您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章將為大家詳細講解有關MyBatis-Ext怎么用,小編覺得挺實用的,因此分享給大家做個參考,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后可以有所收獲。
最近在工作中,接觸到了一個MyBatis擴展工具包MyBatis-Ext,可以說很大程度上減輕了使用mybatis時的工作量。
MyBatis-Ext是MyBatis的增強擴展,和我們平常用的Mybatis-plus非常類似,簡化了MyBatis對單表增刪改查的操作,提供通用的增刪改查,支持函數式編程,支持分頁查詢,支持用戶自定義通用方法,并且能夠防止SQL注入。集成起來也非常簡單,對MyBatis只做增強不做修改。
以spring-boot項目為例,集成非常簡單。pom導入核心依賴:
<dependency> <groupId>tech.wetech.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-ext-core</artifactId> <version>1.5.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>tech.wetech.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-ext-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.5.2</version> </dependency>
需要注意的是,引入mybatis-ext-spring-boot-starter后無需再引入mybatis-spring-boot-starter。
和以往一樣,在application.yml配置一下數據源:
spring: datasource: username: dater password: 123456 url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/datacenter?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource druid: initial-size: 8 min-idle: 1 max-active: 20 mybatis: mapper-locations: classpath:mapping/*Mapper.xml type-aliases-package: com.mybatis.ext.test.mybatisexttest.entity spring: datasource: username: dater password: 123456 url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/datacenter?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource druid: initial-size: 8 min-idle: 1 max-active: 20 mybatis: mapper-locations: classpath:mapping/*Mapper.xml type-aliases-package: com.mybatis.ext.test.mybatisexttest.entity
創建一個映射的實體類:
@Data
@Table(name = "user")
public class User {
@Id
String identifycard;
@Column(name="name")
String name;
String money;
String card;
String phone;
String rate;
}mybatis-ext使用了Jpa的注解,目前實現了@Table、@Id、@Column、@Transient、@Version。其中@Table、@Id是必須添加的注解,其他非必須添加。使用@Table指定數據表名,@Id指定數據表主鍵。
查詢的Mapper接口繼承BaseMapper接口,泛型中填寫實體類:
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
}我們來看一下能夠直接調用的方法,為在BaseMapper中內置了很多通用方法,可以直接調用,非常簡便:
int deleteByPrimaryKey(PK id);
<S extends T> int insert(S record);
<S extends T> int insertAll(Iterable<S> record);
<S extends T> int insertSelective(S record);
<S extends T> S selectByPrimaryKey(PK id);
<S extends T> Optional<S> selectByPrimaryKeyWithOptional(ID id);
<S extends T> int updateByPrimaryKey(S record);
<S extends T> int updateByPrimaryKeySelective(S record);
<S extends T> List<S> selectAll();
<S extends T> List<S> selectList(S record);
<S extends T> S selectOne(S record);
<S extends T> S selectOneWithOptional(S record);
boolean existsByPrimaryKey(PK id);
<S extends T> int count(S record);
<S extends T> List<S> selectByExample(Example<S, Object> example);
<S extends T> int countByExample(Example<S, Object> example);
<S extends T> int deleteByExample(Example<S, Object> example);
<S extends T> int updateByExample(@Param("record") S record, @Param("example") Example<S, Object> example);
<S extends T> int updateByExampleSelective(@Param("record") S record, @Param("example") Example<S, Object> example);來進行一下接口調用的測試,先試一下selectAll方法:
@GetMapping("getUser")
public void getUser(){
List<User> users = userMapper.selectAll();
for (User user : users) {
System.out.println(user.getName()+" "+user.getIdentifycard());
}
}測試結果:
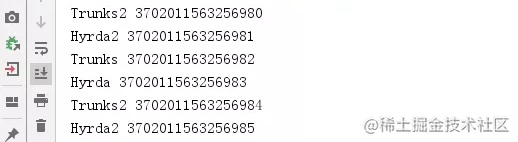
這樣,通過調用內置方法就實現了不寫sql語句直接進行查詢。同樣,如果想根據主鍵進行查詢也很簡單,直接調用selectByPrimaryKey方法:
@PostMapping("getUserById")
public void getUserByIdentifycard(@RequestBody User user){
User retUser = userMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(user);
System.out.println(retUser.toString());
}查詢結果:
另外,還可以使用Optional包裹查詢,修改一下上面主鍵查詢的方法:
@PostMapping("getUserById")
public void getUserByIdentifycard(@RequestBody User user){
User retUser = userMapper.selectByPrimaryKeyWithOptional(user)
.orElseThrow(()->new RuntimeException("未查到數據"));
System.out.println(retUser.toString());
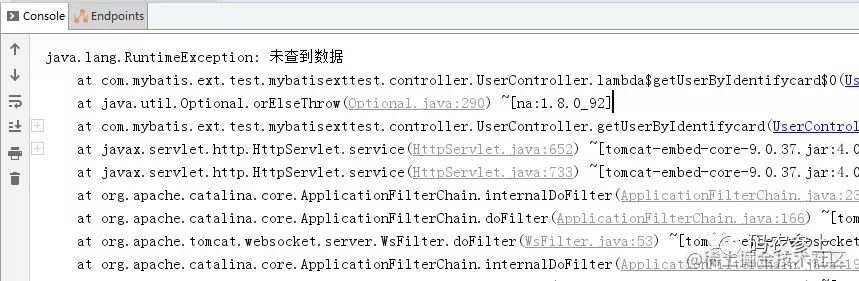
}這樣,在傳入一個不存在的主鍵時,就會直接拋出自定義的異常:
還有其他很多簡單的查詢,大家可以根據上面列出api自行測試一下。此外,還可以使用Criteria,使用邏輯組合,進行函數式查詢:
@GetMapping("criteriaTest")
public void testCreateCriteria(){
List<User> list = userMapper.createCriteria()
.andEqualTo(User::getName, "Trunks")
.andBetween(User::getMoney, 100, 300)
.andNotLike(User::getRate, "6")
.orIn(User::getCard, Arrays.asList("10"))
.selectList();
list.forEach(user -> {
System.out.println(user.toString());
});
}查詢結果:
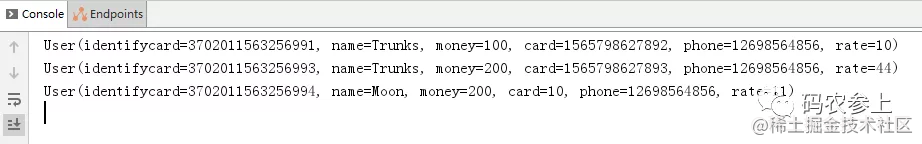
也可以使用Example進行查詢:
@GetMapping("exampleTest")
public void testExample(){
Example<User> example=Example.of(User.class);
example.createCriteria()
.andEqualTo(User::getName, "Trunks")
.andBetween(User::getMoney, 100, 300)
.andNotLike(User::getRate, "6")
.orIn(User::getCard, Arrays.asList("10"));
example.setDistinct(true);
List<User> list = userMapper.selectByExample(example);
list.forEach(user -> {
System.out.println(user.toString());
});
}結果與使用Criteria結果相同。另外,還可以將多個條件組合使用:
GetMapping("testExampleWithSub")
public void selectByExampleWithSub(){
try (SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
UserMapper userMapper1 = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
Example<User> example=Example.of(User.class);
example.and()
.andEqualTo(User::getName, "Trunks");
example.and()
.andEqualTo(User::getCard,"10");
example.and()
.andLessThanOrEqualTo(User::getRate,300);
Criteria<User> criteria=new Criteria<>();
criteria.andIsNotNull(User::getPhone);
example.and(criteria);
List<User> list = userMapper1.selectByExample(example);
list.forEach(user -> {
System.out.println(user.toString());
});
}
}
關于“MyBatis-Ext怎么用”這篇文章就分享到這里了,希望以上內容可以對大家有一定的幫助,使各位可以學到更多知識,如果覺得文章不錯,請把它分享出去讓更多的人看到。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。