您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要為大家展示了“C++中智能指針代碼的示例分析”,內容簡而易懂,條理清晰,希望能夠幫助大家解決疑惑,下面讓小編帶領大家一起研究并學習一下“C++中智能指針代碼的示例分析”這篇文章吧。
如果在程序中使用new從堆分配內存,等到不再需要時,應使用delete將其釋放,C++引入了智能指針auto_ptr,以幫助自動完成這個過程,但是aoto_ptr也有其局限性,因此從Boost庫中又引入了三種智能指針unique_ptr shared_ptr weak_ptr。
// ConsoleApplication1.cpp : 定義控制臺應用程序的入口點。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <ostream>
using namespace std;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
auto_ptr<string> ptr1(new string("this is ptr!"));
auto_ptr<string> ptr2;
ptr2 = ptr1;
cout << &ptr2<<endl;
cout << *ptr2 << endl;
return 0;
}output :
003AFBC0
this is ptr!
但是如果輸出的是ptr1,程序會如何呢?
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <ostream>
using namespace std;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
auto_ptr<string> ptr1(new string("this is ptr!"));
auto_ptr<string> ptr2;
ptr2 = ptr1;
cout << &ptr1 <<endl;
cout << *ptr1 << endl; #這一步程序會崩潰
return 0;
}崩潰原因: 首先ptr2 = ptr1表示ptr1將訪問的權限給了ptr2,同時意味了ptr1已經沒有訪問字符串的權限,因此會報錯。
那如何解決這個問題呢?引入了unique_ptr
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <ostream>
using namespace std;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
unique_ptr<string> ptr1(new string("this is unique_ptr"));
unique_ptr<string> ptr2;
ptr2 = ptr1; #這一步編譯器會報錯
return 0;
}unique_ptr 替代auto_ptr實現獨占式,可以理解成,同一時刻只能有一個unique_ptr指向給定對象,unique_ptr對象始終是關聯的原始指針的唯一所有者。無法復制unique_ptr對象,它只能移動。(這樣可以保證,不會出現auto_ptr那樣運行時會出現的隱藏內存崩潰問題)
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
unique_ptr<string> ptr1(new string("this is unique_ptr"));
unique_ptr<string> ptr2;
cout << &ptr1 << endl;
unique_ptr<string> ptr3(new string("other unique_ptr"));
cout << &ptr3 << endl;
cout << *ptr3 << endl;
return 0;
}output:
00D9F8B4
00D9F89C
other unique_ptr
// ConsoleApplication1.cpp : 定義控制臺應用程序的入口點。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <ostream>
using namespace std;
class base{
public:
base()
{
cout << "begin..." << endl;
};
~base()
{
cout << "end..." << endl;
}
};
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
base *a = new base();
shared_ptr<base> ptr1(a);
//shared_ptr<base> ptr2(a); ## 如果加上這句程序會崩潰,雙重管理陷阱,a對象被刪除了兩次
return 0;
}output:
begin...
end...
share_ptr的循環陷阱
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <ostream>
using namespace std;
class CB;
class CA
{
public:
CA()
{
cout << "CA call ..."<< endl;
}
~CA()
{
cout << "~CA call..."<< endl;
}
void setPtr(shared_ptr<CB> &ptr)
{
m_ptr_b = ptr;
}
int getCount()
{
return m_ptr_b.use_count();
}
private:
shared_ptr<CB> m_ptr_b;
};
class CB
{
public:
CB()
{
cout << "CB call..." << endl;
}
~CB()
{
cout << "~CB call..." << endl;
}
void setPtr(shared_ptr<CA> ptr)
{
m_ptr_a = ptr;
}
int getCount()
{
return m_ptr_a.use_count();
}
private:
shared_ptr<CA> m_ptr_a;
};
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
shared_ptr<CA> ptr_a(new CA);
shared_ptr<CB> ptr_b(new CB);
cout << " CA count is : " << ptr_a->getCount()<<endl;
cout << "CB count is:" << ptr_b->getCount()<< endl;
ptr_a->setPtr(ptr_b);
ptr_b->setPtr(ptr_a);
cout << " CA count is : " << ptr_a->getCount() << endl;
cout << "CB count is:" << ptr_b->getCount() << endl;
return 0;
}上面這段程序的思路用下面張圖可以清晰的表示
圖片和代碼主要參考的是這篇很棒的博文:智能指針(三):weak_ptr淺析
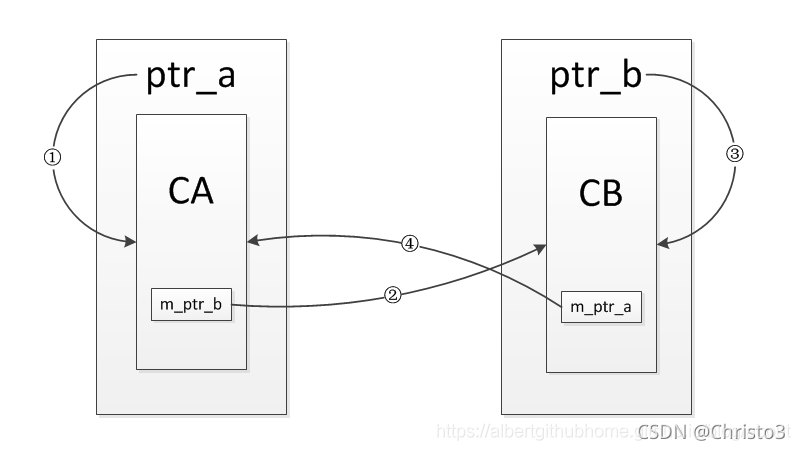

運行結果后發現并沒有調用析構函數釋放內存,以后存在內存泄漏的風險
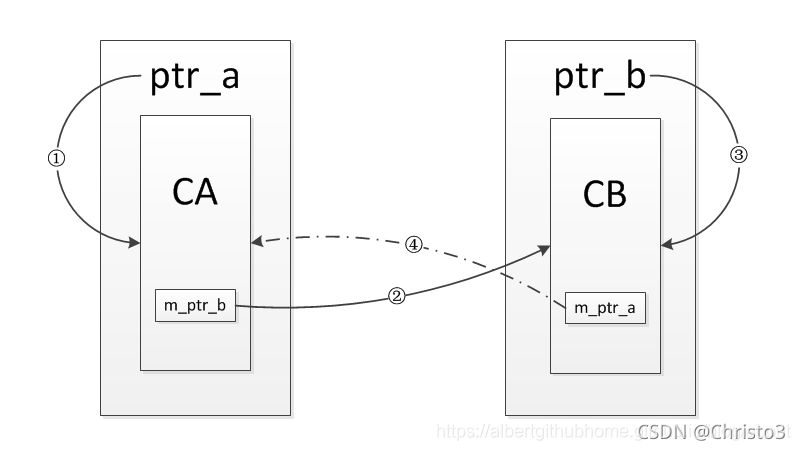
那如何去解決這個問題呢?,可以通過引入weak_ptr來解決,但是weak_ptr需要與share_ptr配合使用
通過在兩個類中的一個成員變量改為weak_ptr對象,因為weak_ptr不會增加引用計數,使得引用形不成環,最后就可以正常的釋放內部的對象,不會造成內存泄漏
class CB
{
public:
CB()
{
cout << "CB call..." << endl;
}
~CB()
{
cout << "~CB call..." << endl;
}
void setPtr(shared_ptr<CA> ptr)
{
m_ptr_a = ptr;
}
int getCount()
{
return m_ptr_a.use_count();
}
private:
///shared_ptr<CA> m_ptr_a;
weak_ptr<CA> m_ptr_a; ## 改為weak_ptr對象
};

以上是“C++中智能指針代碼的示例分析”這篇文章的所有內容,感謝各位的閱讀!相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望分享的內容對大家有所幫助,如果還想學習更多知識,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。