您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹怎么用python寫詞法分析器,文中介紹的非常詳細,具有一定的參考價值,感興趣的小伙伴們一定要看完!
編譯原理老師要求寫一個java的詞法分析器,想了想決定用python寫一個。
目標
能識別出變量,數字,運算符,界符和關鍵字,用excel表打印出來。
有了目標,想想要怎么實現詞法分析器。
1.先進行預處理,把注釋,多余的空格,空行去掉。
2.一行一行掃描,行里逐字掃描,把界符和運算符當做分割符,遇到就先停下開始判斷。
若是以 英文字母、$、下劃線開頭,則可能是變量和關鍵字,在判斷是關鍵字還是變量。
若是數字開頭,則判斷下一位是不是也是數字,直到遇到非數字停止,在把數字取出來。
再來判斷分割符是什么類型,是界符還是運算符。
在給不同詞添加上識別碼
在用excel表打印出來。
代碼實現
1. 用列表創建一個關鍵字表,java關鍵字有50個。
#保留字 key_word = ['abstract','assert','boolean','break','byte', 'case','catch','char','class','const', 'continue','default','do','double','else', 'enum','extends','final','finally','float', 'for','goto','if','implements','import', 'instanceof','int','interface','long','native', 'new','package','private','protected','public', 'return','short','static','strictfp','super', 'switch','synchronized','this','throw','throws', 'transient','try','void','volatile','while']
2.用列表創建一個運算符表。
#運算符 operator = ['+','-','*','/','%','++','--','+=','-=','+=','/=',#算術運算符 '==','!=','>','<','>=','<=',#關系運算符 '&','|','^','~','<<','>>','>>>',#位運算符 '&&','||','!',#邏輯運算符 '=','+=','-=','*=','/=','%=','<<=','>>=','&=','^=','|=',#賦值運算符 '?:']#條件運算符
3. 用列表創建一個界符表。
#界符
delimiters = ['{','}','[',']','(',')','.',',',':',';']4.預處理
用正則表達式把注釋去掉,在把多余的空行去掉
#預處理
def filterResource(file,new_file):
f2 = open(new_file,'w+')
txt = ''.join(open(file,'r').readlines())
deal_txt = re.sub(r'\/\*[\s\S]*\*\/|\/\/.*','',txt)
for line in deal_txt.split('\n'):
line = line.strip()
line = line.replace('\\t','')
line = line.replace('\\n','')
if not line:
continue
else:
f2.write(line+'\n')
f2.close()
return sys.path[0]+'\\'+ new_file5.逐行掃描
按照剛剛的思路進行判斷,把每一行的單詞,添加到word_line列表中,最后在把每一行添加到token列表中。
def Scan(file):
lines = open(file,'r').readlines()
for line in lines:
word = ''
word_line = []
i = 0
while i <len(line):
word +=line[i]
if line[i]==' ' or line[i] in delimiters or line[i] in operator:
if word[0].isalpha() or word[0]=='$' or word[0]=='_':
word = word[:-1]
if searchReserve(word):
# 保留字
word_line.append({word[:-1]:key_word.index(word)})
else:
# 標識符
identifier.append({word:-2})
word_line.append({word:-2})
# 常數
elif word[:-1].isdigit():
word_line.append({word:-1})
#else:
#error_word.append(word)
# 字符是界符
if line[i] in delimiters:
word_line.append({line[i]:len(key_word)+delimiters.index(line[i])})
# 字符是運算符
elif line[i] in operator:
s = line[i] +line[i+1]
if s in operator:
word_line.append({s:len(key_word)+len(delimiters)+operator.index(s)})
i +=1
else:
word_line.append({line[i]:len(key_word)+len(delimiters)+operator.index(line[i])})
word = ''
i+=1
token.append(word_line)6.根據單詞返回是什么類型
按照保留字--界符--運算符--常數的順序來當識別碼。常數識別碼是-1,標識符識別碼是-2
def check(number): hanzi = '' q = len(key_word) w = len(delimiters) e = len(operator) if 0<number<=q: hanzi = '保留字' elif q<number <= q+w: hanzi = '界符' elif q+w<number <=q+w+e: hanzi = '運算符' elif number == -1: hanzi ='常數' elif number == -2: hanzi ='標識符' return hanzi
7. 用thinker寫一個簡單的界面
導入
from tkinter import * from tkinter.filedialog import askdirectory,askopenfilename
root = Tk()
root.title('詞法分析')
root.resizable(0, 0)
path = StringVar()
Label(root,text = "目標路徑:").grid(row = 0, column = 0)
Entry(root, textvariable = path).grid(row = 0, column = 1)
Button(root, text = "路徑選擇", command = openfiles).grid(row = 0, column = 2)
Button(root,text='詞法分析',command= open_excel).grid(row = 0,column = 3)
root.mainloop()打開文件
def openfiles():
fname = askopenfilename(title='打開文件', filetypes=[('All Files', '*')])
path.set(fname)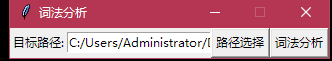
簡單的界面
8.導入到excel表中
需要安裝包xwings
pip install xwings
導入
import xlwings as xw
把token里的單詞,按照 單詞 ---- 識別碼 ---類型 打印到excel表中
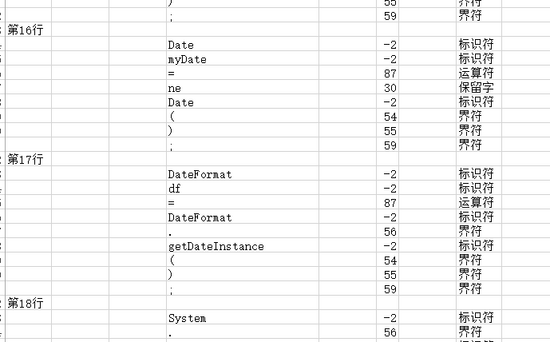
def open_excel(): # 預處理 row,col=0,0 if path.get()!='': txt = java_analysis.filterResource(path.get(),new_file) print(txt) #掃描 java_analysis.Scan(txt) app = xw.App(visible=True,add_book=False) wb =app.books.open(sys.path[0]+'\\'+'test.xlsx') sheet = wb.sheets.active sheet.clear() print(java_analysis.token) for i in range(len(java_analysis.token)): sheet[row,0].value = '第'+str(i+1)+'行' row +=1 for word in java_analysis.token[i]: for k,w in word.items(): sheet[row,3].value = k sheet[row,5].value = w sheet[row,7].value = java_analysis.check(w) row +=1 sheet.autofit()#整個sheet自動調整 #wb.save()
最后就像這樣
以上是“怎么用python寫詞法分析器”這篇文章的所有內容,感謝各位的閱讀!希望分享的內容對大家有幫助,更多相關知識,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。