您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
ServerBootstrap與Bootstrap分別是netty中服務端與客戶端的引導類,主要負責服務端與客戶端初始化、配置及啟動引導等工作,接下來我們就通過netty源碼中的示例對ServerBootstrap與Bootstrap的源碼進行一個簡單的分析。首先我們知道這兩個類都繼承自AbstractBootstrap類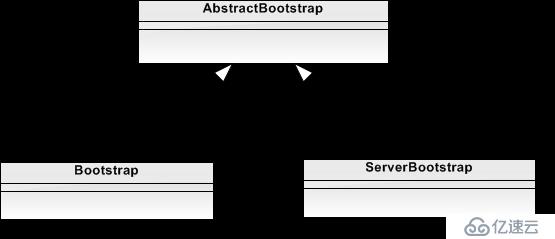
接下來我們就通過netty源碼中ServerBootstrap的實例入手對其進行一個簡單的分析。
// Configure the server.
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
final EchoServerHandler serverHandler = new EchoServerHandler();
try {
//初始化一個服務端引導類
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) //設置線程組
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)//設置ServerSocketChannel的IO模型 分為epoll與Nio
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 100)//設置option參數,保存成一個LinkedHashMap<ChannelOption<?>, Object>()
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))//這個hanlder 只專屬于 ServerSocketChannel 而不是 SocketChannel。
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { //這個handler 將會在每個客戶端連接的時候調用。供 SocketChannel 使用。@Override
br/>@Override
ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline();
if (sslCtx != null) {
p.addLast(sslCtx.newHandler(ch.alloc()));
}
//p.addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO));
p.addLast(serverHandler);
}
});
// Start the server. 啟動服務
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(PORT).sync();
// Wait until the server socket is closed.
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
// Shut down all event loops to terminate all threads.
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
接下來我們主要從服務端的socket在哪里初始化與哪里accept連接這兩個問題入手對netty服務端啟動的流程進行分析;我們首先要知道,netty服務的啟動其實可以分為以下四步:
創建服務端Channel
初始化服務端Channel
注冊Selector
端口綁定
一、創建服務端Channel
1、服務端Channel的創建,主要為以下流程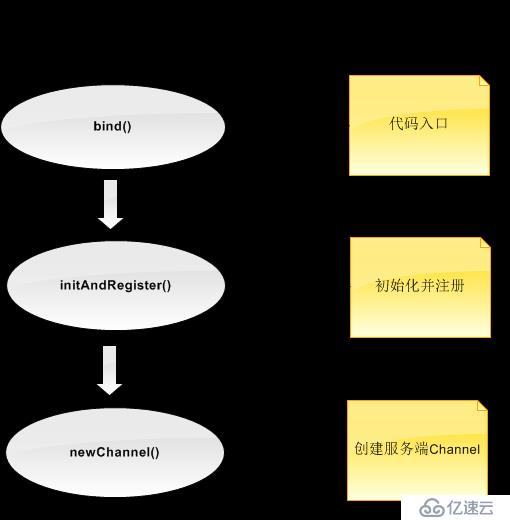
我們通過跟蹤代碼能夠看到
final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();// 初始化并創建 NioServerSocketChannel
我們在initAndRegister()中可以看到channel的初始化。
channel = channelFactory.newChannel(); // 通過 反射工廠創建一個 NioServerSocketChannel
我進一步看newChannel()中的源碼,在ReflectiveChannelFactory這個反射工廠中,通過clazz這個類的反射創建了一個服務端的channel。
@Override
public T newChannel() {
try {
return clazz.getConstructor().newInstance();//反射創建
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new ChannelException("Unable to create Channel from class " + clazz, t);
}
}
既然通過反射,我們就要知道clazz類是什么,那么我我們來看下channelFactory這個工廠類是在哪里初始化的,初始化的時候我們傳入了哪個channel。這里我們需要看下demo實例中初始化ServerBootstrap時.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)這里的具體實現,我們看下源碼
public B channel(Class<? extends C> channelClass) {
if (channelClass == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("channelClass");
}
return channelFactory(new ReflectiveChannelFactory<C>(channelClass));
}
通過上面的代碼我可以直觀的看出正是在這里我們通過NioServerSocketChannel這個類構造了一個反射工廠。那么到這里就很清楚了,我們創建的Channel就是一個NioServerSocketChannel,那么具體的創建我們就需要看下這個類的構造函數。首先我們看下一個NioServerSocketChannel創建的具體流程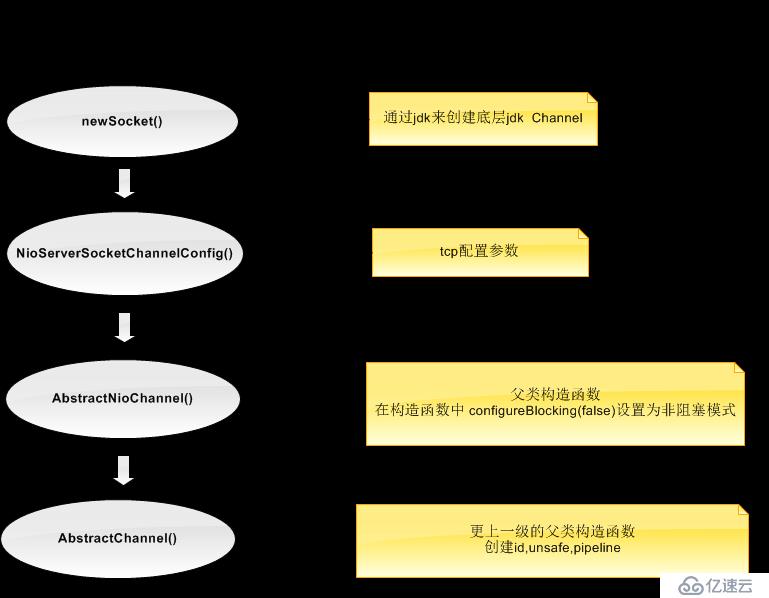
首先是newsocket(),我們先看下具體的代碼,在NioServerSocketChannel的構造函數中我們創建了一個jdk原生的ServerSocketChannel
/**
- Create a new instance
*/
public NioServerSocketChannel() {
this(newSocket(DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER));//傳入默認的SelectorProvider
}
private static ServerSocketChannel newSocket(SelectorProvider provider) {
try {
/**
* Use the {@link SelectorProvider} to open {@link SocketChannel} and so remove condition in
* {@link SelectorProvider#provider()} which is called by each ServerSocketChannel.open() otherwise.
*
* See <a >#2308</a>.
*/
return provider.openServerSocketChannel();//可以看到創建的是jdk底層的ServerSocketChannel
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ChannelException(
"Failed to open a server socket.", e);
}
}
第二步是通過NioServerSocketChannelConfig配置服務端Channel的構造函數,在代碼中我們可以看到我們把NioServerSocketChannel這個類傳入到了NioServerSocketChannelConfig的構造函數中進行配置/**
- Create a new instance using the given {@link ServerSocketChannel}.
*/
public NioServerSocketChannel(ServerSocketChannel channel) {
super(null, channel, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);//調用父類構造函數,傳入創建的channel
config = new NioServerSocketChannelConfig(this, javaChannel().socket());
}
第三步在父類AbstractNioChannel的構造函數中把創建服務端的Channel設置為非阻塞模式/**
- Create a new instance
- @param parent the parent {@link Channel} by which this instance was created. May be {@code null}
- @param ch the underlying {@link SelectableChannel} on which it operates
- @param readInterestOp the ops to set to receive data from the {@link SelectableChannel}
*/
protected AbstractNioChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch, int readInterestOp) {
super(parent);
this.ch = ch;//這個ch就是傳入的通過jdk創建的Channel
this.readInterestOp = readInterestOp;
try {
ch.configureBlocking(false);//設置為非阻塞
} catch (IOException e) {
try {
ch.close();
} catch (IOException e2) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn(
"Failed to close a partially initialized socket.", e2);
}
}
throw new ChannelException("Failed to enter non-blocking mode.", e);
}
}
第四步調用AbstractChannel這個抽象類的構造函數設置Channel的id(每個Channel都有一個id,唯一標識),unsafe(tcp相關底層操作),pipeline(邏輯鏈)等,而不管是服務的Channel還是客戶端的Channel都繼承自這個抽象類,他們也都會有上述相應的屬性。我們看下AbstractChannel的構造函數/**
- Creates a new instance.
- @param parent
- the parent of this channel. {@code null} if there's no parent.
*/
protected AbstractChannel(Channel parent) {
this.parent = parent;
id = newId();//創建Channel唯一標識
unsafe = newUnsafe();//netty封裝的TCP 相關操作類
pipeline = newChannelPipeline();//邏輯鏈
}
2、初始化服務端創建的Channelinit(channel);// 初始化這個 NioServerSocketChannel
我們首先列舉下init(channel)中具體都做了哪了些功能:
設置ChannelOptions、ChannelAttrs ,配置服務端Channel的相關屬性;
設置ChildOptions、ChildAttrs,配置每個新連接的Channel的相關屬性;
Config handler,配置服務端pipeline;
add ServerBootstrapAcceptor,添加連接器,對accpet接受到的新連接進行處理,添加一個nio線程;
那么接下來我們通過代碼,對每一步設置進行一下分析:
首先是在SeverBootstrap的init()方法中對ChannelOptions、ChannelAttrs 的配置的關鍵代碼
final Map<ChannelOption<?>, Object> options = options0();//拿到你設置的option
synchronized (options) {
setChannelOptions(channel, options, logger);//設置NioServerSocketChannel相應的TCP參數,其實這一步就是把options設置到channel的config中
}
final Map<AttributeKey<?>, Object> attrs = attrs0();
synchronized (attrs) {
for (Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object> e: attrs.entrySet()) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
AttributeKey<Object> key = (AttributeKey<Object>) e.getKey();
channel.attr(key).set(e.getValue());
}
}
然后是對ChildOptions、ChildAttrs配置的關鍵代碼//可以看到兩個都是局部變量,會在下面設置pipeline時用到final Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object>[] currentChildOptions;
final Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object>[] currentChildAttrs;
synchronized (childOptions) {
currentChildOptions = childOptions.entrySet().toArray(newOptionArray(0));
}
synchronized (childAttrs) {
currentChildAttrs = childAttrs.entrySet().toArray(newAttrArray(0));
}
第三步對服務端Channel的handler進行配置p.addLast(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {@Override
br/>@Override
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
ChannelHandler handler = config.handler();//拿到我們自定義的hanler
if (handler != null) {
pipeline.addLast(handler);
}
ch.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor(
ch, currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs));
}
});
}
});
第四步添加ServerBootstrapAcceptor連接器,這個是netty向服務端Channel自定義添加的一個handler,用來處理新連接的添加與屬性配置,我們來看下關鍵代碼ch.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {@Override
public void run() {
//在這里會把我們自定義的ChildGroup、ChildHandler、ChildOptions、ChildAttrs相關配置傳入到ServerBootstrapAcceptor構造函數中,并綁定到新的連接上
pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor(
ch, currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs));
}
});
三、注冊Selector
一個服務端的Channel創建完畢后,下一步就是要把它注冊到一個事件輪詢器Selector上,在initAndRegister()中我們把上面初始化的Channel進行注冊
ChannelFuture regFuture = config().group().register(channel);//注冊我們已經初始化過的Channel
而這個register具體實現是在AbstractChannel中的AbstractUnsafe抽象類中的
/**
- 1、先是一系列的判斷。
- 2、判斷當前線程是否是給定的 eventLoop 線程。注意:這點很重要,Netty 線程模型的高性能取決于對于當前執行的Thread 的身份的確定。如果不在當前線程,那么就需要很多同步措施(比如加鎖),上下文切換等耗費性能的操作。
- 3、異步(因為我們這里直到現在還是 main 線程在執行,不屬于當前線程)的執行 register0 方法。*/
@Override
br/>*/
@Override
if (eventLoop == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("eventLoop");
}
if (isRegistered()) {
promise.setFailure(new IllegalStateException("registered to an event loop already"));
return;
}
if (!isCompatible(eventLoop)) {
promise.setFailure(
new IllegalStateException("incompatible event loop type: " + eventLoop.getClass().getName()));
return;
}
AbstractChannel.this.eventLoop = eventLoop;//綁定線程
if (eventLoop.inEventLoop()) {
register0(promise);//實際的注冊過程
} else {
try {
eventLoop.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
register0(promise);
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn(
"Force-closing a channel whose registration task was not accepted by an event loop: {}",
AbstractChannel.this, t);
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}
}首先我們對整個注冊的流程做一個梳理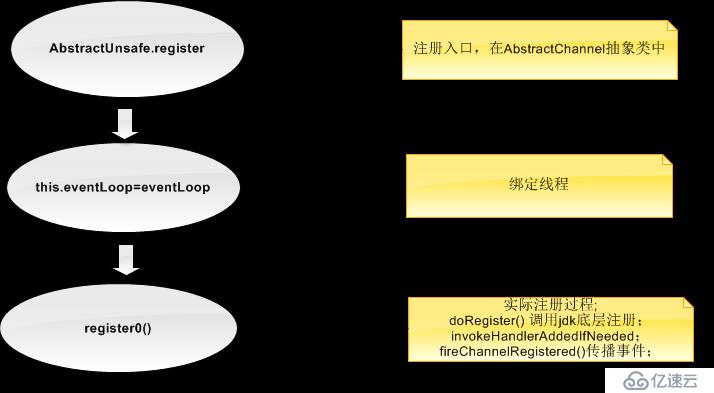
接下來我們進入register0()方法看下注冊過程的具體實現
private void register0(ChannelPromise promise) {
try {
// check if the channel is still open as it could be closed in the mean time when the register
// call was outside of the eventLoop
if (!promise.setUncancellable() || !ensureOpen(promise)) {
return;
}
boolean firstRegistration = neverRegistered;
doRegister();//jdk channel的底層注冊
neverRegistered = false;
registered = true;
// 觸發綁定的handler事件
// Ensure we call handlerAdded(...) before we actually notify the promise. This is needed as the
// user may already fire events through the pipeline in the ChannelFutureListener.
pipeline.invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded();
safeSetSuccess(promise);
pipeline.fireChannelRegistered();
// Only fire a channelActive if the channel has never been registered. This prevents firing
// multiple channel actives if the channel is deregistered and re-registered.
if (isActive()) {
if (firstRegistration) {
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
} else if (config().isAutoRead()) {
// This channel was registered before and autoRead() is set. This means we need to begin read
// again so that we process inbound data.
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/4805
beginRead();
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// Close the channel directly to avoid FD leak.
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}
AbstractNioChannel中doRegister()的具體實現就是把jdk底層的channel綁定到eventLoop的selecor上@Override
protected void doRegister() throws Exception {
boolean selected = false;
for (;;) {
try {
//把channel注冊到eventLoop上的selector上
selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().unwrappedSelector(), 0, this);
return;
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
if (!selected) {
// Force the Selector to select now as the "canceled" SelectionKey may still be
// cached and not removed because no Select.select(..) operation was called yet.
eventLoop().selectNow();
selected = true;
} else {
// We forced a select operation on the selector before but the SelectionKey is still cached
// for whatever reason. JDK bug ?
throw e;
}
}
}
}
到這里netty就把服務端的channel注冊到了指定的selector上,下面就是服務端口的邦迪三、端口綁定
首先我們梳理下netty中服務端口綁定的流程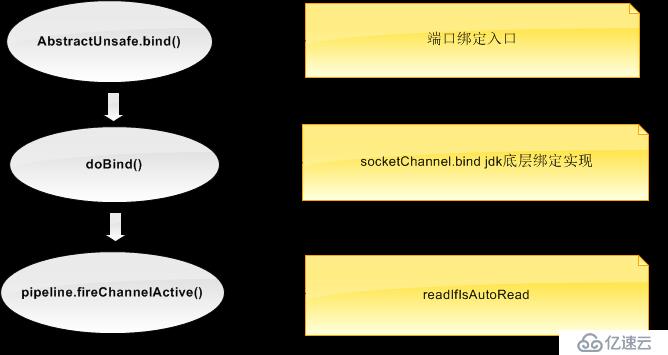
我們來看下AbstarctUnsafe中bind()方法的具體實現
@Override
public final void bind(final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
assertEventLoop();
if (!promise.setUncancellable() || !ensureOpen(promise)) {
return;
}
// See: https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/576
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(config().getOption(ChannelOption.SO_BROADCAST)) &&
localAddress instanceof InetSocketAddress &&
!((InetSocketAddress) localAddress).getAddress().isAnyLocalAddress() &&
!PlatformDependent.isWindows() && !PlatformDependent.maybeSuperUser()) {
// Warn a user about the fact that a non-root user can't receive a
// broadcast packet on *nix if the socket is bound on non-wildcard address.
logger.warn(
"A non-root user can't receive a broadcast packet if the socket " +
"is not bound to a wildcard address; binding to a non-wildcard " +
"address (" + localAddress + ") anyway as requested.");
}
boolean wasActive = isActive();//判斷綁定是否完成
try {
doBind(localAddress);//底層jdk綁定端口
} catch (Throwable t) {
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
closeIfClosed();
return;
}
if (!wasActive && isActive()) {
invokeLater(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
pipeline.fireChannelActive();//觸發ChannelActive事件
}
});
}
safeSetSuccess(promise);
}
在doBind(localAddress)中netty實現了jdk底層端口的綁定@Overrideprotected void doBind(SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {
if (PlatformDependent.javaVersion() >= 7) {
javaChannel().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());
} else {
javaChannel().socket().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());
}
}
在 pipeline.fireChannelActive()中會觸發pipeline中的channelActive()方法
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.fireChannelActive();
readIfIsAutoRead();
}在channelActive中首先會把ChannelActive事件往下傳播,然后調用readIfIsAutoRead()方法出觸發channel的read事件,而它最終調用AbstractNioChannel中的doBeginRead()方法
@Override
protected void doBeginRead() throws Exception {
// Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() was called
final SelectionKey selectionKey = this.selectionKey;
if (!selectionKey.isValid()) {
return;
}
readPending = true;
final int interestOps = selectionKey.interestOps();
if ((interestOps & readInterestOp) == 0) {
selectionKey.interestOps(interestOps | readInterestOp);//readInterestOp為 SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT
}
}在doBeginRead()方法,netty會把accept事件注冊到Selector上。
到此我們對netty服務端的啟動流程有了一個大致的了解,整體可以概括為下面四步:
1、channelFactory.newChannel(),其實就是創建jdk底層channel,并初始化id、piepline等屬性;
2、init(channel),添加option、attr等屬性,并添加ServerBootstrapAcceptor連接器;
3、config().group().register(channel),把jdk底層的channel注冊到eventLoop上的selector上;
4、doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise),完成服務端端口的監聽,并把accept事件注冊到selector上;
以上就是對netty服務端啟動流程進行的一個簡單分析,有很多細節沒有關注與深入,其中如有不足與不正確的地方還望指出與海涵。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。