溫馨提示×
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
點擊 登錄注冊 即表示同意《億速云用戶服務條款》
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章給大家分享的是有關Python實現Canny及Hough算法代碼的案例分析的內容。小編覺得挺實用的,因此分享給大家做個參考。一起跟隨小編過來看看吧。
任務說明:編寫一個錢幣定位系統,其不僅能夠檢測出輸入圖像中各個錢幣的邊緣,同時,還能給出各個錢幣的圓心坐標與半徑。
效果
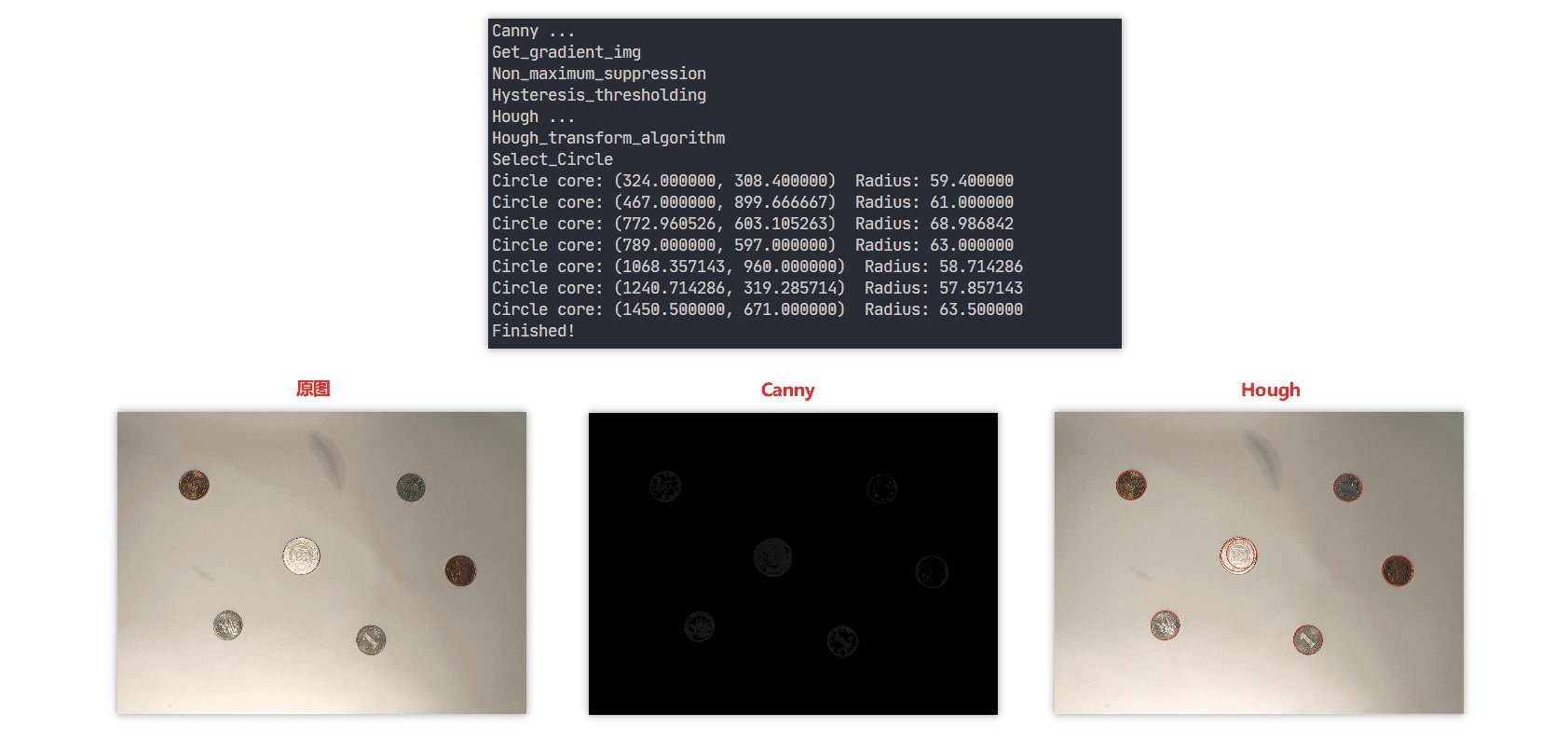
代碼實現
Canny邊緣檢測:
# Author: Ji Qiu (BUPT)
# filename: my_canny.py
import cv2
import numpy as np
class Canny:
def __init__(self, Guassian_kernal_size, img, HT_high_threshold, HT_low_threshold):
'''
:param Guassian_kernal_size: 高斯濾波器尺寸
:param img: 輸入的圖片,在算法過程中改變
:param HT_high_threshold: 滯后閾值法中的高閾值
:param HT_low_threshold: 滯后閾值法中的低閾值
'''
self.Guassian_kernal_size = Guassian_kernal_size
self.img = img
self.y, self.x = img.shape[0:2]
self.angle = np.zeros([self.y, self.x])
self.img_origin = None
self.x_kernal = np.array([[-1, 1]])
self.y_kernal = np.array([[-1], [1]])
self.HT_high_threshold = HT_high_threshold
self.HT_low_threshold = HT_low_threshold
def Get_gradient_img(self):
'''
計算梯度圖和梯度方向矩陣。
:return: 生成的梯度圖
'''
print ('Get_gradient_img')
new_img_x = np.zeros([self.y, self.x], dtype=np.float)
new_img_y = np.zeros([self.y, self.x], dtype=np.float)
for i in range(0, self.x):
for j in range(0, self.y):
if j == 0:
new_img_y[j][i] = 1
else:
new_img_y[j][i] = np.sum(np.array([[self.img[j - 1][i]], [self.img[j][i]]]) * self.y_kernal)
if i == 0:
new_img_x[j][i] = 1
else:
new_img_x[j][i] = np.sum(np.array([self.img[j][i - 1], self.img[j][i]]) * self.x_kernal)
gradient_img, self.angle = cv2.cartToPolar(new_img_x, new_img_y)#返回幅值和相位
self.angle = np.tan(self.angle)
self.img = gradient_img.astype(np.uint8)
return self.img
def Non_maximum_suppression (self):
'''
對生成的梯度圖進行非極大化抑制,將tan值的大小與正負結合,確定離散中梯度的方向。
:return: 生成的非極大化抑制結果圖
'''
print ('Non_maximum_suppression')
result = np.zeros([self.y, self.x])
for i in range(1, self.y - 1):
for j in range(1, self.x - 1):
if abs(self.img[i][j]) <= 4:
result[i][j] = 0
continue
elif abs(self.angle[i][j]) > 1:
gradient2 = self.img[i - 1][j]
gradient4 = self.img[i + 1][j]
# g1 g2
# C
# g4 g3
if self.angle[i][j] > 0:
gradient1 = self.img[i - 1][j - 1]
gradient3 = self.img[i + 1][j + 1]
# g2 g1
# C
# g3 g4
else:
gradient1 = self.img[i - 1][j + 1]
gradient3 = self.img[i + 1][j - 1]
else:
gradient2 = self.img[i][j - 1]
gradient4 = self.img[i][j + 1]
# g1
# g2 C g4
# g3
if self.angle[i][j] > 0:
gradient1 = self.img[i - 1][j - 1]
gradient3 = self.img[i + 1][j + 1]
# g3
# g2 C g4
# g1
else:
gradient3 = self.img[i - 1][j + 1]
gradient1 = self.img[i + 1][j - 1]
temp1 = abs(self.angle[i][j]) * gradient1 + (1 - abs(self.angle[i][j])) * gradient2
temp2 = abs(self.angle[i][j]) * gradient3 + (1 - abs(self.angle[i][j])) * gradient4
if self.img[i][j] >= temp1 and self.img[i][j] >= temp2:
result[i][j] = self.img[i][j]
else:
result[i][j] = 0
self.img = result
return self.img
def Hysteresis_thresholding(self):
'''
對生成的非極大化抑制結果圖進行滯后閾值法,用強邊延伸弱邊,這里的延伸方向為梯度的垂直方向,
將比低閾值大比高閾值小的點置為高閾值大小,方向在離散點上的確定與非極大化抑制相似。
:return: 滯后閾值法結果圖
'''
print ('Hysteresis_thresholding')
for i in range(1, self.y - 1):
for j in range(1, self.x - 1):
if self.img[i][j] >= self.HT_high_threshold:
if abs(self.angle[i][j]) < 1:
if self.img_origin[i - 1][j] > self.HT_low_threshold:
self.img[i - 1][j] = self.HT_high_threshold
if self.img_origin[i + 1][j] > self.HT_low_threshold:
self.img[i + 1][j] = self.HT_high_threshold
# g1 g2
# C
# g4 g3
if self.angle[i][j] < 0:
if self.img_origin[i - 1][j - 1] > self.HT_low_threshold:
self.img[i - 1][j - 1] = self.HT_high_threshold
if self.img_origin[i + 1][j + 1] > self.HT_low_threshold:
self.img[i + 1][j + 1] = self.HT_high_threshold
# g2 g1
# C
# g3 g4
else:
if self.img_origin[i - 1][j + 1] > self.HT_low_threshold:
self.img[i - 1][j + 1] = self.HT_high_threshold
if self.img_origin[i + 1][j - 1] > self.HT_low_threshold:
self.img[i + 1][j - 1] = self.HT_high_threshold
else:
if self.img_origin[i][j - 1] > self.HT_low_threshold:
self.img[i][j - 1] = self.HT_high_threshold
if self.img_origin[i][j + 1] > self.HT_low_threshold:
self.img[i][j + 1] = self.HT_high_threshold
# g1
# g2 C g4
# g3
if self.angle[i][j] < 0:
if self.img_origin[i - 1][j - 1] > self.HT_low_threshold:
self.img[i - 1][j - 1] = self.HT_high_threshold
if self.img_origin[i + 1][j + 1] > self.HT_low_threshold:
self.img[i + 1][j + 1] = self.HT_high_threshold
# g3
# g2 C g4
# g1
else:
if self.img_origin[i - 1][j + 1] > self.HT_low_threshold:
self.img[i + 1][j - 1] = self.HT_high_threshold
if self.img_origin[i + 1][j - 1] > self.HT_low_threshold:
self.img[i + 1][j - 1] = self.HT_high_threshold
return self.img
def canny_algorithm(self):
'''
按照順序和步驟調用以上所有成員函數。
:return: Canny 算法的結果
'''
self.img = cv2.GaussianBlur(self.img, (self.Guassian_kernal_size, self.Guassian_kernal_size), 0)
self.Get_gradient_img()
self.img_origin = self.img.copy()
self.Non_maximum_suppression()
self.Hysteresis_thresholding()
return self.imgHough變換
# Author: Ji Qiu (BUPT)
# filename: my_hough.py
import numpy as np
import math
class Hough_transform:
def __init__(self, img, angle, step=5, threshold=135):
'''
:param img: 輸入的圖像
:param angle: 輸入的梯度方向矩陣
:param step: Hough 變換步長大小
:param threshold: 篩選單元的閾值
'''
self.img = img
self.angle = angle
self.y, self.x = img.shape[0:2]
self.radius = math.ceil(math.sqrt(self.y**2 + self.x**2))
self.step = step
self.vote_matrix = np.zeros([math.ceil(self.y / self.step), math.ceil(self.x / self.step), math.ceil(self.radius / self.step)])
self.threshold = threshold
self.circles = []
def Hough_transform_algorithm(self):
'''
按照 x,y,radius 建立三維空間,根據圖片中邊上的點沿梯度方向對空間中的所有單
元進行投票。每個點投出來結果為一折線。
:return: 投票矩陣
'''
print ('Hough_transform_algorithm')
for i in range(1, self.y - 1):
for j in range(1, self.x - 1):
if self.img[i][j] > 0:
y = i
x = j
r = 0
while y < self.y and x < self.x and y >= 0 and x >= 0:
self.vote_matrix[math.floor(y / self.step)][math.floor(x / self.step)][math.floor(r / self.step)] += 1
y = y + self.step * self.angle[i][j]
x = x + self.step
r = r + math.sqrt((self.step * self.angle[i][j])**2 + self.step**2)
y = i - self.step * self.angle[i][j]
x = j - self.step
r = math.sqrt((self.step * self.angle[i][j])**2 + self.step**2)
while y < self.y and x < self.x and y >= 0 and x >= 0:
self.vote_matrix[math.floor(y / self.step)][math.floor(x / self.step)][math.floor(r / self.step)] += 1
y = y - self.step * self.angle[i][j]
x = x - self.step
r = r + math.sqrt((self.step * self.angle[i][j])**2 + self.step**2)
return self.vote_matrix
def Select_Circle(self):
'''
按照閾值從投票矩陣中篩選出合適的圓,并作極大化抑制,這里的非極大化抑制我采
用的是鄰近點結果取平均值的方法,而非單純的取極大值。
:return: None
'''
print ('Select_Circle')
houxuanyuan = []
for i in range(0, math.ceil(self.y / self.step)):
for j in range(0, math.ceil(self.x / self.step)):
for r in range(0, math.ceil(self.radius / self.step)):
if self.vote_matrix[i][j][r] >= self.threshold:
y = i * self.step + self.step / 2
x = j * self.step + self.step / 2
r = r * self.step + self.step / 2
houxuanyuan.append((math.ceil(x), math.ceil(y), math.ceil(r)))
if len(houxuanyuan) == 0:
print("No Circle in this threshold.")
return
x, y, r = houxuanyuan[0]
possible = []
middle = []
for circle in houxuanyuan:
if abs(x - circle[0]) <= 20 and abs(y - circle[1]) <= 20:
possible.append([circle[0], circle[1], circle[2]])
else:
result = np.array(possible).mean(axis=0)
middle.append((result[0], result[1], result[2]))
possible.clear()
x, y, r = circle
possible.append([x, y, r])
result = np.array(possible).mean(axis=0)
middle.append((result[0], result[1], result[2]))
def takeFirst(elem):
return elem[0]
middle.sort(key=takeFirst)
x, y, r = middle[0]
possible = []
for circle in middle:
if abs(x - circle[0]) <= 20 and abs(y - circle[1]) <= 20:
possible.append([circle[0], circle[1], circle[2]])
else:
result = np.array(possible).mean(axis=0)
print("Circle core: (%f, %f) Radius: %f" % (result[0], result[1], result[2]))
self.circles.append((result[0], result[1], result[2]))
possible.clear()
x, y, r = circle
possible.append([x, y, r])
result = np.array(possible).mean(axis=0)
print("Circle core: (%f, %f) Radius: %f" % (result[0], result[1], result[2]))
self.circles.append((result[0], result[1], result[2]))
def Calculate(self):
'''
按照算法順序調用以上成員函數
:return: 圓形擬合結果圖,圓的坐標及半徑集合
'''
self.Hough_transform_algorithm()
self.Select_Circle()
return self.circles調用
# Author: Ji Qiu (BUPT)
# filename: main.py
import cv2
import math
from my_hough import Hough_transform
from my_canny import Canny
# np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.inf)
Path = "picture_source/picture.jpg"
Save_Path = "picture_result/"
Reduced_ratio = 2
Guassian_kernal_size = 3
HT_high_threshold = 25
HT_low_threshold = 6
Hough_transform_step = 6
Hough_transform_threshold = 110
if __name__ == '__main__':
img_gray = cv2.imread(Path, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
img_RGB = cv2.imread(Path)
y, x = img_gray.shape[0:2]
img_gray = cv2.resize(img_gray, (int(x / Reduced_ratio), int(y / Reduced_ratio)))
img_RGB = cv2.resize(img_RGB, (int(x / Reduced_ratio), int(y / Reduced_ratio)))
# canny takes about 40 seconds
print ('Canny ...')
canny = Canny(Guassian_kernal_size, img_gray, HT_high_threshold, HT_low_threshold)
canny.canny_algorithm()
cv2.imwrite(Save_Path + "canny_result.jpg", canny.img)
# hough takes about 30 seconds
print ('Hough ...')
Hough = Hough_transform(canny.img, canny.angle, Hough_transform_step, Hough_transform_threshold)
circles = Hough.Calculate()
for circle in circles:
cv2.circle(img_RGB, (math.ceil(circle[0]), math.ceil(circle[1])), math.ceil(circle[2]), (28, 36, 237), 2)
cv2.imwrite(Save_Path + "hough_result.jpg", img_RGB)
print ('Finished!')運行效果

感謝各位的閱讀!關于Python實現Canny及Hough算法代碼的案例分析就分享到這里了,希望以上內容可以對大家有一定的幫助,讓大家可以學到更多知識。如果覺得文章不錯,可以把它分享出去讓更多的人看到吧!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。