您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
如何在C#項目中實現一個數據結構堆?相信很多沒有經驗的人對此束手無策,為此本文總結了問題出現的原因和解決方法,通過這篇文章希望你能解決這個問題。
堆是用來排序的,通常是一個可以被看做一棵樹的數組對象。堆滿足已下特性:
1. 堆中某個節點的值總是不大于或不小于其父節點的值
任意節點的值小于(或大于)它的所有后裔,所以最小元(或最大元)在堆的根節點上(堆序性)。堆有大根堆和小根堆,將根節點最大的堆叫做最大堆或大根堆,根節點最小的堆叫做最小堆或小根堆。
2. 堆總是一棵完全二叉樹
除了最底層,其他層的節點都被元素填滿,且最底層盡可能地從左到右填入。
堆示意圖:
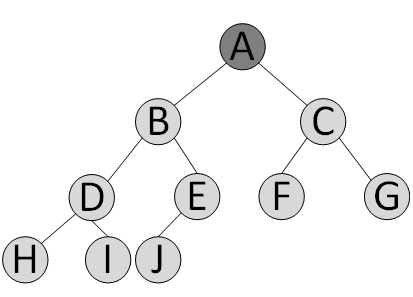
將堆元素從上往下從左到右放進數組對象中,子父節點索引滿足關系:
parentIndex = (index+1)/ 2 - 1;
childLeftIndex = parentIndex * 2 + 1;
childRightIndex = (parentIndex + 1) * 2;
其中:index為任一節點索引;parentIndex該節點父索引;childLeftIndex該父節點下的子左節點;childRightIndex該父節點下的子右節點。
創建堆的大概思路:
1. 向堆中添加元素:
加到數組尾處,循環比對其父節點值(大根堆和小根堆比對策略不一樣),比對結果的目標索引不是父節點索引則交換子父節點元素,繼續向上比對其父父節點…;直至比對過程中目標索引為父節點索引或達到根節點結束,新堆創建完成。
2. 向堆中取出元素:
取出根節點元素,并將堆末尾元素插入根節點(為了保證堆的完全二叉樹特性),從根部再循環向下比對父節點、子左節點、子右節點值,比對結果目標索引不為父節點交換目標索引和父節點的值,向下繼續比對;直至比對過程中目標索引為父節點索引或達到堆尾部結束,新堆創建完成。
因為大根堆和小根堆只是比較策略不同,所以整合了兩者,用的時候可以直接設置堆的類別;默認小根堆,默認比較器。實現代碼如下:
public class Heap<T>
{
private T[] _array;//數組,存放堆數據
private int _count;//堆數據數量
private HeapType _typeName;//堆類型
private const int _DefaultCapacity = 4;//默認數組容量/最小容量
private const int _ShrinkThreshold = 50;//收縮閾值(百分比)
private const int _MinimumGrow = 4;//最小擴容量
private const int _GrowFactor = 200; // 數組擴容百分比,默認2倍
private IComparer<T> _comparer;//比較器
private Func<T, T, bool> _comparerFunc;//比較函數
//堆數據數量
public int Count => _count;
//堆類型
public HeapType TypeName => _typeName;
public Heap() : this(_DefaultCapacity, HeapType.MinHeap, null) { }
public Heap(int capacity) : this(capacity, HeapType.MinHeap, null) { }
public Heap(HeapType heapType) : this(_DefaultCapacity, heapType, null) { }
public Heap(int capacity, HeapType heapType, IComparer<T> comparer)
{
Init(capacity, heapType, comparer);
}
public Heap(IEnumerable<T> collection, HeapType heapType, IComparer<T> comparer)
{
if (collection == null)
throw new IndexOutOfRangeException();
Init(collection.Count(), heapType, comparer);
using (IEnumerator<T> en = collection.GetEnumerator())//避免T在GC堆中有非托管資源,GC不能釋放,需手動
{
while (en.MoveNext())
Enqueue(en.Current);
}
}
private void Init(int capacity, HeapType heapType, IComparer<T> comparer)
{
if (capacity < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfRangeException();
_count = 0;
_array = new T[capacity];
_comparer = comparer ?? Comparer<T>.Default;
_typeName = heapType;
switch (heapType)
{
default:
case HeapType.MinHeap:
_comparerFunc = (T t1, T t2) => _comparer.Compare(t1, t2) > 0;//目標對象t2小
break;
case HeapType.MaxHeap:
_comparerFunc = (T t1, T t2) => _comparer.Compare(t1, t2) < 0;//目標對象t2大
break;
}
}
public T Dequeue()
{
if (_count == 0)
throw new InvalidOperationException();
T result = _array[0];
_array[0] = _array[--_count];
_array[_count] = default(T);
if (_array.Length > _DefaultCapacity && _count * 100 <= _array.Length * _ShrinkThreshold)//縮容
{
int newCapacity = Math.Max(_DefaultCapacity, (int)((long)_array.Length * (long)_ShrinkThreshold / 100));
SetCapacity(newCapacity);
}
AdjustHeap(_array, 0, _count);
return result;
}
public void Enqueue(T item)
{
if (_count >= _array.Length)//擴容
{
int newCapacity = Math.Max(_array.Length+_MinimumGrow, (int)((long)_array.Length * (long)_GrowFactor / 100));
SetCapacity(newCapacity);
}
_array[_count++] = item;
int parentIndex;
int targetIndex;
int targetCount = _count;
while (targetCount > 1)
{
parentIndex = targetCount / 2 - 1;
targetIndex = targetCount - 1;
if (!_comparerFunc.Invoke(_array[parentIndex], _array[targetIndex]))
break;
Swap(_array, parentIndex, targetIndex);
targetCount = parentIndex + 1;
}
}
private void AdjustHeap(T[] array, int parentIndex, int count)
{
if (_count < 2)
return;
int childLeftIndex = parentIndex * 2 + 1;
int childRightIndex = (parentIndex + 1) * 2;
int targetIndex = parentIndex;
if (childLeftIndex < count && _comparerFunc.Invoke(array[parentIndex], array[childLeftIndex]))
targetIndex = childLeftIndex;
if (childRightIndex < count && _comparerFunc.Invoke(array[targetIndex], array[childRightIndex]))
targetIndex = childRightIndex;
if (targetIndex != parentIndex)
{
Swap(_array, parentIndex, targetIndex);
AdjustHeap(_array, targetIndex, _count);
}
}
private void SetCapacity(int capacity)
{
T[] newArray = new T[capacity];
Array.Copy(_array, newArray, _count);
_array = newArray;
}
private void Swap(T[] array, int index1, int index2)
{
T temp = array[index1];
array[index1] = array[index2];
array[index2] = temp;
}
public void Clear()
{
Array.Clear(_array, 0, _count);
Init(_DefaultCapacity, HeapType.MinHeap, null);
}
}
public enum HeapType { MinHeap, MaxHeap }建一個Person類用來測試,例子中Person比較規則是:先按年齡比較,年齡相同再按身高比較。具體比較大小是由選擇堆的類別進行不同的排序規則:如Person類中小根堆先按年齡小者排序,年齡相同者按身高大者排序;而使用大根堆則相反。兩種比較器寫法,前者直接使用默認比較器;后者需要將比較器注入到堆中。
public class Person : IComparable<Person>
{
public string name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public int Height { get; set; }
public override string ToString()
{
return $"我叫{name},年齡{Age},身高{Height}";
}
//小根堆:先排年齡小,年齡相同,按身高大的先排;大根堆相反
public int CompareTo(Person other)
{
if (this.Age.CompareTo(other.Age) != 0)
return this.Age.CompareTo(other.Age);
else if (this.Height.CompareTo(other.Height) != 0)
return ~this.Height.CompareTo(other.Height);
else
return 0;
}
}
public class personComparer : IComparer<Person>
{
//大根堆:先排年齡大,年齡相同,按身高大的先排;小根堆相反
public int Compare(Person x, Person y)
{
if (x.Age.CompareTo(y.Age) != 0)
return x.Age.CompareTo(y.Age);
else if (x.Height.CompareTo(y.Height) != 0)
return x.Height.CompareTo(y.Height);
else
return 0;
}
}主函數調用:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] array = { 3, 5, 8, 3, 7, 1 };
Heap<int> heap0 = new Heap<int>(array, HeapType.MaxHeap, null);
Console.WriteLine(heap0.TypeName);
Console.WriteLine(heap0.Dequeue());
Console.WriteLine(heap0.Dequeue());
Console.WriteLine(heap0.Dequeue());
Console.WriteLine(heap0.Dequeue());
int length = heap0.Count;
for (int count = 0; count < length; count++)
{
Console.WriteLine(heap0.Dequeue());
}
Person person1 = new Person() { Age = 12, Height = 158, name = "張三" };
Person person2 = new Person() { Age = 13, Height = 160, name = "李四" };
Person person3 = new Person() { Age = 10, Height = 150, name = "王二" };
Person person4 = new Person() { Age = 10, Height = 152, name = "麻子" };
Person person5 = new Person() { Age = 12, Height = 150, name = "劉五" };
List<Person> people = new List<Person>();
people.Add(person1);
people.Add(person2);
people.Add(person3);
people.Add(person4);
people.Add(person5);
Heap<Person> heap2 = new Heap<Person>(people, HeapType.MinHeap, null);
Person person6 = new Person() { Age = 9, Height = 145, name = "趙六" };
heap2.Enqueue(person6);
Console.WriteLine(heap2.TypeName);
Console.WriteLine(heap2.Dequeue());
Console.WriteLine(heap2.Dequeue());
Console.WriteLine(heap2.Dequeue());
Console.WriteLine(heap2.Dequeue());
PersonComparer personComparer = new PersonComparer();
Heap<Person> heap3 = new Heap<Person>(1,HeapType.MaxHeap,personComparer);
heap3.Enqueue(person1);
heap3.Enqueue(person2);
heap3.Enqueue(person3);
heap3.Enqueue(person4);
heap3.Enqueue(person5);
heap3.Enqueue(person6);
Console.WriteLine(heap3.TypeName);
Console.WriteLine(heap3.Dequeue());
Console.WriteLine(heap3.Dequeue());
Console.WriteLine(heap3.Dequeue());
Console.WriteLine(heap3.Dequeue());
Console.ReadKey();
}輸出結果:
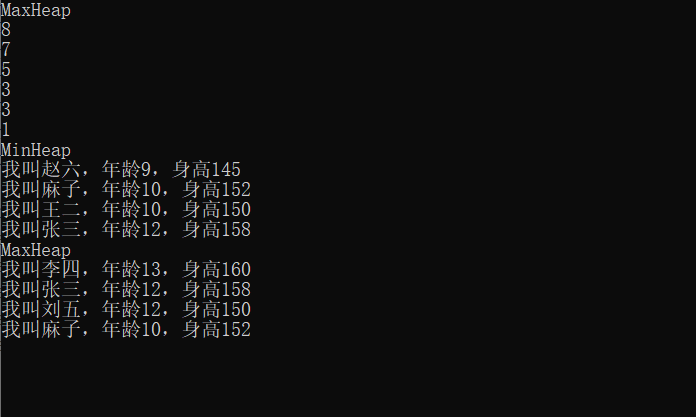
看完上述內容,你們掌握如何在C#項目中實現一個數據結構堆的方法了嗎?如果還想學到更多技能或想了解更多相關內容,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道,感謝各位的閱讀!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。