您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章給大家分享的是有關linux中find命令的用法的內容。小編覺得挺實用的,因此分享給大家做個參考,一起跟隨小編過來看看吧。
在linux中,find命令用于在指定目錄下查找文件,基本語法“find path -option..”。任何位于參數之前的字符串都將被視為欲查找的目錄名;如果使用該命令時,不設置任何參數,則find命令將在當前目錄下查找子目錄與文件。
本教程操作環境:Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.1系統、Dell G3電腦。
Linux find 命令用來在指定目錄下查找文件.
find path -option 【 -print 】 【 -exec -ok |xargs |grep 】 【 command {} \; 】find命令的參數:
1)path:要查找的目錄路徑。
~ 表示$HOME目錄
. 表示當前目錄
/ 表示根目錄
2)print:表示將結果輸出到標準輸出。
3)exec:對匹配的文件執行該參數所給出的shell命令。
形式為command {} \;,注意{}與\;之間有空格
4)ok:與exec作用相同,
區別在于,在執行命令之前,都會給出提示,讓用戶確認是否執行
5)|xargs 與exec作用相同 ,起承接作用
區別在于 |xargs 主要用于承接刪除操作 ,而 -exec 都可用 如復制、移動、重命名等
6)options :表示查找方式
options常用的有下選項:
-name filename #查找名為filename的文件 -perm #按執行權限來查找 -user username #按文件屬主來查找 -group groupname #按組來查找 -mtime -n +n #按文件 更改時間 來查找文件,-n指n天以內,+n指n天以前 -atime -n +n #按文件 訪問時間 來查找文件,-n指n天以內,+n指n天以前 -ctime -n +n #按文件 創建時間 來查找文件,-n指n天以內,+n指n天以前 -nogroup #查無有效屬組的文件,即文件的屬組在/etc/groups中不存在 -nouser #查無有效屬主的文件,即文件的屬主在/etc/passwd中不存 -type b/d/c/p/l/f #查是塊設備、目錄、字符設備、管道、符號鏈接、普通文件 -size n[c] #查長度為n塊[或n字節]的文件 -mount #查文件時不跨越文件系統mount點 -follow #如果遇到符號鏈接文件,就跟蹤鏈接所指的文件 -prune #忽略某個目錄
任何位于參數之前的字符串都將被視為欲查找的目錄名。如果使用該命令時,不設置任何參數,則 find 命令將在當前目錄下查找子目錄與文件。并且將查找到的子目錄和文件全部進行顯示。
下面通過一些簡單的例子來介紹下find的常規用法:
1、按名字查找
在當前目錄及子目錄中,查找大寫字母開頭的txt文件
$ find . -name '[A-Z]*.txt' -print
在/etc及其子目錄中,查找host開頭的文件
$ find /etc -name 'host*' -print
在$HOME目錄及其子目錄中,查找所有文件
$ find ~ -name '*' -print
在當前目錄及子目錄中,查找不是out開頭的txt文件
$ find . -name "out*" -prune -o -name "*.txt" -print
2、按目錄查找
在當前目錄除aa之外的子目錄內搜索 txt文件
$ find . -path "./aa" -prune -o -name "*.txt" -print
在當前目錄及除aa和bb之外的子目錄中查找txt文件
$ find . \( -path './dir0' -o -path './dir1' \) -a -prune -o -name '*.txt' -print
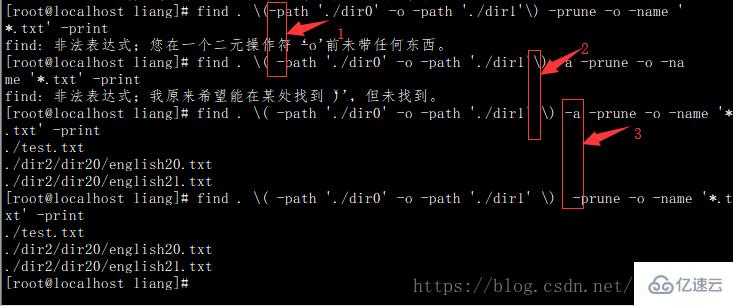
注意:在1、2處都需要加空格,否則會出現如圖所示的報錯
在3處加不加 -a都可以
在當前目錄,不再子目錄中,查找txt文件
$ find . ! -name "." -type d -prune -o -type f -name "*.txt" -print
或者
find . -name *.txt -type f -print
友情鏈接:Linux中find命令-path -prune用法詳解
3、按權限查找
在當前目錄及子目錄中,查找屬主具有讀寫執行,其他具有讀執行權限的文件
$find . -perm 755 -print
查找用戶有寫權限或者組用戶有寫權限的文件或目錄
find ./ -perm /220 find ./ -perm /u+w,g+w find ./ -perm /u=w,g=w
4、按類型查找 (b/d/c/p/l/f )
在當前目錄及子目錄下,查找符號鏈接文件
$ find . -type l -print
5、按屬主及屬組
查找屬主是www的文件
$ find / -user www -type f -print
查找屬主被刪除的文件
$ find / -nouser -type f -print
查找屬組 mysql 的文件
$ find / -group mysql -type f -print
查找用戶組被刪掉的文件
$ find / -nogroup -type f -print
6、按時間查找
查找2天內被更改過的文件
$ find . -mtime -2 -type f -print
查找2天前被更改過的文件
$ find . -mtime +2 -type f -print
查找一天內被訪問的文件
$ find . -atime -1 -type f -print
查找一天前被訪問的文件
$ find . -atime +1 -type f -print
查找一天內狀態被改變的文件
$ find . -ctime -1 -type f -print
查找一天前狀態被改變的文件
$ find . -ctime +1 -type f -print
查找10分鐘以前狀態被改變的文件
$ find . -cmin +10 -type f -print
7、按文件新舊
查找比 aa.txt 新的文件
$ find . -newer "aa.txt" -type f -print
查找比 aa.txt 舊的文件
$ find . ! -newer "aa.txt" -type f -print
查找比aa.txt新,比bb.txt舊的文件
$ find . -newer 'aa.txt' ! -newer 'bb.txt' -type f -print
8、按大小查找
查找超過1M的文件
$ find / -size +1M -type f -print
查找等于6字節的文件
$ find . -size 6c -print
查找小于32k的文件
$ find . -size -32k -print
9、執行命令
1)查找 del.txt 并刪除,刪除前提示確認
$ find . -name 'del.txt' -ok rm {} \; 2) 查找 aa.txt 并備份為aa.txt.bak
$ find . -name 'aa.txt' -exec cp {} {}.bak \;3)查當前目錄下的所有普通文件
# find . -type f -exec ls -l {} \;
-rw-r–r– 1 root root 34928 2003-02-25 ./conf/httpd.conf
-rw-r–r– 1 root root 12959 2003-02-25 ./conf/magic
-rw-r–r– 1 root root 180 2003-02-25 ./conf.d/README查當前目錄下的所有普通文件,并在 - exec 選項中使用 ls -l 命令將它們列出
4)在 /logs 目錄中查找更改時間在5日以前的文件并刪除它們
$ find logs -type f -mtime +5 -exec -ok rm {} \;5)查詢當天修改過的文件
# find ./ -mtime -1 -type f -exec ls -l {} \;6)查詢文件并詢問是否要顯示
# find ./ -mtime -1 -type f -ok ls -l {} \;
< ls … ./classDB.inc.php > ? y
-rw-r–r– 1 cnscn cnscn 13709 1月 12 12:22 ./classDB.inc.php
# find ./ -mtime -1 -type f -ok ls -l {} \;
< ls … ./classDB.inc.php > ? n關于 有沒有 -print 的區別
加 -print
查找目錄并列出目錄下的文件(為找到的每一個目錄單獨執行ls命令,沒有選項-print時文件列表前一行不會顯示目錄名稱)
find /home -type d -print -exec ls {} \;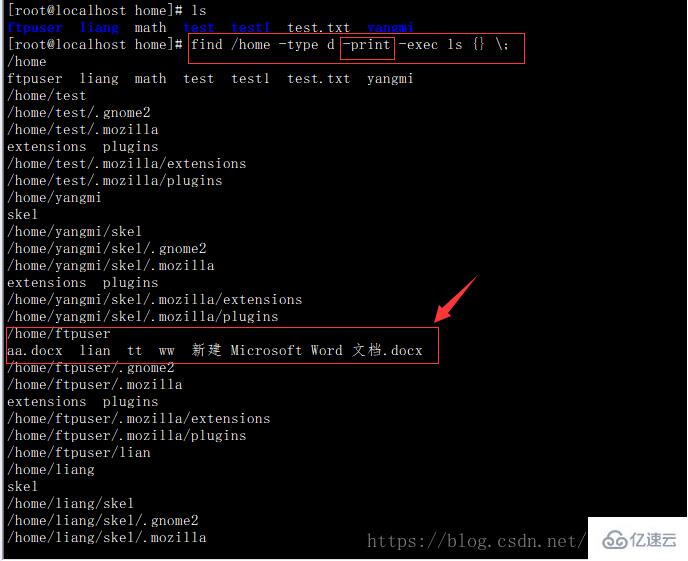
不加 -print
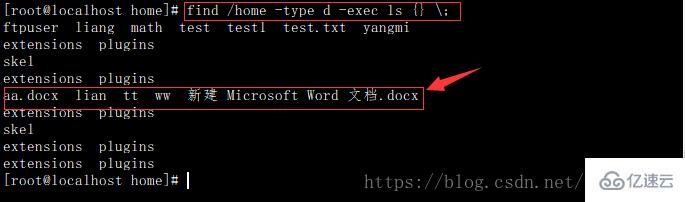
感謝各位的閱讀!關于“linux中find命令的用法”這篇文章就分享到這里了,希望以上內容可以對大家有一定的幫助,讓大家可以學到更多知識,如果覺得文章不錯,可以把它分享出去讓更多的人看到吧!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。