您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
A.循環鏈表的介紹
a.概念上
1.任意數據元素都有一個前驅和一個后繼
2.所有數據元素的關系構成一個邏輯上的環
b.實現上
1.循環鏈表是一種特殊的單鏈表
2.尾節點的指針域保存了首結點的地址
關系圖如下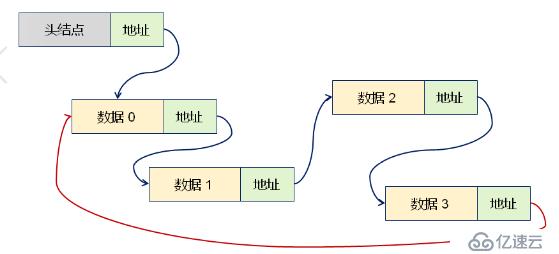 、
、
循環鏈表的繼承層次結構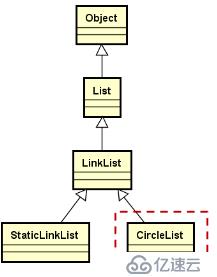
A.思路
1.通過模板定義CircleList類,繼承自LinkList類
2.定義內部函數last_to_first();用于將單鏈表首尾相連
Node* last()const//尾節點
{
return this->position(this->m_length-1)->next;//返回尾節點(m_length-1)
}
void last_to_first()const//將鏈表首尾相連
{
last()->next=this->m_header.next;//尾節點的next指針指向首節點
}
int mod(int i)const//取余的實現
{
return (this->m_length==0) ? 0 : ( i % this->m_length);
}3.特殊處理:首元素的插入操作和刪除操作
4.重新實現:清空操作和遍歷操作
B.實現要點
a.插入位置為0時
1.頭結點和尾結點均指向新結點
2.新結點成為首節點插入鏈表
bool insert(int i,const T& e)
{
bool ret=true;
i=i%(this->m_length+1);//i值取余
ret=LinkList<T>::insert(i,e);//調用父類的insert來實現子類的insert
if(ret&&(i==0))
{
last_to_first();
}
return ret;
}b.刪除位置為0時
1.頭結點和尾結點指向位置為1的結點
2.安全銷毀首結點
bool remove(int i)
{
bool ret= true;
i= mod(i);
if(i==0)
{
Node *toDel=this->m_header.next;
if(toDel!=NULL)
{
this->m_header.next=toDel->next;
this->m_length--;
//鏈表不為空
if(this->m_length>0)
{
last_to_first();
if(this->m_current==toDel)
{
this->m_current=toDel->next;
}
}
else
{ //鏈表為空,置空
this->m_header.next=NULL;
this->m_current=NULL;
}
this->destroy(toDel);//在最后一步刪除首節點 避免了異常安全
}
else
{
ret=false;
}
}
else
{
ret=LinkList<T>::remove(i);
}
return ret;
}
循環鏈表的完整實現代碼如下
#include "LinkList.h"
namespace MyLib
{
template <typename T>
class CircleList:public LinkList<T>
{
protected:
typedef typename LinkList<T>::Node Node;
Node* last()const//尾節點
{
return this->position(this->m_length-1)->next;//返回尾節點(m_length-1)
}
void last_to_first()const//將鏈表首尾相連
{
last()->next=this->m_header.next;//尾節點的next指針指向首節點
}
int mod(int i)const
{
return (this->m_length==0) ? 0 : ( i % this->m_length);
}
public:
bool insert(const T& e)//重載
{
return insert(this->m_length,e);//調用重載的版本
}
bool insert(int i,const T& e)
{
bool ret=true;
i=i%(this->m_length+1);//i值取余
ret=LinkList<T>::insert(i,e);//調用父類的insert來實現子類的insert
if(ret&&(i==0))
{
last_to_first();
}
return ret;
}
bool remove(int i)
{
bool ret= true;
i= mod(i);
if(i==0)
{
Node *toDel=this->m_header.next;
if(toDel!=NULL)
{
this->m_header.next=toDel->next;
this->m_length--;
//鏈表不為空
if(this->m_length>0)
{
last_to_first();
if(this->m_current==toDel)
{
this->m_current=toDel->next;
}
}
else
{ //鏈表為空,置空
this->m_header.next=NULL;
this->m_current=NULL;
}
this->destroy(toDel);//在最后一步刪除首節點 避免了異常安全
}
else
{
ret=false;
}
}
else
{
ret=LinkList<T>::remove(i);
}
return ret;
}
bool set(int i, const T &e)
{
i=mod(i);
return LinkList<T>::set(i,e);//調用父類函數
}
T get(int i)const
{
i=mod(i);
return LinkList<T>::get(i);
}
T get(int i,const T&e) const
{
i=mod(i);
return LinkList<T>::get(i,e);
}
int find(const T &e)const
{
int ret=-1;
Node* slide=this->m_header.next;//指針slide指向首節點
for(int i=0;i<this->m_length;i++)//slide指針遍歷每個元素
{
if(slide->value==e)
{
ret=i;
break;
}
slide=slide->next;
}
return ret;
}
void clear()
{
while(this->m_length>1)
{
remove(1);//這里取1的原因是效率更高
}
if(this->m_length==1)
{
Node* toDel=this->m_header.next;
this->m_header.next=NULL;
this->m_current=NULL;
this->m_length=0;
this->destroy(toDel);
}
}
bool move(int i, int step)//i表示位置
{
i=mod(i);
return LinkList<T>::move(i,step);
}
bool end()
{
return (this->m_length==0)||(this->m_current==NULL);
}
~CircleList()//析構函數直接調用clear()函數
{
clear();
}
};
}1.循環鏈表是一種特殊的單鏈表
2.尾結點的指針域保存了首結點的地址
3.特殊處理首元素的插入操作和刪除操作
4.重新實現清空操作和遍歷操作
由之前的單鏈表我們可以看到單鏈表存在的缺陷
1.單向性==>只能從頭結點開始高效訪問鏈表中的數據元素
2.缺陷==>如果需要逆向訪問單鏈表中的數據元素將極其低效
新的線性表實現
設計思路:在單鏈表的結點中增加一個指針pre,用于指向當前結點的前驅結點
示意圖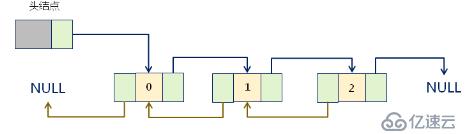
雙向鏈表的繼承層次結構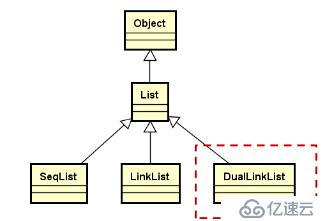
簡單的圖示來說明雙向鏈表的插入和刪除操作
插入操作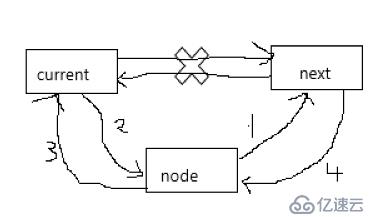
如圖所示四個步驟完成操作
1.將插入結點的next指向next
2.current的next指向插入的結點
3.插入結點的pre指向curret
4.next的pre指向node
實現代碼
bool insert(int i,const T&e)
{
bool ret=((0<=i)&&(i<= m_length));
if(ret)
{
Node* node=creat();
if(node!=NULL)
{
Node* current=positon();
Node* next=current->next;
node->value=e;
node->next=next;//步驟1
current->next=node;//步驟2
if(current!=reinterpret_cast<Node*>(&m_header))
{
node->pre=current;//步驟3
}
else
{
node->pre=NULL;
}
if(next!=NULL)
{
next-pre=node;
}
m_length++;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEoughMemoryException,"NoEoughMemory");
}
}
return ret;
}刪除操作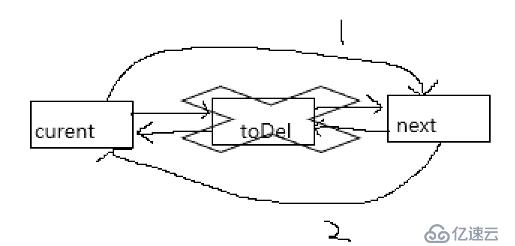
刪除部分3個步驟
1.將current的next指向next
2.將next的pre指向current
3.刪除toDel
代碼實現如下
bool remove(int i)
{
bool ret=((0<=i)&&(i<m_length));
if(ret)
{
Node* current=position(i);
Node* toDel=current->next;
Node* next=toDel->next;
if(m_current==toDel)
{
m_current=next;
}
current->next=next;//步驟1
if(next!=NULL)
{
next->pre=toDel->pre;//步驟2
}
m_length--;
destroy(toDel);//步驟3
//m_length--;
}
return ret;
}雙向鏈表的具體實現
#include "List.h"
#include "Exception.h"
namespace MyLib
{
template <typename T>
class DuaLinkList:public List<T>
{
protected:
struct Node :public Object
{
T value;//數據域 保存數據的值
Node* next;//指針域 指向后繼節點的指針
Node* pre;
};
mutable struct:public Object//沒有類型名的結構
{
char reserved[sizeof(T)];
Node* next;
Node* pre;
} m_header;//頭節點 輔助定位元素
int m_length;
int m_step;
Node* m_current;
Node* position(int i) const//程序優化
{
Node* ret=reinterpret_cast<Node*>(&m_header);//reinterpret_cast強制類型轉換
for(int p=0;p<i;p++)
{
ret=ret->next;
}
return ret;
}
virtual Node* create()
{
return new Node();
}
virtual void destroy(Node* pn)
{
delete pn;
}
public:
DuaLinkList()
{
m_header.next=NULL;
m_header.pre=NULL;
m_length=0;
m_step=1;
m_current=NULL;
}
bool insert(const T&e)
{
return insert(m_length,e);
}
bool insert(int i,const T&e)//i表示插入的位置,e表示插入的數據
{
bool ret=((0<=i)&&(i<= m_length));//m_length表示鏈表的長度
if(ret)
{
Node* node=create();
if(node!=NULL)
{
Node* current=position(i);//定位位置
Node* next=current->next;//表示插入的節點的后繼節點
node->value=e;
node->next=next;
current->next=node;
if(current!=reinterpret_cast<Node*>(&m_header))
{
node->pre=current;
}
else
{
node->pre=NULL;
}
if(next!=NULL)
{
next->pre=node;
}
m_length++;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEoughMemoryException,"No ...");
}
}
return ret;
}
bool remove(int i)
{
bool ret=((0<=i)&&(i<m_length));
if(ret)
{
Node* current=position(i);
Node* toDel=current->next;
Node* next=toDel->next;
if(m_current==toDel)
{
m_current=next;
}
current->next=next;
if(next!=NULL)
{
next->pre=toDel->pre;
}
m_length--;
destroy(toDel);
//m_length--;
}
return ret;
}
bool set(int i,const T&e)
{
bool ret=((0<=i)&&(i<m_length));
if(ret)
{
position(i)->next->value=e;
}
return ret;
}
int find(const T&e) const
{
int ret=-1;
int i=0;
Node* node=m_header.next;
while(node)
{
if(node->value==e)
{
ret=i;
break;
}
else
{
node=node->next;
i++;
}
}
return ret;
}
virtual T get(int i)const
{
T ret;
if(get(i,ret))
{
return ret;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(indexOutOfBoundsException,"...");
}
return ret;
}
bool get(int i,T&e)const
{
bool ret=((0<=i)&&(i<m_length));
if(ret)
{
e=position(i)->next->value;
}
return ret;
}
int length()const
{
return m_length;
}
void clear()
{
while(m_length>0)
{
remove(0);
}
}
virtual bool move(int i,int step=-1)
{
bool ret= (0<=i)&&(i<m_length)&&(step>0);
if(ret)
{
m_current=position(i)->next;
m_step=step;
}
return ret;
}
virtual bool end()
{
return (m_current==NULL);
}
virtual T current()
{
if(!end())
{
return m_current->value;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException,"...");
}
}
virtual bool next()
{
int i=0;
while((i<m_step)&& !end())
{
m_current=m_current->next;
i++;
}
return (i==m_step);
}
virtual bool pre()
{
int i=0;
while((i<m_step)&& !end())
{
m_current=m_current->pre;
i++;
}
return (i==m_step);
}
~DuaLinkList()
{
clear();
}
};
}1.雙向鏈表是為了彌補單鏈表的缺陷而重新設計的
2.在概念上,雙向鏈表不是單鏈表,沒有繼承關系
3.雙向鏈表中的游標能夠直接訪問當前結點的前驅和后繼
4.雙向鏈表是線性表概念的最終實現
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。