您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要講解了“Kubernetes Scheduler的優先級隊列是什么”,文中的講解內容簡單清晰,易于學習與理解,下面請大家跟著小編的思路慢慢深入,一起來研究和學習“Kubernetes Scheduler的優先級隊列是什么”吧!
從Kubernetes 1.8開始,Scheduler提供了基于Pod Priorty的搶占式調度,我在解析Kubernetes 1.8中的基于Pod優先級的搶占式調度和Kubernetes 1.8搶占式調度Preemption源碼分析中對此做過深入分析。但這還不夠,當時調度隊列只有FIFO類型,并不支持優先級隊列,這會導致High Priority Pod搶占Lower Priority Pod后再次進入FIFO隊列中排隊,經常會導致搶占的資源被隊列前面的Lower Priority Pod占用,導致High Priority Pod Starvation的問題。為了減輕這一問題,從Kubernetes 1.9開始提供Pod優先級的調度隊列,即PriorityQueue,這同樣需要用戶打開PodPriority這個Feature Gate。
先看看PriorityQueue的結構定義。
type PriorityQueue struct {
lock sync.RWMutex
cond sync.Cond
activeQ *Heap
unschedulableQ *UnschedulablePodsMap
nominatedPods map[string][]*v1.Pod
receivedMoveRequest bool
}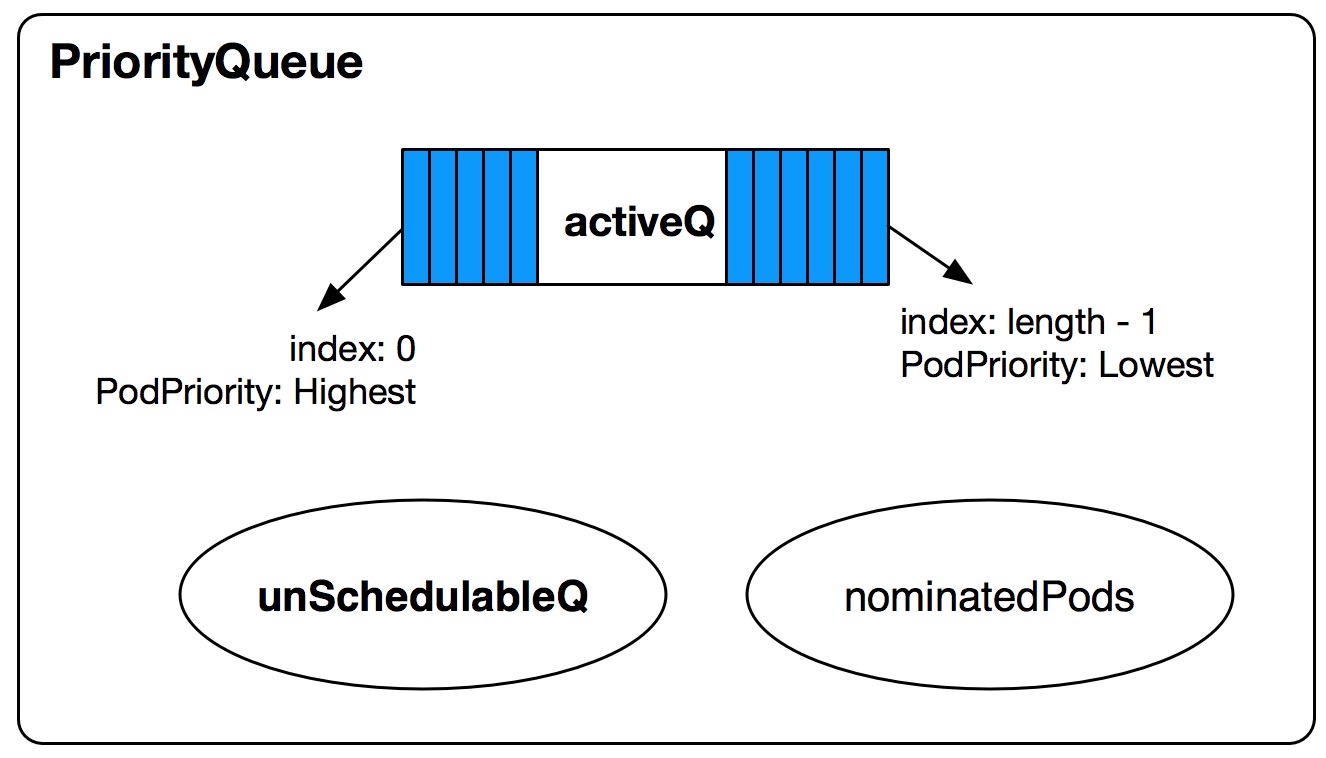
activeQ:PriorityQueue的Sub-Queue之一,是一個有序的Heap結構,按照Pod優先級從高到低遞減的順序存放待調度的Pending Pod相關信息,優先級最高的Pod信息在最上面,Pop Heap時將得到最高優先級的Pod信息。
unschedulableQ:PriorityQueue的Sub-Queue之一,主要是是一個無序的Map,key為pod.Name + "_" + pod.Namespace,value為那些已經嘗試調度并且調度失敗的UnSchedulable的Pod Object。
nominatedPods:為Map結構,key為node name,value為該Node上Nominated Pod Objects。當發生搶占調度時,preemptor pods會打上NominatedNodeName Annotation,表示經過搶占調度的邏輯后,該Pod希望能調度到NominatedNodeName這個Node上,調度時會考慮這個,防止高優先級的Pods進行搶占調度釋放了低優先級Pods到它被再次調度這個時間段內,搶占的資源又被低優先級的Pods占用了。關于scheduler怎么處理Nominated Pods,我后續會單獨寫篇博客來分析。
receivedMoveRequest:當scheduler將Pods從unschedulableQ移到activeQ時,這個值設為true。當scheduler從activeQ中Pop一個Pods時,這個值設為false。這表示當scheduler要調度某個Pod時是否接受到Move請求。當調度發生Error時,會嘗試將UnSchedulable Pod重新加入到調度隊列(unSchedulableQ or activeQ)中,這時只有當receivedMoveRequest為false并且該Pod Condition Status為False或者Unschedulable時,才會將該Pod Add到unschedulableQ(或者Update it)。
active是真正實現優先級調度的Heap,我們繼續看看這個Heap的實現。
type Heap struct {
data *heapData
}
type heapData struct {
items map[string]*heapItem
queue []string
keyFunc KeyFunc
lessFunc LessFunc
}
type heapItem struct {
obj interface{} // The object which is stored in the heap.
index int // The index of the object's key in the Heap.queue.
}heapData是activeQ中真正用來存放items的結構:
items:Map結構,key為Heap中對象的key,通過下面的keyFunc生成,value為heapItem對象,heapItem包括真正的Pod Object及其在Heap中的index。
queue:string array,順序存放Pod對應的key,按照優先級從高到低的順序對應index從0到高。
keyFunc:根據Pod Object生成對應的key的Function,格式為"meta.GetNamespace() + "/" + meta.GetName"。
lessFunc:用來根據Pod優先級比較Heap中的Pod Object(然后決定其在Heap中的index,index為0的Pod優先級最高,隨著index遞增,Pod優先級遞減)。
在scheduler config factory創建時,會注冊podQueue的創建Func為NewSchedulingQueue。NewSchedulingQueue會檢查PodPriority Feature Gate是否enable(截止Kubernetes 1.10版本,默認disable),如果PodPriority enable,則會invoke NewPriorityQueue創建PriorityQueue來管理未調度的Pods。如果PodPriority disable,則使用大家熟悉的FIFO Queue。
func NewSchedulingQueue() SchedulingQueue {
if util.PodPriorityEnabled() {
return NewPriorityQueue()
}
return NewFIFO()
}NewPriorityQueue初始化優先級隊列代碼如下。
// NewPriorityQueue creates a PriorityQueue object.
func NewPriorityQueue() *PriorityQueue {
pq := &PriorityQueue{
activeQ: newHeap(cache.MetaNamespaceKeyFunc, util.HigherPriorityPod),
unschedulableQ: newUnschedulablePodsMap(),
nominatedPods: map[string][]*v1.Pod{},
}
pq.cond.L = &pq.lock
return pq
}主要初始化activeQ、unschedulableQ、nominatedPods。
newHeap初始化activeQ時,注冊heapData對應的keyFunc和lessFunc。
unschedulableQ初始化時,注冊keyFunc。
newHeap構建activeQ的時候,傳入兩個參數,第一個就是keyFunc: MetaNamespaceKeyFunc。
func MetaNamespaceKeyFunc(obj interface{}) (string, error) {
if key, ok := obj.(ExplicitKey); ok {
return string(key), nil
}
meta, err := meta.Accessor(obj)
if err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("object has no meta: %v", err)
}
if len(meta.GetNamespace()) > 0 {
return meta.GetNamespace() + "/" + meta.GetName(), nil
}
return meta.GetName(), nil
}MetaNamespaceKeyFunc根據Pod Object生成對應的key的Function,格式為"meta.GetNamespace() + "/" + meta.GetName"。
newHeap傳入的第二個參數是lessFunc:HigherPriorityPod。
const (
DefaultPriorityWhenNoDefaultClassExists = 0
)
func HigherPriorityPod(pod1, pod2 interface{}) bool {
return GetPodPriority(pod1.(*v1.Pod)) > GetPodPriority(pod2.(*v1.Pod))
}
func GetPodPriority(pod *v1.Pod) int32 {
if pod.Spec.Priority != nil {
return *pod.Spec.Priority
}
return scheduling.DefaultPriorityWhenNoDefaultClassExists
}HigherPriorityPod用來根據Pod優先級比較Heap中的Pod Object,然后決定其在Heap中的index。
index為0的Pod優先級最高,隨著index遞增,Pod優先級遞減。
注意:如果pod.Spec.Priority為nil(意味著這個Pod在創建時集群里還沒有對應的global default PriorityClass Object),并不是去把現在global default PriorityClass中的值設置給這個Pod.Spec.Priority,而是設置為0。個人覺得,設置為默認值比較合理。
unschedulableQ的構建是通過調用newUnschedulablePodsMap完成的,里面進行了UnschedulablePodsMap的pods的初始化,以及pods map中keyFunc的注冊。
func newUnschedulablePodsMap() *UnschedulablePodsMap {
return &UnschedulablePodsMap{
pods: make(map[string]*v1.Pod),
keyFunc: util.GetPodFullName,
}
}
func GetPodFullName(pod *v1.Pod) string {
return pod.Name + "_" + pod.Namespace
}注意:unschedulableQ中keyFunc實現的key生成規則是
pod.Name + "_" + pod.Namespace,不同于activeQ中keyFunc(格式為"meta.GetNamespace() + "/" + meta.GetName")。我也不理解為何要搞成兩種不同的格式,統一按照activeQ中的keyFunc就很好。
前面了解了PriorityQueue的結構,接著我們就要思考怎么往優先級Heap(activeQ)中添加對象了。
func (h *Heap) Add(obj interface{}) error {
key, err := h.data.keyFunc(obj)
if err != nil {
return cache.KeyError{Obj: obj, Err: err}
}
if _, exists := h.data.items[key]; exists {
h.data.items[key].obj = obj
heap.Fix(h.data, h.data.items[key].index)
} else {
heap.Push(h.data, &itemKeyValue{key, obj})
}
return nil
}
func Push(h Interface, x interface{}) {
h.Push(x)
up(h, h.Len()-1)
}
func up(h Interface, j int) {
for {
i := (j - 1) / 2 // parent
if i == j || !h.Less(j, i) {
break
}
h.Swap(i, j)
j = i
}
}
func (h *heapData) Less(i, j int) bool {
if i > len(h.queue) || j > len(h.queue) {
return false
}
itemi, ok := h.items[h.queue[i]]
if !ok {
return false
}
itemj, ok := h.items[h.queue[j]]
if !ok {
return false
}
return h.lessFunc(itemi.obj, itemj.obj)
}往activeQ中添加Pod時,如果該Pod已經存在,則根據其PriorityClass Value更新它在heap中的index,否則把它Push入堆。
Push和Fix類似,都需要對該Pod在activeQ heap中進行重新排序。排序時,通過Less Func進行比較,Less Func最終就是invoke前面注冊的activeQ中的lessFunc,即HigherPriorityPod。也就說Push和Fix時會根據Pod的優先級從高到低依次對應index從小到大。
使用PriorityQueue進行待調度Pod管理時,會從activeQ中Pop一個Pod出來,這個Pod是heap中的第一個Pod,也是優先級最高的Pod。
func (h *Heap) Pop() (interface{}, error) {
obj := heap.Pop(h.data)
if obj != nil {
return obj, nil
}
return nil, fmt.Errorf("object was removed from heap data")
}
func Pop(h Interface) interface{} {
n := h.Len() - 1
h.Swap(0, n)
down(h, 0, n)
return h.Pop()
}
func down(h Interface, i, n int) {
for {
j1 := 2*i + 1
if j1 >= n || j1 < 0 { // j1 < 0 after int overflow
break
}
j := j1 // left child
if j2 := j1 + 1; j2 < n && !h.Less(j1, j2) {
j = j2 // = 2*i + 2 // right child
}
if !h.Less(j, i) {
break
}
h.Swap(i, j)
i = j
}
}從activeQ heap中Pop一個Pod出來時,最終也是通過Less Func進行比較(即HigherPriorityPod)找出最高優先級的Pod。
了解了PriorityQueue及Pod進出Heap的原理之后,我們回到Scheduler Config Factory,看看Scheduler中podInformer、nodeInformer、serviceInformer、pvcInformer等注冊的EventHandler中對PriorityQueue的操作。
func NewConfigFactory(...) scheduler.Configurator {
...
// scheduled pod cache
podInformer.Informer().AddEventHandler(
cache.FilteringResourceEventHandler{
FilterFunc: func(obj interface{}) bool {
switch t := obj.(type) {
case *v1.Pod:
return assignedNonTerminatedPod(t)
case cache.DeletedFinalStateUnknown:
if pod, ok := t.Obj.(*v1.Pod); ok {
return assignedNonTerminatedPod(pod)
}
runtime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("unable to convert object %T to *v1.Pod in %T", obj, c))
return false
default:
runtime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("unable to handle object in %T: %T", c, obj))
return false
}
},
Handler: cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: c.addPodToCache,
UpdateFunc: c.updatePodInCache,
DeleteFunc: c.deletePodFromCache,
},
},
)
// unscheduled pod queue
podInformer.Informer().AddEventHandler(
cache.FilteringResourceEventHandler{
FilterFunc: func(obj interface{}) bool {
switch t := obj.(type) {
case *v1.Pod:
return unassignedNonTerminatedPod(t)
case cache.DeletedFinalStateUnknown:
if pod, ok := t.Obj.(*v1.Pod); ok {
return unassignedNonTerminatedPod(pod)
}
runtime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("unable to convert object %T to *v1.Pod in %T", obj, c))
return false
default:
runtime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("unable to handle object in %T: %T", c, obj))
return false
}
},
Handler: cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: c.addPodToSchedulingQueue,
UpdateFunc: c.updatePodInSchedulingQueue,
DeleteFunc: c.deletePodFromSchedulingQueue,
},
},
)
// ScheduledPodLister is something we provide to plug-in functions that
// they may need to call.
c.scheduledPodLister = assignedPodLister{podInformer.Lister()}
nodeInformer.Informer().AddEventHandler(
cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: c.addNodeToCache,
UpdateFunc: c.updateNodeInCache,
DeleteFunc: c.deleteNodeFromCache,
},
)
c.nodeLister = nodeInformer.Lister()
...
// This is for MaxPDVolumeCountPredicate: add/delete PVC will affect counts of PV when it is bound.
pvcInformer.Informer().AddEventHandler(
cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: c.onPvcAdd,
UpdateFunc: c.onPvcUpdate,
DeleteFunc: c.onPvcDelete,
},
)
c.pVCLister = pvcInformer.Lister()
// This is for ServiceAffinity: affected by the selector of the service is updated.
// Also, if new service is added, equivalence cache will also become invalid since
// existing pods may be "captured" by this service and change this predicate result.
serviceInformer.Informer().AddEventHandler(
cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: c.onServiceAdd,
UpdateFunc: c.onServiceUpdate,
DeleteFunc: c.onServiceDelete,
},
)
c.serviceLister = serviceInformer.Lister()
...
}通過assignedNonTerminatedPod FilterFunc過濾出那些已經Scheduled并且NonTerminated Pods,然后再對這些Pods的Add/Update/Delete Event Handler進行注冊,這里我們只關注對PriorityQueue的操作。
// assignedNonTerminatedPod selects pods that are assigned and non-terminal (scheduled and running).
func assignedNonTerminatedPod(pod *v1.Pod) bool {
if len(pod.Spec.NodeName) == 0 {
return false
}
if pod.Status.Phase == v1.PodSucceeded || pod.Status.Phase == v1.PodFailed {
return false
}
return true
}注冊Add assignedNonTerminatedPod Event Handler為addPodToCache。
func (c *configFactory) addPodToCache(obj interface{}) {
...
c.podQueue.AssignedPodAdded(pod)
}
// AssignedPodAdded is called when a bound pod is added. Creation of this pod
// may make pending pods with matching affinity terms schedulable.
func (p *PriorityQueue) AssignedPodAdded(pod *v1.Pod) {
p.movePodsToActiveQueue(p.getUnschedulablePodsWithMatchingAffinityTerm(pod))
}
func (p *PriorityQueue) movePodsToActiveQueue(pods []*v1.Pod) {
p.lock.Lock()
defer p.lock.Unlock()
for _, pod := range pods {
if err := p.activeQ.Add(pod); err == nil {
p.unschedulableQ.delete(pod)
} else {
glog.Errorf("Error adding pod %v to the scheduling queue: %v", pod.Name, err)
}
}
p.receivedMoveRequest = true
p.cond.Broadcast()
}
// getUnschedulablePodsWithMatchingAffinityTerm returns unschedulable pods which have
// any affinity term that matches "pod".
func (p *PriorityQueue) getUnschedulablePodsWithMatchingAffinityTerm(pod *v1.Pod) []*v1.Pod {
p.lock.RLock()
defer p.lock.RUnlock()
var podsToMove []*v1.Pod
for _, up := range p.unschedulableQ.pods {
affinity := up.Spec.Affinity
if affinity != nil && affinity.PodAffinity != nil {
terms := predicates.GetPodAffinityTerms(affinity.PodAffinity)
for _, term := range terms {
namespaces := priorityutil.GetNamespacesFromPodAffinityTerm(up, &term)
selector, err := metav1.LabelSelectorAsSelector(term.LabelSelector)
if err != nil {
glog.Errorf("Error getting label selectors for pod: %v.", up.Name)
}
if priorityutil.PodMatchesTermsNamespaceAndSelector(pod, namespaces, selector) {
podsToMove = append(podsToMove, up)
break
}
}
}
}
return podsToMove
}addPodToCache除了將pod加入到schedulerCache中之外,還會調用podQueue.AssignedPodAdded。
對于PriorityQueue而言,AssignedPodAdded負責unSchedulableQ中的pods進行與該pod的Pod Affinity檢查,把那些滿足Pod Affinity的pods從unSchedulableQ中移到activeQ中,待scheduler進行調度。
在這里要注意movePodsToActiveQueue中設置了receivedMoveRequest為true。
func (p *PriorityQueue) AddUnschedulableIfNotPresent(pod *v1.Pod) error {
p.lock.Lock()
defer p.lock.Unlock()
if p.unschedulableQ.get(pod) != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("pod is already present in unschedulableQ")
}
if _, exists, _ := p.activeQ.Get(pod); exists {
return fmt.Errorf("pod is already present in the activeQ")
}
if !p.receivedMoveRequest && isPodUnschedulable(pod) {
p.unschedulableQ.addOrUpdate(pod)
p.addNominatedPodIfNeeded(pod)
return nil
}
err := p.activeQ.Add(pod)
if err == nil {
p.addNominatedPodIfNeeded(pod)
p.cond.Broadcast()
}
return err
}如果receivedMoveRequest為false并且該Pod Condition Status為False或者Unschedulable時,才會將該Pod Add/Update到unschedulableQ,否則加入到activeQ。
因此receivedMoveRequest設置錯誤可能會導致該pod本應該加入到unSchedulableQ中,卻被加入到了activeQ中,這會導致scheduler多做一次無效的調度,當然這對性能的影響是很小的。
但是這里應該是有問題的,如果getUnschedulablePodsWithMatchingAffinityTerm得到的podsToMove數組為空時,并沒有pods會真正從unSchedulableQ中移到activeQ中,此時MoveRequest是無效的,receivedMoveRequest仍然應該為false。
上面的receivedMoveRequest設置不對帶來什么問題呢?當某個pod調度發生Error時會調用AddUnschedulableIfNotPresent將該pod加入到unSchedulableQ或者activeQ中。
注冊Update assignedNonTerminatedPod Event Handler為updatePodInCache。
func (c *configFactory) updatePodInCache(oldObj, newObj interface{}) {
...
c.podQueue.AssignedPodUpdated(newPod)
}
// AssignedPodUpdated is called when a bound pod is updated. Change of labels
// may make pending pods with matching affinity terms schedulable.
func (p *PriorityQueue) AssignedPodUpdated(pod *v1.Pod) {
p.movePodsToActiveQueue(p.getUnschedulablePodsWithMatchingAffinityTerm(pod))
}updatePodInCache中對podQueue的操作是AssignedPodUpdated,其實現同AssignedPodAdded,不再多說。
注冊Delete assignedNonTerminatedPod Event Handler為deletePodFromCache。
func (c *configFactory) deletePodFromCache(obj interface{}) {
...
c.podQueue.MoveAllToActiveQueue()
}
func (p *PriorityQueue) MoveAllToActiveQueue() {
p.lock.Lock()
defer p.lock.Unlock()
for _, pod := range p.unschedulableQ.pods {
if err := p.activeQ.Add(pod); err != nil {
glog.Errorf("Error adding pod %v to the scheduling queue: %v", pod.Name, err)
}
}
p.unschedulableQ.clear()
p.receivedMoveRequest = true
p.cond.Broadcast()
}當發生Delete assignedNonTerminatedPod Event時,會調用podQueue.MoveAllToActiveQueue將unSchedulableQ中的所有Pods移到activeQ中,unSchedulableQ也就被清空了。
如果集群中出現頻繁刪除pods的動作,會導致頻繁將unSchedulableQ中的所有Pods移到activeQ中。如果unSchedulableQ中有個High Priority的Pod,那么就會導致頻繁的搶占Lower Priority Pods的調度機會,使得Lower Priority Pod長期處于饑餓狀態。關于這個問題,社區已經在考慮增加對應的back-off機制,減輕這種情況帶來的影響。
通過unassignedNonTerminatedPod FilterFunc過濾出那些還未成功調度的并且NonTerminated Pods,然后再對這些Pods的Add/Update/Delete Event Handler進行注冊,這里我們只關注對PriorityQueue的操作。
// unassignedNonTerminatedPod selects pods that are unassigned and non-terminal.
func unassignedNonTerminatedPod(pod *v1.Pod) bool {
if len(pod.Spec.NodeName) != 0 {
return false
}
if pod.Status.Phase == v1.PodSucceeded || pod.Status.Phase == v1.PodFailed {
return false
}
return true
}注冊Add unassignedNonTerminatedPod Event Handler為addPodToSchedulingQueue。
func (c *configFactory) addPodToSchedulingQueue(obj interface{}) {
if err := c.podQueue.Add(obj.(*v1.Pod)); err != nil {
runtime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("unable to queue %T: %v", obj, err))
}
}
func (p *PriorityQueue) Add(pod *v1.Pod) error {
p.lock.Lock()
defer p.lock.Unlock()
err := p.activeQ.Add(pod)
if err != nil {
glog.Errorf("Error adding pod %v to the scheduling queue: %v", pod.Name, err)
} else {
if p.unschedulableQ.get(pod) != nil {
glog.Errorf("Error: pod %v is already in the unschedulable queue.", pod.Name)
p.deleteNominatedPodIfExists(pod)
p.unschedulableQ.delete(pod)
}
p.addNominatedPodIfNeeded(pod)
p.cond.Broadcast()
}
return err
}當發現有unassigned Pods Add時,addPodToSchedulingQueue負責把該pods加入到activeQ中,并確保unSchedulableQ中沒有這些unassigned pods。
注冊Update unassignedNonTerminatedPod Event Handler為updatePodInSchedulingQueue。
func (c *configFactory) updatePodInSchedulingQueue(oldObj, newObj interface{}) {
pod := newObj.(*v1.Pod)
if c.skipPodUpdate(pod) {
return
}
if err := c.podQueue.Update(oldObj.(*v1.Pod), pod); err != nil {
runtime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("unable to update %T: %v", newObj, err))
}
}updatePodInSchedulingQueue中先調用skipPodUpdate檢查是否該pod update event可以忽略。
如果不能忽略該pod update,再invoke podQueue.Update更新activeQ,如果該pod不在activeQ中,則從unSchedulableQ中刪除該pod,然后把新的pod Push到activeQ中。
func (c *configFactory) skipPodUpdate(pod *v1.Pod) bool {
// Non-assumed pods should never be skipped.
isAssumed, err := c.schedulerCache.IsAssumedPod(pod)
if err != nil {
runtime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("failed to check whether pod %s/%s is assumed: %v", pod.Namespace, pod.Name, err))
return false
}
if !isAssumed {
return false
}
// Gets the assumed pod from the cache.
assumedPod, err := c.schedulerCache.GetPod(pod)
if err != nil {
runtime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("failed to get assumed pod %s/%s from cache: %v", pod.Namespace, pod.Name, err))
return false
}
// Compares the assumed pod in the cache with the pod update. If they are
// equal (with certain fields excluded), this pod update will be skipped.
f := func(pod *v1.Pod) *v1.Pod {
p := pod.DeepCopy()
// ResourceVersion must be excluded because each object update will
// have a new resource version.
p.ResourceVersion = ""
// Spec.NodeName must be excluded because the pod assumed in the cache
// is expected to have a node assigned while the pod update may nor may
// not have this field set.
p.Spec.NodeName = ""
// Annotations must be excluded for the reasons described in
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/issues/52914.
p.Annotations = nil
return p
}
assumedPodCopy, podCopy := f(assumedPod), f(pod)
if !reflect.DeepEqual(assumedPodCopy, podCopy) {
return false
}
glog.V(3).Infof("Skipping pod %s/%s update", pod.Namespace, pod.Name)
return true
}skipPodUpdate檢查到以下情況同時發生時,都會返回true,表示忽略該pod update event。
該pod已經Assumed:檢查scheduler cache中assumePods中是否包含該pod,如果包含,說明它已經Assumed(當pod完成了scheduler的Predicate和Priority后,立刻就設置為Assumed,之后再調用apiserver的Bind接口)。
該pod update只更新了它的ResourceVersion, Spec.NodeName, Annotations三者之一或者全部。
func (p *PriorityQueue) Update(oldPod, newPod *v1.Pod) error {
p.lock.Lock()
defer p.lock.Unlock()
// If the pod is already in the active queue, just update it there.
if _, exists, _ := p.activeQ.Get(newPod); exists {
p.updateNominatedPod(oldPod, newPod)
err := p.activeQ.Update(newPod)
return err
}
// If the pod is in the unschedulable queue, updating it may make it schedulable.
if usPod := p.unschedulableQ.get(newPod); usPod != nil {
p.updateNominatedPod(oldPod, newPod)
if isPodUpdated(oldPod, newPod) {
p.unschedulableQ.delete(usPod)
err := p.activeQ.Add(newPod)
if err == nil {
p.cond.Broadcast()
}
return err
}
p.unschedulableQ.addOrUpdate(newPod)
return nil
}
// If pod is not in any of the two queue, we put it in the active queue.
err := p.activeQ.Add(newPod)
if err == nil {
p.addNominatedPodIfNeeded(newPod)
p.cond.Broadcast()
}
return err
}當skipPodUpdate為true時,接著調用PriorityQueue.Update:
如果該pod已經在activeQ中,則更新它。
如果該pod在unSchedulableQ中,檢查該Pod是不是有效更新(忽略ResourceVersion、Generation、PodStatus)。
如果是有效更新,則從unSchedulableQ中刪除該,并將更新的pod加到activeQ中待調度。
如果是無效更新,則更新unSchedulableQ中的該pod信息。
如果activeQ和unSchedulableQ中都沒有該pod,則把該pod添加到activeQ中。
注冊Delete unassignedNonTerminatedPod Event Handler為deletePodFromSchedulingQueue。
func (c *configFactory) deletePodFromSchedulingQueue(obj interface{}) {
...
if err := c.podQueue.Delete(pod); err != nil {
runtime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("unable to dequeue %T: %v", obj, err))
}
...
}
func (p *PriorityQueue) Delete(pod *v1.Pod) error {
p.lock.Lock()
defer p.lock.Unlock()
p.deleteNominatedPodIfExists(pod)
err := p.activeQ.Delete(pod)
if err != nil { // The item was probably not found in the activeQ.
p.unschedulableQ.delete(pod)
}
return nil
}deletePodFromSchedulingQueue中對podQueue的處理就是調用其Delete接口,將該pod從activeQ或者unSchedulableQ中刪除。
NodeInformer注冊了Node的Add/Update/Delete Event Handler,這里我們只關注這些Handler對PriorityQueue的操作。
注冊Add Node Event Handler為addNodeToCache。
注冊Update Node Event Handler為updateNodeInCache。
注冊Delete Node Event Handler為deleteNodeFromCache。
func (c *configFactory) addNodeToCache(obj interface{}) {
...
c.podQueue.MoveAllToActiveQueue()
}
func (c *configFactory) updateNodeInCache(oldObj, newObj interface{}) {
...
c.podQueue.MoveAllToActiveQueue()
}addNodeToCache和updateNodeInCache對PriorityQueue的操作都是一樣的,調用PriorityQueue.MoveAllToActiveQueue將所有unSchedulableQ中的Pods移到activeQ中,意味著集群中增加或者更新Node時,所有未成功調度的pods都會重新在activeQ中按優先級進行重新排序等待調度。
deleteNodeFromCache中不涉及PodQueue的操作。
同
PodInformer EventHandler for Scheduled Pod中提到的一樣,如果集群中出現頻繁增加或者更新Node的動作,會導致頻繁將unSchedulableQ中的所有Pods移到activeQ中。如果unSchedulableQ中有個High Priority的Pod,那么就會導致頻繁的搶占Lower Priority Pods的調度機會,使得Lower Priority Pod長期處于饑餓狀態。
serviceInformer注冊了Service的Add/Update/Delete Event Handler,這里我們只關注這些Handler對PriorityQueue的操作。
注冊Add Service Event Handler為onServiceAdd。
注冊Update Service Event Handler為onServiceUpdate。
注冊Delete Service Event Handler為onServiceDelete。
func (c *configFactory) onServiceAdd(obj interface{}) {
...
c.podQueue.MoveAllToActiveQueue()
}
func (c *configFactory) onServiceUpdate(oldObj interface{}, newObj interface{}) {
...
c.podQueue.MoveAllToActiveQueue()
}
func (c *configFactory) onServiceDelete(obj interface{}) {
...
c.podQueue.MoveAllToActiveQueue()
}Service的Add/Update/Delete Event Handler對podQueue的操作都是一樣的,調用PriorityQueue.MoveAllToActiveQueue將所有unSchedulableQ中的Pods移到activeQ中,意味著集群中增加、更新或者刪除Service時,所有未成功調度的pods都會重新在activeQ中按優先級進行重新排序等待調度。
同
PodInformer EventHandler for Scheduled Pod中提到的一樣,如果集群中出現頻繁Add/Update/Delete Service的動作,會導致頻繁將unSchedulableQ中的所有Pods移到activeQ中。如果unSchedulableQ中有個High Priority的Pod,那么就會導致頻繁的搶占Lower Priority Pods的調度機會,使得Lower Priority Pod長期處于饑餓狀態。
pvcInformer注冊了pvc的Add/Update/Delete Event Handler,這里我們只關注這些Handler對PriorityQueue的操作。
注冊Add PVC Event Handler為onPvcAdd。
注冊Update PVC Event Handler為onPvcUpdate。
注冊Delete PVC Event Handler為onPvcDelete。
func (c *configFactory) onPvcAdd(obj interface{}) {
...
c.podQueue.MoveAllToActiveQueue()
}
func (c *configFactory) onPvcUpdate(old, new interface{}) {
...
c.podQueue.MoveAllToActiveQueue()
}sheduler對PVC的Add和Update Event的操作都是一樣的,調用PriorityQueue.MoveAllToActiveQueue將所有unSchedulableQ中的Pods移到activeQ中,意味著集群中增加或者更新PVC時,所有未成功調度的pods都會重新在activeQ中按優先級進行重新排序等待調度。
Delete PVC不涉及PodQueue的操作。
PV的Add/Update/Delete也不涉及PodQueue的操作。
同
PodInformer EventHandler for Scheduled Pod中提到的一樣,如果集群中出現頻繁Add/Update PVC的動作,會導致頻繁將unSchedulableQ中的所有Pods移到activeQ中。如果unSchedulableQ中有個High Priority的Pod,那么就會導致頻繁的搶占Lower Priority Pods的調度機會,使得Lower Priority Pod長期處于饑餓狀態。
感謝各位的閱讀,以上就是“Kubernetes Scheduler的優先級隊列是什么”的內容了,經過本文的學習后,相信大家對Kubernetes Scheduler的優先級隊列是什么這一問題有了更深刻的體會,具體使用情況還需要大家實踐驗證。這里是億速云,小編將為大家推送更多相關知識點的文章,歡迎關注!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。