您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹了Spring Bean初始化及銷毀多種實現方式,文中通過示例代碼介紹的非常詳細,對大家的學習或者工作具有一定的參考學習價值,需要的朋友可以參考下
一、前言
日常開發過程有時需要在應用啟動之后加載某些資源,或者在應用關閉之前釋放資源。Spring 框架提供相關功能,圍繞 Spring Bean 生命周期,可以在 Bean 創建過程初始化資源,以及銷毀 Bean 過程釋放資源。Spring 提供多種不同的方式初始化/銷毀 Bean,如果同時使用這幾種方式,Spring 如何處理這幾者之間的順序?
二、姿勢剖析
首先我們先來回顧一下 Spring 初始化/銷毀 Bean 幾種方式,分別為:
PS: 其實還有一種方式,就是繼承 Spring Lifecycle 接口。不過這種方式比較繁瑣,這里就不再分析。
2.1、init-method/destroy-method
這種方式在配置文件文件指定初始化/銷毀方法。XML 配置如下
<bean id="demoService" class="com.dubbo.example.provider.DemoServiceImpl" destroy-method="close" init-method="initMethod"/>
或者也可以使用注解方式配置:
@Configurable
public class AppConfig {
@Bean(initMethod = "init", destroyMethod = "destroy")
public HelloService hello() {
return new HelloService();
}
}
還記得剛開始接觸學習 Spring 框架,使用就是這種方式。
2.2、InitializingBean/DisposableBean
這種方式需要繼承 Spring 接口 InitializingBean/DisposableBean,其中 InitializingBean 用于初始化動作,而 DisposableBean 用于銷毀之前清理動作。使用方式如下:
@Service
public class HelloService implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("hello destroy...");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("hello init....");
}
}
2.3、@PostConstruct/@PreDestroy
這種方式相對于上面兩種方式來說,使用方式最簡單,只需要在相應的方法上使用注解即可。使用方式如下:
@Service
public class HelloService {
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("hello @PostConstruct");
}
@PreDestroy
public void PreDestroy() {
System.out.println("hello @PreDestroy");
}
}
這里踩過一個坑,如果使用 JDK9 之后版本 ,@PostConstruct/@PreDestroy 需要使用 maven 單獨引入 javax.annotation-api,否者注解不會生效。
2.4、ContextStartedEvent/ContextClosedEvent
這種方式使用 Spring 事件機制,日常業務開發比較少見,常用與框架集成中。Spring 啟動之后將會發送 ContextStartedEvent 事件,而關閉之前將會發送 ContextClosedEvent 事件。我們需要繼承 Spring ApplicationListener 才能監聽以上兩種事件。
@Service
public class HelloListener implements ApplicationListener {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if(event instanceof ContextClosedEvent){
System.out.println("hello ContextClosedEvent");
}else if(event instanceof ContextStartedEvent){
System.out.println("hello ContextStartedEvent");
}
}
}
也可以使用 @EventListener注解,使用方式如下:
public class HelloListenerV2 {
@EventListener(value = {ContextClosedEvent.class, ContextStartedEvent.class})
public void receiveEvents(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ContextClosedEvent) {
System.out.println("hello ContextClosedEvent");
} else if (event instanceof ContextStartedEvent) {
System.out.println("hello ContextStartedEvent");
}
}
}
PS:只有調用 ApplicationContext#start 才會發送 ContextStartedEvent。若不想這么麻煩,可以監聽 ContextRefreshedEvent 事件代替。一旦 Spring 容器初始化完成,就會發送 ContextRefreshedEvent。
三、綜合使用
回顧完上面幾種方式,這里我們綜合使用上面的四種方式,來看下 Spring 內部的處理順序。在看結果之前,各位讀者大人可以猜測下這幾種方式的執行順序。
public class HelloService implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("hello @PostConstruct");
}
@PreDestroy
public void PreDestroy() {
System.out.println("hello @PreDestroy");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("bye DisposableBean...");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("hello InitializingBean....");
}
public void xmlinit(){
System.out.println("hello xml-init...");
}
public void xmlDestory(){
System.out.println("bye xmlDestory...");
}
@EventListener(value = {ContextClosedEvent.class, ContextStartedEvent.class})
public void receiveEvents(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ContextClosedEvent) {
System.out.println("bye ContextClosedEvent");
} else if (event instanceof ContextStartedEvent) {
System.out.println("hello ContextStartedEvent");
}
}
}
xml 配置方式如下:
<context:annotation-config /> <context:component-scan base-package="com.dubbo.example.demo"/> <bean class="com.dubbo.example.demo.HelloService" init-method="xmlinit" destroy-method="xmlDestory"/>
應用啟動方法如下:
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring/dubbo-provider.xml");
context.start();
context.close();
程序輸出結果如下所示:
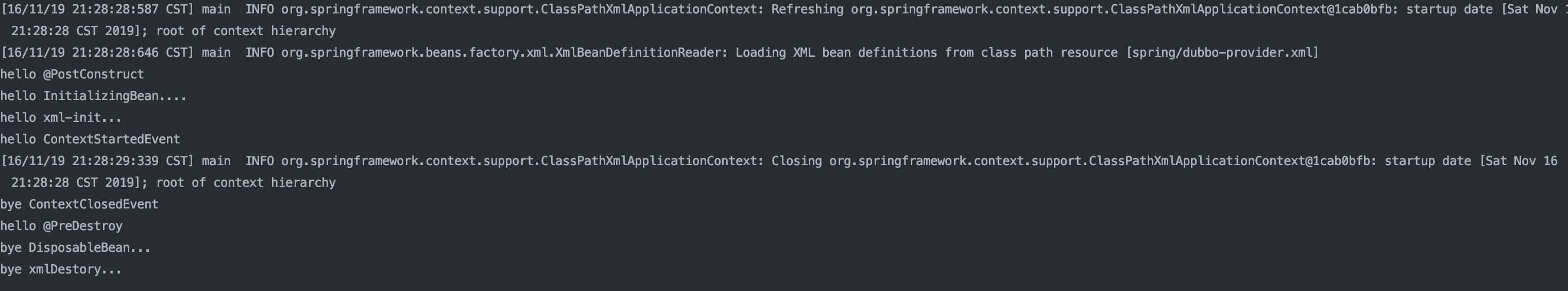
最后采用圖示說明總結以上結果:
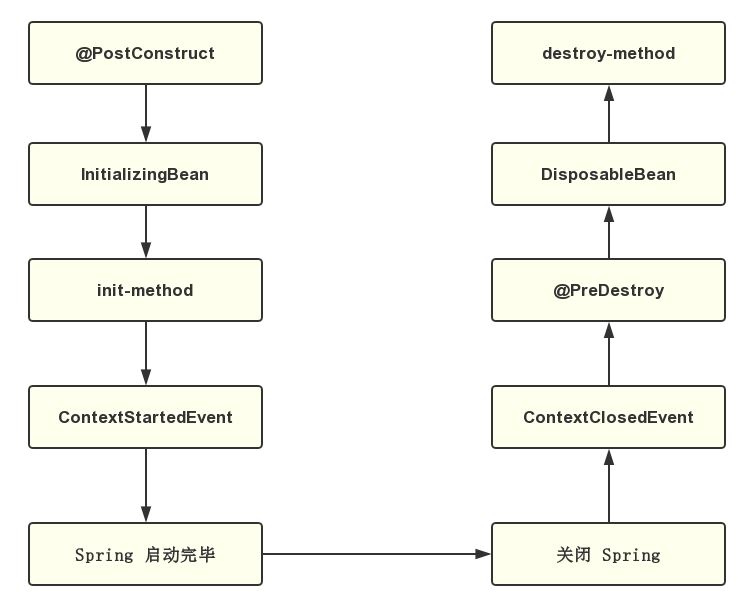
四、源碼解析
不知道各位讀者有沒有猜對這幾種方式的執行順序,下面我們就從源碼角度解析 Spring 內部處理的順序。
4.1、初始化過程
使用 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 啟動 Spring 容器,將會調用 refresh 方法初始化容器。初始化過程將會創建 Bean 。最后當一切準備完畢,將會發送 ContextRefreshedEvent。當容器初始化完畢,調用 context.start() 就發送 ContextStartedEvent 事件。
refresh 方法源碼如下:
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
//... 忽略無關代碼
// 初始化所有非延遲初始化的 Bean
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// 發送 ContextRefreshedEvent
finishRefresh();
//... 忽略無關代碼
}
}
一路跟蹤 finishBeanFactoryInitialization 源碼,直到 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBean,源碼如下:
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 調用 BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
// 初始化 Bean
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
}
BeanPostProcessor 將會起著攔截器的作用,一旦 Bean 符合條件,將會執行一些處理。這里帶有 @PostConstruct 注解的 Bean 都將會被 CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 類攔截,內部將會觸發 @PostConstruct 標注的方法。
接著執行 invokeInitMethods ,方法如下:
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
// 省略無關代碼
// 如果是 Bean 繼承 InitializingBean,將會執行 afterPropertiesSet 方法
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
}
if (mbd != null) {
String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName();
if (initMethodName != null && !(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&
!mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {
// 執行 XML 定義 init-method
invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
}
}
如果 Bean 繼承 InitializingBean 接口,將會執行 afterPropertiesSet 方法,另外如果在 XML 中指定了 init-method ,也將會觸發。
上面源碼其實都是圍繞著 Bean 創建的過程,當所有 Bean 創建完成之后,調用 context#start 將會發送 ContextStartedEvent 。這里源碼比較簡單,如下:
public void start() {
getLifecycleProcessor().start();
publishEvent(new ContextStartedEvent(this));
}
4.2、銷毀過程
調用 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext#close 方法將會關閉容器,具體邏輯將會在 doClose 方法執行。
doClose 這個方法首先發送 ContextClosedEvent,然再后開始銷毀 Bean。
靈魂拷問:如果我們顛倒上面兩者順序,結果會一樣嗎?
doClose 源碼如下:
protected void doClose() {
if (this.active.get() && this.closed.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
// 省略無關代碼
try {
// Publish shutdown event.
publishEvent(new ContextClosedEvent(this));
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.warn("Exception thrown from ApplicationListener handling ContextClosedEvent", ex);
}
// 銷毀 Bean
destroyBeans();
// 省略無關代碼
}
}
destroyBeans 最終將會執行 DisposableBeanAdapter#destroy,@PreDestroy、DisposableBean、destroy-method 三者定義的方法都將會在內部被執行。
首先執行 DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeDestruction,這里方法類似與上面 BeanPostProcessor。
@PreDestroy 注解將會被 CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 攔截,這里類同時也繼承了 DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor。
最后如果 Bean 為 DisposableBean 的子類,將會執行 destroy 方法,如果在 xml 定義了 destroy-method 方法,該方法也會被執行。
public void destroy() {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.beanPostProcessors)) {
for (DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor processor : this.beanPostProcessors) {
processor.postProcessBeforeDestruction(this.bean, this.beanName);
}
}
if (this.invokeDisposableBean) {
// 省略無關代碼
// 如果 Bean 繼承 DisposableBean,執行 destroy 方法
((DisposableBean) bean).destroy();
}
if (this.destroyMethod != null) {
// 執行 xml 指定的 destroy-method 方法
invokeCustomDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethod);
}
else if (this.destroyMethodName != null) {
Method methodToCall = determineDestroyMethod();
if (methodToCall != null) {
invokeCustomDestroyMethod(methodToCall);
}
}
}
五、總結
init-method/destroy-method 這種方式需要使用 XML 配置文件或單獨注解配置類,相對來說比較繁瑣。而InitializingBean/DisposableBean 這種方式需要單獨繼承 Spring 的接口實現相關方法。@PostConstruct/@PreDestroy 這種注解方式使用方式簡單,代碼清晰,比較推薦使用這種方式。
另外 ContextStartedEvent/ContextClosedEvent 這種方式比較適合在一些集成框架使用,比如 Dubbo 2.6.X 優雅停機就是用改機制。
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持億速云。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。