您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要講解了“k8s集群如何安裝redis及監控”,文中的講解內容簡單清晰,易于學習與理解,下面請大家跟著小編的思路慢慢深入,一起來研究和學習“k8s集群如何安裝redis及監控”吧!
k8s集群
root@pi4-master01:~# kubectl get nodes -o wide NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME pi4-master01 Ready master 4d18h v1.15.10 192.168.5.18 <none> Ubuntu 20.04 LTS 5.4.0-1011-raspi docker://18.9.9 pi4-node01 Ready node 4d17h v1.15.10 192.168.5.19 <none> Ubuntu 20.04 LTS 5.4.0-1011-raspi docker://18.9.9 pi4-node02 Ready node 4d17h v1.15.10 192.168.5.20 <none> Ubuntu 20.04 LTS 5.4.0-1011-raspi docker://18.9.9
k8s集群已安裝helm
root@pi4-master01:~/k8s/cluster-monitoring-0.37.0# helm version
Client: &version.Version{SemVer:"v2.15.0", GitCommit:"c2440264ca6c078a06e088a838b0476d2fc14750", GitTreeState:"clean"}
Server: &version.Version{SemVer:"v2.15.0+unreleased", GitCommit:"9668ad4d90c5e95bd520e58e7387607be6b63bb6", GitTreeState:"dirty"}k8s集群已安裝存儲類,并設置為默認存儲
root@pi4-master01:~/k8s/cluster-monitoring-0.37.0# kubectl get storageclass NAME PROVISIONER AGE local-path (default) rancher.io/local-path 4d15h
對了,如果你還沒有樹莓派k8s集群,這里有一篇樹莓派 k8s 集群入坑指南可以參考,歡迎入坑。
這里我們選擇用helm安裝,helm有一個默認倉庫stable,指向https://kubernetes-charts.storage.googleapis.com, 國內訪問比較困難,所以網上很多安裝helm的文檔都以https://kubernetes.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/charts 來代替。但最近發現,這個倉庫也不再更新了,很多chart的最新版本都沒有,這里提供一個新地址http://mirror.azure.cn/kubernetes/charts 。經簡單驗證,發現這個倉庫至少比阿里的那個倉庫新,建議切換。
root@pi4-master01:~# helm repo remove stable "stable" has been removed from your repositories root@pi4-master01:~# helm repo add stable http://mirror.azure.cn/kubernetes/charts/ "stable" has been added to your repositories root@pi4-master01:~# helm repo list NAME URL local http://127.0.0.1:8879/charts stable http://mirror.azure.cn/kubernetes/charts/ root@k8s-master:~# helm search redis NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION stable/prometheus-redis-exporter 3.5.0 1.3.4 Prometheus exporter for Redis metrics stable/redis 10.5.7 5.0.7 DEPRECATED Open source, advanced key-value store. It is o... stable/redis-ha 4.4.4 5.0.6 Highly available Kubernetes implementation of Redis stable/sensu 0.2.3 0.28 Sensu monitoring framework backed by the Redis transport
stable倉庫里有3個關于redis的chart,這里我們選擇第3個stable/redis-ha。該chart是采用Sentinel(哨兵)模式的高可用方案,在集群出現故障的時候自動進行故障轉移,保證集群的可用性。
使用helm安裝redis命令如下
helm install -n redis-ha \ stable/redis-ha \ --set image.repository=arm64v8/redis
通過上述命令,將以默認的配置在Kubernetes中部署Redis。默認情況下,chart會安裝部署3個Sentinel Pod,1個master Pod和2個slave Pod。
該chart中涉及的鏡像均是x86的,只要把相關的鏡像換成arm64v8架構的鏡像即可。另外,該chart默認開啟了持久化存儲,不指定storageclass的話,將使用k8s的默認存儲。因為我們的樹莓派k8s集群已經設置了local-path為默認storageclass,所以不需要關閉持久化存儲既可正常安裝。
查看創建的pod
root@pi4-master01:~# kubectl get pod | grep redis redis-ha-server-0 2/2 Running 0 5m31s redis-ha-server-1 2/2 Running 0 2m12s redis-ha-server-2 2/2 Running 0 93s
查看創建的svc
root@pi4-master01:~# kubectl get svc | grep redis redis-ha ClusterIP None <none> 6379/TCP,26379/TCP 6m redis-ha-announce-0 ClusterIP 10.106.118.26 <none> 6379/TCP,26379/TCP 6m redis-ha-announce-1 ClusterIP 10.106.227.172 <none> 6379/TCP,26379/TCP 6m redis-ha-announce-2 ClusterIP 10.98.139.156 <none> 6379/TCP,26379/TCP 6m
查看創建的pv,pvc
root@pi4-master01:~# kubectl get pvc,pv | grep redis persistentvolumeclaim/data-redis-ha-server-0 Bound pvc-fac03faa-2e92-4255-8fea-ee141b429584 10Gi RWO local-path 6m34s persistentvolumeclaim/data-redis-ha-server-1 Bound pvc-31043858-82f0-4c15-bea4-5a8b050d15d2 10Gi RWO local-path 3m15s persistentvolumeclaim/data-redis-ha-server-2 Bound pvc-3a849e82-8d9c-438d-8019-c0b83791623b 10Gi RWO local-path 2m36s persistentvolume/pvc-31043858-82f0-4c15-bea4-5a8b050d15d2 10Gi RWO Delete Bound default/data-redis-ha-server-1 local-path 3m9s persistentvolume/pvc-3a849e82-8d9c-438d-8019-c0b83791623b 10Gi RWO Delete Bound default/data-redis-ha-server-2 local-path 2m31s persistentvolume/pvc-fac03faa-2e92-4255-8fea-ee141b429584 10Gi RWO Delete Bound default/data-redis-ha-server-0 local-path 6m31s
進入容器
root@pi4-master01:~# kubectl exec -it redis-ha-server-0 sh Defaulting container name to redis. Use 'kubectl describe pod/redis-ha-server-0 -n default' to see all of the containers in this pod. /data $ redis-cli -v redis-cli 5.0.6 /data $ redis-server -v Redis server v=5.0.6 sha=00000000:0 malloc=jemalloc-5.1.0 bits=64 build=81d048c73d7c73a
連接redis服務
/data $ redis-cli 127.0.0.1:6379> keys * 1) "key" 127.0.0.1:6379> get key "hello" 127.0.0.1:6379> set hello redis OK 127.0.0.1:6379> get hello "redis" 127.0.0.1:6379>
基于helm在樹莓派k8s集群安裝redis還是很方便的,只需要使用arm64v8架構的鏡像即可。但是如果想更部署的mysql更具有個性,還是很有必要研究一下該chart的其它配置項,這些配置項我們可以通過helm inspect命令來查看
root@pi4-master01:~# helm inspect values stable/redis-ha
## Configure resource requests and limits
## ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/compute-resources/
##
image:
repository: redis
tag: 5.0.6-alpine
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
## Reference to one or more secrets to be used when pulling images
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/pull-image-private-registry/
## This imagePullSecrets is only for redis images
##
imagePullSecrets: []
# - name: "image-pull-secret"
## replicas number for each component
replicas: 3
## Kubernetes priorityClass name for the redis-ha-server pod
# priorityClassName: ""
## Custom labels for the redis pod
labels: {}
## Pods Service Account
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/configure-service-account/
serviceAccount:
## Specifies whether a ServiceAccount should be created
##
create: true
## The name of the ServiceAccount to use.
## If not set and create is true, a name is generated using the redis-ha.fullname template
# name:
## Enables a HA Proxy for better LoadBalancing / Sentinel Master support. Automatically proxies to Redis master.
## Recommend for externally exposed Redis clusters.
## ref: https://cbonte.github.io/haproxy-dconv/1.9/intro.html
haproxy:
enabled: false
# Enable if you want a dedicated port in haproxy for redis-slaves
readOnly:
enabled: false
port: 6380
replicas: 3
image:
repository: haproxy
tag: 2.0.4
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
## Reference to one or more secrets to be used when pulling images
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/pull-image-private-registry/
##
imagePullSecrets: []
# - name: "image-pull-secret"
annotations: {}
resources: {}
emptyDir: {}
## Enable sticky sessions to Redis nodes via HAProxy
## Very useful for long-living connections as in case of Sentry for example
stickyBalancing: false
## Kubernetes priorityClass name for the haproxy pod
# priorityClassName: ""
## Service type for HAProxy
##
service:
type: ClusterIP
loadBalancerIP:
annotations: {}
serviceAccount:
create: true
## Official HAProxy embedded prometheus metrics settings.
## Ref: https://github.com/haproxy/haproxy/tree/master/contrib/prometheus-exporter
##
metrics:
enabled: false
# prometheus port & scrape path
port: 9101
portName: exporter-port
scrapePath: /metrics
serviceMonitor:
# When set true then use a ServiceMonitor to configure scraping
enabled: false
# Set the namespace the ServiceMonitor should be deployed
# namespace: monitoring
# Set how frequently Prometheus should scrape
# interval: 30s
# Set path to redis-exporter telemtery-path
# telemetryPath: /metrics
# Set labels for the ServiceMonitor, use this to define your scrape label for Prometheus Operator
# labels: {}
# Set timeout for scrape
# timeout: 10s
init:
resources: {}
timeout:
connect: 4s
server: 30s
client: 30s
check: 2s
securityContext:
runAsUser: 1000
fsGroup: 1000
runAsNonRoot: true
## Whether the haproxy pods should be forced to run on separate nodes.
hardAntiAffinity: true
## Additional affinities to add to the haproxy pods.
additionalAffinities: {}
## Override all other affinity settings for the haproxy pods with a string.
affinity: |
## Custom config-haproxy.cfg files used to override default settings. If this file is
## specified then the config-haproxy.cfg above will be ignored.
# customConfig: |-
# Define configuration here
## Place any additional configuration section to add to the default config-haproxy.cfg
# extraConfig: |-
# Define configuration here
## Role Based Access
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/admin/authorization/rbac/
##
rbac:
create: true
sysctlImage:
enabled: false
command: []
registry: docker.io
repository: busybox
tag: 1.31.1
pullPolicy: Always
mountHostSys: false
resources: {}
## Use an alternate scheduler, e.g. "stork".
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/configure-multiple-schedulers/
##
# schedulerName:
## Redis specific configuration options
redis:
port: 6379
masterGroupName: "mymaster" # must match ^[\\w-\\.]+$) and can be templated
config:
## Additional redis conf options can be added below
## For all available options see http://download.redis.io/redis-stable/redis.conf
min-replicas-to-write: 1
min-replicas-max-lag: 5 # Value in seconds
maxmemory: "0" # Max memory to use for each redis instance. Default is unlimited.
maxmemory-policy: "volatile-lru" # Max memory policy to use for each redis instance. Default is volatile-lru.
# Determines if scheduled RDB backups are created. Default is false.
# Please note that local (on-disk) RDBs will still be created when re-syncing with a new slave. The only way to prevent this is to enable diskless replication.
save: "900 1"
# When enabled, directly sends the RDB over the wire to slaves, without using the disk as intermediate storage. Default is false.
repl-diskless-sync: "yes"
rdbcompression: "yes"
rdbchecksum: "yes"
## Custom redis.conf files used to override default settings. If this file is
## specified then the redis.config above will be ignored.
# customConfig: |-
# Define configuration here
resources: {}
# requests:
# memory: 200Mi
# cpu: 100m
# limits:
# memory: 700Mi
## Sentinel specific configuration options
sentinel:
port: 26379
quorum: 2
config:
## Additional sentinel conf options can be added below. Only options that
## are expressed in the format simialar to 'sentinel xxx mymaster xxx' will
## be properly templated expect maxclients option.
## For available options see http://download.redis.io/redis-stable/sentinel.conf
down-after-milliseconds: 10000
## Failover timeout value in milliseconds
failover-timeout: 180000
parallel-syncs: 5
maxclients: 10000
## Custom sentinel.conf files used to override default settings. If this file is
## specified then the sentinel.config above will be ignored.
# customConfig: |-
# Define configuration here
resources: {}
# requests:
# memory: 200Mi
# cpu: 100m
# limits:
# memory: 200Mi
securityContext:
runAsUser: 1000
fsGroup: 1000
runAsNonRoot: true
## Node labels, affinity, and tolerations for pod assignment
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/#nodeselector
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/#taints-and-tolerations-beta-feature
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/#affinity-and-anti-affinity
nodeSelector: {}
## Whether the Redis server pods should be forced to run on separate nodes.
## This is accomplished by setting their AntiAffinity with requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution as opposed to preferred.
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/#inter-pod-affinity-and-anti-affinity-beta-feature
##
hardAntiAffinity: true
## Additional affinities to add to the Redis server pods.
##
## Example:
## nodeAffinity:
## preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
## - weight: 50
## preference:
## matchExpressions:
## - key: spot
## operator: NotIn
## values:
## - "true"
##
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/#affinity-and-anti-affinity
##
additionalAffinities: {}
## Override all other affinity settings for the Redis server pods with a string.
##
## Example:
## affinity: |
## podAntiAffinity:
## requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
## - labelSelector:
## matchLabels:
## app: {{ template "redis-ha.name" . }}
## release: {{ .Release.Name }}
## topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
## preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
## - weight: 100
## podAffinityTerm:
## labelSelector:
## matchLabels:
## app: {{ template "redis-ha.name" . }}
## release: {{ .Release.Name }}
## topologyKey: failure-domain.beta.kubernetes.io/zone
##
affinity: |
# Prometheus exporter specific configuration options
exporter:
enabled: false
image: oliver006/redis_exporter
tag: v1.3.2
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
# prometheus port & scrape path
port: 9121
scrapePath: /metrics
# cpu/memory resource limits/requests
resources: {}
# Additional args for redis exporter
extraArgs: {}
# Used to mount a LUA-Script via config map and use it for metrics-collection
# script: |
# -- Example script copied from: https://github.com/oliver006/redis_exporter/blob/master/contrib/sample_collect_script.lua
# -- Example collect script for -script option
# -- This returns a Lua table with alternating keys and values.
# -- Both keys and values must be strings, similar to a HGETALL result.
# -- More info about Redis Lua scripting: https://redis.io/commands/eval
#
# local result = {}
#
# -- Add all keys and values from some hash in db 5
# redis.call("SELECT", 5)
# local r = redis.call("HGETALL", "some-hash-with-stats")
# if r ~= nil then
# for _,v in ipairs(r) do
# table.insert(result, v) -- alternating keys and values
# end
# end
#
# -- Set foo to 42
# table.insert(result, "foo")
# table.insert(result, "42") -- note the string, use tostring() if needed
#
# return result
serviceMonitor:
# When set true then use a ServiceMonitor to configure scraping
enabled: false
# Set the namespace the ServiceMonitor should be deployed
# namespace: monitoring
# Set how frequently Prometheus should scrape
# interval: 30s
# Set path to redis-exporter telemtery-path
# telemetryPath: /metrics
# Set labels for the ServiceMonitor, use this to define your scrape label for Prometheus Operator
# labels: {}
# Set timeout for scrape
# timeout: 10s
podDisruptionBudget: {}
# maxUnavailable: 1
# minAvailable: 1
## Configures redis with AUTH (requirepass & masterauth conf params)
auth: false
# redisPassword:
## Use existing secret containing key `authKey` (ignores redisPassword)
# existingSecret:
## Defines the key holding the redis password in existing secret.
authKey: auth
persistentVolume:
enabled: true
## redis-ha data Persistent Volume Storage Class
## If defined, storageClassName: <storageClass>
## If set to "-", storageClassName: "", which disables dynamic provisioning
## If undefined (the default) or set to null, no storageClassName spec is
## set, choosing the default provisioner. (gp2 on AWS, standard on
## GKE, AWS & OpenStack)
##
# storageClass: "-"
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
size: 10Gi
annotations: {}
# reclaimPolicy per https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/persistent-volumes/#reclaiming
reclaimPolicy: ""
init:
resources: {}
# To use a hostPath for data, set persistentVolume.enabled to false
# and define hostPath.path.
# Warning: this might overwrite existing folders on the host system!
hostPath:
## path is evaluated as template so placeholders are replaced
# path: "/data/{{ .Release.Name }}"
# if chown is true, an init-container with root permissions is launched to
# change the owner of the hostPath folder to the user defined in the
# security context
chown: true
emptyDir: {}顯然,配置項很豐富,從redis的配置文件、是否開啟監控都能支持。
開啟監控前,需要在集群部署prometheus,否則不會有效果。可以參考樹莓派k8s集群安裝監控prometheus進行部署。
開啟監控,需要設置exporter.enabled和exporter.serviceMonitor.enabled為true,且exporter.image需要設置為支持arm64v8架構的鏡像監控才能使用,這里選擇的鏡像是crisidev/redis-exporter:linux-arm64
使用helm安裝開啟監控的redis命令如下
helm install -n redis-ha \ stable/redis-ha \ --set image.repository=arm64v8/redis \ --set exporter.enabled=true \ --set exporter.image=crisidev/redis-exporter \ --set exporter.tag=linux-arm64 \ --set exporter.serviceMonitor.enabled=true
確認安裝狀態
root@pi4-master01:~# kubectl get pod | grep redis redis-ha-server-0 3/3 Running 0 4m39s redis-ha-server-1 3/3 Running 0 4m4s redis-ha-server-2 3/3 Running 0 2m11s root@pi4-master01:~# kubectl get svc|grep redis redis-ha ClusterIP None <none> 6379/TCP,26379/TCP,9121/TCP 6m19s redis-ha-announce-0 ClusterIP 10.109.95.179 <none> 6379/TCP,26379/TCP,9121/TCP 6m19s redis-ha-announce-1 ClusterIP 10.108.235.236 <none> 6379/TCP,26379/TCP,9121/TCP 6m18s redis-ha-announce-2 ClusterIP 10.97.37.205 <none> 6379/TCP,26379/TCP,9121/TCP 6m18s root@pi4-master01:~# kubectl get servicemonitor|grep redis redis-ha 5m41s
在prometheus查看exporter是否生效
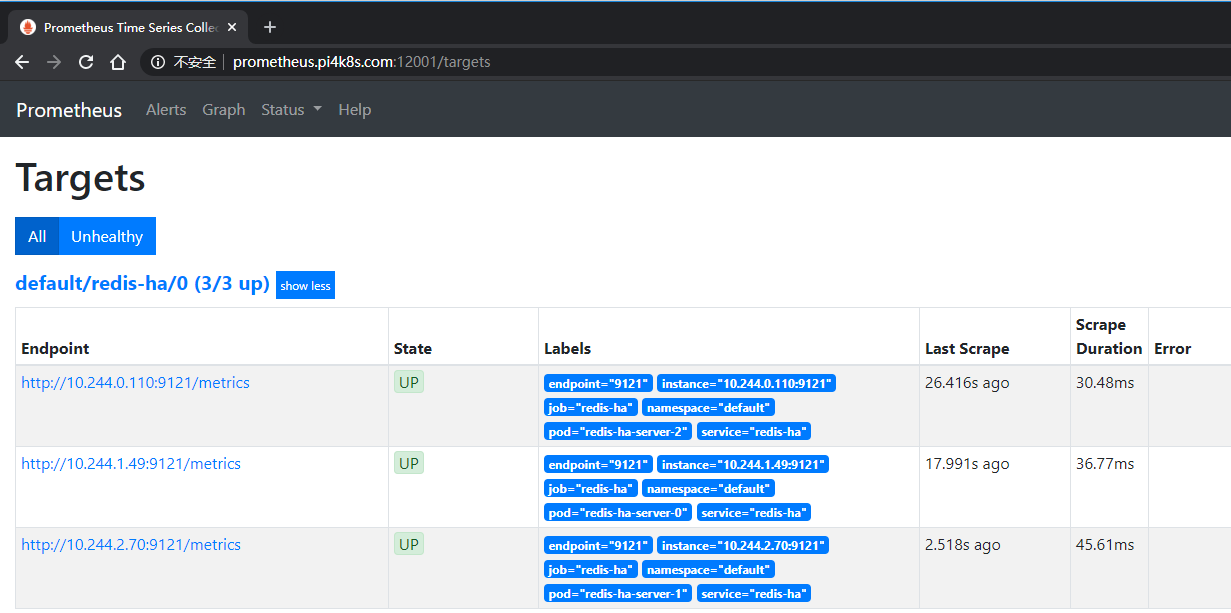
生效后在grafana系統配置redis監控面板
redis監控面板 :https://grafana.com/grafana/dashboards/11835
部署步驟如下:
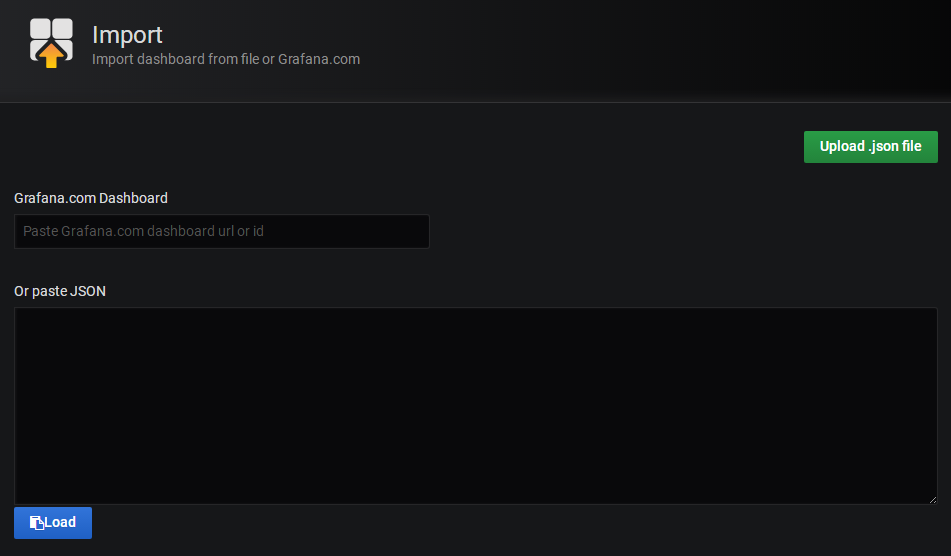
點"Upload .json file"按鈕,選擇已經下載好的redis監控面板文件 ,進入面板設置界面如下
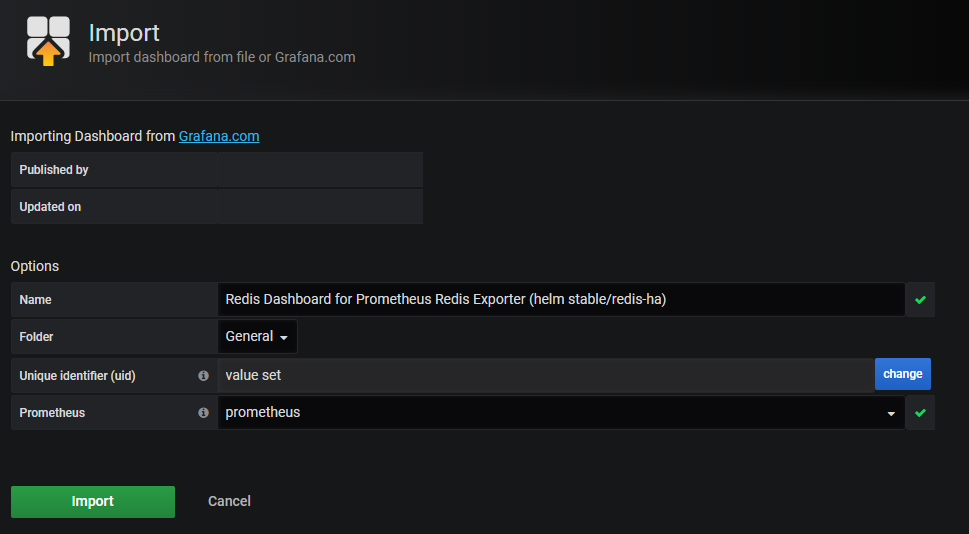 設置好相應參數后,點"Import"按鈕,繼續導入,引導入redis監控頁面如下
設置好相應參數后,點"Import"按鈕,繼續導入,引導入redis監控頁面如下
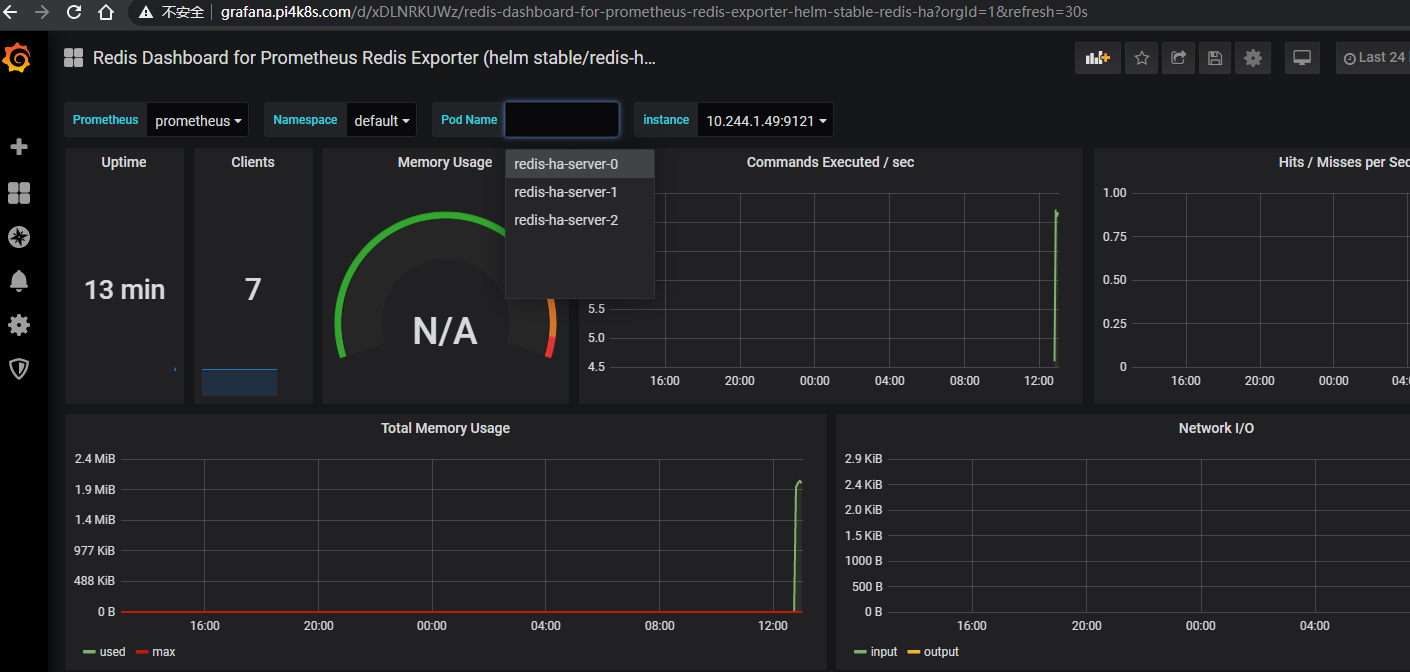
感謝各位的閱讀,以上就是“k8s集群如何安裝redis及監控”的內容了,經過本文的學習后,相信大家對k8s集群如何安裝redis及監控這一問題有了更深刻的體會,具體使用情況還需要大家實踐驗證。這里是億速云,小編將為大家推送更多相關知識點的文章,歡迎關注!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。