您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇文章為大家展示了使用Python怎么刪除列表重復元素,內容簡明扼要并且容易理解,絕對能使你眼前一亮,通過這篇文章的詳細介紹希望你能有所收獲。
python常用的庫:1.requesuts;2.scrapy;3.pillow;4.twisted;5.numpy;6.matplotlib;7.pygama;8.ipyhton等。
一.如果已經有了一個列表l,令h=l,對l操作時同時會影響h,貌似原因是內存共享的,正確的方法是h=l.copy()
二.測試時,發現一個問題,如下面代碼和結果:
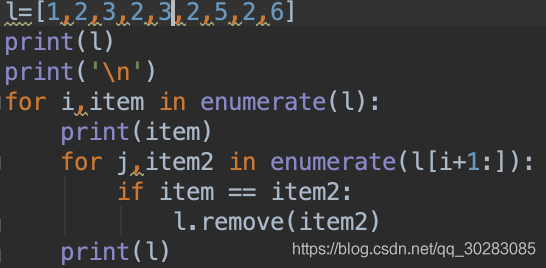

item=2時,并沒有把2全部刪掉,后面重復的3也沒有刪去。
**查閱一些資料后發現:list的遍歷是基于下標的不是基于元素,你刪掉一個元素后,列表就發生了變化,所有的元素都往前移動了一個位置,假設要刪除重的2,一個列表中索引為4,對應的值為2,索引為5,對應的值為2,索引為6,對應的值為3,當前循環刪掉索引4時對應的值2之后,索引4的值為2,索引5,值為3,下一次循環,本來要再刪一個2,但此時索引為5對應的為3,就漏掉了一個2。
(1)倒序循環遍歷:
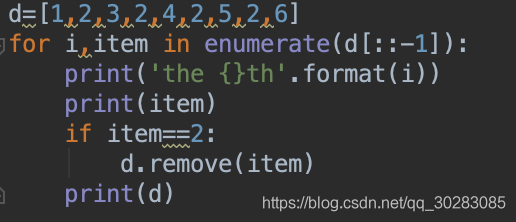
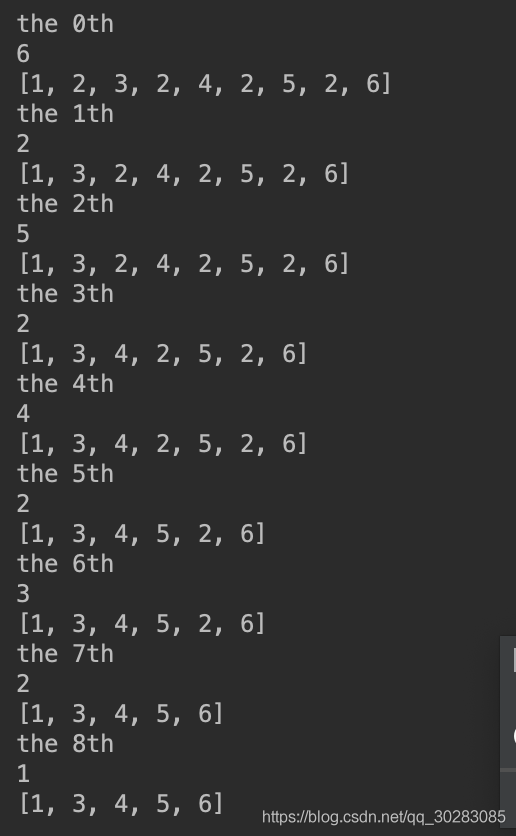
(2)實際用的方法,判斷到重復元素后,將那個item復制為0或‘0',相當于用一個標識符占住重復元素的位置,循環時先判斷是否為‘0',最后通過
list = list(set(list))
list.remove('0')
即可
附圖像去冗余算法,判斷圖像相似通過,感知哈希算法和三通道直方圖,及圖像尺寸
from img_similarity import runtwoImageSimilaryFun
import os
from PIL import Image
import shutil
import time
import numpy as np
def similar(path2, path3):
img1 = Image.open(path2)
img2 = Image.open(path3)
w1 = img1.size[0] # 圖片的寬
h2 = img2.size[1] # 圖片的高
w2 = img2.size[0] # 圖片的寬
h3 = img2.size[1] # 圖片的高
w_err = abs(w1 - w2)/w1
h_err = abs(h2 - h3)/h2
if w_err > 0.1 or h_err >0.1:
return 0
else:
phash, color_hist = runtwoImageSimilaryFun(path2, path3)
if phash <=8 or color_hist >=0.9:
return 1
else:
return 0
path = './crop_img'
result_imgdirs_path = './removed_repeat_img'
folderlist = os.listdir(path)
folderlist.sort()
for item in folderlist:
folder_path = path + '/' + item
new_folder_path = result_imgdirs_path + '/' + item
os.makedirs(new_folder_path)
imglist = os.listdir(folder_path)
imglist.sort()
time_start = time.time()
for i,item1 in enumerate(imglist):
if item1 == '0':
continue
path2 = folder_path + '/' + item1
for j, item2 in enumerate(imglist[i + 1:]):
if item2 == '0':
continue
path3 = folder_path + '/' + item2
t = similar(path2, path3)
if t:
#將判斷為相似的圖片在trans_list中的名字置‘0',代表不需要復制
imglist[i+j+1] = '0'
imglist = list(set(imglist))
imglist.remove('0')
time_end = time.time()
time_c = time_end - time_start
print('{} similarity judgement list time cost {}s'.format(item, time_c))
time_start = time.time()
#移動圖片
for item3 in imglist:
ori_img_path = folder_path + '/' + item3
new_img_path = new_folder_path + '/' + item3
shutil.copy(ori_img_path, new_img_path)
time_end = time.time()
time_c = time_end - time_start # 運行所花時間
print('{} move image time cost {}s'.format(item, time_c))img_similarity.py
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import requests
from io import BytesIO
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('TkAgg')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def aHash(img):
# 均值哈希算法
# 縮放為8*8
img = cv2.resize(img, (8, 8))
# 轉換為灰度圖
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# s為像素和初值為0,hash_str為hash值初值為''
s = 0
hash_str = ''
# 遍歷累加求像素和
for i in range(8):
for j in range(8):
s = s + gray[i, j]
# 求平均灰度
avg = s / 64
# 灰度大于平均值為1相反為0生成圖片的hash值
for i in range(8):
for j in range(8):
if gray[i, j] > avg:
hash_str = hash_str + '1'
else:
hash_str = hash_str + '0'
return hash_str
def dHash(img):
# 差值哈希算法
# 縮放8*8
img = cv2.resize(img, (9, 8))
# 轉換灰度圖
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
hash_str = ''
# 每行前一個像素大于后一個像素為1,相反為0,生成哈希
for i in range(8):
for j in range(8):
if gray[i, j] > gray[i, j + 1]:
hash_str = hash_str + '1'
else:
hash_str = hash_str + '0'
return hash_str
def pHash(img):
# 感知哈希算法
# 縮放32*32
img = cv2.resize(img, (32, 32)) # , interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC
# 轉換為灰度圖
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 將灰度圖轉為浮點型,再進行dct變換
dct = cv2.dct(np.float32(gray))
# opencv實現的掩碼操作
dct_roi = dct[0:8, 0:8]
hash = []
avreage = np.mean(dct_roi)
for i in range(dct_roi.shape[0]):
for j in range(dct_roi.shape[1]):
if dct_roi[i, j] > avreage:
hash.append(1)
else:
hash.append(0)
return hash
def calculate(image1, image2):
# 灰度直方圖算法
# 計算單通道的直方圖的相似值
hist1 = cv2.calcHist([image1], [0], None, [256], [0.0, 255.0])
hist2 = cv2.calcHist([image2], [0], None, [256], [0.0, 255.0])
# 計算直方圖的重合度
degree = 0
for i in range(len(hist1)):
if hist1[i] != hist2[i]:
degree = degree + \
(1 - abs(hist1[i] - hist2[i]) / max(hist1[i], hist2[i]))
else:
degree = degree + 1
degree = degree / len(hist1)
return degree
def classify_hist_with_split(image1, image2, size=(256, 256)):
# RGB每個通道的直方圖相似度
# 將圖像resize后,分離為RGB三個通道,再計算每個通道的相似值
image1 = cv2.resize(image1, size)
image2 = cv2.resize(image2, size)
sub_image1 = cv2.split(image1)
sub_image2 = cv2.split(image2)
sub_data = 0
for im1, im2 in zip(sub_image1, sub_image2):
sub_data += calculate(im1, im2)
sub_data = sub_data / 3
return sub_data
def cmpHash(hash2, hash3):
# Hash值對比
# 算法中1和0順序組合起來的即是圖片的指紋hash。順序不固定,但是比較的時候必須是相同的順序。
# 對比兩幅圖的指紋,計算漢明距離,即兩個64位的hash值有多少是不一樣的,不同的位數越小,圖片越相似
# 漢明距離:一組二進制數據變成另一組數據所需要的步驟,可以衡量兩圖的差異,漢明距離越小,則相似度越高。漢明距離為0,即兩張圖片完全一樣
n = 0
# hash長度不同則返回-1代表傳參出錯
if len(hash2) != len(hash3):
return -1
# 遍歷判斷
for i in range(len(hash2)):
# 不相等則n計數+1,n最終為相似度
if hash2[i] != hash3[i]:
n = n + 1
return n
def getImageByUrl(url):
# 根據圖片url 獲取圖片對象
html = requests.get(url, verify=False)
image = Image.open(BytesIO(html.content))
return image
def PILImageToCV():
# PIL Image轉換成OpenCV格式
path = "/Users/waldenz/Documents/Work/doc/TestImages/t3.png"
img = Image.open(path)
plt.subplot(121)
plt.imshow(img)
print(isinstance(img, np.ndarray))
img = cv2.cvtColor(np.asarray(img), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
print(isinstance(img, np.ndarray))
plt.subplot(122)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
def CVImageToPIL():
# OpenCV圖片轉換為PIL image
path = "/Users/waldenz/Documents/Work/doc/TestImages/t3.png"
img = cv2.imread(path)
# cv2.imshow("OpenCV",img)
plt.subplot(121)
plt.imshow(img)
img2 = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.subplot(122)
plt.imshow(img2)
plt.show()
def bytes_to_cvimage(filebytes):
# 圖片字節流轉換為cv image
image = Image.open(filebytes)
img = cv2.cvtColor(np.asarray(image), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
return img
def runAllImageSimilaryFun(para1, para2):
# 均值、差值、感知哈希算法三種算法值越小,則越相似,相同圖片值為0
# 三直方圖算法和單通道的直方圖 0-1之間,值越大,越相似。 相同圖片為1
# t1,t2 14;19;10; 0.70;0.75
# t1,t3 39 33 18 0.58 0.49
# s1,s2 7 23 11 0.83 0.86 挺相似的圖片
# c1,c2 11 29 17 0.30 0.31
if para1.startswith("http"):
# 根據鏈接下載圖片,并轉換為opencv格式
img1 = getImageByUrl(para1)
img1 = cv2.cvtColor(np.asarray(img1), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
img2 = getImageByUrl(para2)
img2 = cv2.cvtColor(np.asarray(img2), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
else:
# 通過imread方法直接讀取物理路徑
img1 = cv2.imread(para1)
img2 = cv2.imread(para2)
hash2 = aHash(img1)
hash3 = aHash(img2)
n1 = cmpHash(hash2, hash3)
print('均值哈希算法相似度aHash:', n1)
hash2 = dHash(img1)
hash3 = dHash(img2)
n2 = cmpHash(hash2, hash3)
print('差值哈希算法相似度dHash:', n2)
hash2 = pHash(img1)
hash3 = pHash(img2)
n3 = cmpHash(hash2, hash3)
print('感知哈希算法相似度pHash:', n3)
n4 = classify_hist_with_split(img1, img2)
print('三直方圖算法相似度:', n4)
n5 = calculate(img1, img2)
print("單通道的直方圖", n5)
print("%d %d %d %.2f %.2f " % (n1, n2, n3, round(n4[0], 2), n5[0]))
print("%.2f %.2f %.2f %.2f %.2f " % (1 - float(n1 / 64), 1 -
float(n2 / 64), 1 - float(n3 / 64), round(n4[0], 2), n5[0]))
plt.subplot(121)
plt.imshow(Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(img1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)))
plt.subplot(122)
plt.imshow(Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(img2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)))
plt.show()
def runtwoImageSimilaryFun(para1, para2):
# 均值、差值、感知哈希算法三種算法值越小,則越相似,相同圖片值為0
# 三直方圖算法和單通道的直方圖 0-1之間,值越大,越相似。 相同圖片為1
# t1,t2 14;19;10; 0.70;0.75
# t1,t3 39 33 18 0.58 0.49
# s1,s2 7 23 11 0.83 0.86 挺相似的圖片
# c1,c2 11 29 17 0.30 0.31
if para1.startswith("http"):
# 根據鏈接下載圖片,并轉換為opencv格式
img1 = getImageByUrl(para1)
img1 = cv2.cvtColor(np.asarray(img1), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
img2 = getImageByUrl(para2)
img2 = cv2.cvtColor(np.asarray(img2), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
else:
# 通過imread方法直接讀取物理路徑
img1 = cv2.imread(para1)
img2 = cv2.imread(para2)
hash2 = pHash(img1)
hash3 = pHash(img2)
n3 = cmpHash(hash2, hash3)
n4 = classify_hist_with_split(img1, img2)
return n3, n4
if __name__ == "__main__":
p1 = '/Users/Desktop/11/24.jpeg'
p2 = '/Users/Desktop/11/25.jpeg'
runAllImageSimilaryFun(p1, p2)上述內容就是使用Python怎么刪除列表重復元素,你們學到知識或技能了嗎?如果還想學到更多技能或者豐富自己的知識儲備,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。