您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容介紹了“MySQL數據庫回表與索引怎么理解”的有關知識,在實際案例的操作過程中,不少人都會遇到這樣的困境,接下來就讓小編帶領大家學習一下如何處理這些情況吧!希望大家仔細閱讀,能夠學有所成!
先得出結論,根據下面的實驗。如果我要獲得['liu','25']這條記錄。需要什么步驟。
1.先通過['liu']記錄對應到普通索引index(name),獲取到主鍵id:4.
2.再通過clustered index,定位到行記錄。也就是上面說的這條['liu','25']記錄數據。
因此,上述就是說的回表查詢,先定位主鍵值,再定位行記錄。多掃了一遍索引樹。
當然,也就多耗費了CPU,IO,內存等。
create table stu_info ( id int primary key, name varchar(20), age int, index(name) )
mysql> show create table stu_info\G; *************************** 1\. row *************************** Table: stu_info Create Table: CREATE TABLE `stu_info` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL, `name` varchar(20) COLLATE utf8_bin DEFAULT NULL, `age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), KEY `name` (`name`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_bin 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
insert into stu_info values(1,'zhang',20); insert into stu_info values(4,'liu',25); insert into stu_info values(7,'huang',19); insert into stu_info values(10,'allen',27); insert into stu_info values(30,'benjiemin',27); insert into stu_info values(16,'roger',27); insert into stu_info values(28,'peter',16); commit
我們來分析這幾條數據的索引。由于我們name這個列建立了索引。所以name索引存儲會按照【a~z】順序排列。通過select語句,可以得到一些感性認識。如下:
mysql> select name from stu_info; +-----------+ | name | +-----------+ | allen | | benjiemin | | huang | | liu | | peter | | roger | | zhang | +-----------+
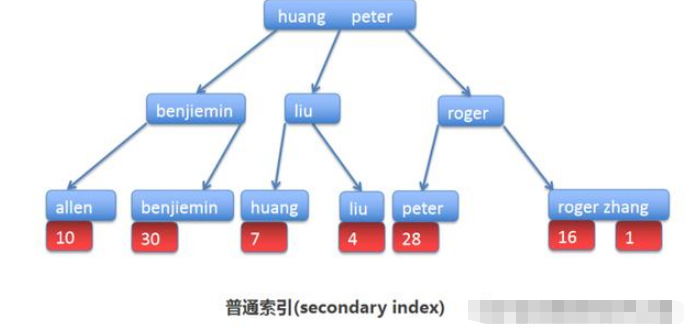
上述的普通索引secondary index在B+樹存儲格式可能如下:
根據舊金山大學提供的可視化B+tree的效果。
如下圖:
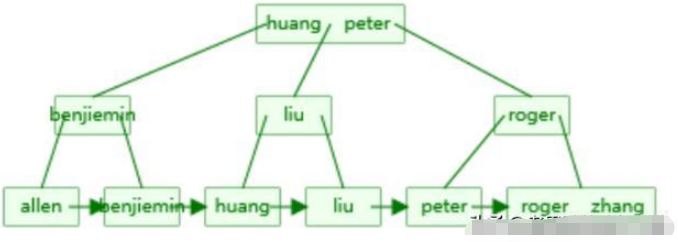
我在根據上面的圖,畫一個自己的。如下圖所示:
也能看到name這幾個數據建立的B+樹是怎么樣的。也能看到我需要找到[liu]這個元素的話,需要兩次查找。
但是,如果我的需求是,除了獲取name之外還需要獲取age的話。這里就需要回表了。為什么?因為我找不到age數據。
普通索引的葉子節點,只存主鍵。
那么clustered index聚集索引是如何保存的呢?繼續使用上述可視化工具,再分析一波。

上圖是聚集索引的示意圖。轉化為我的圖如下:

所以,name='liu'查詢liu的年齡,是需要回表的。首先查詢普通索引的B+樹,再查詢聚集索引的B+樹。最后得到liu的那條行記錄。
我們也可以通過執行計劃來分析一下,如下:
mysql> explain select id,name,age from stu_info where name='liu'\G; *************************** 1\. row *************************** id: 1 select_type: SIMPLE table: stu_info type: ref possible_keys: name key: name key_len: 63 ref: const rows: 1 Extra: Using index condition 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
看到Using index condition,我們這里用到了回表。
如果不取age,只取id和name的話,那么。就不需要回表。如下實驗,繼續看執行計劃:
mysql> explain select id,name from stu_info where name='liu'\G; *************************** 1\. row *************************** id: 1 select_type: SIMPLE table: stu_info type: ref possible_keys: name key: name key_len: 63 ref: const rows: 1 Extra: Using where; Using index 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
那么,如果我們不想回表,不想多做IO的話。我們可以通過建立組合索引來解決這個問題。通過
ALTER TABLE stu_info DROP INDEX name; alter table stu_info add key(name,age);
我們再繼續看執行計劃,如下:
mysql> explain select name,age from stu_info where name='liu'\G; *************************** 1\. row *************************** id: 1 select_type: SIMPLE table: stu_info type: ref possible_keys: name key: name key_len: 63 ref: const rows: 1 Extra: Using where; Using index 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
可以看到額外信息是Using where; Using index而不是Using index condition也就沒有用到回表了。
“MySQL數據庫回表與索引怎么理解”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識可以關注億速云網站,小編將為大家輸出更多高質量的實用文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。