您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容主要講解“SpringBoot中異步調用@Async的方法”,感興趣的朋友不妨來看看。本文介紹的方法操作簡單快捷,實用性強。下面就讓小編來帶大家學習“SpringBoot中異步調用@Async的方法”吧!
在SpringBoot中,只需要給方法加上@Async注解,就能將同步方法變為異步調用。
首先在啟動類上添加@EnableAsync,即開啟異步調用。
/** * @author qcy */ @SpringBootApplication @EnableAsync public class AsyncApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(AsyncApplication.class, args); } }在需要異步調用的方法上加上@Async注解
package com.yang.async; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncResult; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.concurrent.Future; import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask; /** * @author qcy * @create 2020/09/09 14:01:35 */ @Slf4j @Component public class Task { @Async public void method1() { log.info("method1開始,執行線程為" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } log.info("method1結束"); } @Async public void method2() { log.info("method2開始,執行線程為" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } log.info("method2結束"); } }測試一下:
@SpringBootTest @Slf4j public class AsyncApplicationTests { @Autowired Task task; @Test public void testAsyncWithVoidReturn() throws InterruptedException { log.info("main線程開始"); task.method1(); task.method2(); //確保兩個異步調用執行完成 Thread.sleep(6000); log.info("main線程結束"); } }輸出如下:
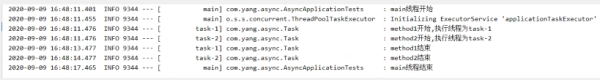
可以看得出,SpringBoot創建了一個名為applicationTaskExecutor的線程池,使用這里面的線程來執行異步調用。
這里值得注意的是,不要在一個類中調用@Async標注的方法,否則不會起到異步調用的作用,至于為什么會產生這樣的問題,需要深入到源碼中一探究竟,會另開篇幅。
既然默認使用的是SpringBoot自己創建的applicationTaskExecutor,那如何自己去定義一個線程池呢?
我們需要手動創建一個名為asynTaskExecutord的Bean
package com.yang.async; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.core.task.AsyncTaskExecutor; import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; /** * @author qcy * @create 2020/09/09 15:31:07 */ @Slf4j @Configuration public class AsyncConfig { @Bean public AsyncTaskExecutor asyncTaskExecutor() { ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor(); executor.setCorePoolSize(8); executor.setMaxPoolSize(16); executor.setQueueCapacity(50); executor.setAllowCoreThreadTimeOut(true); executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(10); executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()); executor.setThreadNamePrefix("async-thread-pool-thread"); return executor; } }對以上參數不了解的同學,可以參考我的這篇文章說說線程池
其他類不需要變動,直接運行剛才的testAsyncWithVoidReturn()方法,輸出:
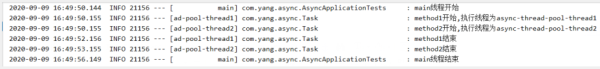
看得出來,現在是我們自定義的線程池
如果關心異步調用的返回值,又怎么處理?
獲取異步調用的結果,需要利用Future機制,可以參考我的另外一篇文章談談Runnable、Future、Callable、FutureTask之間的關系
為Task類增加以下兩個方法:
@Async public Future<String> method3() { log.info("method3開始,執行線程為" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } log.info("method3結束"); return new AsyncResult<>("method3"); } @Async public Future<String> method4() { log.info("method4開始,執行線程為" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } log.info("method4結束"); return new AsyncResult<>("method4"); }測試類:
@Test public void testAsyncWithStringReturn() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { log.info("main線程開始"); Future<String> method3Result = task.method3(); Future<String> method4Result = task.method4(); //get方法為阻塞獲取 log.info("method3執行的返回結果:{}", method3Result.get()); log.info("method4執行的返回結果:{}", method4Result.get()); log.info("main線程結束"); }輸出:
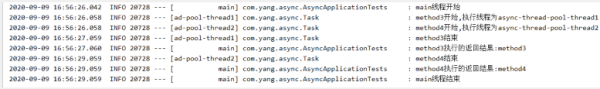
springboot一種全新的編程規范,其設計目的是用來簡化新Spring應用的初始搭建以及開發過程,SpringBoot也是一個服務于框架的框架,服務范圍是簡化配置文件。
到此,相信大家對“SpringBoot中異步調用@Async的方法”有了更深的了解,不妨來實際操作一番吧!這里是億速云網站,更多相關內容可以進入相關頻道進行查詢,關注我們,繼續學習!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。