您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
小編給大家分享一下OpenCV視頻中火焰檢測識別的示例分析,相信大部分人都還不怎么了解,因此分享這篇文章給大家參考一下,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后大有收獲,下面讓我們一起去了解一下吧!
主要完成兩個視頻中火焰的檢測,主要結合RGB判據和HIS判據,設定合適的閾值條件,檢測出火焰對應像素的區域,將原圖二值化,經過中值濾波以及數學形態學的膨脹運算等圖像處理,消除一些噪聲及離散點,連通一些遺漏的區域。基于OpenCV的開源庫,在VS2013平臺上,實現了兩個視頻中火焰的檢測。
利用OpenCV有強大的圖像處理庫,直接將圖像分離為RGB三通道,設置條件限制,找到火焰的像素位置,將原圖處理成二值圖像。對于火焰檢測,本文結合RGB判據和HIS判據,分割出火焰的區域。一般用于人眼觀看的顏色模型是RGB模型,對于火焰而言,紅色分量(R)和綠色分量(G)會很大,并且綠色分量(G)會大于藍色分量(B)。HIS顏色模型分別用H(色度)S(飽和度)I(亮度)描述顏色特性,與人們感受顏色的方式緊密相連。考慮到單一顏色模型的判據準確性不夠高,在RGB判據基礎上,添加HIS約束條件。具體條件[1]為:
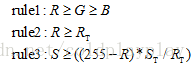
其中,Rt是紅色分量閾值,St是飽和度閾值,火焰像素主要取決于紅色分量(R)的色度和飽和度。若滿足式(1),則判斷該位置為火焰像素,顯示為白色,否則顯示為黑色。判據中閾值的選擇對于火焰檢測是至關重要的,一般靠經驗設定,為了獲取火焰識別最好的效果,設置兩個滑動條,改變閾值Rt和St的大小,選取最合適的值。
由于(1)中只需要用到HIS中的S分量,所以不需要用到顏色模型轉換函數,直接計算S分量即可。
獲取二值圖像后,需要對其預處理,找到遺漏的點,剔除異常的點。由于存在噪聲及離散點,對圖像進行平滑濾波,本文采用的是中值濾波,中值濾波是典型的非線性濾波,用像素點鄰域灰度值的中值來代替該像素點的灰度值,非常利于消除一些誤判斷為火焰的像素點。
由于部分火焰的顏色不是介于紅黃之間,無法識別,需要實現區域的連通,因此對二值圖像進行數學形態學操作。形態學是一種強大的圖像處理工具,它可以實現圖像去噪、圖像分割等功能,最基本的形態學操作有兩種,分別是膨脹與腐蝕。它們可以衍生出很多強大的形態學算法,實現我們想要的功能。采用形態學處理的最基礎的膨脹操作,作用于火焰的二值圖像中。
編寫CheckColor函數,將以上3個功能實現。
為了表示出視頻中火焰的區域,在預處理過后,將火焰輪廓用矩形框標記,編寫了畫矩形框的函數DrawFire,其中使用了OpenCV的尋找輪廓的函數findContours,由于作業中test2的火焰位置是分散在不同地方的,所以對整張圖像進行區域的劃分,分別用不同矩形標記不同區域出現的火焰。
基于OpenCV的庫,在VS2013上實現算法,由于視頻中的火焰檢測是實時動態的,下面截取幾幀畫面用于展示實驗結果:

本文采用RGB判據和HIS判據結合的方法,按照經驗法和不斷地調試,選擇合適的閾值,基于OpenCV在VS2013上實現算法,從test1實驗結果可以看出,在背景比較單調且與火焰差別較大時,效果良好,幾乎沒有任何噪聲對其造成干擾。從test2實驗結果可以看出,當背景復雜或與火焰顏色比較相似時,會不時出現噪聲和誤判,需要進一步提高算法。
列出處理test2視頻的具體代碼:
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<cv.h>
using namespace cv;
int redThre =49; // 115~135
int saturationTh = 7; //55~65
Mat CheckColor(Mat &inImg);
void DrawFire(Mat &inputImg, Mat foreImg);
int main()
{
VideoCapture capture("test2.avi");
while (1)
{
Mat frame;
capture >> frame;
if (frame.empty())
break;
namedWindow("Control", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
cvCreateTrackbar("redThre", "Control", &redThre, 255);
cvCreateTrackbar("saturationTh", "Control", &saturationTh, 255);
CheckColor(frame);
waitKey(1);
}
return 0;
}
//The Color Check is According to "An Early Fire-Detection Method Based on Image Processing"
//The Author is:Thou-Ho (Chao-Ho) Chen, Ping-Hsueh Wu, and Yung-Chuen Chiou
Mat CheckColor(Mat &inImg)
{
Mat fireImg;
fireImg.create(inImg.size(), CV_8UC1);
Mat multiRGB[3];
int a = inImg.channels();
split(inImg, multiRGB); //將圖片拆分成R,G,B,三通道的顏色
for (int i = 0; i < inImg.rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < inImg.cols; j++)
{
float B, G, R;
B = multiRGB[0].at<uchar>(i, j); //每個像素的R,G,B值,動態地址計算法
G = multiRGB[1].at<uchar>(i, j);
R = multiRGB[2].at<uchar>(i, j);
float maxValue = max(max(B, G), R);
float minValue = min(min(B, G), R);
//與HSI中S分量的計算公式
double S = (1 - 3.0*minValue / (R + G + B));//
//R > RT R>=G>=B S>=((255-R)*ST/RT)
if (R > redThre &&R >= G && G>= B && S >((255 - R) * saturationTh / redThre))
{
fireImg.at<uchar>(i, j) = 255;
}
else
{
fireImg.at<uchar>(i, j) = 0;
}
}
}
//erode(fireImg, fireImg, Mat(3, 3, CV_8UC1));
//GaussianBlur(fireImg, fireImg, Size(5, 5), 0, 0);
medianBlur(fireImg, fireImg, 5);
dilate(fireImg, fireImg, Mat(5, 5, CV_8UC1));
imshow("Binary", fireImg);
DrawFire(inImg, fireImg);
return fireImg;
}
void DrawFire(Mat &inputImg, Mat foreImg)
{
vector<vector<Point>> contours_set;//保存輪廓提取后的點集及拓撲關系
findContours(foreImg, contours_set, CV_RETR_EXTERNAL, CV_CHAIN_APPROX_NONE);
Point point1;
Point point2;
float a = 0.4, b = 0.75;
float xmin1 = a*inputImg.cols, ymin1 = inputImg.rows, xmax1 = 0, ymax1 = 0;
float xmin2 = b*inputImg.cols, ymin2 = inputImg.rows, xmax2 = a*inputImg.cols, ymax2 = 0;
float xmin3 = inputImg.cols, ymin3 = inputImg.rows, xmax3 = b*inputImg.cols, ymax3 = 0;
Rect finalRect1;
Rect finalRect2;
Rect finalRect3;
vector<vector<Point> >::iterator iter = contours_set.begin();
for (; iter != contours_set.end();)
{
Rect rect = boundingRect(*iter);
float radius;
Point2f center;
minEnclosingCircle(*iter, center, radius);
if (rect.area()> 0)
{
point1.x = rect.x;
point1.y = rect.y;
point2.x = point1.x + rect.width;
point2.y = point1.y + rect.height;
if (point2.x< a*inputImg.cols)
{
if (point1.x < xmin1)
xmin1 = point1.x;
if (point1.y < ymin1)
ymin1 = point1.y;
if (point2.x > xmax1 && point2.x < xmax2)
xmax1 = point2.x;
if (point2.y > ymax1)
ymax1 = point2.y;
}
if (point2.x < b*inputImg.cols&&point2.x > a*inputImg.cols)
{
if (point1.x < xmin2 && point1.x>xmin1)
xmin2 = point1.x;
if (point1.y < ymin2)
ymin2 = point1.y;
if (point2.x > xmax2 && point2.x < xmax3)
xmax2 = point2.x;
if (point2.y > ymax2)
ymax2 = point2.y;
}
if (point2.x < inputImg.cols&&point2.x > b*inputImg.cols)
{
if (point1.x < xmin3 && point1.x>xmin2)
xmin3 = point1.x;
if (point1.y < ymin3)
ymin3 = point1.y;
if (point2.x > xmax3)
xmax3 = point2.x;
if (point2.y > ymax3)
ymax3 = point2.y;
}
++iter;
}
else
{
iter = contours_set.erase(iter);
}
}
if (xmin1 == a*inputImg.cols&& ymin1 == inputImg.rows&&xmax1 == 0 && ymax1== 0)
{
xmin1 = ymin1 = xmax1 = ymax1 = 0;
}
if (xmin2 == b*inputImg.cols&& ymin2 == inputImg.rows&& xmax2 == a*inputImg.cols&& ymax2 == 0)
{
xmin2 = ymin2 = xmax2 = ymax2 = 0;
}
if (xmin3 == inputImg.cols&&ymin3 == inputImg.rows&& xmax3 == b*inputImg.cols&& ymax3 == 0)
{
xmin3 = ymin3 = xmax3 = ymax3 = 0;
}
finalRect1= Rect(xmin1, ymin1, xmax1 - xmin1, ymax1 - ymin1);
finalRect2 = Rect(xmin2, ymin2, xmax2 - xmin2, ymax2 - ymin2);
finalRect3 = Rect(xmin3, ymin3, xmax3 - xmin3, ymax3 - ymin3);
rectangle(inputImg, finalRect1, Scalar(0, 255, 0));
rectangle(inputImg, finalRect2, Scalar(0, 255, 0));
rectangle(inputImg, finalRect3, Scalar(0, 255, 0));
imshow("Fire_Detection", inputImg);
}以上是“OpenCV視頻中火焰檢測識別的示例分析”這篇文章的所有內容,感謝各位的閱讀!相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望分享的內容對大家有所幫助,如果還想學習更多知識,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。