溫馨提示×
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
點擊 登錄注冊 即表示同意《億速云用戶服務條款》
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
今天就跟大家聊聊有關Detectron2注冊機制Registry實現的示例分析,可能很多人都不太了解,為了讓大家更加了解,小編給大家總結了以下內容,希望大家根據這篇文章可以有所收獲。
在Detectron2 中,經常會對一個類或者函數進行注冊:
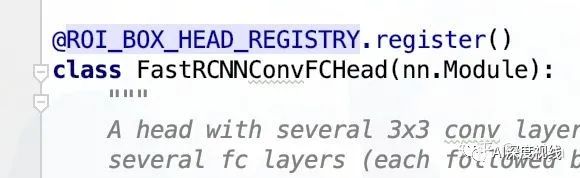
關于這種操作,必須要明確兩點:
registry_machine = Registry('registry_machine')registry_machine.register()def print_hello_world(word):print('hello {}'.format(word))registry_machine.register()def print_hi_world(word):print('hi {}'.format(word))if __name__ == '__main__':cfg1 = 'print_hello_word'registry_machine.get(cfg1)('world')cfg2 = 'print_hi_word'registry_machine.get(cfg2)('world')
可以看到,如果創建了一個Registry的對象,并在方法/類定義的時候用裝飾器裝飾它,則可以通過 registry_machine.get(方法名)的 辦法來間接的調用被注冊的函數
如果是我,我可能會寫出這種可擴展性超級低的暴搓的代碼:
if class_name == 'VGG': model = build_VGG(args)elif class_name == 'ResNet': model = build_ResNet(args)
但是如果用了注冊類,代碼就是這樣的:
class_name = 'VGG' # 'ResNet'model = model_registry(class_name)(args)
可以看到代碼的可擴展性變得非常強了
這部分就直接展示注冊類的代碼了,有興趣的朋友可以研究一下其中的細節,個人覺得對裝飾器的應用是非常的好了
# Copyright (c) Facebook, Inc. and its affiliates. All Rights Reservedclass Registry(object):def __init__(self, name):"""Args:name (str): the name of this registry"""self._name = nameself._obj_map = {}def _do_register(self, name, obj):assert (name not in self._obj_map), "An object named '{}' was already registered in '{}' registry!".format(name, self._name)self._obj_map[name] = objdef register(self, obj=None):"""Register the given object under the the name `obj.__name__`.Can be used as either a decorator or not. See docstring of this class for usage."""if obj is None:# used as a decoratordef deco(func_or_class):name = func_or_class.__name__self._do_register(name, func_or_class)return func_or_classreturn deco# used as a function callname = obj.__name__self._do_register(name, obj)def get(self, name):ret = self._obj_map.get(name)if ret is None:raise KeyError("No object named '{}' found in '{}' registry!".format(name, self._name))return retregistry_machine = Registry('registry_machine')registry_machine.register()def print_hello_world(word):print('hello {}'.format(word))registry_machine.register()def print_hi_world(word):print('hi {}'.format(word))if __name__ == '__main__':cfg1 = 'print_hello_word'registry_machine.get(cfg1)('world')cfg2 = 'print_hi_word'registry_machine.get(cfg2)('world')
看完上述內容,你們對Detectron2注冊機制Registry實現的示例分析有進一步的了解嗎?如果還想了解更多知識或者相關內容,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道,感謝大家的支持。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。