您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
今天小編給大家分享一下Docker的知識點有哪些的相關知識點,內容詳細,邏輯清晰,相信大部分人都還太了解這方面的知識,所以分享這篇文章給大家參考一下,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后有所收獲,下面我們一起來了解一下吧。
一、docker 簡介
docker 兩個主要部件:
docker: 開源的容器虛擬化平臺docker hub: 用于分享、管理 docker 容器的 docker saas 平臺 -- docker hub
docker 使用客戶端-服務器 (c/s) 架構模式。docker 客戶端會與 docker 守護進程進行通信。docker 守護進程會處理復雜繁重的任務,例如建立、運行、發布你的 docker 容器。docker 客戶端和守護進程可以運行在同一個系統上,當然你也可以使用 docker 客戶端去連接一個遠程的 docker 守護進程。docker 客戶端和守護進程之間通過 socket 或者 restful api 進行通信。
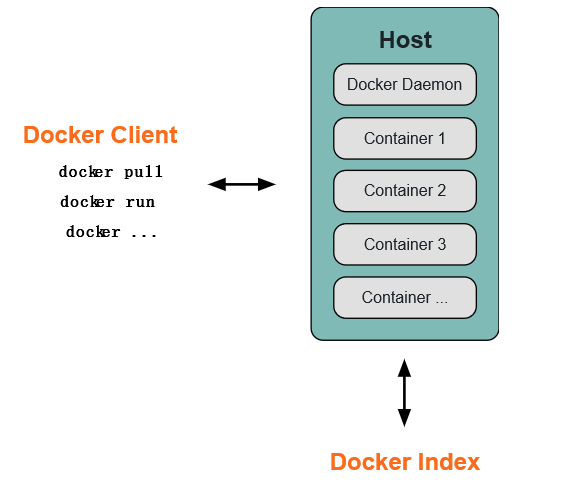
1.1 docker 守護進程
如上圖所示,docker 守護進程運行在一臺主機上。用戶并不直接和守護進程進行交互,而是通過 docker 客戶端間接和其通信。
1.2 docker 客戶端
docker 客戶端,實際上是 docker 的二進制程序,是主要的用戶與 docker 交互方式。它接收用戶指令并且與背后的 docker 守護進程通信,如此來回往復。
1.3 docker 內部
要理解 docker 內部構建,需要理解以下三種部件:
docker 鏡像 - docker imagesdocker 倉庫 - docker registeriesdocker 容器 - docker containersdocker 鏡像
docker 鏡像是 docker 容器運行時的只讀模板,每一個鏡像由一系列的層 (layers) 組成。docker 使用 unionfs 來將這些層聯合到單獨的鏡像中。unionfs 允許獨立文件系統中的文件和文件夾(稱之為分支)被透明覆蓋,形成一個單獨連貫的文件系統。正因為有了這些層的存在,docker 是如此的輕量。當你改變了一個 docker 鏡像,比如升級到某個程序到新的版本,一個新的層會被創建。因此,不用替換整個原先的鏡像或者重新建立(在使用虛擬機的時候你可能會這么做),只是一個新 的層被添加或升級了。現在你不用重新發布整個鏡像,只需要升級,層使得分發 docker 鏡像變得簡單和快速。
docker 倉庫
docker 倉庫用來保存鏡像,可以理解為代碼控制中的代碼倉庫。同樣的,docker 倉庫也有公有和私有的概念。公有的 docker 倉庫名字是 docker hub。docker hub 提供了龐大的鏡像集合供使用。這些鏡像可以是自己創建,或者在別人的鏡像基礎上創建。docker 倉庫是 docker 的分發部分。
docker 容器
docker 容器和文件夾很類似,一個docker容器包含了所有的某個應用運行所需要的環境。每一個 docker 容器都是從 docker 鏡像創建的。docker 容器可以運行、開始、停止、移動和刪除。每一個 docker 容器都是獨立和安全的應用平臺,docker 容器是 docker 的運行部分。
1.4 libcontainer
docker 從 0.9 版本開始使用 libcontainer 替代 lxc,libcontainer 和 linux 系統的交互圖如下:
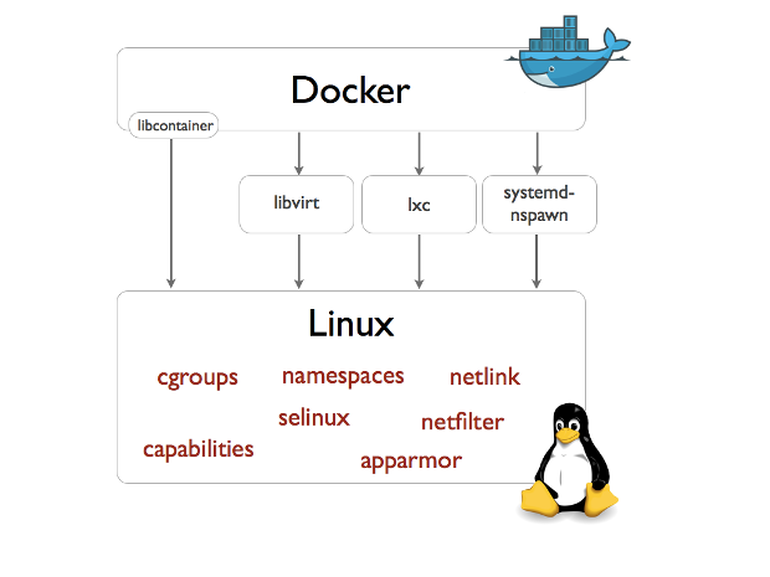
圖片來源: docker 0.9: introducing execution drivers and libcontainer
1.5 命名空間「namespaces」
pid namespace
不同用戶的進程就是通過 pid namespace 隔離開的,且不同 namespace 中可以有相同 pid。具有以下特征:
每個 namespace 中的 pid 是有自己的 pid=1 的進程(類似 /sbin/init 進程)
每個 namespace 中的進程只能影響自己的同一個 namespace 或子 namespace 中的進程
因為 /proc 包含正在運行的進程,因此在 container 中的 pseudo-filesystem 的 /proc 目錄只能看到自己 namespace 中的進程
因為 namespace 允許嵌套,父 namespace 可以影響子 namespace 的進程,所以子 namespace 的進程可以在父 namespace 中看到,但是具有不同的 pid
參考文檔:introduction to linux namespaces – part 3: pid
mnt namespace
類似 chroot,將一個進程放到一個特定的目錄執行。mnt namespace 允許不同 namespace 的進程看到的文件結構不同,這樣每個 namespace 中的進程所看到的文件目錄就被隔離開了。同 chroot 不同,每個 namespace 中的 container 在 /proc/mounts 的信息只包含所在 namespace 的 mount point。
net namespace
網絡隔離是通過 net namespace 實現的, 每個 net namespace 有獨立的 network devices, ip addresses, ip routing tables, /proc/net 目錄。這樣每個 container 的網絡就能隔離開來。 docker 默認采用 veth 的方式將 container 中的虛擬網卡同 host 上的一個 docker bridge 連接在一起。
參考文檔:introduction to linux namespaces – part 5: net
uts namespace
uts ("unix time-sharing system") namespace 允許每個 container 擁有獨立的 hostname 和 domain name, 使其在網絡上可以被視作一個獨立的節點而非 host 上的一個進程。
參考文檔:introduction to linux namespaces – part 1: uts
ipc namespace
container 中進程交互還是采用 linux 常見的進程間交互方法 (interprocess communication - ipc), 包括常見的信號量、消息隊列和共享內存。然而同 vm 不同,container 的進程間交互實際上還是 host 上具有相同 pid namespace 中的進程間交互,因此需要在ipc資源申請時加入 namespace 信息 - 每個 ipc 資源有一個唯一的 32bit id。
參考文檔:introduction to linux namespaces – part 2: ipc
user namespace
每個 container 可以有不同的 user 和 group id, 也就是說可以以 container 內部的用戶在 container 內部執行程序而非 host 上的用戶。
有了以上 6 種 namespace 從進程、網絡、ipc、文件系統、uts 和用戶角度的隔離,一個 container 就可以對外展現出一個獨立計算機的能力,并且不同 container 從 os 層面實現了隔離。 然而不同 namespace 之間資源還是相互競爭的,仍然需要類似 ulimit 來管理每個 container 所能使用的資源 - cgroup。
referencedocker getting start: related knowledgedocker 介紹以及其相關術語、底層原理和技術
1.6 資源配額「cgroups」
cgroups 實現了對資源的配額和度量。 cgroups 的使用非常簡單,提供類似文件的接口,在 /cgroup 目錄下新建一個文件夾即可新建一個 group,在此文件夾中新建 task 文件,并將 pid 寫入該文件,即可實現對該進程的資源控制。具體的資源配置選項可以在該文件夾中新建子 subsystem ,{子系統前綴}.{資源項} 是典型的配置方法, 如 memory.usageinbytes 就定義了該 group 在 subsystem memory 中的一個內存限制選項。 另外,cgroups 中的 subsystem 可以隨意組合,一個 subsystem 可以在不同的 group 中,也可以一個 group 包含多個 subsystem - 也就是說一個 subsystem。
memory內存相關的限制
cpu在 cgroup 中,并不能像硬件虛擬化方案一樣能夠定義 cpu 能力,但是能夠定義 cpu 輪轉的優先級,因此具有較高 cpu 優先級的進程會更可能得到 cpu 運算。 通過將參數寫入 cpu.shares ,即可定義改 cgroup 的 cpu 優先級 - 這里是一個相對權重,而非絕對值blkioblock io 相關的統計和限制,byte/operation 統計和限制 (iops 等),讀寫速度限制等,但是這里主要統計的都是同步 io
devices設備權限限制
參考文檔:how to use cgroup
二、docker 安裝
docker 的相關安裝方法這里不作介紹,具體安裝參考 官檔
獲取當前 docker 版本
$ sudo docker version client version: 1.3.2 client api version: 1.15 go version (client): go1.3.3 git commit (client): 39fa2fa/1.3.2 os/arch (client): linux/amd64 server version: 1.3.2 server api version: 1.15 go version (server): go1.3.3 git commit (server): 39fa2fa/1.3.2
三、docker 基礎用法
docker hub : docker鏡像首頁,包括官方鏡像和其它公開鏡像
因為國情的原因,國內下載 docker hub 官方的相關鏡像比較慢,可以使用 docker.cn 鏡像,鏡像保持和官方一致,關鍵是速度塊,推薦使用。
3.1 search images
$ sudo docker search ubuntu
3.2 pull images
$ sudo docker pull ubuntu # 獲取 ubuntu 官方鏡像 $ sudo docker images # 查看當前鏡像列表
3.3 running an interactive shell
$ sudo docker run -i -t ubuntu:14.04 /bin/bash
docker run - 運行一個容器-t - 分配一個(偽)tty (link is external)-i - 交互模式 (so we can interact with it)ubuntu:14.04 - 使用 ubuntu 基礎鏡像 14.04/bin/bash - 運行命令 bash shell
注: ubuntu 會有多個版本,通過指定 tag 來啟動特定的版本 [image]:[tag]
$ sudo docker ps # 查看當前運行的容器, ps -a 列出當前系統所有的容器 container id image command created status ports names 6c9129e9df10 ubuntu:14.04 /bin/bash 6 minutes ago up 6 minutes cranky_babbage
3.4 相關快捷鍵退出:
ctrl-dorexit
detach:ctrl-p + ctrl-q
attach:docker attach container-id
四、docker 命令幫助
4.1 dockerhelp
docker command
$ sudo docker # docker 命令幫助 commands: attach attach to a running container # 當前 shell 下 attach 連接指定運行鏡像 build build an image from a dockerfile # 通過 dockerfile 定制鏡像 commit create a new image from a container's changes # 提交當前容器為新的鏡像 cp copy files/folders from the containers filesystem to the host path # 從容器中拷貝指定文件或者目錄到宿主機中 create create a new container # 創建一個新的容器,同 run,但不啟動容器 diff inspect changes on a container's filesystem # 查看 docker 容器變化 events get real time events from the server # 從 docker 服務獲取容器實時事件 exec run a command in an existing container # 在已存在的容器上運行命令 export stream the contents of a container as a tar archive # 導出容器的內容流作為一個 tar 歸檔文件[對應 import ] history show the history of an image # 展示一個鏡像形成歷史 images list images # 列出系統當前鏡像 import create a new filesystem image from the contents of a tarball # 從tar包中的內容創建一個新的文件系統映像[對應 export] info display system-wide information # 顯示系統相關信息 inspect return low-level information on a container # 查看容器詳細信息 kill kill a running container # kill 指定 docker 容器 load load an image from a tar archive # 從一個 tar 包中加載一個鏡像[對應 save] login register or login to the docker registry server # 注冊或者登陸一個 docker 源服務器 logout log out from a docker registry server # 從當前 docker registry 退出 logs fetch the logs of a container # 輸出當前容器日志信息 port lookup the public-facing port which is nat-ed to private_port # 查看映射端口對應的容器內部源端口 pause pause all processes within a container # 暫停容器 ps list containers # 列出容器列表 pull pull an image or a repository from the docker registry server # 從docker鏡像源服務器拉取指定鏡像或者庫鏡像 push push an image or a repository to the docker registry server # 推送指定鏡像或者庫鏡像至docker源服務器 restart restart a running container # 重啟運行的容器 rm remove one or more containers # 移除一個或者多個容器 rmi remove one or more images # 移除一個或多個鏡像[無容器使用該鏡像才可刪除,否則需刪除相關容器才可繼續或 -f 強制刪除] run run a command in a new container # 創建一個新的容器并運行一個命令 save save an image to a tar archive # 保存一個鏡像為一個 tar 包[對應 load] search search for an image on the docker hub # 在 docker hub 中搜索鏡像 start start a stopped containers # 啟動容器 stop stop a running containers # 停止容器 tag tag an image into a repository # 給源中鏡像打標簽 top lookup the running processes of a container # 查看容器中運行的進程信息 unpause unpause a paused container # 取消暫停容器 version show the docker version information # 查看 docker 版本號 wait block until a container stops, then print its exit code # 截取容器停止時的退出狀態值 run 'docker command --help' for more information on a command.
docker option
usage of docker: --api-enable-cors=false enable cors headers in the remote api # 遠程 api 中開啟 cors 頭 -b, --bridge="" attach containers to a pre-existing network bridge # 橋接網絡 use 'none' to disable container networking --bip="" use this cidr notation address for the network bridge's ip, not compatible with -b # 和 -b 選項不兼容,具體沒有測試過 -d, --daemon=false enable daemon mode # daemon 模式 -d, --debug=false enable debug mode # debug 模式 --dns=[] force docker to use specific dns servers # 強制 docker 使用指定 dns 服務器 --dns-search=[] force docker to use specific dns search domains # 強制 docker 使用指定 dns 搜索域 -e, --exec-driver="native" force the docker runtime to use a specific exec driver # 強制 docker 運行時使用指定執行驅動器 --fixed-cidr="" ipv4 subnet for fixed ips (ex: 10.20.0.0/16) this subnet must be nested in the bridge subnet (which is defined by -b or --bip) -g, --group="docker" group to assign the unix socket specified by -h when running in daemon mode use '' (the empty string) to disable setting of a group -g, --graph="/var/lib/docker" path to use as the root of the docker runtime # 容器運行的根目錄路徑 -h, --host=[] the socket(s) to bind to in daemon mode # daemon 模式下 docker 指定綁定方式[tcp or 本地 socket] specified using one or more tcp://host:port, unix:///path/to/socket, fd://* or fd://socketfd. --icc=true enable inter-container communication # 跨容器通信 --insecure-registry=[] enable insecure communication with specified registries (no certificate verification for https and enable http fallback) (e.g., localhost:5000 or 10.20.0.0/16) --ip="0.0.0.0" default ip address to use when binding container ports # 指定監聽地址,默認所有 ip --ip-forward=true enable net.ipv4.ip_forward # 開啟轉發 --ip-masq=true enable ip masquerading for bridge's ip range --iptables=true enable docker's addition of iptables rules # 添加對應 iptables 規則 --mtu=0 set the containers network mtu # 設置網絡 mtu if no value is provided: default to the default route mtu or 1500 if no default route is available -p, --pidfile="/var/run/docker.pid" path to use for daemon pid file # 指定 pid 文件位置 --registry-mirror=[] specify a preferred docker registry mirror -s, --storage-driver="" force the docker runtime to use a specific storage driver # 強制 docker 運行時使用指定存儲驅動 --selinux-enabled=false enable selinux support # 開啟 selinux 支持 --storage-opt=[] set storage driver options # 設置存儲驅動選項 --tls=false use tls; implied by tls-verify flags # 開啟 tls --tlscacert="/root/.docker/ca.pem" trust only remotes providing a certificate signed by the ca given here --tlscert="/root/.docker/cert.pem" path to tls certificate file # tls 證書文件位置 --tlskey="/root/.docker/key.pem" path to tls key file # tls key 文件位置 --tlsverify=false use tls and verify the remote (daemon: verify client, client: verify daemon) # 使用 tls 并確認遠程控制主機 -v, --version=false print version information and quit # 輸出 docker 版本信息
4.2 docker search
$ sudo docker search --help usage: docker search term search the docker hub for images # 從 docker hub 搜索鏡像 --automated=false only show automated builds --no-trunc=false don't truncate output -s, --stars=0 only displays with at least xxx stars
示例:
$ sudo docker search -s 100 ubuntu # 查找 star 數至少為 100 的鏡像,找出只有官方鏡像 start 數超過 100,默認不加 s 選項找出所有相關 ubuntu 鏡像 name description stars official automated ubuntu official ubuntu base image 425 [ok]
4.3 docker info
$ sudo docker info containers: 1 # 容器個數 images: 22 # 鏡像個數 storage driver: devicemapper # 存儲驅動 pool name: docker-8:17-3221225728-pool pool blocksize: 65.54 kb data file: /data/docker/devicemapper/devicemapper/data metadata file: /data/docker/devicemapper/devicemapper/metadata data space used: 1.83 gb data space total: 107.4 gb metadata space used: 2.191 mb metadata space total: 2.147 gb library version: 1.02.84-rhel7 (2014-03-26) execution driver: native-0.2 # 存儲驅動 kernel version: 3.10.0-123.el7.x86_64 operating system: centos linux 7 (core)
4.4 docker pull && docker push
$ sudo docker pull --help # pull 拉取鏡像 usage: docker pull [options] name[:tag] pull an image or a repository from the registry -a, --all-tags=false download all tagged images in the repository $ sudo docker push # push 推送指定鏡像 usage: docker push name[:tag] push an image or a repository to the registry
示例:
$ sudo docker pull ubuntu # 下載官方 ubuntu docker 鏡像,默認下載所有 ubuntu 官方庫鏡像 $ sudo docker pull ubuntu:14.04 # 下載指定版本 ubuntu 官方鏡像
$ sudo docker push 192.168.0.100:5000/ubuntu # 推送鏡像庫到私有源[可注冊 docker 官方賬戶,推送到官方自有賬戶] $ sudo docker push 192.168.0.100:5000/ubuntu:14.04 # 推送指定鏡像到私有源
4.5 docker images
列出當前系統鏡像
$ sudo docker images --help usage: docker images [options] [name] list images -a, --all=false show all images (by default filter out the intermediate image layers) # -a 顯示當前系統的所有鏡像,包括過渡層鏡像,默認 docker images 顯示最終鏡像,不包括過渡層鏡像 -f, --filter=[] provide filter values (i.e. 'dangling=true') --no-trunc=false don't truncate output -q, --quiet=false only show numeric ids
示例:
$ sudo docker images # 顯示當前系統鏡像,不包括過渡層鏡像 $ sudo docker images -a # 顯示當前系統所有鏡像,包括過渡層鏡像 $ sudo docker images ubuntu # 顯示當前系統 docker ubuntu 庫中的所有鏡像 repository tag image id created virtual size ubuntu 12.04 ebe4be4dd427 4 weeks ago 210.6 mb ubuntu 14.04 e54ca5efa2e9 4 weeks ago 276.5 mb ubuntu 14.04-ssh 6334d3ac099a 7 weeks ago 383.2 mb
4.6 docker rmi
刪除一個或者多個鏡像
$ sudo docker rmi --help usage: docker rmi image [image...] remove one or more images -f, --force=false force removal of the image # 強制移除鏡像不管是否有容器使用該鏡像 --no-prune=false do not delete untagged parents # 不要刪除未標記的父鏡像
4.7 docker run
$ sudo docker run --help usage: docker run [options] image [command] [arg...] run a command in a new container -a, --attach=[] attach to stdin, stdout or stderr. -c, --cpu-shares=0 cpu shares (relative weight) # 設置 cpu 使用權重 --cap-add=[] add linux capabilities --cap-drop=[] drop linux capabilities --cidfile="" write the container id to the file # 把容器 id 寫入到指定文件 --cpuset="" cpus in which to allow execution (0-3, 0,1) # cpu 綁定 -d, --detach=false detached mode: run container in the background, print new container id # 后臺運行容器 --device=[] add a host device to the container (e.g. --device=/dev/sdc:/dev/xvdc) --dns=[] set custom dns servers # 設置 dns --dns-search=[] set custom dns search domains # 設置 dns 域搜索 -e, --env=[] set environment variables # 定義環境變量 --entrypoint="" overwrite the default entrypoint of the image # ? --env-file=[] read in a line delimited file of env variables # 從指定文件讀取變量值 --expose=[] expose a port from the container without publishing it to your host # 指定對外提供服務端口 -h, --hostname="" container host name # 設置容器主機名 -i, --interactive=false keep stdin open even if not attached # 保持標準輸出開啟即使沒有 attached --link=[] add link to another container (name:alias) # 添加鏈接到另外一個容器 --lxc-conf=[] (lxc exec-driver only) add custom lxc options --lxc-conf="lxc.cgroup.cpuset.cpus = 0,1" -m, --memory="" memory limit (format: <number><optional unit>, where unit = b, k, m or g) # 內存限制 --name="" assign a name to the container # 設置容器名 --net="bridge" set the network mode for the container # 設置容器網絡模式 'bridge': creates a new network stack for the container on the docker bridge 'none': no networking for this container 'container:<name|id>': reuses another container network stack 'host': use the host network stack inside the container. note: the host mode gives the container full access to local system services such as d-bus and is therefore considered insecure. -p, --publish-all=false publish all exposed ports to the host interfaces # 自動映射容器對外提供服務的端口 -p, --publish=[] publish a container's port to the host # 指定端口映射 format: ip:hostport:containerport | ip::containerport | hostport:containerport (use 'docker port' to see the actual mapping) --privileged=false give extended privileges to this container # 提供更多的權限給容器 --restart="" restart policy to apply when a container exits (no, on-failure[:max-retry], always) --rm=false automatically remove the container when it exits (incompatible with -d) # 如果容器退出自動移除和 -d 選項沖突 --security-opt=[] security options --sig-proxy=true proxify received signals to the process (even in non-tty mode). sigchld is not proxied. -t, --tty=false allocate a pseudo-tty # 分配偽終端 -u, --user="" username or uid # 指定運行容器的用戶 uid 或者用戶名 -v, --volume=[] bind mount a volume (e.g., from the host: -v /host:/container, from docker: -v /container) # 掛載卷 --volumes-from=[] mount volumes from the specified container(s) # 從指定容器掛載卷 -w, --workdir="" working directory inside the container # 指定容器工作目錄
示例:
$ sudo docker images ubuntu repository tag image id created virtual size ubuntu 14.04 e54ca5efa2e9 4 weeks ago 276.5 mb ... ... $ sudo docker run -t -i -c 100 -m 512mb -h test1 -d --name="docker_test1" ubuntu /bin/bash # 創建一個 cpu 優先級為 100,內存限制 512mb,主機名為 test1,名為 docker_test1 后臺運行 bash 的容器 a424ca613c9f2247cd3ede95adfbaf8d28400cbcb1d5f9b69a7b56f97b2b52e5 $ sudo docker ps container id image command created status ports names a424ca613c9f ubuntu:14.04 /bin/bash 6 seconds ago up 5 seconds docker_test1 $ sudo docker attach docker_test1 root@test1:/# pwd / root@test1:/# exit exit
關于cpu優先級:
by default all groups have 1024 shares. a group with 100 shares will get a ~10% portion of the cpu time -archlinux cgroups
4.8 docker start|stop|kill... ...
dockerstart|stop|kill|restart|pause|unpause|rm|commit|inspect|logs
docker start container [container...]# 運行一個或多個停止的容器
docker stop container [container...]
# 停掉一個或多個運行的容器-t選項可指定超時時間
docker kill [options] container [container...]# 默認 kill 發送 sigkill 信號-s可以指定發送 kill 信號類型
docker restart [options] container [container...]# 重啟一個或多個運行的容器-t選項可指定超時時間
docker pause container# 暫停一個容器,方便 commitdocker unpause container# 繼續暫停的容器
docker rm [options] container [container...]
# 移除一個或多個容器
-f, --force=false force removal of running container
-l, --link=false remove the specified link and not the underlying container
-v, --volumes=false remove the volumes associated with the container
docker commit [options] container [repository[:tag]]
# 提交指定容器為鏡像
-a, --author="" author (e.g., "john hannibal smith hannibal@a-team.com")
-m, --message="" commit message
-p, --pause=true pause container during commit# 默認 commit 是暫停狀態
docker inspect container|image [container|image...]
# 查看容器或者鏡像的詳細信息docker logs container# 輸出指定容器日志信息
-f, --follow=false follow log output# 類似 tail -f
-t, --timestamps=false show timestamps
--tail="all" output the specified number of lines at the end of logs (defaults to all logs)
參考文檔:docker run reference
4.9 docker 1.3 新增特性和命令digital signature verification
docker 1.3 版本將使用數字簽名自動驗證所有官方庫的來源和完整性,如果一個官方鏡像被篡改或者被破壞,目前 docker 只會對這種情況發出警告而并不阻止容器的運行。
docker exec --help usage: docker exec [options] container command [arg...] run a command in an existing container -d, --detach=false detached mode: run command in the background -i, --interactive=false keep stdin open even if not attached -t, --tty=false allocate a pseudo-tty
為了簡化調試,可以使用docker exec命令通過 docker api 和 cli 在運行的容器上運行程序。
$ docker exec -it ubuntu_bash bash
上例將在容器 ubuntu_bash 中創建一個新的 bash 會話。
tune container lifecycles withdocker create
我們可以通過docker run <image name>命令創建一個容器并運行其中的程序,因為有很多用戶要求創建容器的時候不啟動容器,所以docker create應運而生了。
$ docker create -t -i fedora bash6d8af538ec541dd581ebc2a24153a28329acb5268abe5ef868c1f1a261221752
上例創建了一個可寫的容器層 (并且打印出容器 id),但是并不運行它,可以使用以下命令運行該容器:
$ docker start -a -i 6d8af538ec5bash-4.2#
security options
通過--security-opt選項,運行容器時用戶可自定義 selinux 和 apparmor 卷標和配置。
$ docker run --security-opt label:type:svirt_apache -i -t centos \ bash
上例只允許容器監聽在 apache 端口,這個選項的好處是用戶不需要運行 docker 的時候指定--privileged選項,降低安全風險。
參考文檔:docker 1.3: signed images, process injection, security options, mac shared directories
4.10 docker 1.5 新特性
參考文檔:docker 1.5 新特性
五、docker 端口映射
# find ip address of container with id <container_id> 通過容器 id 獲取 ip $ sudo docker inspect <container_id> | grep ipaddress | cut -d '"' -f 4
無論如何,這些 ip 是基于本地系統的并且容器的端口非本地主機是訪問不到的。此外,除了端口只能本地訪問外,對于容器的另外一個問題是這些 ip 在容器每次啟動的時候都會改變。
docker 解決了容器的這兩個問題,并且給容器內部服務的訪問提供了一個簡單而可靠的方法。docker 通過端口綁定主機系統的接口,允許非本地客戶端訪問容器內部運行的服務。為了簡便的使得容器間通信,docker 提供了這種連接機制。
5.1 自動映射端口
-p使用時需要指定--expose選項,指定需要對外提供服務的端口
$ sudo docker run -t -p --expose 22 --name server ubuntu:14.04
使用docker run -p自動綁定所有對外提供服務的容器端口,映射的端口將會從沒有使用的端口池中 (49000..49900) 自動選擇,你可以通過docker ps、docker inspect <container_id>或者docker port <container_id> <port>確定具體的綁定信息。
5.2 綁定端口到指定接口
基本語法
$ sudo docker run -p [([<host_interface>:[host_port]])|(<host_port>):]<container_port>[/udp] <image> <cmd>
默認不指定綁定 ip 則監聽所有網絡接口。
綁定 tcp 端口
# bind tcp port 8080 of the container to tcp port 80 on 127.0.0.1 of the host machine. $ sudo docker run -p 127.0.0.1:80:8080 <image> <cmd> # bind tcp port 8080 of the container to a dynamically allocated tcp port on 127.0.0.1 of the host machine. $ sudo docker run -p 127.0.0.1::8080 <image> <cmd> # bind tcp port 8080 of the container to tcp port 80 on all available interfaces of the host machine. $ sudo docker run -p 80:8080 <image> <cmd> # bind tcp port 8080 of the container to a dynamically allocated tcp port on all available interfaces $ sudo docker run -p 8080 <image> <cmd>
綁定 udp 端口
# bind udp port 5353 of the container to udp port 53 on 127.0.0.1 of the host machine. $ sudo docker run -p 127.0.0.1:53:5353/udp <image> <cmd>
六、docker 網絡配置
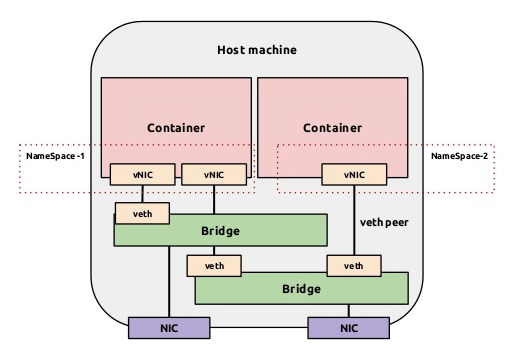
圖: docker - container and lightweight virtualization
dokcer 通過使用 linux 橋接提供容器之間的通信,docker0 橋接接口的目的就是方便 docker 管理。當 docker daemon 啟動時需要做以下操作:
creates the docker0 bridge if not present
# 如果 docker0 不存在則創建
searches for an ip address range which doesn't overlap with an existing route
# 搜索一個與當前路由不沖突的 ip 段
picks an ip in the selected range
# 在確定的范圍中選擇 ip
assigns this ip to the docker0 bridge
# 綁定 ip 到 docker06.1 docker 四種網絡模式
四種網絡模式摘自 docker 網絡詳解及 pipework 源碼解讀與實踐
docker run 創建 docker 容器時,可以用 --net 選項指定容器的網絡模式,docker 有以下 4 種網絡模式:
host 模式,使用 --net=host 指定。
container 模式,使用 --net=container:nameorid 指定。
none 模式,使用 --net=none 指定。
bridge 模式,使用 --net=bridge 指定,默認設置
host 模式
如果啟動容器的時候使用 host 模式,那么這個容器將不會獲得一個獨立的 network namespace,而是和宿主機共用一個 network namespace。容器將不會虛擬出自己的網卡,配置自己的 ip 等,而是使用宿主機的 ip 和端口。
例如,我們在 10.10.101.105/24 的機器上用 host 模式啟動一個含有 web 應用的 docker 容器,監聽 tcp 80 端口。當我們在容器中執行任何類似 ifconfig 命令查看網絡環境時,看到的都是宿主機上的信息。而外界訪問容器中的應用,則直接使用 10.10.101.105:80 即可,不用任何 nat 轉換,就如直接跑在宿主機中一樣。但是,容器的其他方面,如文件系統、進程列表等還是和宿主機隔離的。
container 模式
這個模式指定新創建的容器和已經存在的一個容器共享一個 network namespace,而不是和宿主機共享。新創建的容器不會創建自己的網卡,配置自己的 ip,而是和一個指定的容器共享 ip、端口范圍等。同樣,兩個容器除了網絡方面,其他的如文件系統、進程列表等還是隔離的。兩個容器的進程可以通過 lo 網卡設備通信。
none模式
這個模式和前兩個不同。在這種模式下,docker 容器擁有自己的 network namespace,但是,并不為 docker容器進行任何網絡配置。也就是說,這個 docker 容器沒有網卡、ip、路由等信息。需要我們自己為 docker 容器添加網卡、配置 ip 等。
bridge模式
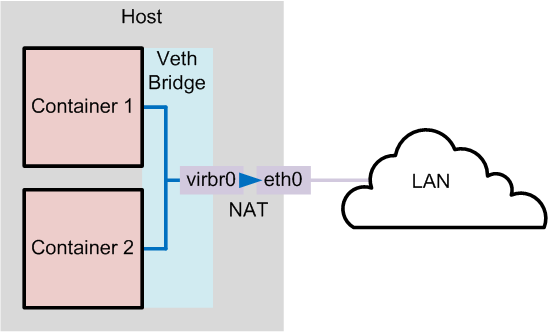
圖:the container world | part 2 networking
bridge 模式是 docker 默認的網絡設置,此模式會為每一個容器分配 network namespace、設置 ip 等,并將一個主機上的 docker 容器連接到一個虛擬網橋上。當 docker server 啟動時,會在主機上創建一個名為 docker0 的虛擬網橋,此主機上啟動的 docker 容器會連接到這個虛擬網橋上。虛擬網橋的工作方式和物理交換機類似,這樣主機上的所有容器就通過交換機連在了一個二層網絡中。接下來就要為容器分配 ip 了,docker 會從 rfc1918 所定義的私有 ip 網段中,選擇一個和宿主機不同的ip地址和子網分配給 docker0,連接到 docker0 的容器就從這個子網中選擇一個未占用的 ip 使用。如一般 docker 會使用 172.17.0.0/16 這個網段,并將 172.17.42.1/16 分配給 docker0 網橋(在主機上使用 ifconfig 命令是可以看到 docker0 的,可以認為它是網橋的管理接口,在宿主機上作為一塊虛擬網卡使用)
6.2 列出當前主機網橋
$ sudo brctl show # brctl 工具依賴 bridge-utils 軟件包 bridge name bridge id stp enabled interfacesdocker0 8000.000000000000 no
6.3 查看當前 docker0 ip
$ sudo ifconfig docker0docker0 link encap:ethernet hwaddr xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xxinet addr:172.17.42.1 bcast:0.0.0.0 mask:255.255.0.0
在容器運行時,每個容器都會分配一個特定的虛擬機口并橋接到 docker0。每個容器都會配置同 docker0 ip 相同網段的專用 ip 地址,docker0 的 ip 地址被用于所有容器的默認網關。
6.4 運行一個容器
$ sudo docker run -t -i -d ubuntu /bin/bash52f811c5d3d69edddefc75aff5a4525fc8ba8bcfa1818132f9dc7d4f7c7e78b4 $ sudo brctl showbridge name bridge id stp enabled interfacesdocker0 8000.fef213db5a66 no vethqcdy1n
以上, docker0 扮演著 52f811c5d3d6 container 這個容器的虛擬接口 vethqcdy1n interface 橋接的角色。
使用特定范圍的 ip
docker 會嘗試尋找沒有被主機使用的 ip 段,盡管它適用于大多數情況下,但是它不是萬能的,有時候我們還是需要對 ip 進一步規劃。docker 允許你管理 docker0 橋接或者通過-b選項自定義橋接網卡,需要安裝bridge-utils軟件包。
基本步驟如下:
ensure docker is stopped
# 確保 docker 的進程是停止的
create your own bridge (bridge0 for example)
# 創建自定義網橋
assign a specific ip to this bridge
# 給網橋分配特定的
ipstart docker with the -b=bridge0 parameter
# 以 -b 的方式指定網橋
# stopping docker and removing docker0 $ sudo service docker stop $ sudo ip link set dev docker0 down $ sudo brctl delbr docker0 # create our own bridge $ sudo brctl addbr bridge0 $ sudo ip addr add 192.168.5.1/24 dev bridge0 $ sudo ip link set dev bridge0 up # confirming that our bridge is up and running $ ip addr show bridge0 4: bridge0: <broadcast,multicast> mtu 1500 qdisc noop state up group default link/ether 66:38:d0:0d:76:18 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 192.168.5.1/24 scope global bridge0 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever # tell docker about it and restart (on ubuntu) $ echo 'docker_opts="-b=bridge0"' >> /etc/default/docker $ sudo service docker start
參考文檔: network configuration
6.5 不同主機間容器通信
不同容器之間的通信可以借助于 pipework 這個工具:
$ git clone https://github.com/jpetazzo/pipework.git$ sudo cp -rp pipework/pipework /usr/local/bin/
安裝相應依賴軟件
$ sudo apt-get install iputils-arping bridge-utils -y
橋接網絡
橋接網絡可以參考 日常問題處理 tips 關于橋接的配置說明,這里不再贅述。
# brctl showbridge name bridge id stp enabled interfacesbr0 8000.000c291412cd no eth0docker0 8000.56847afe9799 no vetheb48029
可以刪除 docker0,直接把 docker 的橋接指定為 br0。也可以保留使用默認的配置,這樣單主機容器之間的通信可以通過 docker0,而跨主機不同容器之間通過 pipework 新建 docker 容器的網卡橋接到 br0,這樣跨主機容器之間就可以通信了。
ubuntu
$ sudo service docker stop $ sudo ip link set dev docker0 down$ sudo brctl delbr docker0 $ echo 'docker_opts="-b=br0"' >> /etc/default/docker $ sudo service docker start
centos 7/rhel 7
$ sudo systemctl stop docker $ sudo ip link set dev docker0 down$ sudo brctl delbr docker0 $ cat /etc/sysconfig/docker | grep 'options='options=--selinux-enabled -b=br0 -h fd:// $ sudo systemctl start docker
pipework
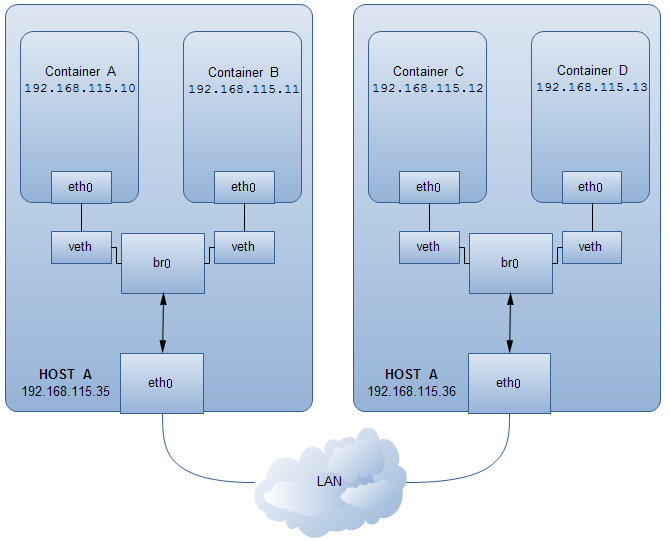
不同容器之間的通信可以借助于 pipework 這個工具給 docker 容器新建虛擬網卡并綁定 ip 橋接到 br0
$ git clone https://github.com/jpetazzo/pipework.git $ sudo cp -rp pipework/pipework /usr/local/bin/ $ pipework syntax: pipework <hostinterface> [-i containerinterface] <guest> <ipaddr>/<subnet>[@default_gateway] [macaddr][@vlan] pipework <hostinterface> [-i containerinterface] <guest> dhcp [macaddr][@vlan] pipework --wait [-i containerinterface]
如果刪除了默認的 docker0 橋接,把 docker 默認橋接指定到了 br0,則最好在創建容器的時候加上--net=none,防止自動分配的 ip 在局域網中有沖突。
$ sudo docker run --rm -ti --net=none ubuntu:14.04 /bin/bash root@a46657528059:/# $ # ctrl-p + ctrl-q 回到宿主機 shell,容器 detach 狀態 $ sudo docker ps container id image command created status ports names a46657528059 ubuntu:14.04 "/bin/bash" 4 minutes ago up 4 minutes hungry_lalande $ sudo pipework br0 -i eth0 a46657528059 192.168.115.10/24@192.168.115.2 # 默認不指定網卡設備名,則默認添加為 eth1 # 另外 pipework 不能添加靜態路由,如果有需求則可以在 run 的時候加上 --privileged=true 權限在容器中手動添加, # 但這種安全性有缺陷,可以通過 ip netns 操作 $ sudo docker attach a46657528059 root@a46657528059:/# ifconfig eth0 eth0 link encap:ethernet hwaddr 86:b6:6b:e8:2e:4d inet addr:192.168.115.10 bcast:0.0.0.0 mask:255.255.255.0 inet6 addr: fe80::84b6:6bff:fee8:2e4d/64 scope:link up broadcast running multicast mtu:1500 metric:1 rx packets:8 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 tx packets:9 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 rx bytes:648 (648.0 b) tx bytes:690 (690.0 b) root@a46657528059:/# route -n kernel ip routing table destination gateway genmask flags metric ref use iface 0.0.0.0 192.168.115.2 0.0.0.0 ug 0 0 0 eth0 192.168.115.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 u 0 0
使用ip netns添加靜態路由,避免創建容器使用--privileged=true選項造成一些不必要的安全問題:
$ docker inspect --format="{{ .state.pid }}" a46657528059 # 獲取指定容器 pid
6350
$ sudo ln -s /proc/6350/ns/net /var/run/netns/6350
$ sudo ip netns exec 6350 ip route add 192.168.0.0/16 dev eth0 via 192.168.115.2
$ sudo ip netns exec 6350 ip route # 添加成功
192.168.0.0/16 via 192.168.115.2 dev eth0
... ...在其它宿主機進行相應的配置,新建容器并使用 pipework 添加虛擬網卡橋接到 br0,測試通信情況即可。
另外,pipework 可以創建容器的 vlan 網絡,這里不作過多的介紹了,官方文檔已經寫的很清楚了,可以查看以下兩篇文章:
pipework 官方文檔docker 網絡詳解及 pipework 源碼解讀與實踐七、dockerfile
docker 可以通過 dockerfile 的內容來自動構建鏡像。dockerfile 是一個包含創建鏡像所有命令的文本文件,通過docker build命令可以根據 dockerfile 的內容構建鏡像,在介紹如何構建之前先介紹下 dockerfile 的基本語法結構。
dockerfile 有以下指令選項:
from
maintainer
run
cmd
expose
env
add
copy
entrypoint
volume
user
workdir
onbuild
7.1 from
用法:
from <image>
或者
from <image>
from指定構建鏡像的基礎源鏡像,如果本地沒有指定的鏡像,則會自動從 docker 的公共庫 pull 鏡像下來。
from必須是 dockerfile 中非注釋行的第一個指令,即一個 dockerfile 從from語句開始。
from可以在一個 dockerfile 中出現多次,如果有需求在一個 dockerfile 中創建多個鏡像。
如果from語句沒有指定鏡像標簽,則默認使用latest標簽。
7.2 maintainer
用法:
maintainer <name>
指定創建鏡像的用戶
run 有兩種使用方式
run
run "executable", "param1", "param2"
每條run指令將在當前鏡像基礎上執行指定命令,并提交為新的鏡像,后續的run都在之前run提交后的鏡像為基礎,鏡像是分層的,可以通過一個鏡像的任何一個歷史提交點來創建,類似源碼的版本控制。
exec 方式會被解析為一個 json 數組,所以必須使用雙引號而不是單引號。exec 方式不會調用一個命令 shell,所以也就不會繼承相應的變量,如:
run [ "echo", "$home" ]
這種方式是不會達到輸出 home 變量的,正確的方式應該是這樣的
run [ "sh", "-c", "echo", "$home" ]
run產生的緩存在下一次構建的時候是不會失效的,會被重用,可以使用--no-cache選項,即docker build --no-cache,如此便不會緩存。
7.3 cmd
cmd有三種使用方式:
cmd "executable","param1","param2"cmd "param1","param2"cmd command param1 param2 (shell form)
cmd指定在 dockerfile 中只能使用一次,如果有多個,則只有最后一個會生效。
cmd的目的是為了在啟動容器時提供一個默認的命令執行選項。如果用戶啟動容器時指定了運行的命令,則會覆蓋掉cmd指定的命令。
cmd會在啟動容器的時候執行,build 時不執行,而run只是在構建鏡像的時候執行,后續鏡像構建完成之后,啟動容器就與run無關了,這個初學者容易弄混這個概念,這里簡單注解一下。
7.4 expose
expose <port> [<port>...]
告訴 docker 服務端容器對外映射的本地端口,需要在 docker run 的時候使用-p或者-p選項生效。
7.5 env
env <key> <value> # 只能設置一個變量env <key>=<value> ... # 允許一次設置多個變量
指定一個環節變量,會被后續run指令使用,并在容器運行時保留。
例子:
env myname="john doe" mydog=rex\ the\ dog \ mycat=fluffy
等同于
env myname john doeenv mydog rex the dogenv mycat fluffy
7.6 add
add <src>... <dest>
add復制本地主機文件、目錄或者遠程文件 urls 從 并且添加到容器指定路徑中 。
支持通過 go 的正則模糊匹配,具體規則可參見 go filepath.match
add hom* /mydir/ # adds all files starting with "hom"add hom?.txt /mydir/ # ? is replaced with any single character
路徑必須是絕對路徑,如果 不存在,會自動創建對應目錄路徑必須是 dockerfile 所在路徑的相對路徑如果是一個目錄,只會復制目錄下的內容,而目錄本身則不會被復制7.7 copy
copy <src>... <dest>
copy復制新文件或者目錄從 并且添加到容器指定路徑中 。用法同add,唯一的不同是不能指定遠程文件 urls。
7.8 entrypointentrypoint "executable", "param1", "param2"entrypoint command param1 param2 (shell form)
配置容器啟動后執行的命令,并且不可被 docker run 提供的參數覆蓋,而cmd是可以被覆蓋的。如果需要覆蓋,則可以使用docker run --entrypoint選項。
每個 dockerfile 中只能有一個entrypoint,當指定多個時,只有最后一個生效。
exec form entrypoint 例子
通過entrypoint使用 exec form 方式設置穩定的默認命令和選項,而使用cmd添加默認之外經常被改動的選項。
from ubuntuentrypoint ["top", "-b"]cmd ["-c"]
通過 dockerfile 使用entrypoint展示前臺運行 apache 服務
from debian:stablerun apt-get update && apt-get install -y --force-yes apache2expose 80 443volume ["/var/www", "/var/log/apache2", "/etc/apache2"]entrypoint ["/usr/sbin/apache2ctl", "-d", "foreground"]
shell form entrypoint 例子
這種方式會在/bin/sh -c中執行,會忽略任何cmd或者docker run命令行選項,為了確保docker stop能夠停止長時間運行entrypoint的容器,確保執行的時候使用exec選項。
from ubuntuentrypoint exec top -b
如果在entrypoint忘記使用exec選項,則可以使用cmd補上:
from ubuntuentrypoint top -bcmd --ignored-param1 # --ignored-param2 ... --ignored-param3 ... 依此類推
7.9 volume
volume ["/data"]
創建一個可以從本地主機或其他容器掛載的掛載點,后續具體介紹。
7.10 user
user daemon
指定運行容器時的用戶名或 uid,后續的run、cmd、entrypoint也會使用指定用戶。
7.11 workdir
workdir /path/to/workdir
為后續的run、cmd、entrypoint指令配置工作目錄。可以使用多個workdir指令,后續命令如果參數是相對路徑,則會基于之前命令指定的路徑。
workdir /aworkdir bworkdir crun pwd
最終路徑是/a/b/c。
workdir指令可以在env設置變量之后調用環境變量:
env dirpath /pathworkdir
$dirpath/$dirname
最終路徑則為 /path/$dirname。
7.12 onbuild
onbuild [instruction]
配置當所創建的鏡像作為其它新創建鏡像的基礎鏡像時,所執行的操作指令。
例如,dockerfile 使用如下的內容創建了鏡像 image-a:
[...]onbuild add . /app/srconbuild
run /usr/local/bin/python-build --dir /app/src[...]
如果基于 image-a 創建新的鏡像時,新的 dockerfile 中使用 from image-a 指定基礎鏡像時,會自動執行 onbuild 指令內容,等價于在后面添加了兩條指令。
# automatically run the following
add . /app/src
run /usr/local/bin/python-build --dir /app/src
使用onbuild指令的鏡像,推薦在標簽中注明,例如 ruby:1.9-onbuild。
7.13 dockerfile examples
# nginx # # version 0.0.1 from ubuntu maintainer victor vieux <victor@docker.com> run apt-get update && apt-get install -y inotify-tools nginx apache2 openssh-server # firefox over vnc # # version 0.3 from ubuntu # install vnc, xvfb in order to create a 'fake' display and firefox run apt-get update && apt-get install -y x11vnc xvfb firefox run mkdir ~/.vnc # setup a password run x11vnc -storepasswd 1234 ~/.vnc/passwd # autostart firefox (might not be the best way, but it does the trick) run bash -c 'echo "firefox" >> /.bashrc' expose 5900 cmd ["x11vnc", "-forever", "-usepw", "-create"] # multiple images example # # version 0.1 from ubuntu run echo foo > bar # will output something like ===> 907ad6c2736f from ubuntu run echo moo > oink # will output something like ===> 695d7793cbe4 # you?ll now have two images, 907ad6c2736f with /bar, and 695d7793cbe4 with # /oink.
7.14 docker build
$ docker build --help usage: docker build [options] path | url | - build a new image from the source code at path --force-rm=false always remove intermediate containers, even after unsuccessful builds # 移除過渡容器,即使構建失敗 --no-cache=false do not use cache when building the image # 不實用 cache -q, --quiet=false suppress the verbose output generated by the containers --rm=true remove intermediate containers after a successful build # 構建成功后移除過渡層容器 -t, --tag="" repository name (and optionally a tag) to be applied to the resulting image in case of success
參考文檔:dockerfile reference
7.15 dockerfile 最佳實踐使用.dockerignore文件
為了在docker build過程中更快上傳和更加高效,應該使用一個.dockerignore文件用來排除構建鏡像時不需要的文件或目錄。例如,除非.git在構建過程中需要用到,否則你應該將它添加到.dockerignore文件中,這樣可以節省很多時間。
避免安裝不必要的軟件包
為了降低復雜性、依賴性、文件大小以及構建時間,應該避免安裝額外的或不必要的包。例如,不需要在一個數據庫鏡像中安裝一個文本編輯器。
每個容器都跑一個進程
在大多數情況下,一個容器應該只單獨跑一個程序。解耦應用到多個容器使其更容易橫向擴展和重用。如果一個服務依賴另外一個服務,可以參考 linking containers together。
最小化層
我們知道每執行一個指令,都會有一次鏡像的提交,鏡像是分層的結構,對于dockerfile,應該找到可讀性和最小化層之間的平衡。
多行參數排序
如果可能,通過字母順序來排序,這樣可以避免安裝包的重復并且更容易更新列表,另外可讀性也會更強,添加一個空行使用\換行:
run apt-get update && apt-get install -y \ bzr \ cvs \ git \ mercurial \ subversion
創建緩存
鏡像構建過程中會按照dockerfile的順序依次執行,每執行一次指令 docker 會尋找是否有存在的鏡像緩存可復用,如果沒有則創建新的鏡像。如果不想使用緩存,則可以在docker build時添加--no-cache=true選項。
從基礎鏡像開始就已經在緩存中了,下一個指令會對比所有的子鏡像尋找是否執行相同的指令,如果沒有則緩存失效。在大多數情況下只對比dockerfile指令和子鏡像就足夠了。add和copy指令除外,執行add和copy時存放到鏡像的文件也是需要檢查的,完成一個文件的校驗之后再利用這個校驗在緩存中查找,如果檢測的文件改變則緩存失效。run apt-get -y update命令只檢查命令是否匹配,如果匹配就不會再執行更新了。
為了有效地利用緩存,你需要保持你的 dockerfile 一致,并且盡量在末尾修改。
dockerfile 指令from: 只要可能就使用官方鏡像庫作為基礎鏡像run: 為保持可讀性、方便理解、可維護性,把長或者復雜的run語句使用\分隔符分成多行不建議run apt-get update獨立成行,否則如果后續包有更新,那么也不會再執行更新避免使用run apt-get upgrade或者dist-upgrade,很多必要的包在一個非privileged權限的容器里是無法升級的。如果知道某個包更新,使用apt-get install -y xxx標準寫法run apt-get update && apt-get install -y package-bar package-foo
例子:
run apt-get update && apt-get install -y \ aufs-tools \ automake \ btrfs-tools \ build-essential \ curl \ dpkg-sig \ git \ iptables \ libapparmor-dev \ libcap-dev \ libsqlite3-dev \ lxc=1.0* \ mercurial \ parallel \ reprepro \ ruby1.9.1 \ ruby1.9.1-dev \ s3cmd=1.1.0*
cmd: 推薦使用cmd [“executable”, “param1”, “param2”…]這種格式,cmd [“param”, “param”]則配合entrypoint使用
expose: dockerfile 指定要公開的端口,使用docker run時指定映射到宿主機的端口即可env: 為了使新的軟件更容易運行,可以使用env更新path變量。如env path /usr/local/nginx/bin:$path確保cmd ["nginx"]即可運行
env也可以這樣定義變量:
env pg_major 9.3 env pg_version 9.3.4 run curl -sl http://example.com/postgres-$pg_version.tar.xz | tar -xjc /usr/src/postgress && … env path /usr/local/postgres-$pg_major/bin:$path
addorcopy:add比copy多一些特性「tar 文件自動解包和支持遠程 url」,不推薦添加遠程 url
如不推薦這種方式:
add http://example.com/big.tar.xz /usr/src/things/
run tar -xjf /usr/src/things/big.tar.xz -c /usr/src/things
run make -c /usr/src/things all
推薦使用 curl 或者 wget 替換,使用如下方式:
run mkdir -p /usr/src/things \
&& curl -sl http://example.com/big.tar.gz \ | tar -xjc /usr/src/things \
&& make -c /usr/src/things all
如果不需要添加 tar 文件,推薦使用copy。
參考文檔:
best practices for writing dockerfilesdockerfile最佳實踐(一)dockerfile最佳實踐(二)八、容器數據管理
docker管理數據的方式有兩種:
數據卷數據卷容器8.1 數據卷
數據卷是一個或多個容器專門指定繞過union file system的目錄,為持續性或共享數據提供一些有用的功能:
數據卷可以在容器間共享和重用數據卷數據改變是直接修改的數據卷數據改變不會被包括在容器中數據卷是持續性的,直到沒有容器使用它們添加一個數據卷
你可以使用-v選項添加一個數據卷,或者可以使用多次-v選項為一個 docker 容器運行掛載多個數據卷。
$ sudo docker run --name data -v /data -t -i ubuntu:14.04 /bin/bash # 創建數據卷綁定到到新建容器,新建容器中會創建 / data 數據卷 bash-4.1# ls -ld /data/drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 jul 23 06:59 /data/bash-4.1 # df -thfilesystem type size used avail use% mounted on... ... ext4 91g 4.6g 82g 6% /data
創建的數據卷可以通過docker inspect獲取宿主機對應路徑
$ sudo docker inspect data... ...
"volumes": { "/data": "/var/lib/docker/vfs/dir/151de401d268226f96d824fdf444e77a4500aed74c495de5980c807a2ffb7ea9" }, # 可以看到創建的數據卷宿主機路徑 ... ...或者直接指定獲取
$ sudo docker inspect --format="{{ .volumes }}" datamap[/data: /var/lib/docker/vfs/dir/151de401d268226f96d824fdf444e77a4500aed74c495de5980c807a2ffb7ea9]
掛載宿主機目錄為一個數據卷
-v選項除了可以創建卷,也可以掛載當前主機的一個目錄到容器中。
$ sudo docker run --name web -v /source/:/web -t -i ubuntu:14.04 /bin/bashbash-4.1# ls -ld /web/drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 jul 23 06:59 /web/bash-4.1# df -th... ... ext4 91g 4.6g 82g 6% /webbash-4.1# exit
默認掛載卷是可讀寫的,可以在掛載時指定只讀
$ sudo docker run --rm --name test -v /source/:/test:ro -t -i ubuntu:14.04 /bin/bash
8.2 創建和掛載一個數據卷容器
如果你有一些持久性的數據并且想在容器間共享,或者想用在非持久性的容器上,最好的方法是創建一個數據卷容器,然后從此容器上掛載數據。
創建數據卷容器
使用--volumes-from選項在另一個容器中掛載 /test 卷。不管 test 容器是否運行,其它容器都可以掛載該容器數據卷,當然如果只是單獨的數據卷是沒必要運行容器的。
添加另一個容器
$ sudo docker run -t -i -d --volumes-from test --name test2 ubuntu:14.04 /bin/bash
也可以繼承其它掛載有 /test 卷的容器
$ sudo docker run -t -i -d --volumes-from test1 --name test3 ubuntu:14.04 /bin/bash

8.3 備份、恢復或遷移數據卷備份
$ sudo docker run --rm --volumes-from test -v $(pwd):/backup ubuntu:14.04 tar cvf /backup/test.tar /testtar: removing leading `/' from member names/test//test/b/test/d/test/c/test/a
啟動一個新的容器并且從test容器中掛載卷,然后掛載當前目錄到容器中為 backup,并備份 test 卷中所有的數據為 test.tar,執行完成之后刪除容器--rm,此時備份就在當前的目錄下,名為test.tar。
$ ls # 宿主機當前目錄下產生了 test 卷的備份文件 test.tar test.tar
恢復
你可以恢復給同一個容器或者另外的容器,新建容器并解壓備份文件到新的容器數據卷
$ sudo docker run -t -i -d -v /test --name test4 ubuntu:14.04 /bin/bash $ sudo docker run --rm --volumes-from test4 -v $(pwd):/backup ubuntu:14.04 tar xvf /backup/test.tar -c / # 恢復之前的文件到新建卷中,執行完后自動刪除容器 test/ test/b test/d test/c test/a
8.4 刪除 volumes
volume 只有在下列情況下才能被刪除:
docker rm -v刪除容器時添加了-v選項docker run --rm運行容器時添加了--rm選項
否則,會在/var/lib/docker/vfs/dir目錄中遺留很多不明目錄。
參考文檔:
managing data in containers深入理解docker volume(一)深入理解docker volume(二)九、鏈接容器
docker 允許把多個容器連接在一起,相互交互信息。docker 鏈接會創建一種容器父子級別的關系,其中父容器可以看到其子容器提供的信息。
9.1 容器命名
在創建容器時,如果不指定容器的名字,則默認會自動創建一個名字,這里推薦給容器命名:
1、給容器命名方便記憶,如命名運行 web 應用的容器為 web2、為 docker 容器提供一個參考,允許方便其他容器調用,如把容器 web 鏈接到容器 db
可以通過--name選項給容器自定義命名:
$ sudo docker run -d -t -i --name test ubuntu:14.04 bash $ sudo docker inspect --format="{{ .nmae }}" test/test
注:容器名稱必須唯一,即你只能命名一個叫test的容器。如果你想復用容器名,則必須在創建新的容器前通過docker rm刪除舊的容器或者創建容器時添加--rm選項。
9.2 鏈接容器
鏈接允許容器間安全通信,使用--link選項創建鏈接。
$ sudo docker run -d --name db training/postgre
基于 training/postgres 鏡像創建一個名為 db 的容器,然后下面創建一個叫做 web 的容器,并且將它與 db 相互連接在一起
$ sudo docker run -d -p --name web --link db:db training/webapp python app.py
--link <name or id>:alias選項指定鏈接到的容器。
查看 web 容器的鏈接關系:
$ sudo docker inspect -f "{{ .hostconfig.links }}" web[/db:/web/db]
可以看到 web 容器被鏈接到 db 容器為/web/db,這允許 web 容器訪問 db 容器的信息。
容器之間的鏈接實際做了什么?一個鏈接允許一個源容器提供信息訪問給一個接收容器。在本例中,web 容器作為一個接收者,允許訪問源容器 db 的相關服務信息。docker 創建了一個安全隧道而不需要對外公開任何端口給外部容器,因此不需要在創建容器的時候添加-p或-p指定對外公開的端口,這也是鏈接容器的最大好處,本例為 postgresql 數據庫。
docker 主要通過以下兩個方式提供連接信息給接收容器:
環境變量更新/etc/hosts文件環境變量
當兩個容器鏈接,docker 會在目標容器上設置一些環境變量,以獲取源容器的相關信息。
首先,docker 會在每個通過--link選項指定別名的目標容器上設置一個<alias>_name環境變量。如果一個名為 web 的容器通過--link db:webdb被鏈接到一個名為 db 的數據庫容器,那么 web 容器上會設置一個環境變量為webdb_name=/web/webdb.
以之前的為例,docker 還會設置端口變量:
$ sudo docker run --rm --name web2 --link db:db training/webapp env. . .db_name=/web2/dbdb_port=tcp://172.17.0.5:5432 db_port_5432_tcp=tcp://172.17.0.5:5432 # <name>_port_<port>_<protocol> 協議可以是 tcp 或 udpdb_port_5432_tcp_proto=tcpdb_port_5432_tcp_port=5432db_port_5432_tcp_addr=172.17.0.5. . .
注:這些環境變量只設置給容器中的第一個進程,類似一些守護進程 (如 sshd ) 當他們派生 shells 時會清除這些變量
更新/etc/hosts文件
除了環境變量,docker 會在目標容器上添加相關主機條目到/etc/hosts中,上例中就是 web 容器。
$ sudo docker run -t -i --rm --link db:db training/webapp /bin/bashroot@aed84ee21bde:/opt/webapp # cat /etc/hosts172.17.0.7 aed84ee21bde. . .172.17.0.5 db
/etc/host文件在源容器被重啟之后會自動更新 ip 地址,而環境變量中的 ip 地址則不會自動更新的。
十、構建私有庫
docker 官方提供了 docker registry 的構建方法 docker-registry
10.1 快速構建
快速構建 docker registry 通過以下兩步:
安裝 docker運行 registry:docker run -p 5000:5000 registry
這種方法通過 docker hub 使用官方鏡像 official image from the docker hub
10.2 不使用容器構建 registry安裝必要的軟件
$ sudo apt-get install build-essential python-dev libevent-dev python-pip liblzma-dev
配置 docker-registry
sudo pip install docker-registry
或者 使用 github clone 手動安裝
$ git clone https://github.com/dotcloud/docker-registry.git $ cd docker-registry/ $ cp config/config_sample.yml config/config.yml$ mkdir /data/registry -p $ pip install .
運行
docker-registry
高級啟動方式 [不推薦]
使用gunicorn控制:
gunicorn -c contrib/gunicorn_config.py docker_registry.wsgi:application
或者對外監聽開放
gunicorn --access-logfile - --error-logfile - -k gevent -b 0.0.0.0:5000 -w 4 --max-requests 100 docker_registry.wsgi:application
10.3 提交指定容器到私有庫
$ docker tag ubuntu:12.04 私有庫ip:5000/ubuntu:12.04$ docker push 私有庫ip:5000/ubuntu
以上就是“Docker的知識點有哪些”這篇文章的所有內容,感謝各位的閱讀!相信大家閱讀完這篇文章都有很大的收獲,小編每天都會為大家更新不同的知識,如果還想學習更多的知識,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。