您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章將為大家詳細講解有關Spring中使用@within與@target的區別有哪些,小編覺得挺實用的,因此分享給大家做個參考,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后可以有所收獲。
項目里用到@within時,出現了一些問題,使用@target就可以解決,但又會出現一些新的問題,因此本文探討了在spring中,使用@within和@target的一些區別。
項目里有一個動態切換數據源的功能,我們是用切面來實現的,是基于注解來實現的,但是父類的方法是可以切換數據源的,如果有一個類直接繼承這個類,調用這個子類時,這個子類是不能夠切換數據源的,除非這個子類重寫父類的方法。
模擬項目例子
注解定義:
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String value() default "me";
}
切面定義:
@Order(-1)
@Aspect
@Component
public class MyAspect {
@Before("@within(myAnnotation)")
public void switchDataSource(JoinPoint point, MyAnnotation myAnnotation) {
System.out.println("before, myAnnotation.value : " + myAnnotation.value());
}
}
父類Bean:
@MyAnnotation("father")
public class Father {
public void hello() {
System.out.println("father.hello()");
}
public void hello2() {
System.out.println("father.hello2()");
}
}
子類Bean:
@MyAnnotation("son")
public class Son extends Father {
@Override
public void hello() {
System.out.println("son.hello()");
}
}
配置類:
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(exposeProxy = true)
public class Config {
@Bean
public Father father() {
return new Father();
}
@Bean
public Son son() {
return new Son();
}
}
測試類:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class,
MyAspect.class);
Father father = context.getBean("father", Father.class);
father.hello();
father.hello2();
Son son = context.getBean(Son.class);
son.hello();
son.hello2();
}
}我們定義了一個@Before通知,方法參數有point, myAnnotation,方法里輸出了myAnnotation.value的值
下面是輸出結果:
before, myAnnotation.value : father
father.hello()
before, myAnnotation.value : father
father.hello2()
before, myAnnotation.value : son
son.hello()
before, myAnnotation.value : father
father.hello2()
從上面的輸出結果看出:Son類重寫了hello方法,myAnnotation.value的輸出的值是son,hello2方法沒有重寫,myAnnotation.value的輸出的值是father
根據需求,我們肯定希望調用Son類的所有方法時,都希望myAnnotation.value的輸出的值是son,因此就需要重寫父類的所有public方法
那有沒有辦法不重寫這些方法也能達到相同的效果呢,答案是可以的。
看看使用@within和@target的區別
我們分別在父類和子類上加上注解和去掉注解,一起來看看對應的結果
@within
父類無注解,子類有注解:
father.hello() father.hello2() before, myAnnotation.value : son son.hello() father.hello2()
父類有注解,子類無注解:
before, myAnnotation.value : father father.hello() before, myAnnotation.value : father father.hello2() before, myAnnotation.value : father son.hello() before, myAnnotation.value : father father.hello2()
父類有注解,子類有注解(其實就是上面那個例子的結果):
before, myAnnotation.value : father father.hello() before, myAnnotation.value : father father.hello2() before, myAnnotation.value : son son.hello() before, myAnnotation.value : father father.hello2()
@target
把切面代碼改成如下:
@Order(-1)
@Aspect
@Component
public class MyAspect {
@Before("@target(myAnnotation)")
public void switchDataSource(JoinPoint point, MyAnnotation myAnnotation) {
System.out.println("before, myAnnotation.value : " + myAnnotation.value());
}
}我們再一起來看看測試結果:
父類無注解,子類有注解:
father.hello() father.hello2() before, myAnnotation.value : son son.hello() before, myAnnotation.value : son father.hello2()
父類有注解,子類無注解:
before, myAnnotation.value : father father.hello() before, myAnnotation.value : father father.hello2() son.hello() father.hello2()
父類有注解,子類有注解
before, myAnnotation.value : father father.hello() before, myAnnotation.value : father father.hello2() before, myAnnotation.value : son son.hello() before, myAnnotation.value : son father.hello2()
我們從上面總結出一套規律:@within:@Before通知方法的myAnnotation參數指的是調用方法所在的類上面的注解,就是這個方法是在哪個類上定義的@target:@Before通知方法的myAnnotation參數指的是調用方法運行時所屬于的類上面的注解
我們最后總結一下,如果父類和子類上都標有注解,@within和@target的所得到實際注解的區別
@within | @target | |
|---|---|---|
| 父類方法 | 父類注解 | 父類注解 |
| 子類不重寫方法 | 父類注解 | 子類注解 |
| 子類重寫方法 | 子類注解 | 子類注解 |
@target 看起來跟合理一點
從上面的分析可以看出,其實用@target更符合我們想要的結果,在某個類上面加一個注解,攔截的時候就會獲取這個類上面的注解,跟父類完全沒有關系了
但這個時候會遇到一個問題,就是不相關的類都會生從代理類,
例子如下:
public class NormalBean {
public void hello() {
}
}
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(exposeProxy = true)
public class Config {
@Bean
public Father father() {
return new Father();
}
@Bean
public Son son() {
return new Son();
}
@Bean
public NormalBean normalBean() {
return new NormalBean();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class,
MyAspect.class);
Father father = context.getBean("father", Father.class);
father.hello();
father.hello2();
Son son = context.getBean(Son.class);
son.hello();
son.hello2();
NormalBean normalBean = context.getBean(NormalBean.class);
System.out.println(normalBean.getClass());
}
}輸出:
class cn.eagleli.spring.aop.demo.NormalBean$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$eebc2a39
可以看出NormalBean自己什么都沒做,但卻被代理了
我們再把@target換成@within:
class cn.eagleli.spring.aop.demo.NormalBean
可以看出使用@within時,不相關的類沒有被代理
我們一起來看看為什么
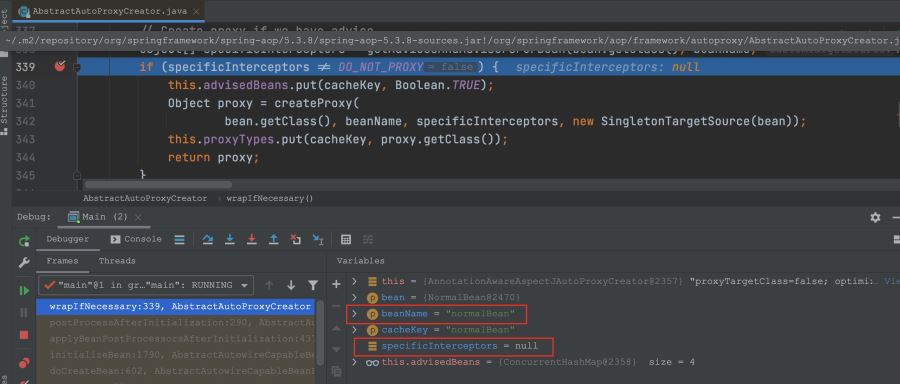
在AbstractAutoProxyCreator類中的wrapIfNecessary方法打斷點,看看什么情況:
@within
@target
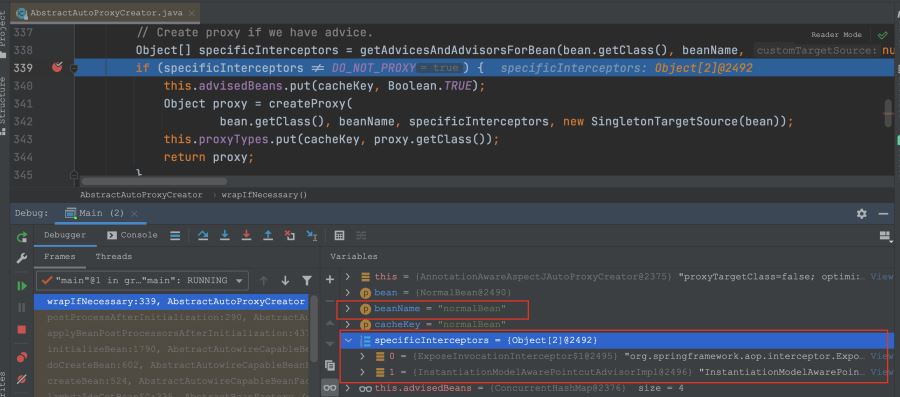
我們從上面的圖片就可以理解為什么@target會生成代理類
我們再深入看一下:
@within會走到如下:
public class ExactAnnotationTypePattern extends AnnotationTypePattern {
@Override
public FuzzyBoolean matches(AnnotatedElement annotated, ResolvedType[] parameterAnnotations) {
// ......
}
}我沒深入研究,大致意思就是只要這個類或者這個類的祖先們帶有這個注解,即匹配成功
@target會走到如下:
public class ThisOrTargetAnnotationPointcut extends NameBindingPointcut {
@Override
protected FuzzyBoolean matchInternal(Shadow shadow) {
if (!couldMatch(shadow)) {
return FuzzyBoolean.NO;
}
ResolvedType toMatchAgainst = (isThis ? shadow.getThisType() : shadow.getTargetType()).resolve(shadow.getIWorld());
annotationTypePattern.resolve(shadow.getIWorld());
if (annotationTypePattern.matchesRuntimeType(toMatchAgainst).alwaysTrue()) {
return FuzzyBoolean.YES;
} else {
// a subtype may match at runtime
return FuzzyBoolean.MAYBE;
}
}
}
public class AspectJExpressionPointcut extends AbstractExpressionPointcut
implements ClassFilter, IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher, BeanFactoryAware {
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
obtainPointcutExpression();
ShadowMatch shadowMatch = getTargetShadowMatch(method, targetClass);
// Special handling for this, target, @this, @target, @annotation
// in Spring - we can optimize since we know we have exactly this class,
// and there will never be matching subclass at runtime.
if (shadowMatch.alwaysMatches()) {
return true;
}
else if (shadowMatch.neverMatches()) {
return false;
}
else {
// the maybe case
if (hasIntroductions) {
return true;
}
// A match test returned maybe - if there are any subtype sensitive variables
// involved in the test (this, target, at_this, at_target, at_annotation) then
// we say this is not a match as in Spring there will never be a different
// runtime subtype.
RuntimeTestWalker walker = getRuntimeTestWalker(shadowMatch);
return (!walker.testsSubtypeSensitiveVars() || walker.testTargetInstanceOfResidue(targetClass)); // 這里會返回true
}
}
}我沒深入研究,大致意思是匹配的話就返回YES,否則就返回MAYBE,匹配邏輯是和@within一樣的
因此所有不相關的類都會是一個MAYBE的結果,這個結果會讓不相關的類最后生成代理類
通知方法中注解參數的值為什么是不一樣的
經過調試,最終是在這里獲取的:
public final class ReflectionVar extends Var {
static final int THIS_VAR = 0;
static final int TARGET_VAR = 1;
static final int ARGS_VAR = 2;
static final int AT_THIS_VAR = 3;
static final int AT_TARGET_VAR = 4;
static final int AT_ARGS_VAR = 5;
static final int AT_WITHIN_VAR = 6;
static final int AT_WITHINCODE_VAR = 7;
static final int AT_ANNOTATION_VAR = 8;
public Object getBindingAtJoinPoint(
Object thisObject,
Object targetObject,
Object[] args,
Member subject,
Member withinCode,
Class withinType) {
switch( this.varType) {
case THIS_VAR: return thisObject;
case TARGET_VAR: return targetObject;
case ARGS_VAR:
if (this.argsIndex > (args.length - 1)) return null;
return args[argsIndex];
case AT_THIS_VAR:
if (annotationFinder != null) {
return annotationFinder.getAnnotation(getType(), thisObject);
} else return null;
case AT_TARGET_VAR:
if (annotationFinder != null) {
return annotationFinder.getAnnotation(getType(), targetObject);
} else return null;
case AT_ARGS_VAR:
if (this.argsIndex > (args.length - 1)) return null;
if (annotationFinder != null) {
return annotationFinder.getAnnotation(getType(), args[argsIndex]);
} else return null;
case AT_WITHIN_VAR:
if (annotationFinder != null) {
return annotationFinder.getAnnotationFromClass(getType(), withinType);
} else return null;
case AT_WITHINCODE_VAR:
if (annotationFinder != null) {
return annotationFinder.getAnnotationFromMember(getType(), withinCode);
} else return null;
case AT_ANNOTATION_VAR:
if (annotationFinder != null) {
return annotationFinder.getAnnotationFromMember(getType(), subject);
} else return null;
}
return null;
}
}@within:
case AT_WITHIN_VAR:
if (annotationFinder != null) {
return annotationFinder.getAnnotationFromClass(getType(), withinType);
} else return null;withinType追蹤到如下:
public class PointcutExpressionImpl implements PointcutExpression {
private ShadowMatch matchesExecution(Member aMember) {
Shadow s = ReflectionShadow.makeExecutionShadow(world, aMember, this.matchContext);
ShadowMatchImpl sm = getShadowMatch(s);
sm.setSubject(aMember);
sm.setWithinCode(null);
sm.setWithinType(aMember.getDeclaringClass()); // 這里設置withinType
return sm;
}
}
public abstract class AopUtils {
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null");
if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {
return false;
}
MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher();
if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) {
// No need to iterate the methods if we're matching any method anyway...
return true;
}
IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null;
if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) {
introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher;
}
Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<>();
if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
classes.add(ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetClass));
}
classes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass));
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz);
for (Method method : methods) { // 這里獲取所有method
if (introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null ?
introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions) :
methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}@target:
case AT_TARGET_VAR:
if (annotationFinder != null) {
return annotationFinder.getAnnotation(getType(), targetObject);
} else return null;targetObject 追蹤到如下:
public abstract class AbstractAutoProxyCreator extends ProxyProcessorSupport
implements SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor, BeanFactoryAware {
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean)); // 這里,targetObject就是生成的bean
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
public SingletonTargetSource(Object target) {
Assert.notNull(target, "Target object must not be null");
this.target = target;
}
}想用@within,但又想得到想要的注解
@Order(-1)
@Aspect
@Component
public class MyAspect {
@Before("@within(myAnnotation)")
public void switchDataSource(JoinPoint point, MyAnnotation myAnnotation) {
System.out.println(point.getTarget() + " " + point + " " + myAnnotation.value() + " " +
point.getTarget().getClass().getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class).value());
}
}很簡單,從JoinPoint中得到target,然后從這個類上得到對應的注解即可
此時,父類和子類都加有注解,一起來看看輸出結果:
cn.eagleli.spring.aop.demo.Father@194fad1 execution(void cn.eagleli.spring.aop.demo.Father.hello()) father father
cn.eagleli.spring.aop.demo.Father@194fad1 execution(void cn.eagleli.spring.aop.demo.Father.hello2()) father father
cn.eagleli.spring.aop.demo.Son@14fc5f04 execution(void cn.eagleli.spring.aop.demo.Son.hello()) son son
cn.eagleli.spring.aop.demo.Son@14fc5f04 execution(void cn.eagleli.spring.aop.demo.Father.hello2()) father son
關于“Spring中使用@within與@target的區別有哪些”這篇文章就分享到這里了,希望以上內容可以對大家有一定的幫助,使各位可以學到更多知識,如果覺得文章不錯,請把它分享出去讓更多的人看到。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。