Runtime.getRuntime();
Process proc = rt.exec("javac");
int exitVal = proc.waitFor();
System.out.println("Process exitValue: " + exitVal);
} catch (Throwable t)
{
t.printStackTrace();
}
}
}因此,為避免此陷阱,請捕獲IllegalThreadStateException或等待該過程完成。
由于某些本機平臺僅為標準輸入和輸出流提供有限的緩沖區大小,因此未能及時寫入子流程的輸入流或讀取子流程的輸出流可能導致子流程阻塞,甚至死鎖。
現在,讓我們關注JDK文檔并處理javac過程的輸出。當您javac不帶任何參數運行時,它會生成一組用法語句,這些用法語句描述了如何運行程序以及所有可用程序選項的含義。知道這將stderr流到流,您可以輕松地編寫一個程序以在等待進程退出之前耗盡該流。清單4.3完成了該任務。盡管此方法行之有效,但這不是一個好的通用解決方案。因此,清單4.3的程序被命名為MediocreExecJavac;。它僅提供平庸的解決方案。更好的解決方案將同時清空標準錯誤流和標準輸出流。最好的解決方案是同時清空這些流(稍后再說明)
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class MediocreExecJavac
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
try
{
Runtime rt = Runtime.getRuntime();
Process proc = rt.exec("javac");
InputStream stderr = proc.getErrorStream();
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(stderr);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
String line = null;
System.out.println("<ERROR>");
while ( (line = br.readLine()) != null)
System.out.println(line);
System.out.println("</ERROR>");
int exitVal = proc.waitFor();
System.out.println("Process exitValue: " + exitVal);
} catch (Throwable t)
{
t.printStackTrace();
}
}
}感謝各位的閱讀,以上就是“怎么理解java.lang.Runtime.exec的流輸入和流讀取”的內容了,經過本文的學習后,相信大家對怎么理解java.lang.Runtime.exec的流輸入和流讀取這一問題有了更深刻的體會,具體使用情況還需要大家實踐驗證。這里是億速云,小編將為大家推送更多相關知識點的文章,歡迎關注!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。