您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要為大家展示了“如何利用lambda表達式樹優化反射”,內容簡而易懂,條理清晰,希望能夠幫助大家解決疑惑,下面讓小編帶領大家一起研究并學習一下“如何利用lambda表達式樹優化反射”這篇文章吧。
前言
本節重點不講反射機制,而是講lambda表達式樹來替代反射中常用的獲取屬性和方法,來達到相同的效果但卻比反射高效。
每個人都知道,用反射調用一個方法或者對屬性執行SetValue和GetValue操作的時候都會比直接調用慢很多,這其中設計到CLR中內部的處理,不做深究。然而,我們在某些情況下又無法不使用反射,比如:在一個ORM框架中,你要將一個DataRow轉化為一個對象,但你又不清楚該對象有什么屬性,這時候你就需要寫一個通用的泛型方法來處理,以下代碼寫得有點惡心,但不妨礙理解意思:
//將DataReader轉化為一個對象
private static T GetObj<T>(SqliteDataReader reader) where T : class
{
T obj = new T();
PropertyInfo[] pros = obj.GetType().GetProperties();
foreach (PropertyInfo item in pros)
{
try
{
Int32 Index = reader.GetOrdinal(item.Name);
String result = reader.GetString(Index);
if (typeof(String) == item.PropertyType)
{
item.SetValue(obj, result);
continue;
}
if (typeof(DateTime) == item.PropertyType)
{
item.SetValue(obj, Convert.ToDateTime(result));
continue;
}
if (typeof(Boolean) == item.PropertyType)
{
item.SetValue(obj, Convert.ToBoolean(result));
continue;
}
if (typeof(Int32) == item.PropertyType)
{
item.SetValue(obj, Convert.ToInt32(result));
continue;
}
if (typeof(Single) == item.PropertyType)
{
item.SetValue(obj, Convert.ToSingle(result));
continue;
}
if (typeof(Single) == item.PropertyType)
{
item.SetValue(obj, Convert.ToSingle(result));
continue;
}
if (typeof(Double) == item.PropertyType)
{
item.SetValue(obj, Convert.ToDouble(result));
continue;
}
if (typeof(Decimal) == item.PropertyType)
{
item.SetValue(obj, Convert.ToDecimal(result));
continue;
}
if (typeof(Byte) == item.PropertyType)
{
item.SetValue(obj, Convert.ToByte(result));
continue;
}
}
catch (ArgumentOutOfRangeException ex)
{
continue;
}
}
return obj;
}對于這種情況,其執行效率是特別低下的,具體多慢在下面例子會在.Net Core平臺上和.Net Framework4.0運行測試案例.對于以上我舉例的情況,效率上我們還可以得到提升。但對于想在運行時修改一下屬性的名稱或其他操作,反射還是一項特別的神器,因此在某些情況下反射還是無法避免的。
但是對于只是簡單的SetValue或者GetValue,包括用反射構造函數,我們可以想一個中繼的方法,那就是使用表達式樹。對于不理解表達式樹的,可以到微軟文檔查看,點擊我。表達式樹很容易通過對象模型表示表達式,因此強烈建議學習。查看以下代碼:
static void Main()
{
Dog dog = new Dog();
PropertyInfo propertyInfo = dog.GetType().GetProperty(nameof(dog.Name)); //獲取對象Dog的屬性
MethodInfo SetterMethodInfo = propertyInfo.GetSetMethod(); //獲取屬性Name的set方法
ParameterExpression param = Expression.Parameter(typeof(Dog), "param");
Expression GetPropertyValueExp = Expression.Lambda(Expression.Property(param, nameof(dog.Name)), param);
Expression<Func<Dog, String>> GetPropertyValueLambda = (Expression<Func<Dog, String>>)GetPropertyValueExp;
ParameterExpression paramo = Expression.Parameter(typeof(Dog), "param");
ParameterExpression parami = Expression.Parameter(typeof(String), "newvalue");
MethodCallExpression MethodCallSetterOfProperty = Expression.Call(paramo, SetterMethodInfo, parami);
Expression SetPropertyValueExp = Expression.Lambda(MethodCallSetterOfProperty, paramo, parami);
Expression<Action<Dog, String>> SetPropertyValueLambda = (Expression<Action<Dog, String>>)SetPropertyValueExp;
//創建了屬性Name的Get方法表達式和Set方法表達式,當然只是最簡單的
Func<Dog, String> Getter = GetPropertyValueLambda.Compile();
Action<Dog, String> Setter = SetPropertyValueLambda.Compile();
Setter?.Invoke(dog, "WLJ"); //我們現在對dog這個對象的Name屬性賦值
String dogName = Getter?.Invoke(dog); //獲取屬性Name的值
Console.WriteLine(dogName);
Console.ReadKey();
}
public class Dog
{
public String Name { get; set; }
}以下代碼可能很難看得懂,但只要知道我們創建了屬性的Get、Set這兩個方法就行,其結果最后也能輸出狗的名字 WLJ,擁有ExpressionTree的好處是他有一個名為Compile()的方法,它創建一個代表表達式的代碼塊。現在是最有趣的部分,假設你在編譯時不知道類型(在這篇文章中包含的代碼我在不同的程序集上創建了一個類型)你仍然可以應用這種技術,我將對于常用的屬性的set,get操作進行分裝。
/// <summary>
/// 屬性類,仿造反射中的PropertyInfo
/// </summary>
public class Property
{
private readonly PropertyGetter getter;
private readonly PropertySetter setter;
public String Name { get; private set; }
public PropertyInfo Info { get; private set; }
public Property(PropertyInfo propertyInfo)
{
if (propertyInfo == null)
throw new NullReferenceException("屬性不能為空");
this.Name = propertyInfo.Name;
this.Info = propertyInfo;
if (this.Info.CanRead)
{
this.getter = new PropertyGetter(propertyInfo);
}
if (this.Info.CanWrite)
{
this.setter = new PropertySetter(propertyInfo);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 獲取對象的值
/// </summary>
/// <param name="instance"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public Object GetValue(Object instance)
{
return getter?.Invoke(instance);
}
/// <summary>
/// 賦值操作
/// </summary>
/// <param name="instance"></param>
/// <param name="value"></param>
public void SetValue(Object instance, Object value)
{
this.setter?.Invoke(instance, value);
}
private static readonly ConcurrentDictionary<Type, Core.Reflection.Property[]> securityCache = new ConcurrentDictionary<Type, Property[]>();
public static Core.Reflection.Property[] GetProperties(Type type)
{
return securityCache.GetOrAdd(type, t => t.GetProperties().Select(p => new Property(p)).ToArray());
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 屬性Get操作類
/// </summary>
public class PropertyGetter
{
private readonly Func<Object, Object> funcGet;
public PropertyGetter(PropertyInfo propertyInfo) : this(propertyInfo?.DeclaringType, propertyInfo.Name)
{
}
public PropertyGetter(Type declareType, String propertyName)
{
if (declareType == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(declareType));
}
if (propertyName == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(propertyName));
}
this.funcGet = CreateGetValueDeleagte(declareType, propertyName);
}
//代碼核心部分
private static Func<Object, Object> CreateGetValueDeleagte(Type declareType, String propertyName)
{
// (object instance) => (object)((declaringType)instance).propertyName
var param_instance = Expression.Parameter(typeof(Object));
var body_objToType = Expression.Convert(param_instance, declareType);
var body_getTypeProperty = Expression.Property(body_objToType, propertyName);
var body_return = Expression.Convert(body_getTypeProperty, typeof(Object));
return Expression.Lambda<Func<Object, Object>>(body_return, param_instance).Compile();
}
public Object Invoke(Object instance)
{
return this.funcGet?.Invoke(instance);
}
}
public class PropertySetter
{
private readonly Action<Object, Object> setFunc;
public PropertySetter(PropertyInfo property)
{
if (property == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(property));
}
this.setFunc = CreateSetValueDelagate(property);
}
private static Action<Object, Object> CreateSetValueDelagate(PropertyInfo property)
{
// (object instance, object value) =>
// ((instanceType)instance).Set_XXX((propertyType)value)
//聲明方法需要的參數
var param_instance = Expression.Parameter(typeof(Object));
var param_value = Expression.Parameter(typeof(Object));
var body_instance = Expression.Convert(param_instance, property.DeclaringType);
var body_value = Expression.Convert(param_value, property.PropertyType);
var body_call = Expression.Call(body_instance, property.GetSetMethod(), body_value);
return Expression.Lambda<Action<Object, Object>>(body_call, param_instance, param_value).Compile();
}
public void Invoke(Object instance, Object value)
{
this.setFunc?.Invoke(instance, value);
}
}在將代碼應用到實例:
Dog dog = new Dog(); PropertyInfo propertyInfo = dog.GetType().GetProperty(nameof(dog.Name)); //反射操作 propertyInfo.SetValue(dog, "WLJ"); String result = propertyInfo.GetValue(dog) as String; Console.WriteLine(result); //表達式樹的操作 Property property = new Property(propertyInfo); property.SetValue(dog, "WLJ2"); String result2 = propertyInfo.GetValue(dog) as String; Console.WriteLine(result2);
發現其實現的目的與反射一致,但效率卻有明顯的提高。
以下測試以下他們兩之間的效率。測試代碼如下:
Student student = new Student();
PropertyInfo propertyInfo = student.GetType().GetProperty(nameof(student.Name));
Property ExpProperty = new Property(propertyInfo);
Int32 loopCount = 1000000;
CodeTimer.Initialize(); //測試環境初始化
//下面該方法個執行1000000次
CodeTimer.Time("基礎反射", loopCount, () => {
propertyInfo.SetValue(student, "Fode",null);
});
CodeTimer.Time("lambda表達式樹", loopCount, () => {
ExpProperty.SetValue(student, "Fode");
});
CodeTimer.Time("直接賦值", loopCount, () => {
student.Name = "Fode";
});
Console.ReadKey();其.Net4.0環境下運行結果如下:
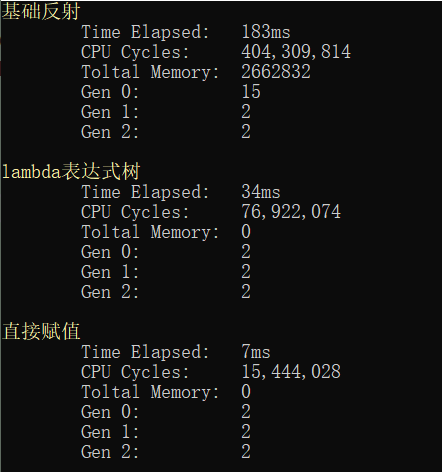
.Net Core環境下運行結果:
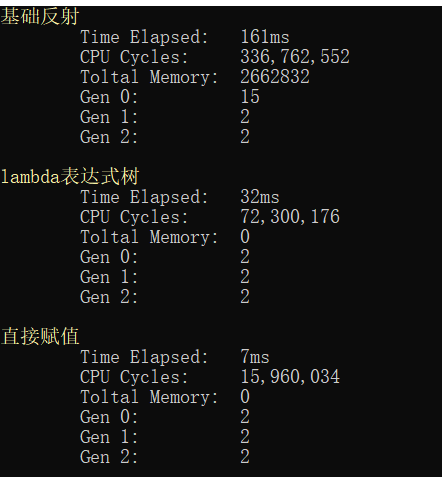
從以上結果可以知道,迭代同樣的次數反射需要183ms,而用表達式只要34ms,直接賦值需要7ms,在效率上,使用表達式這種方法有顯著的提高,您可以看到使用此技術可以完全避免使用反射時的性能損失。反射之所以效率有點低主要取決于其加載的時候時在運行期下,而表達式則在編譯期,下篇有空將會介紹用Emit技術優化反射,會比表達式略快一點。
注:對于常用對象的屬性,最好將其緩存起來,這樣效率會更高。。
以上是“如何利用lambda表達式樹優化反射”這篇文章的所有內容,感謝各位的閱讀!相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望分享的內容對大家有所幫助,如果還想學習更多知識,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。