您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹NanoDet是什么,文中介紹的非常詳細,具有一定的參考價值,感興趣的小伙伴們一定要看完!
NanoDet 是一個速度超快和輕量級的移動端 Anchor-free 目標檢測模型。
YOLO、SSD、Fast R-CNN等模型在目標檢測方面速度較快和精度較高,但是這些模型比較大,不太適合移植到移動端或嵌入式設備;輕量級模型 NanoDet-m,對單階段檢測模型三大模塊(Head、Neck、Backbone)進行輕量化,目標加檢測速度很快;模型文件大小僅幾兆(小于4M)。
NanoDet作者開源代碼地址 :https://github.com/RangiLyu/nanodet (致敬)
基于NanoDet項目進行小裁剪,專門用來實現Python語言、PyTorch 版本的代碼地址: https://github.com/guo-pu/NanoDet-PyTorch
下載直接能使用,支持圖片、視頻文件、攝像頭實時目標檢測
先看一下NanoDet目標檢測的效果:
同時檢測多輛汽車:

查看多目標、目標之間重疊、同時存在小目標和大目標的檢測效果:

NanoDet 是一種 FCOS 式的單階段 anchor-free 目標檢測模型,它使用 ATSS 進行目標采樣,使用 Generalized Focal Loss 損失函數執行分類和邊框回歸(box regression)。
NanoDet-m模型和YoloV3-Tiny、YoloV4-Tiny作對比:
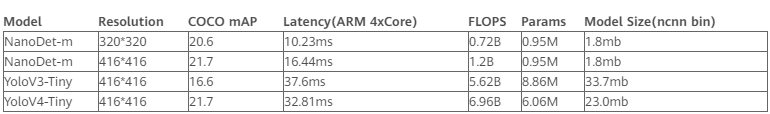
備注:以上性能基于 ncnn 和麒麟 980 (4xA76+4xA55) ARM CPU 獲得的。使用 COCO mAP (0.5:0.95) 作為評估指標,兼顧檢測和定位的精度,在 COCO val 5000 張圖片上測試,并且沒有使用 Testing-Time-Augmentation。
NanoDet作者將 ncnn 部署到手機(基于 ARM 架構的 CPU 麒麟 980,4 個 A76 核心和 4 個 A55 核心)上之后跑了一下 benchmark,模型前向計算時間只要 10 毫秒左右,而 yolov3 和 v4 tiny 均在 30 毫秒的量級。在安卓攝像頭 demo app 上,算上圖片預處理、檢測框后處理以及繪制檢測框的時間,NanoDet 也能輕松跑到 40+FPS。
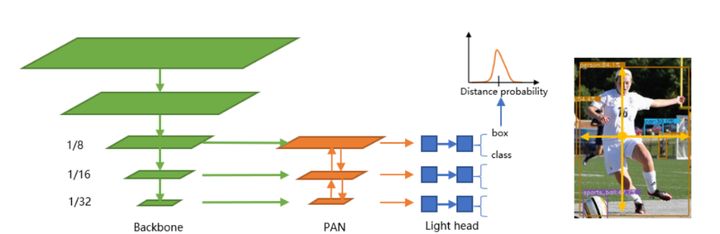
NanoDet 使用了李翔等人提出的 Generalized Focal Loss 損失函數。該函數能夠去掉 FCOS 的 Centerness 分支,省去這一分支上的大量卷積,從而減少檢測頭的計算開銷,非常適合移動端的輕量化部署。
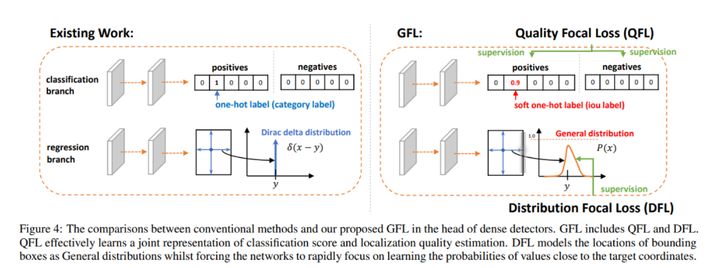
詳細請參考:Generalized Focal Loss: Learning Qualified and Distributed Bounding Boxes for Dense Object Detection
NanoDet 是一個速度超快和輕量級的移動端 Anchor-free 目標檢測模型。該模型具備以下優勢:
超輕量級:模型文件大小僅幾兆(小于4M——nanodet_m.pth);
速度超快:在移動 ARM CPU 上的速度達到 97fps(10.23ms);
訓練友好:GPU 內存成本比其他模型低得多。GTX1060 6G 上的 Batch-size 為 80 即可運行;
方便部署:提供了基于 ncnn 推理框架的 C++ 實現和 Android demo。
基于NanoDet項目進行小裁剪,專門用來實現Python語言、PyTorch 版本的代碼地址:
同時檢測出四位少年
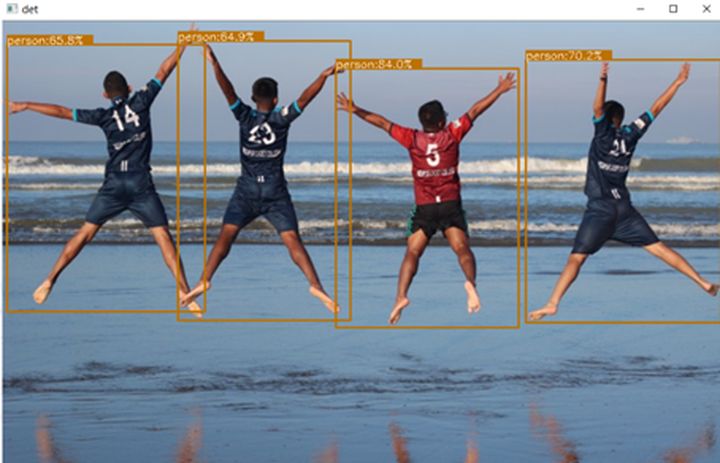

在復雜街道中,檢測出行人、汽車:

通過測試發現NanoDet確實很快,但識別精度和效果比YOLOv4差不少的。
測試環境參數
系統:Windows 編程語言:Python 3.8 整合開發環境:Anaconda
深度學習框架:PyTorch2.7.0+cu101 (torch>=1.3 即可) 開發代碼IDE:PyCharm
開發具體環境要求如下:
Cython
termcolor
numpy
torch>=1.3
torchvision
tensorboard
pycocotools
matplotlib
pyaml
opencv-python
tqdm
通常測試感覺GPU加速(顯卡驅動、cudatoolkit 、cudnn)、PyTorch、pycocotools相對難裝一點
Windows開發環境安裝可以參考:
安裝cudatoolkit 10.1、cudnn7.6請參考 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41204464/article/details/108807165
安裝PyTorch請參考 https://blog.csdn.net/u014723479/article/details/103001861
安裝pycocotools請參考 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41166529/article/details/109997105
下載代碼,打開工程
先到githug下載代碼,然后解壓工程,然后使用PyCharm工具打開工程;
githug代碼下載地址:https://github.com/guo-pu/NanoDet-PyTorch
說明:該代碼是基于NanoDet項目進行小裁剪,專門用來實現Python語言、PyTorch 版本的代碼
NanoDet作者開源代碼地址: https://github.com/RangiLyu/nanodet (致敬)
使用PyCharm工具打開工程
選擇開發環境】
文件(file)——>設置(setting)——>項目(Project)——>Project Interpreters 選擇搭建的開發環境;
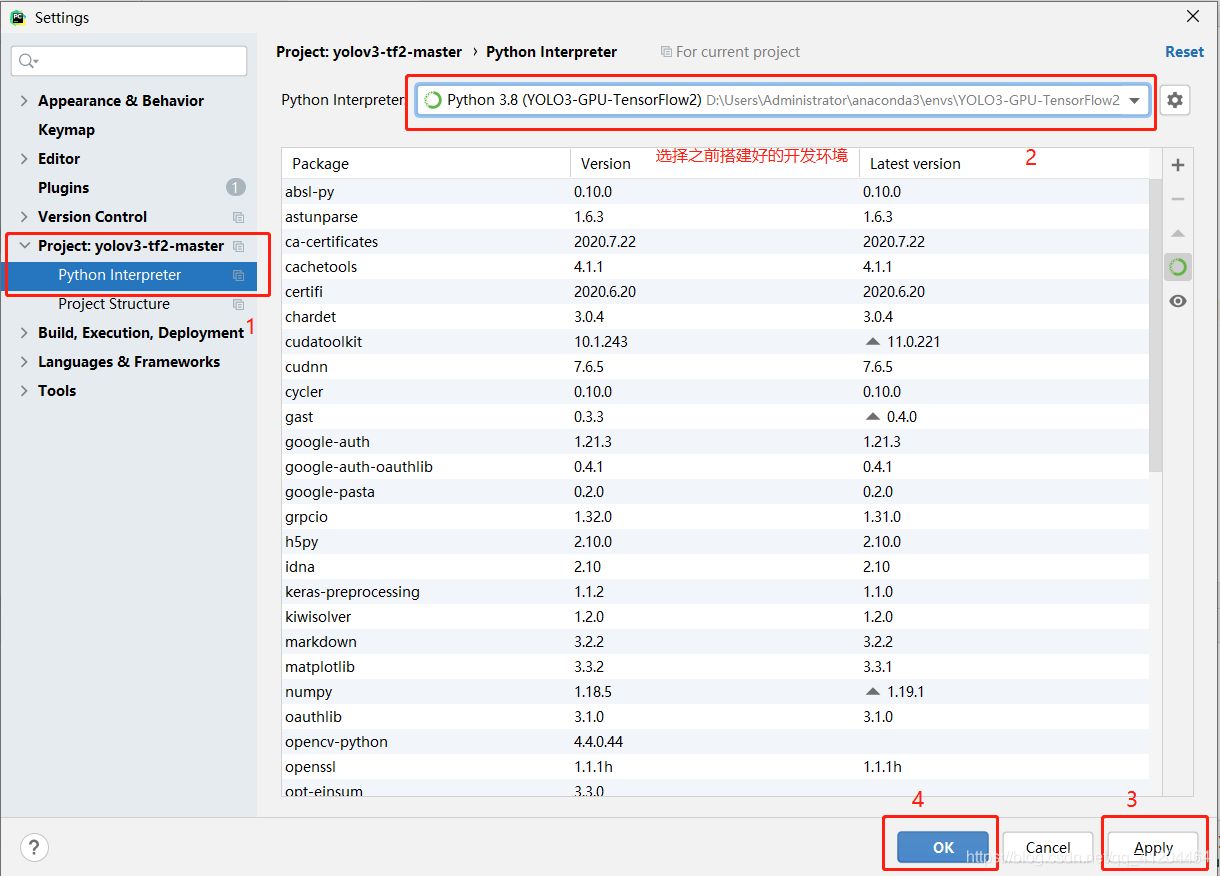
然后先點擊Apply,等待加載完成,再點擊OK;
進行目標檢測
具體命令請參考:
'''目標檢測-圖片''' python detect_main.py image --config ./config/nanodet-m.yml --model model/nanodet_m.pth --path street.png '''目標檢測-視頻文件''' python detect_main.py video --config ./config/nanodet-m.yml --model model/nanodet_m.pth --path test.mp4 '''目標檢測-攝像頭''' python detect_main.py webcam --config ./config/nanodet-m.yml --model model/nanodet_m.pth --path 0
【目標檢測-圖片】

【目標檢測-視頻文件】
檢測的是1080*1920的圖片,很流暢毫不卡頓,就是目前識別精度不太高

detect_main.py 代碼:
import cv2
import os
import time
import torch
import argparse
from nanodet.util import cfg, load_config, Logger
from nanodet.model.arch import build_model
from nanodet.util import load_model_weight
from nanodet.data.transform import Pipeline
image_ext = ['.jpg', '.jpeg', '.webp', '.bmp', '.png']
video_ext = ['mp4', 'mov', 'avi', 'mkv']
'''目標檢測-圖片'''
# python detect_main.py image --config ./config/nanodet-m.yml --model model/nanodet_m.pth --path street.png
'''目標檢測-視頻文件'''
# python detect_main.py video --config ./config/nanodet-m.yml --model model/nanodet_m.pth --path test.mp4
'''目標檢測-攝像頭'''
# python detect_main.py webcam --config ./config/nanodet-m.yml --model model/nanodet_m.pth --path 0
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('demo', default='image', help='demo type, eg. image, video and webcam')
parser.add_argument('--config', help='model config file path')
parser.add_argument('--model', help='model file path')
parser.add_argument('--path', default='./demo', help='path to images or video')
parser.add_argument('--camid', type=int, default=0, help='webcam demo camera id')
args = parser.parse_args()
return args
class Predictor(object):
def __init__(self, cfg, model_path, logger, device='cuda:0'):
self.cfg = cfg
self.device = device
model = build_model(cfg.model)
ckpt = torch.load(model_path, map_location=lambda storage, loc: storage)
load_model_weight(model, ckpt, logger)
self.model = model.to(device).eval()
self.pipeline = Pipeline(cfg.data.val.pipeline, cfg.data.val.keep_ratio)
def inference(self, img):
img_info = {}
if isinstance(img, str):
img_info['file_name'] = os.path.basename(img)
img = cv2.imread(img)
else:
img_info['file_name'] = None
height, width = img.shape[:2]
img_info['height'] = height
img_info['width'] = width
meta = dict(img_info=img_info,
raw_img=img,
img=img)
meta = self.pipeline(meta, self.cfg.data.val.input_size)
meta['img'] = torch.from_numpy(meta['img'].transpose(2, 0, 1)).unsqueeze(0).to(self.device)
with torch.no_grad():
results = self.model.inference(meta)
return meta, results
def visualize(self, dets, meta, class_names, score_thres, wait=0):
time1 = time.time()
self.model.head.show_result(meta['raw_img'], dets, class_names, score_thres=score_thres, show=True)
print('viz time: {:.3f}s'.format(time.time()-time1))
def get_image_list(path):
image_names = []
for maindir, subdir, file_name_list in os.walk(path):
for filename in file_name_list:
apath = os.path.join(maindir, filename)
ext = os.path.splitext(apath)[1]
if ext in image_ext:
image_names.append(apath)
return image_names
def main():
args = parse_args()
torch.backends.cudnn.enabled = True
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True
load_config(cfg, args.config)
logger = Logger(-1, use_tensorboard=False)
predictor = Predictor(cfg, args.model, logger, device='cuda:0')
logger.log('Press "Esc", "q" or "Q" to exit.')
if args.demo == 'image':
if os.path.isdir(args.path):
files = get_image_list(args.path)
else:
files = [args.path]
files.sort()
for image_name in files:
meta, res = predictor.inference(image_name)
predictor.visualize(res, meta, cfg.class_names, 0.35)
ch = cv2.waitKey(0)
if ch == 27 or ch == ord('q') or ch == ord('Q'):
break
elif args.demo == 'video' or args.demo == 'webcam':
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(args.path if args.demo == 'video' else args.camid)
while True:
ret_val, frame = cap.read()
meta, res = predictor.inference(frame)
predictor.visualize(res, meta, cfg.class_names, 0.35)
ch = cv2.waitKey(1)
if ch == 27 or ch == ord('q') or ch == ord('Q'):
break
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()以上是“NanoDet是什么”這篇文章的所有內容,感謝各位的閱讀!希望分享的內容對大家有幫助,更多相關知識,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。