您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹“Redux-actions的原理和使用”,在日常操作中,相信很多人在Redux-actions的原理和使用問題上存在疑惑,小編查閱了各式資料,整理出簡單好用的操作方法,希望對大家解答”Redux-actions的原理和使用”的疑惑有所幫助!接下來,請跟著小編一起來學習吧!
一、前言
為什么介紹redux-actions呢?
第一次見到主要是接手公司原有的項目,發現有之前的大佬在處理redux的時候引入了它。
發現也確實 使得 在對redux的處理上方便了許多,而我為了更好地使用一個組件或者插件,都會去去嘗試閱讀源碼并寫成文章 ,這個也不例外。
發現也確實有意思,推薦大家使用redux的時候也引入redux-actions
在這里就介紹一下其使用方式,并且自己手寫實現一個簡單的redux-actions
二、介紹
學習 redux 中,總覺得 action 和 reducer 的代碼過于呆板,比如
2.1 創建action
let increment = ()=>({type:"increment"})2.2 reducer
let reducer = (state,action)=>{ switch(action.type){ case "increment":return {count:state.count+1};break; case "decrement":return {count:state.count-1};break; default:return state; } }2.3 觸發action
dispatch(increment())
綜上所示,我們難免會覺得 increment 和 reducer 做一個小 demo 還行,遇到邏輯偏復雜的項目后,項目管理維護就呈現弊端了。所以最后的方式就是將它們獨立出來,同時在 reducer 中給與開發者更多的主動權,不能僅停留在數字的增增減減。
redux-actions主要函數有createAction、createActions、handleAction、handleActions、combineActions。
基本上就是只有用到createAction,handleActions,handleAction
所以這里我們就只討論這三個個。
三、 認識與手寫createAction()
3.1 用法
一般創建Action方式:
let increment = ()=>({type:"increment"}) let incrementObj = increment();// { type:"increment"}使用createAction 創建 action
import { createAction } from 'redux-actions'; const increment = createAction('increment'); let incrementObj = increment();// { type:"increment"} let objincrement = increment(10);// {type:"increment",paylaod:10}我們可以看到
let increment = ()=>({type:"increment"}) let incrementObj = increment();// { type:"increment"}與
const increment = createAction('increment'); let incrementObj = increment();// { type:"increment"}是等效的,那為什么不直接用傳統方式呢?
不難發現有兩點:
鴻蒙官方戰略合作共建——HarmonyOS技術社區
傳統方式,需要自己寫個函數來返回incrementObj,而利用封裝好的createAtion就不用自己寫函數
傳統方式,在返回的incrementObj若是有payload需要自己添加上去,這是多么麻煩的事情啊,你看下面的代碼,如此的不方便。但是用了createAction返回的increment,我們添加上payload,十分簡單,直接傳個參數,它就直接把它作為payload的值了。
let increment = ()=>({type:"increment",payload:123})3.2 原理實現
我們先實現個簡單,值傳入 type參數的,也就是實現下面這段代碼的功能
const increment = createAction('increment'); let incrementObj = increment();// { type:"increment"}我們發現createAction('increment')()才返回最終的action對象。這不就是個柯里化函數嗎?
所以我們可以非常簡單的寫出來,如下面代碼所示,我們把type類型當作action對象的一個屬性了
function createAction(type) { return () => { const action = { type }; return action; }; }好了現在,現在實現下面這個功能,也就是有payload的情況
const increment = createAction('increment'); let objincrement = increment(10);// {type:"increment",paylaod:10}很明顯,這個payload是 在createAction('increment')返回的函數的參數,所以我們輕而易舉地給action添加上了payload。
function createAction(type) { return (payload) => { const action = { type, payload }; return action; }; }但是像第一種情況我們是不傳payload的,也就是說返回的action是不希望帶有payload的,但是這里我們寫成這樣就是 默認一定要傳入payload的了。
所以我們需要添加個判斷,當不傳payload的時候,action就不添加payload屬性。
function createAction(type) { return (payload) => { const action = { type, }; if(payload !== undefined){ action.payload = payload } return action; }; }在實際項目中我更喜歡下面這種寫法,但它是等價于上面這種寫法的
function createAction(type) { return (payload) => { const action = { type, ...payload?{payload}:{} }; return action; }; }其實createAction的參數除了type,還可以傳入一個回調函數,這個函數表示對payload的處理。
const increment = createAction('increment'); let objincrement = increment(10);// {type:"increment",paylaod:10}像上面的代碼所示,我們希望的是傳入10之后是返回的action中的payload是我們傳入的2倍數
const increment = createAction('increment',(t)=> t * 2); let objincrement = increment(10);// {type:"increment",paylaod:20}現在,就讓我們實現一下。
function createAction(type,payloadCreator) { return (payload) => { const action = { type, }; if(payload !== undefined){ action.payload = payloadCreator(payload) } return action; };}
function createAction(type,payloadCreator) { return (payload) => { const action = { type, }; if(payload !== undefined){ action.payload = payloadCreator(payload) } return action; }; }太簡單了吧!但是我們又犯了前邊同樣的錯誤,就是我們使用createAction的時候,不一定會傳入payloadCreator這個回調函數,所以我們還需要判斷下
function createAction(type,payloadCreator) { return (payload) => { const action = { type, }; if(payload !== undefined){ action.payload = payloadCreator?payloadCreator(payload):payload } return action; }; }完美。
接下來看看 redux-action的 handleActions吧
四、認識handleActions
我們先看看傳統的reducer是怎么使用的
let reducer = (state,action)=>{ switch(action.type){ case "increment":return {count:state.count+1};break; case "decrement":return {count:state.count-1};break; default:return state; } }再看看使用了handleActions
const INCREMENT = "increment" const DECREMENT = "decrement" var reducer = handleActions({ [INCREMENT]: (state, action) => ({ counter: state.counter + action.payload }), [DECREMENT]: (state, action) => ({ counter: state.counter - action.payload }) },initstate)這里大家不要被{[DECREMENT]:(){}} 的寫法嚇住哈,就是把屬性寫成變量了而已。
我們在控制臺 console.log(reducer) 看下結果
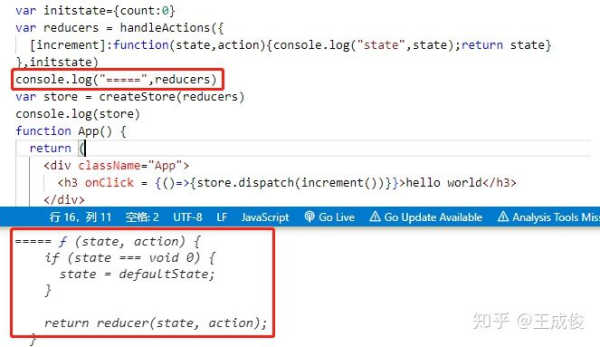
最后返回的就是一個 reducer 函數。
這樣就實現了 reducer 中功能化的自由,想寫什么程序,我們只要寫在
{[increment]:(state,action)=>{}}這個函數內就行,同時也可以把這些函數獨立成一個文件,再引入進來就行
import {increment,decrement}from "./reducers.js" var initstate = {count:0} var reducer = createReducer({ [INCREMENT]: increment, [DECREMENT]: decrement },initstate)reducers.js
//reducers.js export let increment = (state,action)=>({counter: state.counter + action.payload}) export let decrement = (state,action)=>({counter: state.counter - action.payload})可見,
handleactions 可以簡化 reducers 的寫法 不用那么多 switch 而且可以把函數獨立出來,這樣reducer就再也不會有一大堆代碼了。
本來要講handleActions的實現了,但是在這之前,我們必須先講一下handleAction,對,你仔細看,沒有s
五、認識與手寫實現handleAction
5.1 用法
看下使用方式
const incrementReducer = handleAction(INCREMENT, (state, action) => { return {counter: state.counter + action.payload} }, initialState);可以看出來,跟handleActions的區別 就是,handleAction生成的reducer是專門來處理一個action的。
5.2 原理實現
如果你看過redux原理的話(如果你沒看過的話,推薦你去看下我之前的文章Redux 源碼解析系列(一) -- Redux的實現思想),相信你應該知道reducer(state,action)返回的結果是一個新的state,然后這個新的state會和舊的state進行對比,如果發現兩者不一樣的話,就會重新渲染使用了state的組件,并且把新的state賦值給舊的state.
也就是說handleAction()返回一個reducer函數,然后incrementReducer()返回一個新的state。
先實現返回一個reducer函數
function handleAction(type, callback) { return (state, action) => { }; }接下來應當是執行reducer(state,action)是時候返回state,也就是執行下面返回的這個
(state, action) => { };而其實就是執行callback(state) 然后返回一個新的 state
function handleAction(type, callback) { return (state, action) => { return callback(state) }; }或許你會有疑問,為什么要這么搞,而不直接像下面這樣,就少了一層包含。
function handleAction(state,type, callback) { return callback(state) }這才是它的巧妙之處。它在handleAction()返回的reducer()時,可不一定會執行callback(state),只有handleAction傳入的type跟reducer()中傳入的action.type匹配到了才會執行,否則就直接return state。表示沒有任何處理
function handleAction(type, callback) { return (state, action) => { return callback(state) }; }因此我們需要多加一層判斷
function handleAction(type, callback) { return (state, action) => { if (action.type !== type) { return state; } return callback(state) }; }多么完美啊!
好了現在我們來實現下handleActions
六、handleActions原理實現
function handleActions(handlers, defaultState) { const reducers = Object.keys(handlers).map(type => { return handleAction(type, handlers[type]); }); const reducer = reduceReducers(...reducers) return (state = defaultState, action) => reducer(state, action) }看,就這幾行代碼,是不是很簡單,不過應該不好理解,不過沒關系,我依舊將它講得粗俗易懂。
我們拿上面用到的例子來講好了
var reducer = handleActions({
[INCREMENT]: (state, action) => ({
counter: state.counter + action.payload
}),
[DECREMENT]: (state, action) => ({
counter: state.counter - action.payload
})
},initstate)
{ [INCREMENT]: (state, action) => ({ counter: state.counter + action.payload }), [DECREMENT]: (state, action) => ({ counter: state.counter - action.payload }) }上面這個對象,經過下面的代碼之后
const reducers = Object.keys(handlers).map(type => { return handleAction(type, handlers[type]); });返回的reducer,其實就是
[ handleAction(INCREMENT,(state, action) => ({ counter: state.counter + action.payload })), handleAction(DECREMENT,(state, action) => ({ counter: state.counter + action.payload })), ]為什么要變成一個handleAction的數組,
我大概想到了,是想每次dispatch(action)的時候,就要遍歷去執行這個數組中的所有handleAction。
那豈不是每個handleAction返回的reducer都要執行?確實,但是別忘了我們上面講到的,如果handleAction 判斷到 type和action.type 是不會對state進行處理的而是直接返回state
function handleAction(type, callback) { return (state, action) => { if (action.type !== type) { return state; } return callback(state) }; }沒有即使每個 handleAction 都執行了也沒關系
那應該怎么遍歷執行,用map,forEach?不,都不對。我們看回源碼
function handleActions(handlers, defaultState) { const reducers = Object.keys(handlers).map(type => { return handleAction(type, handlers[type]); }); const reducer = reduceReducers(...reducers) return (state = defaultState, action) => reducer(state, action) }使用了
const reducer = reduceReducers(...reducers)
用了reduceReducers這個方法,顧名思義,看這方法名,意思就是用reduce這個來遍歷執行reducers這個數組。也就是這個數組。
[ handleAction(INCREMENT,(state, action) => ({ counter: state.counter + action.payload })), handleAction(DECREMENT,(state, action) => ({ counter: state.counter + action.payload })), ]我們看下reduceReducers的內部原理
function reduceReducers(...args) { const reducers = args; return (prevState, value) => { return reducers.reduce((newState, reducer, index) => { return reducer(newState, value); }, prevState); }; };我們發現將reducers這個數組放入reduceReducers,然后執行reduceReducers,就會返回
(prevState, value) => { return reducers.reduce((newState, reducer, index) => { return reducer(newState, value); }, prevState); };這個方法,也就是說執行這個方法就會 執行
return reducers.reduce((newState, reducer, index) => { return reducer(newState, value); }, prevState);也就是會使用reduce遍歷執行reducers,為什么要用reduce來遍歷呢?
這是因為需要把上一個handleAction執行后返回的state傳遞給下一個。
這個思想有一點我們之間之前講的關于compose函數的思想,感興趣的話,可以去看一下【前端進階之認識與手寫compose方法】
function handleActions(handlers, defaultState) { const reducers = Object.keys(handlers).map(type => { return handleAction(type, handlers[type]); }); const reducer = reduceReducers(...reducers) return (state = defaultState, action) => reducer(state, action) }現在也就是說這里的reducer是reduceReducers(...reducers)返回的結果,也就
reducer = (prevState, value) => { return reducers.reduce((newState, reducer, index) => { return reducer(newState, value); }, prevState); };而handleActions返回
(state = defaultState, action) => reducer(state, action)
也就是說handleActions其實是返回這樣一個方法。
(state = defaultState, action) => { return reducers.reduce((newState, reducer, index) => { return reducer(newState, value); }, state); }好家伙,在handleAction之間利用reduce來傳遞state,真是個好方法,學到了。
貼一下github 的redux-action的源碼地址,感興趣的朋友可以親自去閱讀一下,畢竟本文是做了簡化的 redux-actions:https://github.com/redux-utilities/redux-actions
到此,關于“Redux-actions的原理和使用”的學習就結束了,希望能夠解決大家的疑惑。理論與實踐的搭配能更好的幫助大家學習,快去試試吧!若想繼續學習更多相關知識,請繼續關注億速云網站,小編會繼續努力為大家帶來更多實用的文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。