您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
Suppose you need to repeatedly execute some test method in your unit test case, for example, you would like to test getPrice based on the first set of test data 5 times in test method test1() while for the second set of test data, only one time should be executed.
The below class RepeatDemoOne is a bad example, where this special LOOP operation is mixed with test method implementation.
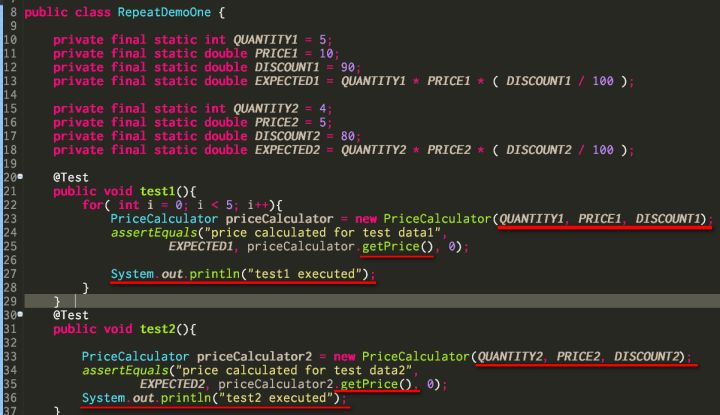
Ideally the test method should only contain the pure logic to operate on the method being tested. So we have a better solution RepeatDemoTwo: It could easily be observed that now the test method test1 and test2 are rather clean: no more for LOOP and System.out.println exist any more.
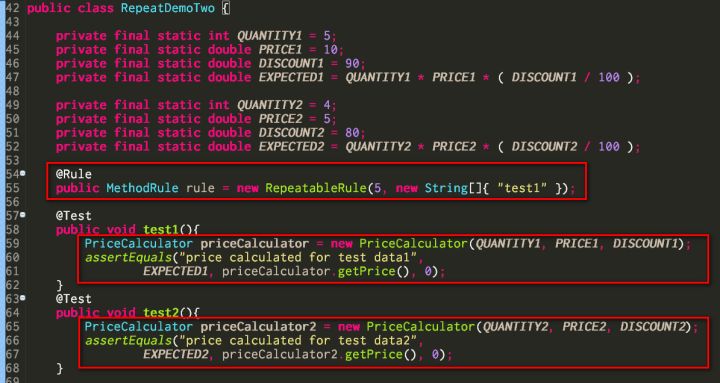
Instead, I put the LOOP logic and print out operation into class RepeatableRule which implements interface MethodRule. The concrete rule implementation is done by overriding method apply as below:
class RepeatableRule implements MethodRule{
int times = 1;
String[] testMethods = null;
RepeatableRule(int times, String[] testMethods){
this.times = times;
this.testMethods = testMethods;
}
@Override
public Statement apply(final Statement base, final FrameworkMethod method, Object target) {
return new Statement() {
@Override
public void evaluate() throws Throwable {
int loopTime = 1;
if(Arrays.asList(testMethods).contains(method.getName())) {
loopTime = times;
}
for(int i = 0; i < loopTime; i++ ) {
base.evaluate();
System.out.println(method.getName() + " executed.");
}
}
};
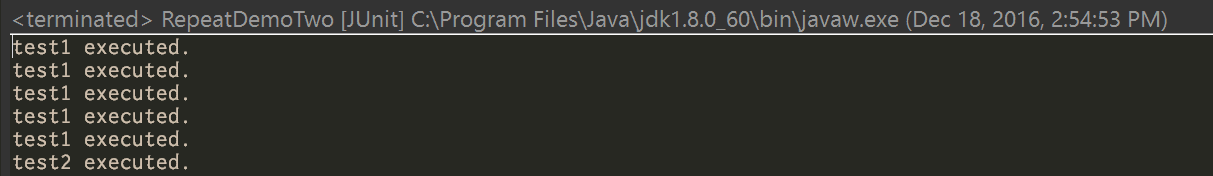
} }When I execute this test case, I can get exactly the same result as RepeatDemoOne:
With the help of @Rule, we can achieve the same as @Test(expected=).

For example, we can use an instance of class ExpectedException to manually declare within a test method itself that a test method expects a given type of exception class.

Besides exception, we can also manually specify a sub string which is expected to appear in an error message, and add our custom error message in Junit report if a test method fails. See following code for example:
public class RuleWithException {
@Rule
public ExpectedException exp = ExpectedException.none();
@Test
public void expectMessage()
{
exp.expectMessage("Hello World");
throw new RuntimeException("Hello World will throw exception.");
}
@Test
public void expectCourse()
{
exp.expectCause(new BaseMatcher<IllegalArgumentException>()
{
public boolean matches(Object item)
{
return item instanceof IllegalArgumentException;
}
@Override
public void describeTo(org.hamcrest.Description description) {
description.appendText("Expected exception with type IllegalArgumentException "
+ "raised in test method! ");
}
});
Throwable cause = new IllegalArgumentException("Cause Test.");
throw new RuntimeException(cause);
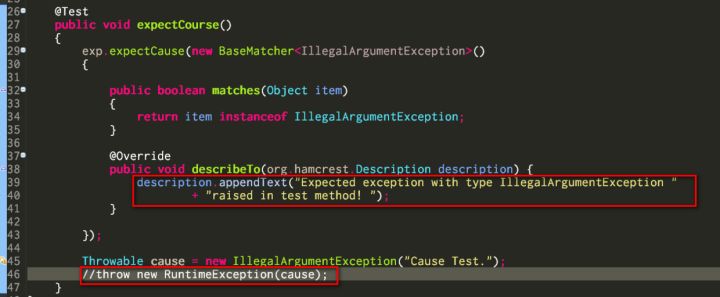
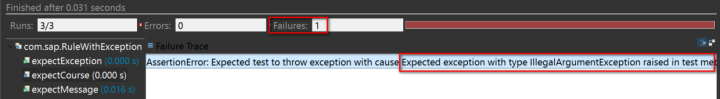
}}In this example, if we comment out line 46, the customed message defined in method describeTo will be printed out in JUnit console:
要獲取更多Jerry的原創文章,請關注公眾號"汪子熙":

免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。