您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
小編給大家分享一下python怎么使用__slots__讓你的代碼更加節省內存,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章之后都有所收獲,下面讓我們一起去探討吧!
現在來說說python中dict為什么比list浪費內存?
和list相比,dict 查找和插入的速度極快,不會隨著key的增加而增加;dict需要占用大量的內存,內存浪費多。
而list查找和插入的時間隨著元素的增加而增加;占用空間小,浪費的內存很少。
python解釋器是Cpython,這兩個數據結構應該對應C的哈希表和數組。因為哈希表需要額外內存記錄映射關系,而數組只需要通過索引就能計算出下一個節點的位置,所以哈希表占用的內存比數組大,也就是dict比list占用的內存更大。
如果想更加詳細了解,可以查看C的源代碼。python官方鏈接:https://www.python.org/downloads/source/
如下代碼是我從python官方截取的代碼片段:
List 源碼:
typedef struct {
PyObject_VAR_HEAD
/* Vector of pointers to list elements. list[0] is ob_item[0], etc. */
PyObject **ob_item;
/* ob_item contains space for 'allocated' elements. The number
* currently in use is ob_size.
* Invariants:
* 0 <= ob_size <= allocated
* len(list) == ob_size
* ob_item == NULL implies ob_size == allocated == 0
* list.sort() temporarily sets allocated to -1 to detect mutations.
*
* Items must normally not be NULL, except during construction when
* the list is not yet visible outside the function that builds it.
*/
Py_ssize_t allocated;
} PyListObject;Dict源碼:
/* PyDict_MINSIZE is the minimum size of a dictionary. This many slots are
* allocated directly in the dict object (in the ma_smalltable member).
* It must be a power of 2, and at least 4. 8 allows dicts with no more
* than 5 active entries to live in ma_smalltable (and so avoid an
* additional malloc); instrumentation suggested this suffices for the
* majority of dicts (consisting mostly of usually-small instance dicts and
* usually-small dicts created to pass keyword arguments).
*/
#define PyDict_MINSIZE 8
typedef struct {
/* Cached hash code of me_key. Note that hash codes are C longs.
* We have to use Py_ssize_t instead because dict_popitem() abuses
* me_hash to hold a search finger.
*/
Py_ssize_t me_hash;
PyObject *me_key;
PyObject *me_value;
} PyDictEntry;
/*
To ensure the lookup algorithm terminates, there must be at least one Unused
slot (NULL key) in the table.
The value ma_fill is the number of non-NULL keys (sum of Active and Dummy);
ma_used is the number of non-NULL, non-dummy keys (== the number of non-NULL
values == the number of Active items).
To avoid slowing down lookups on a near-full table, we resize the table when
it's two-thirds full.
*/
typedef struct _dictobject PyDictObject;
struct _dictobject {
PyObject_HEAD
Py_ssize_t ma_fill; /* # Active + # Dummy */
Py_ssize_t ma_used; /* # Active */
/* The table contains ma_mask + 1 slots, and that's a power of 2.
* We store the mask instead of the size because the mask is more
* frequently needed.
*/
Py_ssize_t ma_mask;
/* ma_table points to ma_smalltable for small tables, else to
* additional malloc'ed memory. ma_table is never NULL! This rule
* saves repeated runtime null-tests in the workhorse getitem and
* setitem calls.
*/
PyDictEntry *ma_table;
PyDictEntry *(*ma_lookup)(PyDictObject *mp, PyObject *key, long hash);
PyDictEntry ma_smalltable[PyDict_MINSIZE];
};PyObject_HEAD 源碼:
#ifdef Py_TRACE_REFS /* Define pointers to support a doubly-linked list of all live heap objects. */ #define _PyObject_HEAD_EXTRA \ struct _object *_ob_next; \ struct _object *_ob_prev; #define _PyObject_EXTRA_INIT 0, 0, #else #define _PyObject_HEAD_EXTRA #define _PyObject_EXTRA_INIT #endif /* PyObject_HEAD defines the initial segment of every PyObject. */ #define PyObject_HEAD \ _PyObject_HEAD_EXTRA \ Py_ssize_t ob_refcnt; \ struct _typeobject *ob_type;
PyObject_VAR_HEAD 源碼:
/* PyObject_VAR_HEAD defines the initial segment of all variable-size * container objects. These end with a declaration of an array with 1 * element, but enough space is malloc'ed so that the array actually * has room for ob_size elements. Note that ob_size is an element count, * not necessarily a byte count. */ #define PyObject_VAR_HEAD \ PyObject_HEAD \ Py_ssize_t ob_size; /* Number of items in variable part */
現在知道了dict為什么比list 占用的內存空間更大。接下來如何讓你的類更加的節省內存。
其實有兩種解決方案:
第一種是使用__slots__ ;另外一種是使用Collection.namedtuple 實現。
首先用標準的方式寫一個類:
#!/usr/bin/env python class Foobar(object): def __init__(self, x): self.x = x @profile def main(): f = [Foobar(42) for i in range(1000000)] if __name__ == "__main__": main()
然后,創建一個類Foobar(),然后實例化100W次。通過@profile查看內存使用情況。
運行結果:
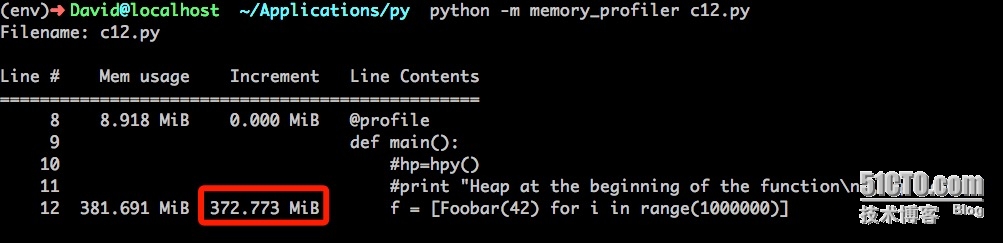
該代碼共使用了372M內存。
接下來通過__slots__代碼實現該代碼:
#!/usr/bin/env python class Foobar(object): __slots__ = 'x' def __init__(self, x): self.x = x @profile def main(): f = [Foobar(42) for i in range(1000000)] if __name__ == "__main__": main()
運行結果:
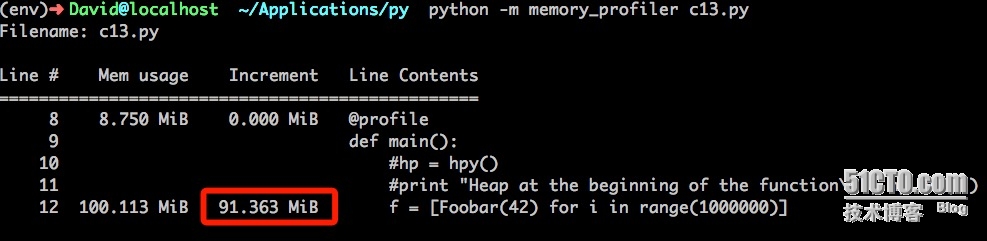
使用__slots__使用了91M內存,比使用__dict__存儲屬性值節省了4倍。
其實使用collection模塊的namedtuple也可以實現__slots__相同的功能。namedtuple其實就是繼承自tuple,同時也因為__slots__的值被設置成了一個空tuple以避免創建__dict__。
看看collection是如何實現的:
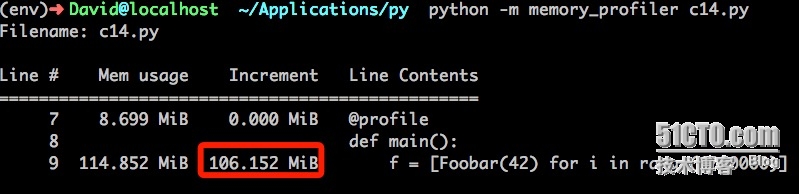
collection 和普通創建類方式相比,也節省了不少的內存。所在在確定類的屬性值固定的情況下,可以使用__slots__方式對內存進行優化。但是這項技術不應該被濫用于靜態類或者其他類似場合,那不是python程序的精神所在。
看完了這篇文章,相信你對“python怎么使用__slots__讓你的代碼更加節省內存”有了一定的了解,如果想了解更多相關知識,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道,感謝各位的閱讀!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。