您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容介紹了“Java怎么實現Spring的IoC容器的操作”的有關知識,在實際案例的操作過程中,不少人都會遇到這樣的困境,接下來就讓小編帶領大家學習一下如何處理這些情況吧!希望大家仔細閱讀,能夠學有所成!
實現的功能:
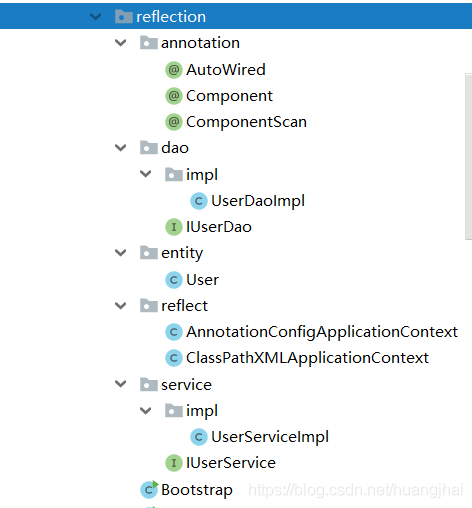
項目結構
下面是程序的項目結構圖:
自定義注解
容器實現
測試
實體類User的定義:
默認情況下將掃描整個項目的文件
可以使用@ComponentScan注解配置掃描路徑
只將被@Component注解修飾的類裝載到容器中
可以使用@AutoWired注解實現自動裝配
讀取配置文件中的聲明的類并注冊到容器中
下面是自定義的三個注解: @AutoWired,@Component,@ComponentScan。
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface AutoWired {
}
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Component {
}
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ComponentScan {
String[] value();
}其中AnnotationConfigApplicationContext和ClassPathXMLApplicationContext為核心的類,其中
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext類實現掃描文件和解析注解等功能。
package learn.reflection.reflect;
import learn.reflection.Bootstrap;
import learn.reflection.annotation.AutoWired;
import learn.reflection.annotation.Component;
import learn.reflection.annotation.ComponentScan;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
public class AnnotationConfigApplicationContext<T>{
//使用HaspMap存儲Bean
private HashMap<Class,Object> beanFactory=new HashMap<>();
//獲取Bean的方法
public T getBean(Class clazz){
return (T) beanFactory.get(clazz);
}
String path;//編譯后的字節碼存儲路徑
/**
* 初始化ApplicationContext,加載注解修飾的Bean到beanFactory
*/
public void initContextByAnnotation(){
//編譯后的項目根目錄:D:/idea_workplace/javaAppliTechnology/target/classes/
path = AnnotationConfigApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader().getResource("").getFile();
//查看啟動類Bootstrap是否有定義掃描包
ComponentScan annotation = Bootstrap.class.getAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
if (annotation!=null){
//有定義就只掃描自定義的
String[] definedPaths = annotation.value();
if (definedPaths!=null&&definedPaths.length>0){
loadClassInDefinedDir(path,definedPaths);
}
}else{
//默認掃描整個項目的目錄
System.out.println(path);
findClassFile(new File(path));
}
assembleObject();
}
/**
* 給@AutoWired修飾的屬性賦值
*/
private void assembleObject(){
Set<Map.Entry<Class, Object>> entries = beanFactory.entrySet();
//掃描所有容器中的Bean
for (Map.Entry<Class, Object> entry : entries) {
Object value = entry.getValue();
//獲取所有屬性
Field[] fields = value.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
//如果被@AutoWired注解修飾則進行賦值
AutoWired annotation = field.getAnnotation(AutoWired.class);
if (annotation!=null){
try {
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(value,beanFactory.get(field.getType()));
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 掃描用戶自定義的包
* @param path
* @param definedPaths
*/
private void loadClassInDefinedDir(String path, String[] definedPaths){
for (String definedPath : definedPaths) {
//轉換成絕對路徑
String s = definedPath.replaceAll("\\.", "/");
String fullName=path+s;
System.out.println(s);
findClassFile(new File(fullName));
}
}
/**
* 掃描項目中的每一個文件夾找到所有的class文件
*/
private void findClassFile(File pathParent) {
//路徑是否是目錄,子目錄是否為空
if (pathParent.isDirectory()) {
File[] childrenFiles = pathParent.listFiles();
if (childrenFiles == null || childrenFiles.length == 0) {
return;
}
for (File childrenFile : childrenFiles) {
if (childrenFile.isDirectory()) {
//遞歸調用直到找到所有的文件
findClassFile(childrenFile);
} else {
//找到文件
loadClassWithAnnotation(childrenFile);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 裝配找到的所有帶有@Component注解的類到容器
*/
private void loadClassWithAnnotation(File file) {
//1.去掉前面的項目絕對路徑
String pathWithClass=file.getAbsolutePath().substring(path.length()-1);
//2.將路徑的“/”轉化為“.”和去掉后面的.class
if (pathWithClass.contains(".class")){
String fullName = pathWithClass.replaceAll("\\\\", ".").replace(".class", "");
/**
* 根據獲取到的類的全限定名使用反射將實例添加到beanFactory中
*/
try {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(fullName);
//3.判斷是不是接口,不是接口才創建實例
if (!clazz.isInterface()){
//4.是否具有@Bean注解
Component annotation = clazz.getAnnotation(Component.class);
if (annotation!=null){
//5.創建實例對象
Object instance = clazz.newInstance();
//6.判斷是否有實現的接口
Class<?>[] interfaces = clazz.getInterfaces();
if (interfaces!=null&&interfaces.length>0){
//如果是有接口就將其接口的class作為key,實例對象作為value
System.out.println("正在加載【"+interfaces[0].getName()+"】 實例對象:"+instance.getClass().getName());
beanFactory.put(interfaces[0],instance);
}else{
System.out.println("正在加載【"+clazz.getName()+"】 實例對象:"+instance.getClass().getName());
beanFactory.put(clazz,instance);
}
//如果沒有接口就將自己的class作為key,實例對象作為value
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}ClassPathXMLApplicationContext類實現解析xml配置文件,并裝載組件到容器中。
package learn.reflection.reflect;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.jdom2.Document;
import org.jdom2.JDOMException;
import org.jdom2.Element;
import org.jdom2.xpath.XPath;
import org.jdom2.input.SAXBuilder;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.net.URISyntaxException;
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
/**
* @author Hai
* @date 2020/5/17 - 18:47
*/
public class ClassPathXMLApplicationContext{
private File file;
private Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap();
public ClassPathXMLApplicationContext(String config_file) {
URL url = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(config_file);
try {
file = new File(url.toURI());
XMLParsing();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void XMLParsing() throws Exception {
SAXBuilder builder = new SAXBuilder();
Document document = builder.build(file);
Element root = document.getRootElement();
List elementList = root.getChildren("bean");
Iterator i = elementList.iterator();
//讀取bean節點的所有信息
while (i.hasNext()) {
Element bean = (Element) i.next();
String id = bean.getAttributeValue("id");
//根據class創建實例
String cls = bean.getAttributeValue("class");
Object obj = Class.forName(cls).newInstance();
Method[] method = obj.getClass().getDeclaredMethods();
List<Element> list = bean.getChildren("property");
for (Element el : list) {
for (int n = 0; n < method.length; n++) {
String name = method[n].getName();
String temp = null;
//找到屬性對應的setter方法進行賦值
if (name.startsWith("set")) {
temp = name.substring(3, name.length()).toLowerCase();
if (el.getAttribute("name") != null) {
if (temp.equals(el.getAttribute("name").getValue())) {
method[n].invoke(obj, el.getAttribute("value").getValue());
}
}
}
}
}
map.put(id, obj);
}
}
public Object getBean(String name) {
return map.get(name);
}
}@Component
public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
public User(String username, String password) {
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
public User() {
}
//省略getter,setter方法
}在UserServiceImpl類中添加@Component注解,并使用@AutoWired注解注入容器中的IUerDao接口的實現類UserDaoImpl。
@Component
public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService {
@AutoWired
private IUserDao userDao;
@Override
public void login(User user) {
System.out.println("調用UserDaoImpl的login方法");
userDao.loginByUsername(user);
}
}UserDaoImpl類同樣添加@Component注解
@Component
public class UserDaoImpl implements IUserDao {
@Override
public void loginByUsername(User user) {
System.out.println("驗證用戶【"+user.getUsername()+"】登錄");
}
}在beans.xml中配置注冊User類,文件beans.xml的內容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans> <bean id="user" class="learn.reflection.entity.User"> <property name="username" value="張三" /> <property name="password" value="123" /> </bean> </beans>
下面同時使用 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext類和 ClassPathXMLApplicationContext類。
Bootstrap類作為啟動類添加注解@ComponentScan,指定掃描learn.reflection.dao和learn.reflection.service這兩個包。
@ComponentScan(value = {"learn.reflection.dao","learn.reflection.service"})
public class Bootstrap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
applicationContext.initContextByAnnotation();
UserServiceImpl userService = (UserServiceImpl) applicationContext.getBean(IUserService.class);
ClassPathXMLApplicationContext xmlApplicationContext = new ClassPathXMLApplicationContext("beans.xml");
User user = (User) xmlApplicationContext.getBean("user");
System.out.println(user);
userService.login(user);
}
}運行Bootstrap類,程序運行結果如下:
learn/reflection/dao
正在加載【learn.reflection.dao.IUserDao】 實例對象:learn.reflection.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl
learn/reflection/service
正在加載【learn.reflection.service.IUserService】 實例對象:learn.reflection.service.impl.UserServiceImpl
User{username='張三', password='123'}
調用UserDaoImpl的login方法
驗證用戶【張三】登錄
“Java怎么實現Spring的IoC容器的操作”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識可以關注億速云網站,小編將為大家輸出更多高質量的實用文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。